library_name: transformers
license: cc-by-nc-4.0
pipeline_tag: text-generation
tags:
- text-to-sql
- reinforcement-learning
SLM-SQL: An Exploration of Small Language Models for Text-to-SQL
Important Links
📖Hugging Face Paper | 📚arXiv Paper | 💻GitHub Repository | 🤗Hugging Face Models Collection | 🤖ModelScope Models Collection |
News
July 31, 2025: Upload model to modelscope and huggingface.July 30, 2025: Publish the paper to arxiv
Introduction
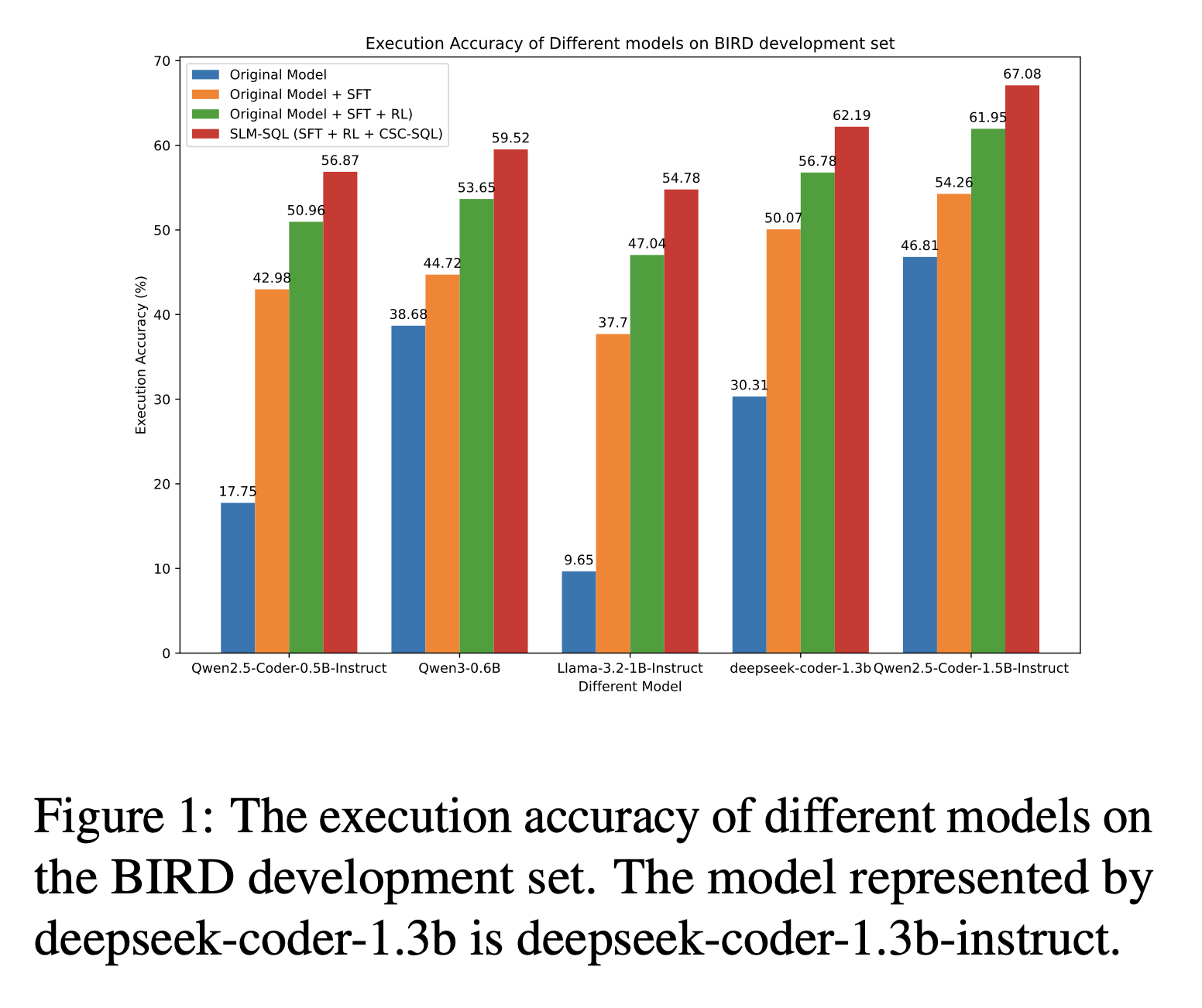
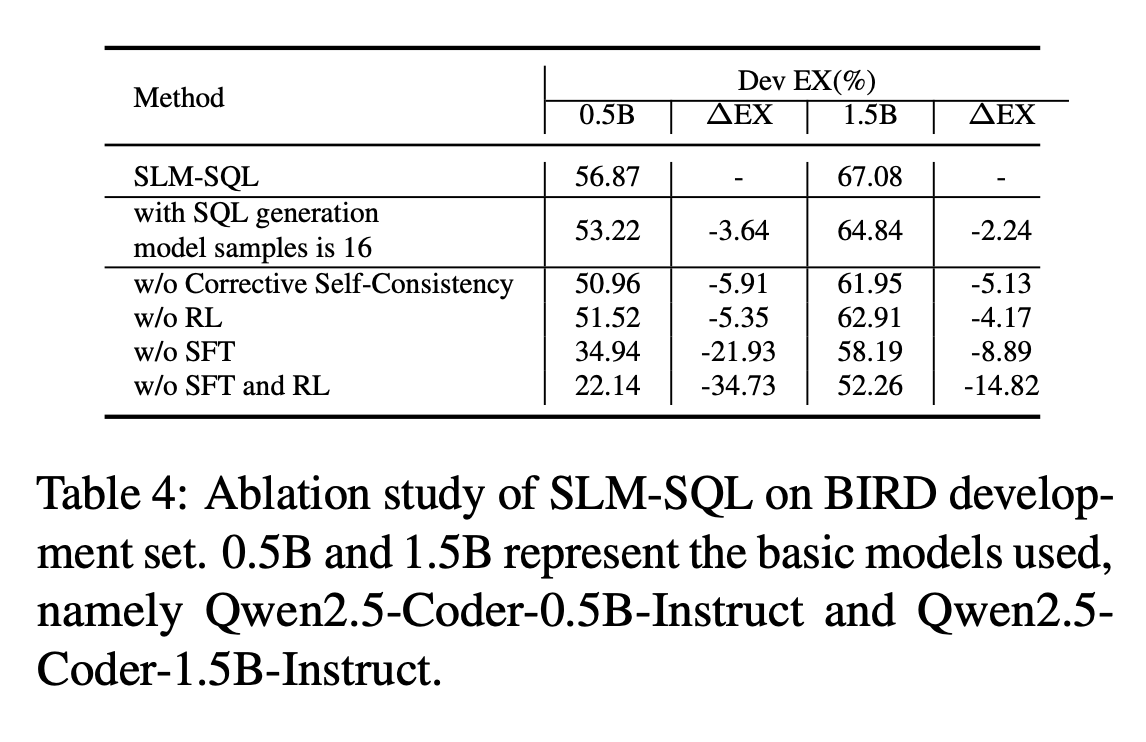
Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated strong performance in translating natural language questions into SQL queries (Text-to-SQL). In contrast, small language models (SLMs) ranging from 0.5B to 1.5B parameters currently underperform on Text-to-SQL tasks due to their limited logical reasoning capabilities. However, SLMs offer inherent advantages in inference speed and suitability for edge deployment. To explore their potential in Text-to-SQL applications, we leverage recent advancements in post-training techniques. Specifically, we used the open-source SynSQL-2.5M dataset to construct two derived datasets: SynSQL-Think-916K for SQL generation and SynSQL-Merge-Think-310K for SQL merge revision. We then applied supervised fine-tuning and reinforcement learning-based post-training to the SLM, followed by inference using a corrective self-consistency approach. Experimental results validate the effectiveness and generalizability of our method, SLM-SQL. On the BIRD development set, the five evaluated models achieved an average improvement of 31.4 points. Notably, the 0.5B model reached 56.87% execution accuracy (EX), while the 1.5B model achieved 67.08% EX.
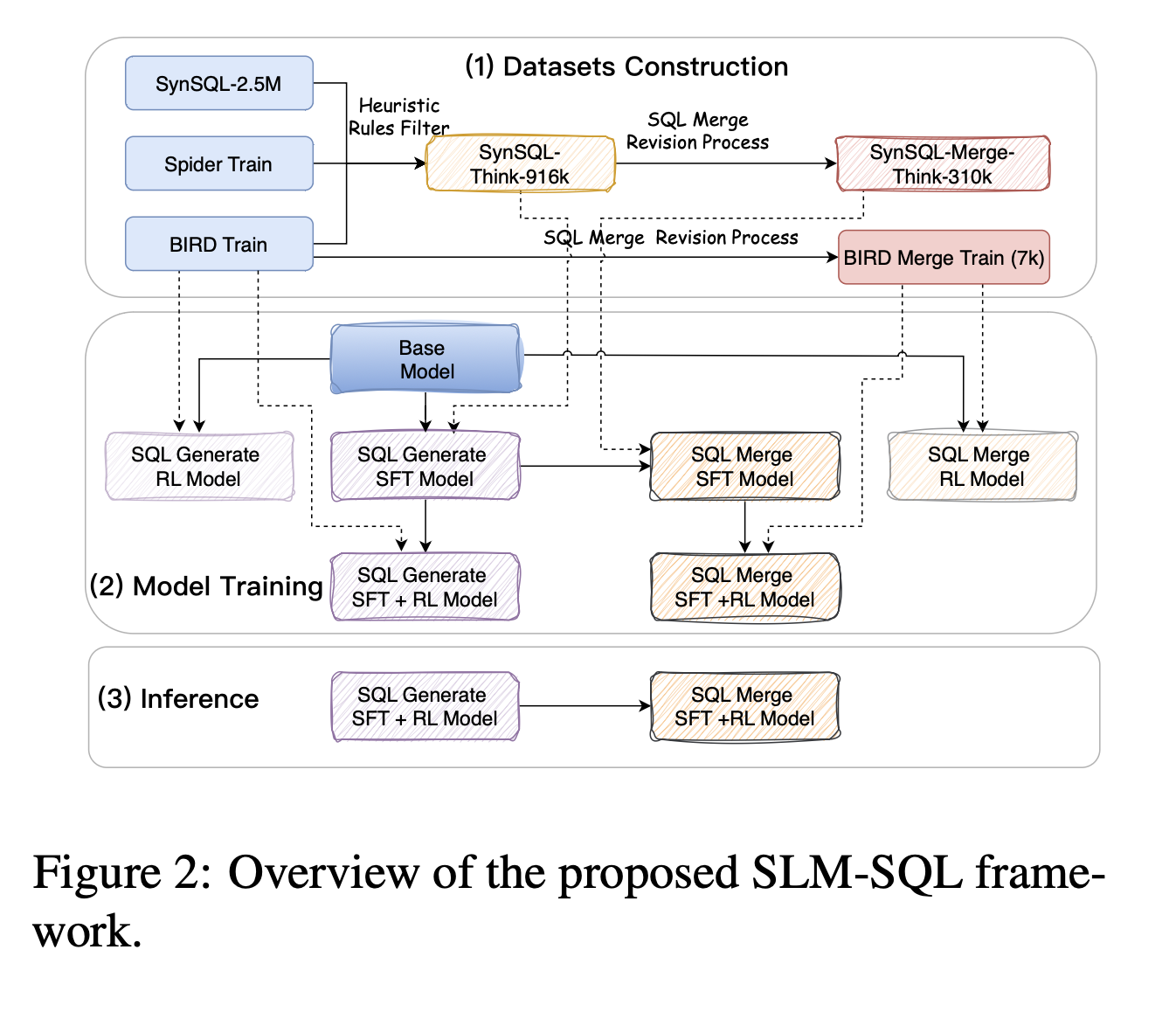
Framework
Main Results
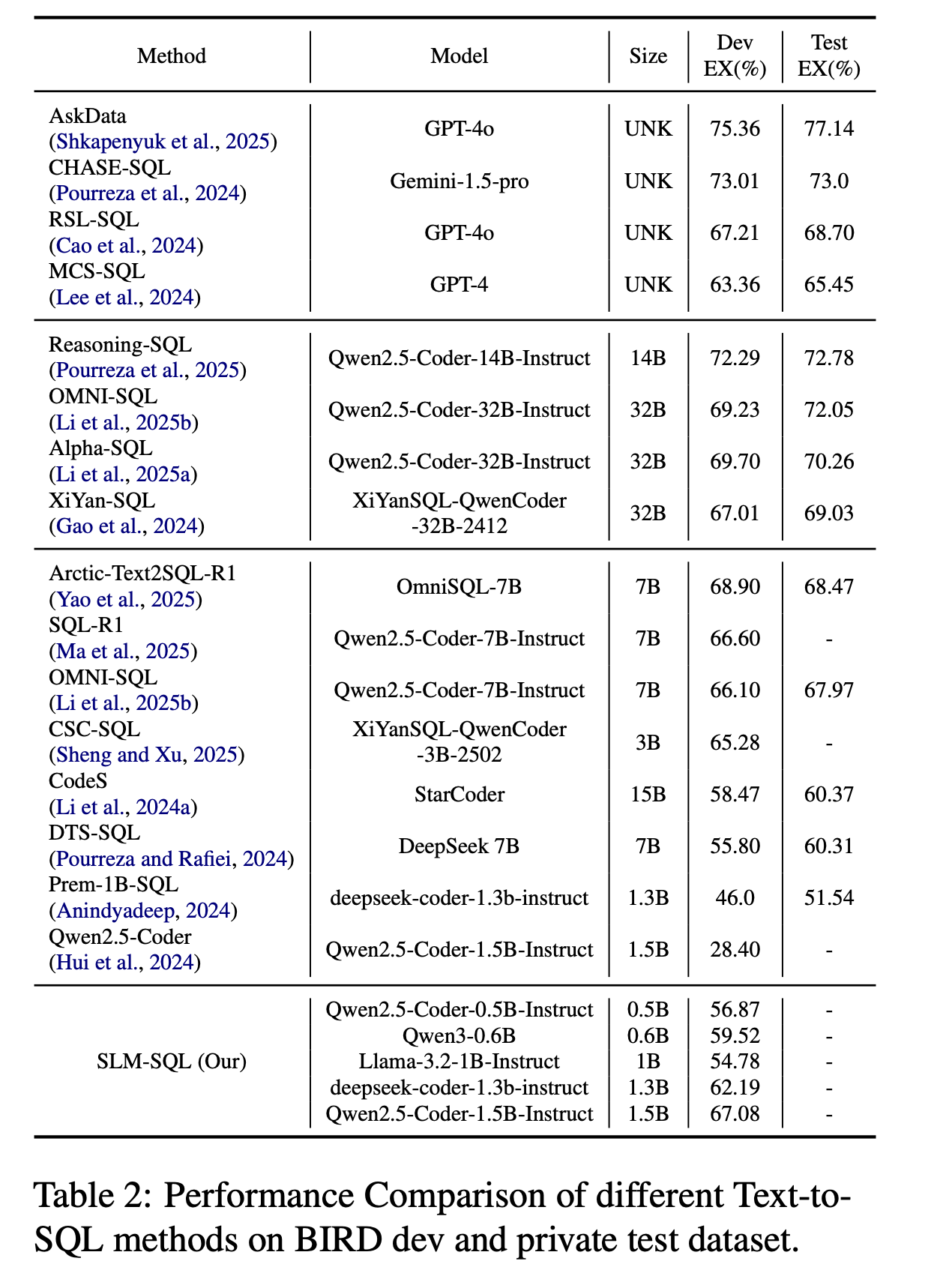
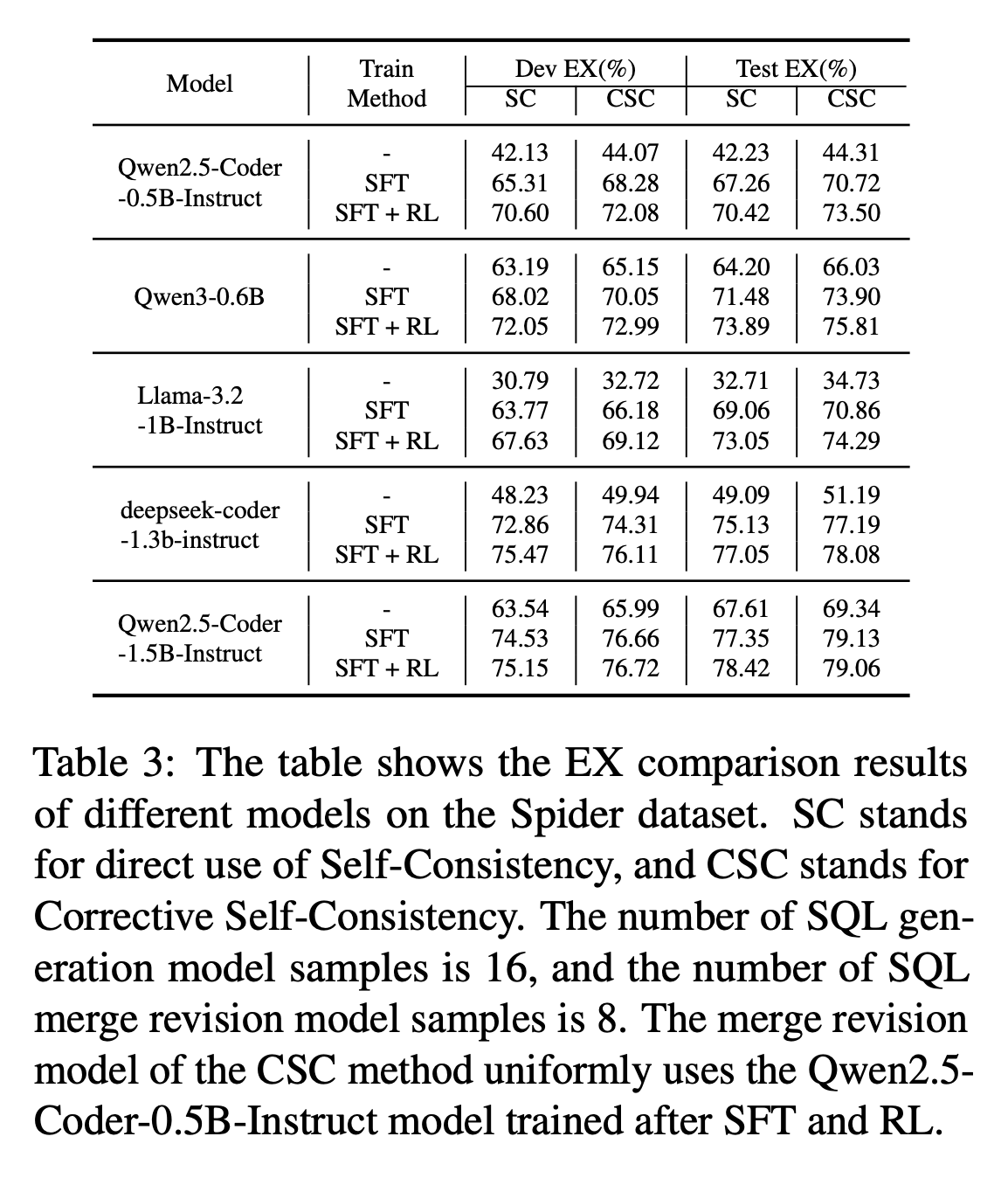
Performance Comparison of different Text-to-SQL methods on BIRD dev and test dataset.
Usage
This model can be used with the Hugging Face transformers library for text-to-SQL generation.
import torch
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForCausalLM
# Load model and tokenizer
# Replace "cycloneboy/SLM-SQL-0.5B" with the specific model checkpoint you want to use.
model_id = "cycloneboy/SLM-SQL-0.5B"
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_id, trust_remote_code=True)
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_id, torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16, device_map="auto", trust_remote_code=True)
# Set the model to evaluation mode
model.eval()
# Define the natural language question and database schema (replace with your data)
user_query = "What are the names of all employees who earn more than 50000?"
database_schema = """
CREATE TABLE employees (
employee_id INT PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR(255),
salary DECIMAL(10, 2)
);
"""
# Construct the conversation using the model's chat template
# The model expects schema and question to generate the SQL query.
# The prompt format below is a common way to combine schema and question for Text-to-SQL.
full_prompt = f"""
You are a Text-to-SQL model.
Given the following database schema:
{database_schema}
Generate the SQL query for the question:
{user_query}
"""
messages = [
{"role": "user", "content": full_prompt.strip()}
]
# Apply the chat template and tokenize inputs
input_text = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(messages, tokenize=False, add_generation_prompt=True)
inputs = tokenizer(input_text, return_tensors="pt").to(model.device)
# Generate the SQL query
with torch.no_grad():
outputs = model.generate(**inputs, max_new_tokens=256, temperature=0.6, top_p=0.9, do_sample=True,
eos_token_id=[tokenizer.eos_token_id, tokenizer.convert_tokens_to_ids("<|im_end|>")])
# Decode the generated text and extract the assistant's response
generated_text = tokenizer.decode(outputs[0], skip_special_tokens=False)
# The Qwen-style chat template wraps assistant's response between <|im_start|>assistant
and <|im_end|>
assistant_prefix = "<|im_start|>assistant\
"
if assistant_prefix in generated_text:
sql_query = generated_text.split(assistant_prefix, 1)[1].strip()
# Remove any trailing special tokens like <|im_end|>
sql_query = sql_query.split("<|im_end|>", 1)[0].strip()
else:
sql_query = generated_text # Fallback in case prompt format differs unexpectedly
print(f"User Query: {user_query}
Generated SQL: {sql_query}")
# Example of a potential output for the given query and schema:
# Generated SQL: SELECT name FROM employees WHERE salary > 50000;
Model
| Model | Base Model | Train Method | Modelscope | HuggingFace |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SLM-SQL-Base-0.5B | Qwen2.5-Coder-0.5B-Instruct | SFT | 🤖 Modelscope | 🤗 HuggingFace |
| SLM-SQL-0.5B | Qwen2.5-Coder-0.5B-Instruct | SFT + GRPO | 🤖 Modelscope | 🤗 HuggingFace |
| CscSQL-Merge-Qwen2.5-Coder-0.5B-Instruct | Qwen2.5-Coder-0.5B-Instruct | SFT + GRPO | 🤖 Modelscope | 🤗 HuggingFace |
| SLM-SQL-Base-1.5B | Qwen2.5-Coder-1.5B-Instruct | SFT | 🤖 Modelscope | 🤗 HuggingFace |
| SLM-SQL-1.5B | Qwen2.5-Coder-1.5B-Instruct | SFT + GRPO | 🤖 Modelscope | 🤗 HuggingFace |
| CscSQL-Merge-Qwen2.5-Coder-1.5B-Instruct | Qwen2.5-Coder-1.5B-Instruct | SFT + GRPO | 🤖 Modelscope | 🤗 HuggingFace |
| SLM-SQL-Base-0.6B | Qwen3-0.6B | SFT | 🤖 Modelscope | 🤗 HuggingFace |
| SLM-SQL-0.6B | Qwen3-0.6B | SFT + GRPO | 🤖 Modelscope | 🤗 HuggingFace |
| SLM-SQL-Base-1.3B | deepseek-coder-1.3b-instruct | SFT | 🤖 Modelscope | 🤗 HuggingFace |
| SLM-SQL-1.3B | deepseek-coder-1.3b-instruct | SFT + GRPO | 🤖 Modelscope | 🤗 HuggingFace |
| SLM-SQL-Base-1B | Llama-3.2-1B-Instruct | SFT | 🤖 Modelscope | 🤗 HuggingFace |
Dataset
| Dataset | Modelscope | HuggingFace |
|---|---|---|
| SynsQL-Think-916k | 🤖 Modelscope | 🤗 HuggingFace |
| SynsQL-Merge-Think-310k | 🤖 Modelscope | 🤗 HuggingFace |
| bird train and dev dataset | 🤖 Modelscope | 🤗 HuggingFace |
TODO
- Release inference code
- Upload Model
- Release training code
- Fix bug
- Update doc
Thanks to the following projects
Citation
@misc{sheng2025slmsqlexplorationsmalllanguage,
title={SLM-SQL: An Exploration of Small Language Models for Text-to-SQL},
author={Lei Sheng and Shuai-Shuai Xu},
year={2025},
eprint={2507.22478},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CL},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2507.22478},
}
@misc{sheng2025cscsqlcorrectiveselfconsistencytexttosql,
title={CSC-SQL: Corrective Self-Consistency in Text-to-SQL via Reinforcement Learning},
author={Lei Sheng and Shuai-Shuai Xu},
year={2025},
eprint={2505.13271},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CL},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2505.13271},
}