🚨 Note: This is a draft model card. Actual model links can be found in this collection.
VibeVoice-AcousticTokenizer
VibeVoice is a novel framework designed for generating expressive, long-form, multi-speaker conversational audio, such as podcasts, from text. It addresses significant challenges in traditional Text-to-Speech (TTS) systems, particularly in scalability, speaker consistency, and natural turn-taking.
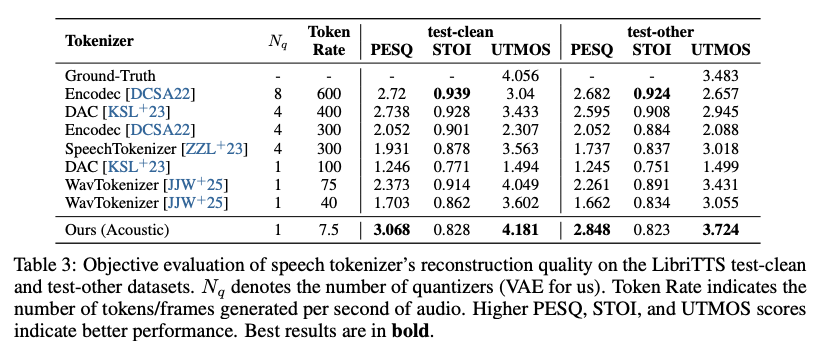
A core innovation of VibeVoice is its use of continuous speech tokenizers (Acoustic and Semantic) operating at an ultra-low frame rate of 7.5 Hz. These tokenizers efficiently preserve audio fidelity while significantly boosting computational efficiency for processing long sequences. VibeVoice employs a next-token diffusion framework, leveraging a Large Language Model (LLM) to understand textual context and dialogue flow, and a diffusion head to generate high-fidelity acoustic details.
The model can synthesize speech up to 90 minutes long with up to 4 distinct speakers, surpassing the typical 1-2 speaker limits of many prior models.
➡️ Technical Report: VibeVoice Technical Report
➡️ Project Page: microsoft/VibeVoice
Models
🚨 Note: This is a draft model card. Actual model links can be found in this collection.
| Model | Context Length | Generation Length | Weight |
|---|---|---|---|
| VibeVoice-1.5B | 64K | ~90 min | HF link |
| VibeVoice-7B | 32K | ~45 min | HF link |
| VibeVoice-AcousticTokenizer | - | - | This model |
| VibeVoice-SemanticTokenizer | - | - | HF link |
| VibeVoice-0.5B-Streaming | - | - | On the way |
Usage
Setup
VibeVoice is not yet merged into Transformers but can be used by pulling the source code from the following fork:
git clone git@github.com:pengzhiliang/transformers.git transformers-vibevoice
cd transformers-vibevoice
pip install -e .
pip install diffusers
Example
Encoding and decoding
import torch
from transformers import VibeVoiceFeatureExtractor, VibeVoiceAcousticTokenizerModel
from transformers.audio_utils import load_audio_librosa
from scipy.io import wavfile
model_path = "bezzam/VibeVoice-AcousticTokenizer"
fe_path = "bezzam/VibeVoice-1.5B"
sampling_rate = 24000
# load audio
audio = load_audio_librosa(
"https://hf.co/datasets/bezzam/vibevoice_samples/resolve/main/voices/en-Alice_woman.wav",
sampling_rate=sampling_rate
)
# load model
torch_device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
feature_extractor = VibeVoiceFeatureExtractor.from_pretrained(fe_path)
model = VibeVoiceAcousticTokenizerModel.from_pretrained(
model_path, device_map=torch_device,
).to(torch_device).eval()
# preprocess audio
inputs = feature_extractor(
audio,
sampling_rate=sampling_rate,
padding=True,
pad_to_multiple_of=3200,
return_attention_mask=False,
return_tensors="pt"
).to(torch_device)
print("Input audio shape:", inputs.input_features.shape)
# Input audio shape: torch.Size([1, 1, 224000])
# encode
with torch.no_grad():
encoded_outputs = model.encode(inputs.input_features)
print("Latent shape:", encoded_outputs.latents.shape)
# Latent shape: torch.Size([1, 70, 64])
# decode
with torch.no_grad():
decoded_outputs = model.decode(**encoded_outputs)
print("Reconstructed audio shape:", decoded_outputs.audio.shape)
# Reconstructed audio shape: torch.Size([1, 1, 224000])
# Save audio
output_fp = "vibevoice_acoustic_tokenizer_reconstructed.wav"
wavfile.write(output_fp, sampling_rate, decoded_outputs.audio.squeeze().cpu().numpy())
Original audio
Encoded/decoded audio
- Downloads last month
- 137