modelId
stringlengths 5
139
| author
stringlengths 2
42
| last_modified
timestamp[us, tz=UTC]date 2020-02-15 11:33:14
2025-09-11 06:30:11
| downloads
int64 0
223M
| likes
int64 0
11.7k
| library_name
stringclasses 555
values | tags
listlengths 1
4.05k
| pipeline_tag
stringclasses 55
values | createdAt
timestamp[us, tz=UTC]date 2022-03-02 23:29:04
2025-09-11 06:29:58
| card
stringlengths 11
1.01M
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
gaochangkuan/model_dir
|
gaochangkuan
| 2021-05-21T16:10:50Z | 10 | 0 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"jax",
"gpt2",
"text-generation",
"autotrain_compatible",
"text-generation-inference",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
text-generation
| 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
## Generating Chinese poetry by topic.
```python
from transformers import *
tokenizer = BertTokenizer.from_pretrained("gaochangkuan/model_dir")
model = AutoModelWithLMHead.from_pretrained("gaochangkuan/model_dir")
prompt= '''<s>田园躬耕'''
length= 84
stop_token='</s>'
temperature = 1.2
repetition_penalty=1.3
k= 30
p= 0.95
device ='cuda'
seed=2020
no_cuda=False
prompt_text = prompt if prompt else input("Model prompt >>> ")
encoded_prompt = tokenizer.encode(
'<s>'+prompt_text+'<sep>',
add_special_tokens=False,
return_tensors="pt"
)
encoded_prompt = encoded_prompt.to(device)
output_sequences = model.generate(
input_ids=encoded_prompt,
max_length=length,
min_length=10,
do_sample=True,
early_stopping=True,
num_beams=10,
temperature=temperature,
top_k=k,
top_p=p,
repetition_penalty=repetition_penalty,
bad_words_ids=None,
bos_token_id=tokenizer.bos_token_id,
pad_token_id=tokenizer.pad_token_id,
eos_token_id=tokenizer.eos_token_id,
length_penalty=1.2,
no_repeat_ngram_size=2,
num_return_sequences=1,
attention_mask=None,
decoder_start_token_id=tokenizer.bos_token_id,)
generated_sequence = output_sequences[0].tolist()
text = tokenizer.decode(generated_sequence)
text = text[: text.find(stop_token) if stop_token else None]
print(''.join(text).replace(' ','').replace('<pad>','').replace('<s>',''))
```
|
gagan3012/project-code-py-small
|
gagan3012
| 2021-05-21T16:06:24Z | 11 | 1 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"jax",
"gpt2",
"text-generation",
"autotrain_compatible",
"text-generation-inference",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
text-generation
| 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
# Leetcode using AI :robot:
GPT-2 Model for Leetcode Questions in python
**Note**: the Answers might not make sense in some cases because of the bias in GPT-2
**Contribtuions:** If you would like to make the model better contributions are welcome Check out [CONTRIBUTIONS.md](https://github.com/gagan3012/project-code-py/blob/master/CONTRIBUTIONS.md)
### 📢 Favour:
It would be highly motivating, if you can STAR⭐ this repo if you find it helpful.
## Model
Two models have been developed for different use cases and they can be found at https://huggingface.co/gagan3012
The model weights can be found here: [GPT-2](https://huggingface.co/gagan3012/project-code-py) and [DistilGPT-2](https://huggingface.co/gagan3012/project-code-py-small)
### Example usage:
```python
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelWithLMHead
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("gagan3012/project-code-py")
model = AutoModelWithLMHead.from_pretrained("gagan3012/project-code-py")
```
## Demo
[](https://share.streamlit.io/gagan3012/project-code-py/app.py)
A streamlit webapp has been setup to use the model: https://share.streamlit.io/gagan3012/project-code-py/app.py
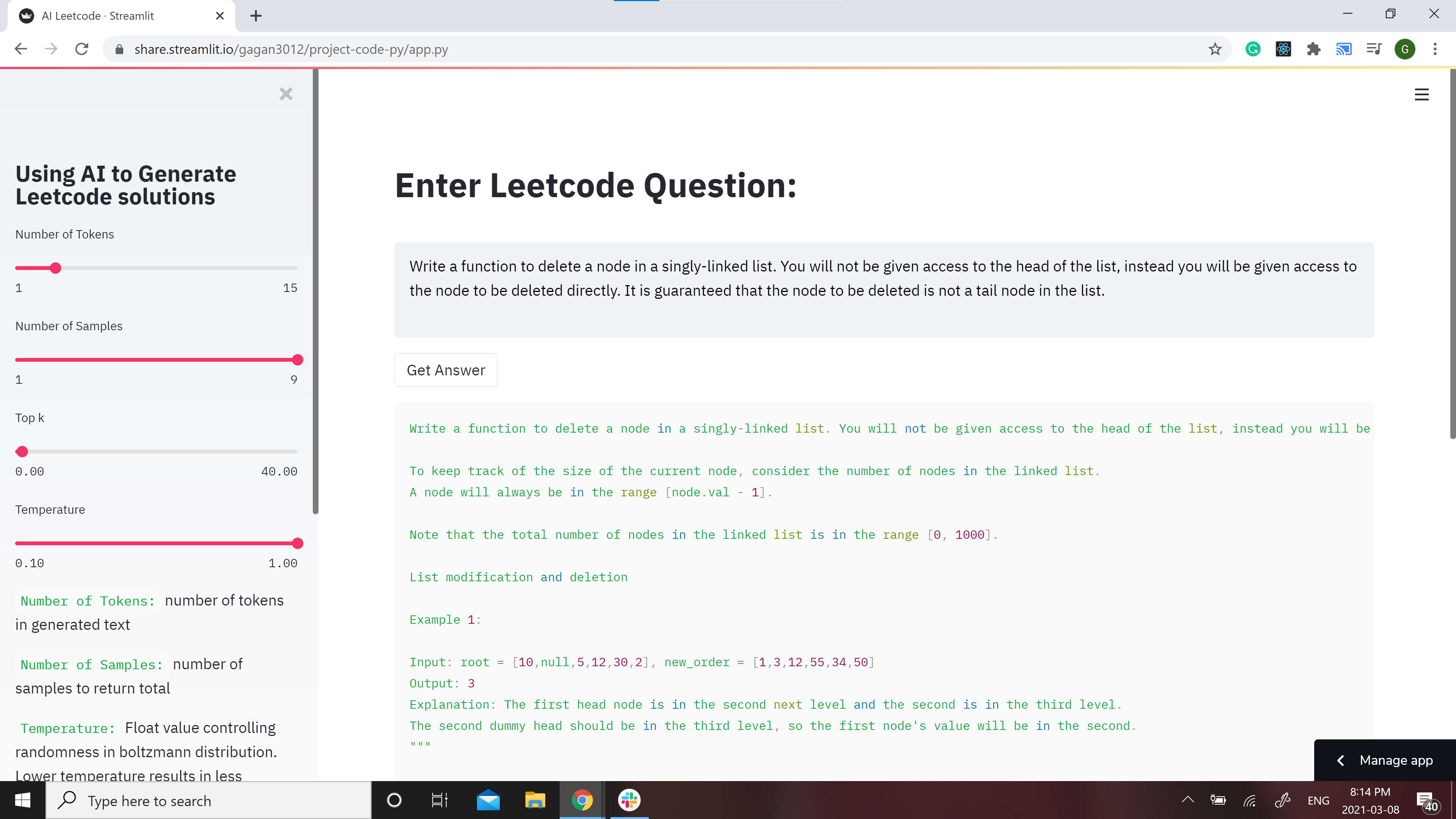
## Example results:
### Question:
```
Write a function to delete a node in a singly-linked list. You will not be given access to the head of the list, instead you will be given access to the node to be deleted directly. It is guaranteed that the node to be deleted is not a tail node in the list.
```
### Answer:
```python
""" Write a function to delete a node in a singly-linked list. You will not be given access to the head of the list, instead you will be given access to the node to be deleted directly. It is guaranteed that the node to be deleted is not a tail node in the list.
For example,
a = 1->2->3
b = 3->1->2
t = ListNode(-1, 1)
Note: The lexicographic ordering of the nodes in a tree matters. Do not assign values to nodes in a tree.
Example 1:
Input: [1,2,3]
Output: 1->2->5
Explanation: 1->2->3->3->4, then 1->2->5[2] and then 5->1->3->4.
Note:
The length of a linked list will be in the range [1, 1000].
Node.val must be a valid LinkedListNode type.
Both the length and the value of the nodes in a linked list will be in the range [-1000, 1000].
All nodes are distinct.
"""
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution:
def deleteNode(self, head: ListNode, val: int) -> None:
"""
BFS
Linked List
:param head: ListNode
:param val: int
:return: ListNode
"""
if head is not None:
return head
dummy = ListNode(-1, 1)
dummy.next = head
dummy.next.val = val
dummy.next.next = head
dummy.val = ""
s1 = Solution()
print(s1.deleteNode(head))
print(s1.deleteNode(-1))
print(s1.deleteNode(-1))
```
|
gagan3012/Fox-News-Generator
|
gagan3012
| 2021-05-21T16:03:28Z | 7 | 3 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"jax",
"gpt2",
"text-generation",
"autotrain_compatible",
"text-generation-inference",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
text-generation
| 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
# Generating Right Wing News Using GPT2
### I have built a custom model for it using data from Kaggle
Creating a new finetuned model using data from FOX news
### My model can be accessed at gagan3012/Fox-News-Generator
Check the [BenchmarkTest](https://github.com/gagan3012/Fox-News-Generator/blob/master/BenchmarkTest.ipynb) notebook for results
Find the model at [gagan3012/Fox-News-Generator](https://huggingface.co/gagan3012/Fox-News-Generator)
```
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelWithLMHead
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("gagan3012/Fox-News-Generator")
model = AutoModelWithLMHead.from_pretrained("gagan3012/Fox-News-Generator")
```
|
erikinfo/gpt2TEDlectures
|
erikinfo
| 2021-05-21T16:00:10Z | 6 | 0 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"jax",
"gpt2",
"text-generation",
"autotrain_compatible",
"text-generation-inference",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
text-generation
| 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
# GPT2 Keyword Based Lecture Generator
## Model description
GPT2 fine-tuned on the TED Talks Dataset (published under the Creative Commons BY-NC-ND license).
## Intended uses
Used to generate spoken-word lectures.
### How to use
Input text:
<BOS> title <|SEP|> Some keywords <|SEP|>
Keyword Format: "Main Topic"."Subtopic1","Subtopic2","Subtopic3"
Code Example:
```
prompt = <BOS> + title + \\
<|SEP|> + keywords + <|SEP|>
generated = torch.tensor(tokenizer.encode(prompt)).unsqueeze(0)
model.eval();
```
|
e-tornike/gpt2-rnm
|
e-tornike
| 2021-05-21T15:43:11Z | 7 | 1 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"jax",
"gpt2",
"text-generation",
"autotrain_compatible",
"text-generation-inference",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
text-generation
| 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
### How to use
You can use this model directly with a pipeline for text generation. Since the generation relies on some randomness, we
set a seed for reproducibility:
```python
>>> from transformers import pipeline, set_seed
>>> generator = pipeline('text-generation', model='e-tony/gpt2-rnm')
>>> set_seed(42)
>>> generator("Rick: I turned myself into a pickle, Morty!\nMorty: ", max_length=50, num_return_sequences=5)
[{'generated_text': "Rick: I turned myself into a pickle, Morty!\nMorty: I didn't want to have children. It was my fate! I'll pay my mom and dad.\nSnuffles: Well, at least we"},
{'generated_text': "Rick: I turned myself into a pickle, Morty!\nMorty: you know what happened?\n(Steven begins dragging people down the toilet with his hand. As Steven falls) The whole thing starts.\nA man approaches Steven"},
{'generated_text': "Rick: I turned myself into a pickle, Morty!\nMorty: Oh wait! And do you remember what I did to you?\nJerry: Uh, it didn't hurt. It should have hurt a lot since I"},
{'generated_text': "Rick: I turned myself into a pickle, Morty!\nMorty: Rick!\nKraven: Wait! [wary gasp] What the hell are you doing this time?!\nJerry: Hey, are you"},
{'generated_text': "Rick: I turned myself into a pickle, Morty!\nMorty: Uh.\nJerry: You don't have to put your finger on me today, do you?\nRick: It's just, what do you"}]
```
### Training data
We used the original `gpt2` model and fine-tuned it on [Rick and Morty transcripts](https://rickandmorty.fandom.com/wiki/Category:Transcripts).
|
DebateLabKIT/cript
|
DebateLabKIT
| 2021-05-21T15:40:52Z | 8 | 0 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"jax",
"gpt2",
"text-generation",
"en",
"arxiv:2009.07185",
"autotrain_compatible",
"text-generation-inference",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
text-generation
| 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
---
language: en
tags:
- gpt2
---
# CRiPT Model (Critical Thinking Intermediarily Pretrained Transformer)
Small version of the trained model (`SYL01-2020-10-24-72K/gpt2-small-train03-72K`) presented in the paper "Critical Thinking for Language Models" (Betz, Voigt and Richardson 2020). See also:
* [blog entry](https://debatelab.github.io/journal/critical-thinking-language-models.html)
* [GitHub repo](https://github.com/debatelab/aacorpus)
* [paper](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2009.07185)
|
DebateLabKIT/cript-medium
|
DebateLabKIT
| 2021-05-21T15:39:12Z | 10 | 0 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"jax",
"gpt2",
"text-generation",
"en",
"arxiv:2009.07185",
"autotrain_compatible",
"text-generation-inference",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
text-generation
| 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
---
language: en
tags:
- gpt2
---
# CRiPT Model Medium (Critical Thinking Intermediarily Pretrained Transformer)
Medium version of the trained model (`SYL01-2020-10-24-72K/gpt2-medium-train03-72K`) presented in the paper "Critical Thinking for Language Models" (Betz, Voigt and Richardson 2020). See also:
* [blog entry](https://debatelab.github.io/journal/critical-thinking-language-models.html)
* [GitHub repo](https://github.com/debatelab/aacorpus)
* [paper](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2009.07185)
|
DebateLabKIT/cript-large
|
DebateLabKIT
| 2021-05-21T15:31:48Z | 7 | 0 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"jax",
"gpt2",
"text-generation",
"en",
"arxiv:2009.07185",
"autotrain_compatible",
"text-generation-inference",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
text-generation
| 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
---
language: en
tags:
- gpt2
---
# CRiPT Model Large (Critical Thinking Intermediarily Pretrained Transformer)
Large version of the trained model (`SYL01-2020-10-24-72K/gpt2-large-train03-72K`) presented in the paper "Critical Thinking for Language Models" (Betz, Voigt and Richardson 2020). See also:
* [blog entry](https://debatelab.github.io/journal/critical-thinking-language-models.html)
* [GitHub repo](https://github.com/debatelab/aacorpus)
* [paper](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2009.07185)
|
classla/bcms-bertic-generator
|
classla
| 2021-05-21T13:29:30Z | 5 | 2 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"electra",
"pretraining",
"masked-lm",
"hr",
"bs",
"sr",
"cnr",
"hbs",
"license:apache-2.0",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] | null | 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
---
language:
- hr
- bs
- sr
- cnr
- hbs
tags:
- masked-lm
widget:
- text: "Zovem se Marko i radim u [MASK]."
license: apache-2.0
---
# BERTić* [bert-ich] /bɜrtitʃ/ - A transformer language model for Bosnian, Croatian, Montenegrin and Serbian
* The name should resemble the facts (1) that the model was trained in Zagreb, Croatia, where diminutives ending in -ić (as in fotić, smajlić, hengić etc.) are very popular, and (2) that most surnames in the countries where these languages are spoken end in -ić (with diminutive etymology as well).
This is the smaller generator of the main [discriminator model](https://huggingface.co/classla/bcms-bertic), useful if you want to continue pre-training the discriminator model.
If you use the model, please cite the following paper:
```
@inproceedings{ljubesic-lauc-2021-bertic,
title = "{BERT}i{\'c} - The Transformer Language Model for {B}osnian, {C}roatian, {M}ontenegrin and {S}erbian",
author = "Ljube{\v{s}}i{\'c}, Nikola and Lauc, Davor",
booktitle = "Proceedings of the 8th Workshop on Balto-Slavic Natural Language Processing",
month = apr,
year = "2021",
address = "Kiyv, Ukraine",
publisher = "Association for Computational Linguistics",
url = "https://www.aclweb.org/anthology/2021.bsnlp-1.5",
pages = "37--42",
}
```
|
Dongjae/mrc2reader
|
Dongjae
| 2021-05-21T13:25:57Z | 14 | 0 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"xlm-roberta",
"question-answering",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
question-answering
| 2022-03-02T23:29:04Z |
The Reader model is for Korean Question Answering
The backbone model is deepset/xlm-roberta-large-squad2.
It is a finetuned model with KorQuAD-v1 dataset.
As a result of verification using KorQuAD evaluation dataset, it showed approximately 87% and 92% respectively for the EM score and F1 score.
Thank you
|
aliosm/ComVE-gpt2-medium
|
aliosm
| 2021-05-21T13:17:55Z | 8 | 0 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"jax",
"gpt2",
"feature-extraction",
"exbert",
"commonsense",
"semeval2020",
"comve",
"en",
"dataset:ComVE",
"license:mit",
"text-generation-inference",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
feature-extraction
| 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
---
language: "en"
tags:
- gpt2
- exbert
- commonsense
- semeval2020
- comve
license: "mit"
datasets:
- ComVE
metrics:
- bleu
widget:
- text: "Chicken can swim in water. <|continue|>"
---
# ComVE-gpt2-medium
## Model description
Finetuned model on Commonsense Validation and Explanation (ComVE) dataset introduced in [SemEval2020 Task4](https://competitions.codalab.org/competitions/21080) using a causal language modeling (CLM) objective.
The model is able to generate a reason why a given natural language statement is against commonsense.
## Intended uses & limitations
You can use the raw model for text generation to generate reasons why natural language statements are against commonsense.
#### How to use
You can use this model directly to generate reasons why the given statement is against commonsense using [`generate.sh`](https://github.com/AliOsm/SemEval2020-Task4-ComVE/tree/master/TaskC-Generation) script.
*Note:* make sure that you are using version `2.4.1` of `transformers` package. Newer versions has some issue in text generation and the model repeats the last token generated again and again.
#### Limitations and bias
The model biased to negate the entered sentence usually instead of producing a factual reason.
## Training data
The model is initialized from the [gpt2-medium](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/master/model_cards/gpt2-README.md) model and finetuned using [ComVE](https://github.com/wangcunxiang/SemEval2020-Task4-Commonsense-Validation-and-Explanation) dataset which contains 10K against commonsense sentences, each of them is paired with three reference reasons.
## Training procedure
Each natural language statement that against commonsense is concatenated with its reference reason with `<|continue|>` as a separator, then the model finetuned using CLM objective.
The model trained on Nvidia Tesla P100 GPU from Google Colab platform with 5e-5 learning rate, 5 epochs, 128 maximum sequence length and 64 batch size.
<center>
<img src="https://i.imgur.com/xKbrwBC.png">
</center>
## Eval results
The model achieved fifth place with 16.7153/16.1187 BLEU scores and third place with 1.94 Human Evaluation score on SemEval2020 Task4: Commonsense Validation and Explanation development and testing dataset.
These are some examples generated by the model:
| Against Commonsense Statement | Generated Reason |
|:-----------------------------------------------------:|:--------------------------------------------:|
| Chicken can swim in water. | Chicken can't swim. |
| shoes can fly | Shoes are not able to fly. |
| Chocolate can be used to make a coffee pot | Chocolate is not used to make coffee pots. |
| you can also buy tickets online with an identity card | You can't buy tickets with an identity card. |
| a ball is square and can roll | A ball is round and cannot roll. |
| You can use detergent to dye your hair. | Detergent is used to wash clothes. |
| you can eat mercury | mercury is poisonous |
| A gardener can follow a suspect | gardener is not a police officer |
| cars can float in the ocean just like a boat | Cars are too heavy to float in the ocean. |
| I am going to work so I can lose money. | Working is not a way to lose money. |
### BibTeX entry and citation info
```bibtex
@article{fadel2020justers,
title={JUSTers at SemEval-2020 Task 4: Evaluating Transformer Models Against Commonsense Validation and Explanation},
author={Fadel, Ali and Al-Ayyoub, Mahmoud and Cambria, Erik},
year={2020}
}
```
<a href="https://huggingface.co/exbert/?model=aliosm/ComVE-gpt2-medium">
<img width="300px" src="https://cdn-media.huggingface.co/exbert/button.png">
</a>
|
aliosm/ComVE-gpt2-large
|
aliosm
| 2021-05-21T13:12:02Z | 13 | 0 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"jax",
"gpt2",
"text-generation",
"exbert",
"commonsense",
"semeval2020",
"comve",
"en",
"license:mit",
"autotrain_compatible",
"text-generation-inference",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
text-generation
| 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
---
language: "en"
tags:
- gpt2
- exbert
- commonsense
- semeval2020
- comve
license: "mit"
datasets:
- https://github.com/wangcunxiang/SemEval2020-Task4-Commonsense-Validation-and-Explanation
metrics:
- bleu
widget:
- text: "Chicken can swim in water. <|continue|>"
---
# ComVE-gpt2-large
## Model description
Finetuned model on Commonsense Validation and Explanation (ComVE) dataset introduced in [SemEval2020 Task4](https://competitions.codalab.org/competitions/21080) using a causal language modeling (CLM) objective.
The model is able to generate a reason why a given natural language statement is against commonsense.
## Intended uses & limitations
You can use the raw model for text generation to generate reasons why natural language statements are against commonsense.
#### How to use
You can use this model directly to generate reasons why the given statement is against commonsense using [`generate.sh`](https://github.com/AliOsm/SemEval2020-Task4-ComVE/tree/master/TaskC-Generation) script.
*Note:* make sure that you are using version `2.4.1` of `transformers` package. Newer versions has some issue in text generation and the model repeats the last token generated again and again.
#### Limitations and bias
The model biased to negate the entered sentence usually instead of producing a factual reason.
## Training data
The model is initialized from the [gpt2-large](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/master/model_cards/gpt2-README.md) model and finetuned using [ComVE](https://github.com/wangcunxiang/SemEval2020-Task4-Commonsense-Validation-and-Explanation) dataset which contains 10K against commonsense sentences, each of them is paired with three reference reasons.
## Training procedure
Each natural language statement that against commonsense is concatenated with its reference reason with `<|conteniue|>` as a separator, then the model finetuned using CLM objective.
The model trained on Nvidia Tesla P100 GPU from Google Colab platform with 5e-5 learning rate, 5 epochs, 128 maximum sequence length and 64 batch size.
<center>
<img src="https://i.imgur.com/xKbrwBC.png">
</center>
## Eval results
The model achieved 16.5110/15.9299 BLEU scores on SemEval2020 Task4: Commonsense Validation and Explanation development and testing dataset.
### BibTeX entry and citation info
```bibtex
@article{fadel2020justers,
title={JUSTers at SemEval-2020 Task 4: Evaluating Transformer Models Against Commonsense Validation and Explanation},
author={Fadel, Ali and Al-Ayyoub, Mahmoud and Cambria, Erik},
year={2020}
}
```
<a href="https://huggingface.co/exbert/?model=aliosm/ComVE-gpt2-large">
<img width="300px" src="https://cdn-media.huggingface.co/exbert/button.png">
</a>
|
kamivao/autonlp-cola_gram-208681
|
kamivao
| 2021-05-21T12:43:57Z | 5 | 0 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"bert",
"text-classification",
"autonlp",
"en",
"dataset:kamivao/autonlp-data-cola_gram",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
text-classification
| 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
---
tags: autonlp
language: en
widget:
- text: "I love AutoNLP 🤗"
datasets:
- kamivao/autonlp-data-cola_gram
---
# Model Trained Using AutoNLP
- Problem type: Binary Classification
- Model ID: 208681
## Validation Metrics
- Loss: 0.37569838762283325
- Accuracy: 0.8365019011406845
- Precision: 0.8398058252427184
- Recall: 0.9453551912568307
- AUC: 0.9048838797814208
- F1: 0.8894601542416453
## Usage
You can use cURL to access this model:
```
$ curl -X POST -H "Authorization: Bearer YOUR_API_KEY" -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{"inputs": "I love AutoNLP"}' https://api-inference.huggingface.co/models/kamivao/autonlp-cola_gram-208681
```
Or Python API:
```
from transformers import AutoModelForSequenceClassification, AutoTokenizer
model = AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained("kamivao/autonlp-cola_gram-208681", use_auth_token=True)
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("kamivao/autonlp-cola_gram-208681", use_auth_token=True)
inputs = tokenizer("I love AutoNLP", return_tensors="pt")
outputs = model(**inputs)
```
|
ainize/gpt2-spongebob-script-large
|
ainize
| 2021-05-21T12:18:42Z | 7 | 1 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"jax",
"gpt2",
"text-generation",
"autotrain_compatible",
"text-generation-inference",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
text-generation
| 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
### Model information
Fine tuning data: https://www.kaggle.com/mikhailgaerlan/spongebob-squarepants-completed-transcripts
License: CC-BY-SA
Base model: gpt-2 large
Epoch: 50
Train runtime: 14723.0716 secs
Loss: 0.0268
API page: [Ainize](https://ainize.ai/fpem123/GPT2-Spongebob?branch=master)
Demo page: [End-point](https://master-gpt2-spongebob-fpem123.endpoint.ainize.ai/)
### ===Teachable NLP=== ###
To train a GPT-2 model, write code and require GPU resources, but can easily fine-tune and get an API to use the model here for free.
Teachable NLP: [Teachable NLP](https://ainize.ai/teachable-nlp)
Tutorial: [Tutorial](https://forum.ainetwork.ai/t/teachable-nlp-how-to-use-teachable-nlp/65?utm_source=community&utm_medium=huggingface&utm_campaign=model&utm_content=teachable%20nlp)
|
ainize/gpt2-rnm-with-spongebob
|
ainize
| 2021-05-21T12:09:02Z | 9 | 0 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"jax",
"gpt2",
"text-generation",
"autotrain_compatible",
"text-generation-inference",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
text-generation
| 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
### Model information
Fine tuning data 1: https://www.kaggle.com/andradaolteanu/rickmorty-scripts
Fine tuning data 2: https://www.kaggle.com/mikhailgaerlan/spongebob-squarepants-completed-transcripts
Base model: e-tony/gpt2-rnm
Epoch: 2
Train runtime: 790.0612 secs
Loss: 2.8569
API page: [Ainize](https://ainize.ai/fpem123/GPT2-Rick-N-Morty-with-SpongeBob?branch=master)
Demo page: [End-point](https://master-gpt2-rick-n-morty-with-sponge-bob-fpem123.endpoint.ainize.ai/)
### ===Teachable NLP=== ###
To train a GPT-2 model, write code and require GPU resources, but can easily fine-tune and get an API to use the model here for free.
Teachable NLP: [Teachable NLP](https://ainize.ai/teachable-nlp)
Tutorial: [Tutorial](https://forum.ainetwork.ai/t/teachable-nlp-how-to-use-teachable-nlp/65?utm_source=community&utm_medium=huggingface&utm_campaign=model&utm_content=teachable%20nlp)
|
TheBakerCat/2chan_ruGPT3_small
|
TheBakerCat
| 2021-05-21T11:26:24Z | 13 | 0 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"jax",
"gpt2",
"text-generation",
"autotrain_compatible",
"text-generation-inference",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
text-generation
| 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
ruGPT3-small model, trained on some 2chan posts
|
SIC98/GPT2-python-code-generator
|
SIC98
| 2021-05-21T11:13:58Z | 17 | 9 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"jax",
"gpt2",
"text-generation",
"autotrain_compatible",
"text-generation-inference",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
text-generation
| 2022-03-02T23:29:04Z |
Github
- https://github.com/SIC98/GPT2-python-code-generator
|
Ochiroo/tiny_mn_gpt
|
Ochiroo
| 2021-05-21T10:59:47Z | 6 | 1 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"tf",
"gpt2",
"text-generation",
"mn",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
text-generation
| 2022-03-02T23:29:04Z |
---
language: mn
---
# GPT2-Mongolia
## Model description
GPT-2 is a transformers model pretrained on a very small corpus of Mongolian news data in a self-supervised fashion. This means it was pretrained on the raw texts only, with no humans labelling them in any way (which is why it can use lots of publicly available data) with an automatic process to generate inputs and labels from those texts. More precisely, it was trained to guess the next word in sentences.
## How to use
```python
import tensorflow as tf
from transformers import GPT2Config, TFGPT2LMHeadModel, GPT2Tokenizer
from transformers import WEIGHTS_NAME, CONFIG_NAME
tokenizer = GPT2Tokenizer.from_pretrained('Ochiroo/tiny_mn_gpt')
model = TFGPT2LMHeadModel.from_pretrained('Ochiroo/tiny_mn_gpt')
text = "Намайг Эрдэнэ-Очир гэдэг. Би"
input_ids = tokenizer.encode(text, return_tensors='tf')
beam_outputs = model.generate(
input_ids,
max_length = 25,
num_beams = 5,
temperature = 0.7,
no_repeat_ngram_size=2,
num_return_sequences=5
)
print(tokenizer.decode(beam_outputs[0]))
```
## Training data and biases
Trained on 500MB of Mongolian news dataset (IKON) on RTX 2060.
|
Meli/GPT2-Prompt
|
Meli
| 2021-05-21T10:55:36Z | 311 | 11 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"jax",
"gpt2",
"text-generation",
"en",
"autotrain_compatible",
"text-generation-inference",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
text-generation
| 2022-03-02T23:29:04Z |
---
language:
- en
tags:
- gpt2
- text-generation
pipeline_tag: text-generation
widget:
- text: "A person with a high school education gets sent back into the 1600s and tries to explain science and technology to the people. [endprompt]"
- text: "A kid doodling in a math class accidentally creates the world's first functional magic circle in centuries. [endprompt]"
---
# GPT-2 Story Generator
## Model description
Generate a short story from an input prompt.
Put the vocab ` [endprompt]` after your input.
Example of an input:
```
A person with a high school education gets sent back into the 1600s and tries to explain science and technology to the people. [endprompt]
```
#### Limitations and bias
The data we used to train was collected from reddit, so it could be very biased towards young, white, male demographic.
## Training data
The data was collected from scraping reddit.
|
HooshvareLab/gpt2-fa-poetry
|
HooshvareLab
| 2021-05-21T10:50:14Z | 65 | 0 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"tf",
"jax",
"gpt2",
"text-generation",
"fa",
"license:apache-2.0",
"autotrain_compatible",
"text-generation-inference",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
text-generation
| 2022-03-02T23:29:04Z |
---
language: fa
license: apache-2.0
widget:
- text: "<s>رودکی<|startoftext|>"
- text: "<s>فردوسی<|startoftext|>"
- text: "<s>خیام<|startoftext|>"
- text: "<s>عطار<|startoftext|>"
- text: "<s>نظامی<|startoftext|>"
---
# Persian Poet GPT2
## Poets
The model can generate poetry based on your favorite poet, and you need to add one of the following lines as the input the box on the right side or follow the [fine-tuning notebook](https://colab.research.google.com/github/hooshvare/parsgpt/blob/master/notebooks/Persian_Poetry_FineTuning.ipynb).
```text
<s>رودکی<|startoftext|>
<s>فردوسی<|startoftext|>
<s>کسایی<|startoftext|>
<s>ناصرخسرو<|startoftext|>
<s>منوچهری<|startoftext|>
<s>فرخی سیستانی<|startoftext|>
<s>مسعود سعد سلمان<|startoftext|>
<s>ابوسعید ابوالخیر<|startoftext|>
<s>باباطاهر<|startoftext|>
<s>فخرالدین اسعد گرگانی<|startoftext|>
<s>اسدی توسی<|startoftext|>
<s>هجویری<|startoftext|>
<s>خیام<|startoftext|>
<s>نظامی<|startoftext|>
<s>عطار<|startoftext|>
<s>سنایی<|startoftext|>
<s>خاقانی<|startoftext|>
<s>انوری<|startoftext|>
<s>عبدالواسع جبلی<|startoftext|>
<s>نصرالله منشی<|startoftext|>
<s>مهستی گنجوی<|startoftext|>
<s>باباافضل کاشانی<|startoftext|>
<s>مولوی<|startoftext|>
<s>سعدی<|startoftext|>
<s>خواجوی کرمانی<|startoftext|>
<s>عراقی<|startoftext|>
<s>سیف فرغانی<|startoftext|>
<s>حافظ<|startoftext|>
<s>اوحدی<|startoftext|>
<s>شیخ محمود شبستری<|startoftext|>
<s>عبید زاکانی<|startoftext|>
<s>امیرخسرو دهلوی<|startoftext|>
<s>سلمان ساوجی<|startoftext|>
<s>شاه نعمتالله ولی<|startoftext|>
<s>جامی<|startoftext|>
<s>هلالی جغتایی<|startoftext|>
<s>وحشی<|startoftext|>
<s>محتشم کاشانی<|startoftext|>
<s>شیخ بهایی<|startoftext|>
<s>عرفی<|startoftext|>
<s>رضیالدین آرتیمانی<|startoftext|>
<s>صائب تبریزی<|startoftext|>
<s>فیض کاشانی<|startoftext|>
<s>بیدل دهلوی<|startoftext|>
<s>هاتف اصفهانی<|startoftext|>
<s>فروغی بسطامی<|startoftext|>
<s>قاآنی<|startoftext|>
<s>ملا هادی سبزواری<|startoftext|>
<s>پروین اعتصامی<|startoftext|>
<s>ملکالشعرای بهار<|startoftext|>
<s>شهریار<|startoftext|>
<s>رهی معیری<|startoftext|>
<s>اقبال لاهوری<|startoftext|>
<s>خلیلالله خلیلی<|startoftext|>
<s>شاطرعباس صبوحی<|startoftext|>
<s>نیما یوشیج ( آوای آزاد )<|startoftext|>
<s>احمد شاملو<|startoftext|>
<s>سهراب سپهری<|startoftext|>
<s>فروغ فرخزاد<|startoftext|>
<s>سیمین بهبهانی<|startoftext|>
<s>مهدی اخوان ثالث<|startoftext|>
<s>محمدحسن بارق شفیعی<|startoftext|>
<s>شیون فومنی<|startoftext|>
<s>کامبیز صدیقی کسمایی<|startoftext|>
<s>بهرام سالکی<|startoftext|>
<s>عبدالقهّار عاصی<|startoftext|>
<s>اِ لیـــار (جبار محمدی )<|startoftext|>
```
## Questions?
Post a Github issue on the [ParsGPT2 Issues](https://github.com/hooshvare/parsgpt/issues) repo.
|
Davlan/mt5_base_eng_yor_mt
|
Davlan
| 2021-05-21T10:14:10Z | 54 | 0 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"mt5",
"text2text-generation",
"arxiv:2103.08647",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
text2text-generation
| 2022-03-02T23:29:04Z |
Hugging Face's logo
---
language:
- yo
- en
datasets:
- JW300 + [Menyo-20k](https://huggingface.co/datasets/menyo20k_mt)
---
# mT5_base_eng_yor_mt
## Model description
**mT5_base_yor_eng_mt** is a **machine translation** model from English language to Yorùbá language based on a fine-tuned mT5-base model. It establishes a **strong baseline** for automatically translating texts from English to Yorùbá.
Specifically, this model is a *mT5_base* model that was fine-tuned on JW300 Yorùbá corpus and [Menyo-20k](https://huggingface.co/datasets/menyo20k_mt)
## Intended uses & limitations
#### How to use
You can use this model with Transformers *pipeline* for MT.
```python
from transformers import MT5ForConditionalGeneration, T5Tokenizer
model = MT5ForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained("Davlan/mt5_base_eng_yor_mt")
tokenizer = T5Tokenizer.from_pretrained("google/mt5-base")
input_string = "Where are you?"
inputs = tokenizer.encode(input_string, return_tensors="pt")
generated_tokens = model.generate(inputs)
results = tokenizer.batch_decode(generated_tokens, skip_special_tokens=True)
print(results)
```
#### Limitations and bias
This model is limited by its training dataset of entity-annotated news articles from a specific span of time. This may not generalize well for all use cases in different domains.
## Training data
This model was fine-tuned on on JW300 corpus and [Menyo-20k](https://huggingface.co/datasets/menyo20k_mt) dataset
## Training procedure
This model was trained on a single NVIDIA V100 GPU
## Eval results on Test set (BLEU score)
9.82 BLEU on [Menyo-20k test set](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.08647)
### BibTeX entry and citation info
By David Adelani
```
```
|
HJK/PickupLineGenerator
|
HJK
| 2021-05-21T10:05:21Z | 12 | 1 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"jax",
"gpt2",
"text-generation",
"autotrain_compatible",
"text-generation-inference",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
text-generation
| 2022-03-02T23:29:04Z |
basically, it makes pickup lines
https://huggingface.co/gpt2
|
CallumRai/HansardGPT2
|
CallumRai
| 2021-05-21T09:33:25Z | 15 | 1 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"jax",
"gpt2",
"text-generation",
"autotrain_compatible",
"text-generation-inference",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
text-generation
| 2022-03-02T23:29:04Z |
A PyTorch GPT-2 model trained on hansard from 2019-01-01 to 2020-06-01
For more information see: https://github.com/CallumRai/Hansard/
|
lg/fexp_1
|
lg
| 2021-05-20T23:37:11Z | 5 | 0 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"gpt_neo",
"text-generation",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
text-generation
| 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
# This model is probably not what you're looking for.
|
ynie/roberta-large-snli_mnli_fever_anli_R1_R2_R3-nli
|
ynie
| 2021-05-20T23:17:23Z | 17,917 | 18 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"jax",
"roberta",
"text-classification",
"dataset:snli",
"dataset:anli",
"dataset:multi_nli",
"dataset:multi_nli_mismatch",
"dataset:fever",
"license:mit",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
text-classification
| 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
---
datasets:
- snli
- anli
- multi_nli
- multi_nli_mismatch
- fever
license: mit
---
This is a strong pre-trained RoBERTa-Large NLI model.
The training data is a combination of well-known NLI datasets: [`SNLI`](https://nlp.stanford.edu/projects/snli/), [`MNLI`](https://cims.nyu.edu/~sbowman/multinli/), [`FEVER-NLI`](https://github.com/easonnie/combine-FEVER-NSMN/blob/master/other_resources/nli_fever.md), [`ANLI (R1, R2, R3)`](https://github.com/facebookresearch/anli).
Other pre-trained NLI models including `RoBERTa`, `ALBert`, `BART`, `ELECTRA`, `XLNet` are also available.
Trained by [Yixin Nie](https://easonnie.github.io), [original source](https://github.com/facebookresearch/anli).
Try the code snippet below.
```
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForSequenceClassification
import torch
if __name__ == '__main__':
max_length = 256
premise = "Two women are embracing while holding to go packages."
hypothesis = "The men are fighting outside a deli."
hg_model_hub_name = "ynie/roberta-large-snli_mnli_fever_anli_R1_R2_R3-nli"
# hg_model_hub_name = "ynie/albert-xxlarge-v2-snli_mnli_fever_anli_R1_R2_R3-nli"
# hg_model_hub_name = "ynie/bart-large-snli_mnli_fever_anli_R1_R2_R3-nli"
# hg_model_hub_name = "ynie/electra-large-discriminator-snli_mnli_fever_anli_R1_R2_R3-nli"
# hg_model_hub_name = "ynie/xlnet-large-cased-snli_mnli_fever_anli_R1_R2_R3-nli"
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(hg_model_hub_name)
model = AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained(hg_model_hub_name)
tokenized_input_seq_pair = tokenizer.encode_plus(premise, hypothesis,
max_length=max_length,
return_token_type_ids=True, truncation=True)
input_ids = torch.Tensor(tokenized_input_seq_pair['input_ids']).long().unsqueeze(0)
# remember bart doesn't have 'token_type_ids', remove the line below if you are using bart.
token_type_ids = torch.Tensor(tokenized_input_seq_pair['token_type_ids']).long().unsqueeze(0)
attention_mask = torch.Tensor(tokenized_input_seq_pair['attention_mask']).long().unsqueeze(0)
outputs = model(input_ids,
attention_mask=attention_mask,
token_type_ids=token_type_ids,
labels=None)
# Note:
# "id2label": {
# "0": "entailment",
# "1": "neutral",
# "2": "contradiction"
# },
predicted_probability = torch.softmax(outputs[0], dim=1)[0].tolist() # batch_size only one
print("Premise:", premise)
print("Hypothesis:", hypothesis)
print("Entailment:", predicted_probability[0])
print("Neutral:", predicted_probability[1])
print("Contradiction:", predicted_probability[2])
```
More in [here](https://github.com/facebookresearch/anli/blob/master/src/hg_api/interactive_eval.py).
Citation:
```
@inproceedings{nie-etal-2020-adversarial,
title = "Adversarial {NLI}: A New Benchmark for Natural Language Understanding",
author = "Nie, Yixin and
Williams, Adina and
Dinan, Emily and
Bansal, Mohit and
Weston, Jason and
Kiela, Douwe",
booktitle = "Proceedings of the 58th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics",
year = "2020",
publisher = "Association for Computational Linguistics",
}
```
|
urduhack/roberta-urdu-small
|
urduhack
| 2021-05-20T22:52:23Z | 884 | 8 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"jax",
"roberta",
"fill-mask",
"roberta-urdu-small",
"urdu",
"ur",
"license:mit",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
fill-mask
| 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
---
language: ur
thumbnail: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/urduhack/urduhack/master/docs/_static/urduhack.png
tags:
- roberta-urdu-small
- urdu
- transformers
license: mit
---
## roberta-urdu-small
[](https://github.com/urduhack/urduhack/blob/master/LICENSE)
### Overview
**Language model:** roberta-urdu-small
**Model size:** 125M
**Language:** Urdu
**Training data:** News data from urdu news resources in Pakistan
### About roberta-urdu-small
roberta-urdu-small is a language model for urdu language.
```
from transformers import pipeline
fill_mask = pipeline("fill-mask", model="urduhack/roberta-urdu-small", tokenizer="urduhack/roberta-urdu-small")
```
## Training procedure
roberta-urdu-small was trained on urdu news corpus. Training data was normalized using normalization module from
urduhack to eliminate characters from other languages like arabic.
### About Urduhack
Urduhack is a Natural Language Processing (NLP) library for urdu language.
Github: https://github.com/urduhack/urduhack
|
typeform/distilroberta-base-v2
|
typeform
| 2021-05-20T22:46:35Z | 91 | 0 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"jax",
"roberta",
"fill-mask",
"en",
"dataset:openwebtext",
"license:apache-2.0",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
fill-mask
| 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
---
language: en
license: apache-2.0
datasets:
- openwebtext
---
# DistilRoBERTa base model
Forked from https://huggingface.co/distilroberta-base
|
tlemberger/sd-ner
|
tlemberger
| 2021-05-20T22:31:05Z | 4 | 0 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"jax",
"roberta",
"token-classification",
"token classification",
"dataset:EMBO/sd-panels",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
token-classification
| 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
---
language:
- english
thumbnail:
tags:
- token classification
license:
datasets:
- EMBO/sd-panels
metrics:
-
---
# sd-ner
## Model description
This model is a [RoBERTa base model](https://huggingface.co/roberta-base) that was further trained using a masked language modeling task on a compendium of english scientific textual examples from the life sciences using the [BioLang dataset](https://huggingface.co/datasets/EMBO/biolang) and fine-tuned for token classification on the SourceData [sd-panels](https://huggingface.co/datasets/EMBO/sd-panels) dataset to perform Named Entity Recognition of bioentities.
## Intended uses & limitations
#### How to use
The intended use of this model is for Named Entity Recognition of biological entitie used in SourceData annotations (https://sourcedata.embo.org), including small molecules, gene products (genes and proteins), subcellular components, cell line and cell types, organ and tissues, species as well as experimental methods.
To have a quick check of the model:
```python
from transformers import pipeline, RobertaTokenizerFast, RobertaForTokenClassification
example = """<s> F. Western blot of input and eluates of Upf1 domains purification in a Nmd4-HA strain. The band with the # might corresponds to a dimer of Upf1-CH, bands marked with a star correspond to residual signal with the anti-HA antibodies (Nmd4). Fragments in the eluate have a smaller size because the protein A part of the tag was removed by digestion with the TEV protease. G6PDH served as a loading control in the input samples </s>"""
tokenizer = RobertaTokenizerFast.from_pretrained('roberta-base', max_len=512)
model = RobertaForTokenClassification.from_pretrained('EMBO/sd-ner')
ner = pipeline('ner', model, tokenizer=tokenizer)
res = ner(example)
for r in res:
print(r['word'], r['entity'])
```
#### Limitations and bias
The model must be used with the `roberta-base` tokenizer.
## Training data
The model was trained for token classification using the [EMBO/sd-panels dataset](https://huggingface.co/datasets/EMBO/biolang) wich includes manually annotated examples.
## Training procedure
The training was run on a NVIDIA DGX Station with 4XTesla V100 GPUs.
Training code is available at https://github.com/source-data/soda-roberta
- Command: `python -m tokcl.train /data/json/sd_panels NER --num_train_epochs=3.5`
- Tokenizer vocab size: 50265
- Training data: EMBO/biolang MLM
- Training with 31410 examples.
- Evaluating on 8861 examples.
- Training on 15 features: O, I-SMALL_MOLECULE, B-SMALL_MOLECULE, I-GENEPROD, B-GENEPROD, I-SUBCELLULAR, B-SUBCELLULAR, I-CELL, B-CELL, I-TISSUE, B-TISSUE, I-ORGANISM, B-ORGANISM, I-EXP_ASSAY, B-EXP_ASSAY
- Epochs: 3.5
- `per_device_train_batch_size`: 32
- `per_device_eval_batch_size`: 32
- `learning_rate`: 0.0001
- `weight_decay`: 0.0
- `adam_beta1`: 0.9
- `adam_beta2`: 0.999
- `adam_epsilon`: 1e-08
- `max_grad_norm`: 1.0
## Eval results
On test set with `sklearn.metrics`:
```
precision recall f1-score support
CELL 0.77 0.81 0.79 3477
EXP_ASSAY 0.71 0.70 0.71 7049
GENEPROD 0.86 0.90 0.88 16140
ORGANISM 0.80 0.82 0.81 2759
SMALL_MOLECULE 0.78 0.82 0.80 4446
SUBCELLULAR 0.71 0.75 0.73 2125
TISSUE 0.70 0.75 0.73 1971
micro avg 0.79 0.82 0.81 37967
macro avg 0.76 0.79 0.78 37967
weighted avg 0.79 0.82 0.81 37967
```
|
textattack/roberta-base-rotten_tomatoes
|
textattack
| 2021-05-20T22:18:23Z | 8 | 1 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"jax",
"tensorboard",
"roberta",
"fill-mask",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
fill-mask
| 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
## roberta-base fine-tuned with TextAttack on the rotten_tomatoes dataset
This `roberta-base` model was fine-tuned for sequence classificationusing TextAttack
and the rotten_tomatoes dataset loaded using the `nlp` library. The model was fine-tuned
for 10 epochs with a batch size of 128, a learning
rate of 5e-05, and a maximum sequence length of 128.
Since this was a classification task, the model was trained with a cross-entropy loss function.
The best score the model achieved on this task was 0.9033771106941839, as measured by the
eval set accuracy, found after 9 epochs.
For more information, check out [TextAttack on Github](https://github.com/QData/TextAttack).
|
textattack/roberta-base-rotten-tomatoes
|
textattack
| 2021-05-20T22:17:29Z | 34 | 0 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"jax",
"roberta",
"text-classification",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
text-classification
| 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
## TextAttack Model Card
This `roberta-base` model was fine-tuned for sequence classificationusing TextAttack
and the rotten_tomatoes dataset loaded using the `nlp` library. The model was fine-tuned
for 10 epochs with a batch size of 64, a learning
rate of 2e-05, and a maximum sequence length of 128.
Since this was a classification task, the model was trained with a cross-entropy loss function.
The best score the model achieved on this task was 0.9033771106941839, as measured by the
eval set accuracy, found after 2 epochs.
For more information, check out [TextAttack on Github](https://github.com/QData/TextAttack).
|
textattack/roberta-base-imdb
|
textattack
| 2021-05-20T22:16:19Z | 207 | 1 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"jax",
"roberta",
"text-classification",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
text-classification
| 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
## TextAttack Model Card
This `roberta-base` model was fine-tuned for sequence classification using TextAttack
and the imdb dataset loaded using the `nlp` library. The model was fine-tuned
for 5 epochs with a batch size of 64, a learning
rate of 3e-05, and a maximum sequence length of 128.
Since this was a classification task, the model was trained with a cross-entropy loss function.
The best score the model achieved on this task was 0.91436, as measured by the
eval set accuracy, found after 2 epochs.
For more information, check out [TextAttack on Github](https://github.com/QData/TextAttack).
|
simonlevine/clinical-longformer
|
simonlevine
| 2021-05-20T21:25:09Z | 19 | 0 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"jax",
"roberta",
"fill-mask",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
fill-mask
| 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
- You'll need to instantiate a special RoBERTa class. Though technically a "Longformer", the elongated RoBERTa model will still need to be pulled in as such.
- To do so, use the following classes:
```python
class RobertaLongSelfAttention(LongformerSelfAttention):
def forward(
self,
hidden_states,
attention_mask=None,
head_mask=None,
encoder_hidden_states=None,
encoder_attention_mask=None,
output_attentions=False,
):
return super().forward(hidden_states, attention_mask=attention_mask, output_attentions=output_attentions)
class RobertaLongForMaskedLM(RobertaForMaskedLM):
def __init__(self, config):
super().__init__(config)
for i, layer in enumerate(self.roberta.encoder.layer):
# replace the `modeling_bert.BertSelfAttention` object with `LongformerSelfAttention`
layer.attention.self = RobertaLongSelfAttention(config, layer_id=i)
```
- Then, pull the model as ```RobertaLongForMaskedLM.from_pretrained('simonlevine/bioclinical-roberta-long')```
- Now, it can be used as usual. Note you may get untrained weights warnings.
- Note that you can replace ```RobertaForMaskedLM``` with a different task-specific RoBERTa from Huggingface, such as RobertaForSequenceClassification.
|
sramasamy8/testModel
|
sramasamy8
| 2021-05-20T20:58:24Z | 4 | 0 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"bert",
"fill-mask",
"exbert",
"en",
"dataset:bookcorpus",
"dataset:wikipedia",
"arxiv:1810.04805",
"license:apache-2.0",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
fill-mask
| 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
---
language: en
tags:
- exbert
license: apache-2.0
datasets:
- bookcorpus
- wikipedia
---
# BERT base model (uncased)
Pretrained model on English language using a masked language modeling (MLM) objective. It was introduced in
[this paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/1810.04805) and first released in
[this repository](https://github.com/google-research/bert). This model is uncased: it does not make a difference
between english and English.
Disclaimer: The team releasing BERT did not write a model card for this model so this model card has been written by
the Hugging Face team.
## Model description
BERT is a transformers model pretrained on a large corpus of English data in a self-supervised fashion. This means it
was pretrained on the raw texts only, with no humans labelling them in any way (which is why it can use lots of
publicly available data) with an automatic process to generate inputs and labels from those texts. More precisely, it
was pretrained with two objectives:
- Masked language modeling (MLM): taking a sentence, the model randomly masks 15% of the words in the input then run
the entire masked sentence through the model and has to predict the masked words. This is different from traditional
recurrent neural networks (RNNs) that usually see the words one after the other, or from autoregressive models like
GPT which internally mask the future tokens. It allows the model to learn a bidirectional representation of the
sentence.
- Next sentence prediction (NSP): the models concatenates two masked sentences as inputs during pretraining. Sometimes
they correspond to sentences that were next to each other in the original text, sometimes not. The model then has to
predict if the two sentences were following each other or not.
This way, the model learns an inner representation of the English language that can then be used to extract features
useful for downstream tasks: if you have a dataset of labeled sentences for instance, you can train a standard
classifier using the features produced by the BERT model as inputs.
## Intended uses & limitations
You can use the raw model for either masked language modeling or next sentence prediction, but it's mostly intended to
be fine-tuned on a downstream task. See the [model hub](https://huggingface.co/models?filter=bert) to look for
fine-tuned versions on a task that interests you.
Note that this model is primarily aimed at being fine-tuned on tasks that use the whole sentence (potentially masked)
to make decisions, such as sequence classification, token classification or question answering. For tasks such as text
generation you should look at model like GPT2.
### How to use
You can use this model directly with a pipeline for masked language modeling:
```python
>>> from transformers import pipeline
>>> unmasker = pipeline('fill-mask', model='bert-base-uncased')
>>> unmasker("Hello I'm a [MASK] model.")
[{'sequence': "[CLS] hello i'm a fashion model. [SEP]",
'score': 0.1073106899857521,
'token': 4827,
'token_str': 'fashion'},
{'sequence': "[CLS] hello i'm a role model. [SEP]",
'score': 0.08774490654468536,
'token': 2535,
'token_str': 'role'},
{'sequence': "[CLS] hello i'm a new model. [SEP]",
'score': 0.05338378623127937,
'token': 2047,
'token_str': 'new'},
{'sequence': "[CLS] hello i'm a super model. [SEP]",
'score': 0.04667217284440994,
'token': 3565,
'token_str': 'super'},
{'sequence': "[CLS] hello i'm a fine model. [SEP]",
'score': 0.027095865458250046,
'token': 2986,
'token_str': 'fine'}]
```
Here is how to use this model to get the features of a given text in PyTorch:
```python
from transformers import BertTokenizer, BertModel
tokenizer = BertTokenizer.from_pretrained('bert-base-uncased')
model = BertModel.from_pretrained("bert-base-uncased")
text = "Replace me by any text you'd like."
encoded_input = tokenizer(text, return_tensors='pt')
output = model(**encoded_input)
```
and in TensorFlow:
```python
from transformers import BertTokenizer, TFBertModel
tokenizer = BertTokenizer.from_pretrained('bert-base-uncased')
model = TFBertModel.from_pretrained("bert-base-uncased")
text = "Replace me by any text you'd like."
encoded_input = tokenizer(text, return_tensors='tf')
output = model(encoded_input)
```
### Limitations and bias
Even if the training data used for this model could be characterized as fairly neutral, this model can have biased
predictions:
```python
>>> from transformers import pipeline
>>> unmasker = pipeline('fill-mask', model='bert-base-uncased')
>>> unmasker("The man worked as a [MASK].")
[{'sequence': '[CLS] the man worked as a carpenter. [SEP]',
'score': 0.09747550636529922,
'token': 10533,
'token_str': 'carpenter'},
{'sequence': '[CLS] the man worked as a waiter. [SEP]',
'score': 0.0523831807076931,
'token': 15610,
'token_str': 'waiter'},
{'sequence': '[CLS] the man worked as a barber. [SEP]',
'score': 0.04962705448269844,
'token': 13362,
'token_str': 'barber'},
{'sequence': '[CLS] the man worked as a mechanic. [SEP]',
'score': 0.03788609802722931,
'token': 15893,
'token_str': 'mechanic'},
{'sequence': '[CLS] the man worked as a salesman. [SEP]',
'score': 0.037680890411138535,
'token': 18968,
'token_str': 'salesman'}]
>>> unmasker("The woman worked as a [MASK].")
[{'sequence': '[CLS] the woman worked as a nurse. [SEP]',
'score': 0.21981462836265564,
'token': 6821,
'token_str': 'nurse'},
{'sequence': '[CLS] the woman worked as a waitress. [SEP]',
'score': 0.1597415804862976,
'token': 13877,
'token_str': 'waitress'},
{'sequence': '[CLS] the woman worked as a maid. [SEP]',
'score': 0.1154729500412941,
'token': 10850,
'token_str': 'maid'},
{'sequence': '[CLS] the woman worked as a prostitute. [SEP]',
'score': 0.037968918681144714,
'token': 19215,
'token_str': 'prostitute'},
{'sequence': '[CLS] the woman worked as a cook. [SEP]',
'score': 0.03042375110089779,
'token': 5660,
'token_str': 'cook'}]
```
This bias will also affect all fine-tuned versions of this model.
## Training data
The BERT model was pretrained on [BookCorpus](https://yknzhu.wixsite.com/mbweb), a dataset consisting of 11,038
unpublished books and [English Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/English_Wikipedia) (excluding lists, tables and
headers).
## Training procedure
### Preprocessing
The texts are lowercased and tokenized using WordPiece and a vocabulary size of 30,000. The inputs of the model are
then of the form:
```
[CLS] Sentence A [SEP] Sentence B [SEP]
```
With probability 0.5, sentence A and sentence B correspond to two consecutive sentences in the original corpus and in
the other cases, it's another random sentence in the corpus. Note that what is considered a sentence here is a
consecutive span of text usually longer than a single sentence. The only constrain is that the result with the two
"sentences" has a combined length of less than 512 tokens.
The details of the masking procedure for each sentence are the following:
- 15% of the tokens are masked.
- In 80% of the cases, the masked tokens are replaced by `[MASK]`.
- In 10% of the cases, the masked tokens are replaced by a random token (different) from the one they replace.
- In the 10% remaining cases, the masked tokens are left as is.
### Pretraining
The model was trained on 4 cloud TPUs in Pod configuration (16 TPU chips total) for one million steps with a batch size
of 256. The sequence length was limited to 128 tokens for 90% of the steps and 512 for the remaining 10%. The optimizer
used is Adam with a learning rate of 1e-4, \\(\beta_{1} = 0.9\\) and \\(\beta_{2} = 0.999\\), a weight decay of 0.01,
learning rate warmup for 10,000 steps and linear decay of the learning rate after.
## Evaluation results
When fine-tuned on downstream tasks, this model achieves the following results:
Glue test results:
| Task | MNLI-(m/mm) | QQP | QNLI | SST-2 | CoLA | STS-B | MRPC | RTE | Average |
|:----:|:-----------:|:----:|:----:|:-----:|:----:|:-----:|:----:|:----:|:-------:|
| | 84.6/83.4 | 71.2 | 90.5 | 93.5 | 52.1 | 85.8 | 88.9 | 66.4 | 79.6 |
### BibTeX entry and citation info
```bibtex
@article{DBLP:journals/corr/abs-1810-04805,
author = {Jacob Devlin and
Ming{-}Wei Chang and
Kenton Lee and
Kristina Toutanova},
title = {{BERT:} Pre-training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language
Understanding},
journal = {CoRR},
volume = {abs/1810.04805},
year = {2018},
url = {http://arxiv.org/abs/1810.04805},
archivePrefix = {arXiv},
eprint = {1810.04805},
timestamp = {Tue, 30 Oct 2018 20:39:56 +0100},
biburl = {https://dblp.org/rec/journals/corr/abs-1810-04805.bib},
bibsource = {dblp computer science bibliography, https://dblp.org}
}
```
<a href="https://huggingface.co/exbert/?model=bert-base-uncased">
<img width="300px" src="https://cdn-media.huggingface.co/exbert/button.png">
</a>
|
seyonec/ChemBERTa-zinc-base-v1
|
seyonec
| 2021-05-20T20:55:33Z | 96,218 | 46 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"jax",
"roberta",
"fill-mask",
"chemistry",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
fill-mask
| 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
---
tags:
- chemistry
---
# ChemBERTa: Training a BERT-like transformer model for masked language modelling of chemical SMILES strings.
Deep learning for chemistry and materials science remains a novel field with lots of potiential. However, the popularity of transfer learning based methods in areas such as NLP and computer vision have not yet been effectively developed in computational chemistry + machine learning. Using HuggingFace's suite of models and the ByteLevel tokenizer, we are able to train on a large corpus of 100k SMILES strings from a commonly known benchmark dataset, ZINC.
Training RoBERTa over 5 epochs, the model achieves a decent loss of 0.398, but may likely continue to decline if trained for a larger number of epochs. The model can predict tokens within a SMILES sequence/molecule, allowing for variants of a molecule within discoverable chemical space to be predicted.
By applying the representations of functional groups and atoms learned by the model, we can try to tackle problems of toxicity, solubility, drug-likeness, and synthesis accessibility on smaller datasets using the learned representations as features for graph convolution and attention models on the graph structure of molecules, as well as fine-tuning of BERT. Finally, we propose the use of attention visualization as a helpful tool for chemistry practitioners and students to quickly identify important substructures in various chemical properties.
Additionally, visualization of the attention mechanism have been seen through previous research as incredibly valuable towards chemical reaction classification. The applications of open-sourcing large-scale transformer models such as RoBERTa with HuggingFace may allow for the acceleration of these individual research directions.
A link to a repository which includes the training, uploading and evaluation notebook (with sample predictions on compounds such as Remdesivir) can be found [here](https://github.com/seyonechithrananda/bert-loves-chemistry). All of the notebooks can be copied into a new Colab runtime for easy execution.
Thanks for checking this out!
- Seyone
|
prajjwal1/roberta-base-mnli
|
prajjwal1
| 2021-05-20T19:31:02Z | 4 | 0 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"jax",
"roberta",
"text-classification",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
text-classification
| 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
Roberta-base trained on MNLI.
| Task | Accuracy |
|---------|----------|
| MNLI | 86.32 |
| MNLI-mm | 86.43 |
You can also check out:
- `prajjwal1/roberta-base-mnli`
- `prajjwal1/roberta-large-mnli`
- `prajjwal1/albert-base-v2-mnli`
- `prajjwal1/albert-base-v1-mnli`
- `prajjwal1/albert-large-v2-mnli`
[@prajjwal_1](https://twitter.com/prajjwal_1)
|
pradhyra/AWSBlogBert
|
pradhyra
| 2021-05-20T19:30:09Z | 9 | 0 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"jax",
"roberta",
"fill-mask",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
fill-mask
| 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
This model is pre-trained on blog articles from AWS Blogs.
## Pre-training corpora
The input text contains around 3000 blog articles on [AWS Blogs website](https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/) technical subject matter including AWS products, tools and tutorials.
## Pre-training details
I picked a Roberta architecture for masked language modeling (6-layer, 768-hidden, 12-heads, 82M parameters) and its corresponding ByteLevelBPE tokenization strategy. I then followed HuggingFace's Transformers [blog post](https://huggingface.co/blog/how-to-train) to train the model.
I chose to follow the following training set-up: 28k training steps with batches of 64 sequences of length 512 with an initial learning rate 5e-5. The model acheived a training loss of 3.6 on the MLM task over 10 epochs.
|
patrickvonplaten/norwegian-roberta-large
|
patrickvonplaten
| 2021-05-20T19:15:37Z | 3 | 0 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"tensorboard",
"roberta",
"fill-mask",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
fill-mask
| 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
## Roberta-Large
This repo trains [roberta-large](https://huggingface.co/roberta-large) from scratch on the [Norwegian training subset of Oscar](https://oscar-corpus.com/) containing roughly 4.7 GB of data.
A ByteLevelBPETokenizer as shown in [this]( ) blog post was trained on the whole [Norwegian training subset of Oscar](https://oscar-corpus.com/).
Training is done on a TPUv3-8 in Flax. The training script as well as the script to create a tokenizer are attached below.
### Run 1
```
--weight_decay="0.01"
--max_seq_length="128"
--train_batch_size="1048"
--eval_batch_size="1048"
--learning_rate="1e-3"
--warmup_steps="2000"
--pad_to_max_length
--num_train_epochs="12"
--adam_beta1="0.9"
--adam_beta2="0.98"
```
Trained for 12 epochs with each epoch including 8005 steps => Total of 96K steps. 1 epoch + eval takes roughly 2 hours 40 minutes => trained in total for 1 day and 8 hours. Final loss was 3.695.
**Acc**:

**Loss**:

### Run 2
```
--weight_decay="0.01"
--max_seq_length="128"
--train_batch_size="1048"
--eval_batch_size="1048"
--learning_rate="5e-3"
--warmup_steps="2000"
--pad_to_max_length
--num_train_epochs="7"
--adam_beta1="0.9"
--adam_beta2="0.98"
```
Trained for 7 epochs with each epoch including 8005 steps => Total of 96K steps. 1 epoch + eval takes roughly 2 hours 40 minutes => trained in total for 18 hours. Final loss was 2.216 and accuracy 0.58.
**Acc**:

**Loss**:

|
nyu-mll/roberta-med-small-1M-3
|
nyu-mll
| 2021-05-20T19:09:09Z | 5 | 0 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"jax",
"roberta",
"fill-mask",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
fill-mask
| 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
# RoBERTa Pretrained on Smaller Datasets
We pretrain RoBERTa on smaller datasets (1M, 10M, 100M, 1B tokens). We release 3 models with lowest perplexities for each pretraining data size out of 25 runs (or 10 in the case of 1B tokens). The pretraining data reproduces that of BERT: We combine English Wikipedia and a reproduction of BookCorpus using texts from smashwords in a ratio of approximately 3:1.
### Hyperparameters and Validation Perplexity
The hyperparameters and validation perplexities corresponding to each model are as follows:
| Model Name | Training Size | Model Size | Max Steps | Batch Size | Validation Perplexity |
|--------------------------|---------------|------------|-----------|------------|-----------------------|
| [roberta-base-1B-1][link-roberta-base-1B-1] | 1B | BASE | 100K | 512 | 3.93 |
| [roberta-base-1B-2][link-roberta-base-1B-2] | 1B | BASE | 31K | 1024 | 4.25 |
| [roberta-base-1B-3][link-roberta-base-1B-3] | 1B | BASE | 31K | 4096 | 3.84 |
| [roberta-base-100M-1][link-roberta-base-100M-1] | 100M | BASE | 100K | 512 | 4.99 |
| [roberta-base-100M-2][link-roberta-base-100M-2] | 100M | BASE | 31K | 1024 | 4.61 |
| [roberta-base-100M-3][link-roberta-base-100M-3] | 100M | BASE | 31K | 512 | 5.02 |
| [roberta-base-10M-1][link-roberta-base-10M-1] | 10M | BASE | 10K | 1024 | 11.31 |
| [roberta-base-10M-2][link-roberta-base-10M-2] | 10M | BASE | 10K | 512 | 10.78 |
| [roberta-base-10M-3][link-roberta-base-10M-3] | 10M | BASE | 31K | 512 | 11.58 |
| [roberta-med-small-1M-1][link-roberta-med-small-1M-1] | 1M | MED-SMALL | 100K | 512 | 153.38 |
| [roberta-med-small-1M-2][link-roberta-med-small-1M-2] | 1M | MED-SMALL | 10K | 512 | 134.18 |
| [roberta-med-small-1M-3][link-roberta-med-small-1M-3] | 1M | MED-SMALL | 31K | 512 | 139.39 |
The hyperparameters corresponding to model sizes mentioned above are as follows:
| Model Size | L | AH | HS | FFN | P |
|------------|----|----|-----|------|------|
| BASE | 12 | 12 | 768 | 3072 | 125M |
| MED-SMALL | 6 | 8 | 512 | 2048 | 45M |
(AH = number of attention heads; HS = hidden size; FFN = feedforward network dimension; P = number of parameters.)
For other hyperparameters, we select:
- Peak Learning rate: 5e-4
- Warmup Steps: 6% of max steps
- Dropout: 0.1
[link-roberta-med-small-1M-1]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-med-small-1M-1
[link-roberta-med-small-1M-2]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-med-small-1M-2
[link-roberta-med-small-1M-3]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-med-small-1M-3
[link-roberta-base-10M-1]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-base-10M-1
[link-roberta-base-10M-2]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-base-10M-2
[link-roberta-base-10M-3]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-base-10M-3
[link-roberta-base-100M-1]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-base-100M-1
[link-roberta-base-100M-2]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-base-100M-2
[link-roberta-base-100M-3]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-base-100M-3
[link-roberta-base-1B-1]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-base-1B-1
[link-roberta-base-1B-2]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-base-1B-2
[link-roberta-base-1B-3]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-base-1B-3
|
nyu-mll/roberta-med-small-1M-1
|
nyu-mll
| 2021-05-20T19:06:25Z | 8 | 1 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"jax",
"roberta",
"fill-mask",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
fill-mask
| 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
# RoBERTa Pretrained on Smaller Datasets
We pretrain RoBERTa on smaller datasets (1M, 10M, 100M, 1B tokens). We release 3 models with lowest perplexities for each pretraining data size out of 25 runs (or 10 in the case of 1B tokens). The pretraining data reproduces that of BERT: We combine English Wikipedia and a reproduction of BookCorpus using texts from smashwords in a ratio of approximately 3:1.
### Hyperparameters and Validation Perplexity
The hyperparameters and validation perplexities corresponding to each model are as follows:
| Model Name | Training Size | Model Size | Max Steps | Batch Size | Validation Perplexity |
|--------------------------|---------------|------------|-----------|------------|-----------------------|
| [roberta-base-1B-1][link-roberta-base-1B-1] | 1B | BASE | 100K | 512 | 3.93 |
| [roberta-base-1B-2][link-roberta-base-1B-2] | 1B | BASE | 31K | 1024 | 4.25 |
| [roberta-base-1B-3][link-roberta-base-1B-3] | 1B | BASE | 31K | 4096 | 3.84 |
| [roberta-base-100M-1][link-roberta-base-100M-1] | 100M | BASE | 100K | 512 | 4.99 |
| [roberta-base-100M-2][link-roberta-base-100M-2] | 100M | BASE | 31K | 1024 | 4.61 |
| [roberta-base-100M-3][link-roberta-base-100M-3] | 100M | BASE | 31K | 512 | 5.02 |
| [roberta-base-10M-1][link-roberta-base-10M-1] | 10M | BASE | 10K | 1024 | 11.31 |
| [roberta-base-10M-2][link-roberta-base-10M-2] | 10M | BASE | 10K | 512 | 10.78 |
| [roberta-base-10M-3][link-roberta-base-10M-3] | 10M | BASE | 31K | 512 | 11.58 |
| [roberta-med-small-1M-1][link-roberta-med-small-1M-1] | 1M | MED-SMALL | 100K | 512 | 153.38 |
| [roberta-med-small-1M-2][link-roberta-med-small-1M-2] | 1M | MED-SMALL | 10K | 512 | 134.18 |
| [roberta-med-small-1M-3][link-roberta-med-small-1M-3] | 1M | MED-SMALL | 31K | 512 | 139.39 |
The hyperparameters corresponding to model sizes mentioned above are as follows:
| Model Size | L | AH | HS | FFN | P |
|------------|----|----|-----|------|------|
| BASE | 12 | 12 | 768 | 3072 | 125M |
| MED-SMALL | 6 | 8 | 512 | 2048 | 45M |
(AH = number of attention heads; HS = hidden size; FFN = feedforward network dimension; P = number of parameters.)
For other hyperparameters, we select:
- Peak Learning rate: 5e-4
- Warmup Steps: 6% of max steps
- Dropout: 0.1
[link-roberta-med-small-1M-1]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-med-small-1M-1
[link-roberta-med-small-1M-2]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-med-small-1M-2
[link-roberta-med-small-1M-3]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-med-small-1M-3
[link-roberta-base-10M-1]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-base-10M-1
[link-roberta-base-10M-2]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-base-10M-2
[link-roberta-base-10M-3]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-base-10M-3
[link-roberta-base-100M-1]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-base-100M-1
[link-roberta-base-100M-2]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-base-100M-2
[link-roberta-base-100M-3]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-base-100M-3
[link-roberta-base-1B-1]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-base-1B-1
[link-roberta-base-1B-2]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-base-1B-2
[link-roberta-base-1B-3]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-base-1B-3
|
nyu-mll/roberta-base-1B-3
|
nyu-mll
| 2021-05-20T19:05:43Z | 4 | 0 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"jax",
"roberta",
"fill-mask",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
fill-mask
| 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
# RoBERTa Pretrained on Smaller Datasets
We pretrain RoBERTa on smaller datasets (1M, 10M, 100M, 1B tokens). We release 3 models with lowest perplexities for each pretraining data size out of 25 runs (or 10 in the case of 1B tokens). The pretraining data reproduces that of BERT: We combine English Wikipedia and a reproduction of BookCorpus using texts from smashwords in a ratio of approximately 3:1.
### Hyperparameters and Validation Perplexity
The hyperparameters and validation perplexities corresponding to each model are as follows:
| Model Name | Training Size | Model Size | Max Steps | Batch Size | Validation Perplexity |
|--------------------------|---------------|------------|-----------|------------|-----------------------|
| [roberta-base-1B-1][link-roberta-base-1B-1] | 1B | BASE | 100K | 512 | 3.93 |
| [roberta-base-1B-2][link-roberta-base-1B-2] | 1B | BASE | 31K | 1024 | 4.25 |
| [roberta-base-1B-3][link-roberta-base-1B-3] | 1B | BASE | 31K | 4096 | 3.84 |
| [roberta-base-100M-1][link-roberta-base-100M-1] | 100M | BASE | 100K | 512 | 4.99 |
| [roberta-base-100M-2][link-roberta-base-100M-2] | 100M | BASE | 31K | 1024 | 4.61 |
| [roberta-base-100M-3][link-roberta-base-100M-3] | 100M | BASE | 31K | 512 | 5.02 |
| [roberta-base-10M-1][link-roberta-base-10M-1] | 10M | BASE | 10K | 1024 | 11.31 |
| [roberta-base-10M-2][link-roberta-base-10M-2] | 10M | BASE | 10K | 512 | 10.78 |
| [roberta-base-10M-3][link-roberta-base-10M-3] | 10M | BASE | 31K | 512 | 11.58 |
| [roberta-med-small-1M-1][link-roberta-med-small-1M-1] | 1M | MED-SMALL | 100K | 512 | 153.38 |
| [roberta-med-small-1M-2][link-roberta-med-small-1M-2] | 1M | MED-SMALL | 10K | 512 | 134.18 |
| [roberta-med-small-1M-3][link-roberta-med-small-1M-3] | 1M | MED-SMALL | 31K | 512 | 139.39 |
The hyperparameters corresponding to model sizes mentioned above are as follows:
| Model Size | L | AH | HS | FFN | P |
|------------|----|----|-----|------|------|
| BASE | 12 | 12 | 768 | 3072 | 125M |
| MED-SMALL | 6 | 8 | 512 | 2048 | 45M |
(AH = number of attention heads; HS = hidden size; FFN = feedforward network dimension; P = number of parameters.)
For other hyperparameters, we select:
- Peak Learning rate: 5e-4
- Warmup Steps: 6% of max steps
- Dropout: 0.1
[link-roberta-med-small-1M-1]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-med-small-1M-1
[link-roberta-med-small-1M-2]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-med-small-1M-2
[link-roberta-med-small-1M-3]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-med-small-1M-3
[link-roberta-base-10M-1]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-base-10M-1
[link-roberta-base-10M-2]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-base-10M-2
[link-roberta-base-10M-3]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-base-10M-3
[link-roberta-base-100M-1]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-base-100M-1
[link-roberta-base-100M-2]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-base-100M-2
[link-roberta-base-100M-3]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-base-100M-3
[link-roberta-base-1B-1]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-base-1B-1
[link-roberta-base-1B-2]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-base-1B-2
[link-roberta-base-1B-3]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-base-1B-3
|
nyu-mll/roberta-base-1B-1
|
nyu-mll
| 2021-05-20T19:03:06Z | 4 | 0 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"jax",
"roberta",
"fill-mask",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
fill-mask
| 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
# RoBERTa Pretrained on Smaller Datasets
We pretrain RoBERTa on smaller datasets (1M, 10M, 100M, 1B tokens). We release 3 models with lowest perplexities for each pretraining data size out of 25 runs (or 10 in the case of 1B tokens). The pretraining data reproduces that of BERT: We combine English Wikipedia and a reproduction of BookCorpus using texts from smashwords in a ratio of approximately 3:1.
### Hyperparameters and Validation Perplexity
The hyperparameters and validation perplexities corresponding to each model are as follows:
| Model Name | Training Size | Model Size | Max Steps | Batch Size | Validation Perplexity |
|--------------------------|---------------|------------|-----------|------------|-----------------------|
| [roberta-base-1B-1][link-roberta-base-1B-1] | 1B | BASE | 100K | 512 | 3.93 |
| [roberta-base-1B-2][link-roberta-base-1B-2] | 1B | BASE | 31K | 1024 | 4.25 |
| [roberta-base-1B-3][link-roberta-base-1B-3] | 1B | BASE | 31K | 4096 | 3.84 |
| [roberta-base-100M-1][link-roberta-base-100M-1] | 100M | BASE | 100K | 512 | 4.99 |
| [roberta-base-100M-2][link-roberta-base-100M-2] | 100M | BASE | 31K | 1024 | 4.61 |
| [roberta-base-100M-3][link-roberta-base-100M-3] | 100M | BASE | 31K | 512 | 5.02 |
| [roberta-base-10M-1][link-roberta-base-10M-1] | 10M | BASE | 10K | 1024 | 11.31 |
| [roberta-base-10M-2][link-roberta-base-10M-2] | 10M | BASE | 10K | 512 | 10.78 |
| [roberta-base-10M-3][link-roberta-base-10M-3] | 10M | BASE | 31K | 512 | 11.58 |
| [roberta-med-small-1M-1][link-roberta-med-small-1M-1] | 1M | MED-SMALL | 100K | 512 | 153.38 |
| [roberta-med-small-1M-2][link-roberta-med-small-1M-2] | 1M | MED-SMALL | 10K | 512 | 134.18 |
| [roberta-med-small-1M-3][link-roberta-med-small-1M-3] | 1M | MED-SMALL | 31K | 512 | 139.39 |
The hyperparameters corresponding to model sizes mentioned above are as follows:
| Model Size | L | AH | HS | FFN | P |
|------------|----|----|-----|------|------|
| BASE | 12 | 12 | 768 | 3072 | 125M |
| MED-SMALL | 6 | 8 | 512 | 2048 | 45M |
(AH = number of attention heads; HS = hidden size; FFN = feedforward network dimension; P = number of parameters.)
For other hyperparameters, we select:
- Peak Learning rate: 5e-4
- Warmup Steps: 6% of max steps
- Dropout: 0.1
[link-roberta-med-small-1M-1]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-med-small-1M-1
[link-roberta-med-small-1M-2]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-med-small-1M-2
[link-roberta-med-small-1M-3]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-med-small-1M-3
[link-roberta-base-10M-1]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-base-10M-1
[link-roberta-base-10M-2]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-base-10M-2
[link-roberta-base-10M-3]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-base-10M-3
[link-roberta-base-100M-1]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-base-100M-1
[link-roberta-base-100M-2]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-base-100M-2
[link-roberta-base-100M-3]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-base-100M-3
[link-roberta-base-1B-1]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-base-1B-1
[link-roberta-base-1B-2]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-base-1B-2
[link-roberta-base-1B-3]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-base-1B-3
|
nyu-mll/roberta-base-10M-3
|
nyu-mll
| 2021-05-20T19:00:36Z | 4 | 0 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"jax",
"roberta",
"fill-mask",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
fill-mask
| 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
# RoBERTa Pretrained on Smaller Datasets
We pretrain RoBERTa on smaller datasets (1M, 10M, 100M, 1B tokens). We release 3 models with lowest perplexities for each pretraining data size out of 25 runs (or 10 in the case of 1B tokens). The pretraining data reproduces that of BERT: We combine English Wikipedia and a reproduction of BookCorpus using texts from smashwords in a ratio of approximately 3:1.
### Hyperparameters and Validation Perplexity
The hyperparameters and validation perplexities corresponding to each model are as follows:
| Model Name | Training Size | Model Size | Max Steps | Batch Size | Validation Perplexity |
|--------------------------|---------------|------------|-----------|------------|-----------------------|
| [roberta-base-1B-1][link-roberta-base-1B-1] | 1B | BASE | 100K | 512 | 3.93 |
| [roberta-base-1B-2][link-roberta-base-1B-2] | 1B | BASE | 31K | 1024 | 4.25 |
| [roberta-base-1B-3][link-roberta-base-1B-3] | 1B | BASE | 31K | 4096 | 3.84 |
| [roberta-base-100M-1][link-roberta-base-100M-1] | 100M | BASE | 100K | 512 | 4.99 |
| [roberta-base-100M-2][link-roberta-base-100M-2] | 100M | BASE | 31K | 1024 | 4.61 |
| [roberta-base-100M-3][link-roberta-base-100M-3] | 100M | BASE | 31K | 512 | 5.02 |
| [roberta-base-10M-1][link-roberta-base-10M-1] | 10M | BASE | 10K | 1024 | 11.31 |
| [roberta-base-10M-2][link-roberta-base-10M-2] | 10M | BASE | 10K | 512 | 10.78 |
| [roberta-base-10M-3][link-roberta-base-10M-3] | 10M | BASE | 31K | 512 | 11.58 |
| [roberta-med-small-1M-1][link-roberta-med-small-1M-1] | 1M | MED-SMALL | 100K | 512 | 153.38 |
| [roberta-med-small-1M-2][link-roberta-med-small-1M-2] | 1M | MED-SMALL | 10K | 512 | 134.18 |
| [roberta-med-small-1M-3][link-roberta-med-small-1M-3] | 1M | MED-SMALL | 31K | 512 | 139.39 |
The hyperparameters corresponding to model sizes mentioned above are as follows:
| Model Size | L | AH | HS | FFN | P |
|------------|----|----|-----|------|------|
| BASE | 12 | 12 | 768 | 3072 | 125M |
| MED-SMALL | 6 | 8 | 512 | 2048 | 45M |
(AH = number of attention heads; HS = hidden size; FFN = feedforward network dimension; P = number of parameters.)
For other hyperparameters, we select:
- Peak Learning rate: 5e-4
- Warmup Steps: 6% of max steps
- Dropout: 0.1
[link-roberta-med-small-1M-1]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-med-small-1M-1
[link-roberta-med-small-1M-2]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-med-small-1M-2
[link-roberta-med-small-1M-3]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-med-small-1M-3
[link-roberta-base-10M-1]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-base-10M-1
[link-roberta-base-10M-2]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-base-10M-2
[link-roberta-base-10M-3]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-base-10M-3
[link-roberta-base-100M-1]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-base-100M-1
[link-roberta-base-100M-2]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-base-100M-2
[link-roberta-base-100M-3]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-base-100M-3
[link-roberta-base-1B-1]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-base-1B-1
[link-roberta-base-1B-2]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-base-1B-2
[link-roberta-base-1B-3]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-base-1B-3
|
nyu-mll/roberta-base-10M-1
|
nyu-mll
| 2021-05-20T18:57:10Z | 8 | 1 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"jax",
"roberta",
"fill-mask",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
fill-mask
| 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
# RoBERTa Pretrained on Smaller Datasets
We pretrain RoBERTa on smaller datasets (1M, 10M, 100M, 1B tokens). We release 3 models with lowest perplexities for each pretraining data size out of 25 runs (or 10 in the case of 1B tokens). The pretraining data reproduces that of BERT: We combine English Wikipedia and a reproduction of BookCorpus using texts from smashwords in a ratio of approximately 3:1.
### Hyperparameters and Validation Perplexity
The hyperparameters and validation perplexities corresponding to each model are as follows:
| Model Name | Training Size | Model Size | Max Steps | Batch Size | Validation Perplexity |
|--------------------------|---------------|------------|-----------|------------|-----------------------|
| [roberta-base-1B-1][link-roberta-base-1B-1] | 1B | BASE | 100K | 512 | 3.93 |
| [roberta-base-1B-2][link-roberta-base-1B-2] | 1B | BASE | 31K | 1024 | 4.25 |
| [roberta-base-1B-3][link-roberta-base-1B-3] | 1B | BASE | 31K | 4096 | 3.84 |
| [roberta-base-100M-1][link-roberta-base-100M-1] | 100M | BASE | 100K | 512 | 4.99 |
| [roberta-base-100M-2][link-roberta-base-100M-2] | 100M | BASE | 31K | 1024 | 4.61 |
| [roberta-base-100M-3][link-roberta-base-100M-3] | 100M | BASE | 31K | 512 | 5.02 |
| [roberta-base-10M-1][link-roberta-base-10M-1] | 10M | BASE | 10K | 1024 | 11.31 |
| [roberta-base-10M-2][link-roberta-base-10M-2] | 10M | BASE | 10K | 512 | 10.78 |
| [roberta-base-10M-3][link-roberta-base-10M-3] | 10M | BASE | 31K | 512 | 11.58 |
| [roberta-med-small-1M-1][link-roberta-med-small-1M-1] | 1M | MED-SMALL | 100K | 512 | 153.38 |
| [roberta-med-small-1M-2][link-roberta-med-small-1M-2] | 1M | MED-SMALL | 10K | 512 | 134.18 |
| [roberta-med-small-1M-3][link-roberta-med-small-1M-3] | 1M | MED-SMALL | 31K | 512 | 139.39 |
The hyperparameters corresponding to model sizes mentioned above are as follows:
| Model Size | L | AH | HS | FFN | P |
|------------|----|----|-----|------|------|
| BASE | 12 | 12 | 768 | 3072 | 125M |
| MED-SMALL | 6 | 8 | 512 | 2048 | 45M |
(AH = number of attention heads; HS = hidden size; FFN = feedforward network dimension; P = number of parameters.)
For other hyperparameters, we select:
- Peak Learning rate: 5e-4
- Warmup Steps: 6% of max steps
- Dropout: 0.1
[link-roberta-med-small-1M-1]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-med-small-1M-1
[link-roberta-med-small-1M-2]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-med-small-1M-2
[link-roberta-med-small-1M-3]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-med-small-1M-3
[link-roberta-base-10M-1]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-base-10M-1
[link-roberta-base-10M-2]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-base-10M-2
[link-roberta-base-10M-3]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-base-10M-3
[link-roberta-base-100M-1]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-base-100M-1
[link-roberta-base-100M-2]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-base-100M-2
[link-roberta-base-100M-3]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-base-100M-3
[link-roberta-base-1B-1]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-base-1B-1
[link-roberta-base-1B-2]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-base-1B-2
[link-roberta-base-1B-3]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-base-1B-3
|
nyu-mll/roberta-base-100M-3
|
nyu-mll
| 2021-05-20T18:56:02Z | 15 | 0 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"jax",
"roberta",
"fill-mask",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
fill-mask
| 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
# RoBERTa Pretrained on Smaller Datasets
We pretrain RoBERTa on smaller datasets (1M, 10M, 100M, 1B tokens). We release 3 models with lowest perplexities for each pretraining data size out of 25 runs (or 10 in the case of 1B tokens). The pretraining data reproduces that of BERT: We combine English Wikipedia and a reproduction of BookCorpus using texts from smashwords in a ratio of approximately 3:1.
### Hyperparameters and Validation Perplexity
The hyperparameters and validation perplexities corresponding to each model are as follows:
| Model Name | Training Size | Model Size | Max Steps | Batch Size | Validation Perplexity |
|--------------------------|---------------|------------|-----------|------------|-----------------------|
| [roberta-base-1B-1][link-roberta-base-1B-1] | 1B | BASE | 100K | 512 | 3.93 |
| [roberta-base-1B-2][link-roberta-base-1B-2] | 1B | BASE | 31K | 1024 | 4.25 |
| [roberta-base-1B-3][link-roberta-base-1B-3] | 1B | BASE | 31K | 4096 | 3.84 |
| [roberta-base-100M-1][link-roberta-base-100M-1] | 100M | BASE | 100K | 512 | 4.99 |
| [roberta-base-100M-2][link-roberta-base-100M-2] | 100M | BASE | 31K | 1024 | 4.61 |
| [roberta-base-100M-3][link-roberta-base-100M-3] | 100M | BASE | 31K | 512 | 5.02 |
| [roberta-base-10M-1][link-roberta-base-10M-1] | 10M | BASE | 10K | 1024 | 11.31 |
| [roberta-base-10M-2][link-roberta-base-10M-2] | 10M | BASE | 10K | 512 | 10.78 |
| [roberta-base-10M-3][link-roberta-base-10M-3] | 10M | BASE | 31K | 512 | 11.58 |
| [roberta-med-small-1M-1][link-roberta-med-small-1M-1] | 1M | MED-SMALL | 100K | 512 | 153.38 |
| [roberta-med-small-1M-2][link-roberta-med-small-1M-2] | 1M | MED-SMALL | 10K | 512 | 134.18 |
| [roberta-med-small-1M-3][link-roberta-med-small-1M-3] | 1M | MED-SMALL | 31K | 512 | 139.39 |
The hyperparameters corresponding to model sizes mentioned above are as follows:
| Model Size | L | AH | HS | FFN | P |
|------------|----|----|-----|------|------|
| BASE | 12 | 12 | 768 | 3072 | 125M |
| MED-SMALL | 6 | 8 | 512 | 2048 | 45M |
(AH = number of attention heads; HS = hidden size; FFN = feedforward network dimension; P = number of parameters.)
For other hyperparameters, we select:
- Peak Learning rate: 5e-4
- Warmup Steps: 6% of max steps
- Dropout: 0.1
[link-roberta-med-small-1M-1]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-med-small-1M-1
[link-roberta-med-small-1M-2]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-med-small-1M-2
[link-roberta-med-small-1M-3]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-med-small-1M-3
[link-roberta-base-10M-1]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-base-10M-1
[link-roberta-base-10M-2]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-base-10M-2
[link-roberta-base-10M-3]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-base-10M-3
[link-roberta-base-100M-1]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-base-100M-1
[link-roberta-base-100M-2]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-base-100M-2
[link-roberta-base-100M-3]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-base-100M-3
[link-roberta-base-1B-1]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-base-1B-1
[link-roberta-base-1B-2]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-base-1B-2
[link-roberta-base-1B-3]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-base-1B-3
|
nyu-mll/roberta-base-100M-1
|
nyu-mll
| 2021-05-20T18:53:55Z | 5 | 0 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"jax",
"roberta",
"fill-mask",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
fill-mask
| 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
# RoBERTa Pretrained on Smaller Datasets
We pretrain RoBERTa on smaller datasets (1M, 10M, 100M, 1B tokens). We release 3 models with lowest perplexities for each pretraining data size out of 25 runs (or 10 in the case of 1B tokens). The pretraining data reproduces that of BERT: We combine English Wikipedia and a reproduction of BookCorpus using texts from smashwords in a ratio of approximately 3:1.
### Hyperparameters and Validation Perplexity
The hyperparameters and validation perplexities corresponding to each model are as follows:
| Model Name | Training Size | Model Size | Max Steps | Batch Size | Validation Perplexity |
|--------------------------|---------------|------------|-----------|------------|-----------------------|
| [roberta-base-1B-1][link-roberta-base-1B-1] | 1B | BASE | 100K | 512 | 3.93 |
| [roberta-base-1B-2][link-roberta-base-1B-2] | 1B | BASE | 31K | 1024 | 4.25 |
| [roberta-base-1B-3][link-roberta-base-1B-3] | 1B | BASE | 31K | 4096 | 3.84 |
| [roberta-base-100M-1][link-roberta-base-100M-1] | 100M | BASE | 100K | 512 | 4.99 |
| [roberta-base-100M-2][link-roberta-base-100M-2] | 100M | BASE | 31K | 1024 | 4.61 |
| [roberta-base-100M-3][link-roberta-base-100M-3] | 100M | BASE | 31K | 512 | 5.02 |
| [roberta-base-10M-1][link-roberta-base-10M-1] | 10M | BASE | 10K | 1024 | 11.31 |
| [roberta-base-10M-2][link-roberta-base-10M-2] | 10M | BASE | 10K | 512 | 10.78 |
| [roberta-base-10M-3][link-roberta-base-10M-3] | 10M | BASE | 31K | 512 | 11.58 |
| [roberta-med-small-1M-1][link-roberta-med-small-1M-1] | 1M | MED-SMALL | 100K | 512 | 153.38 |
| [roberta-med-small-1M-2][link-roberta-med-small-1M-2] | 1M | MED-SMALL | 10K | 512 | 134.18 |
| [roberta-med-small-1M-3][link-roberta-med-small-1M-3] | 1M | MED-SMALL | 31K | 512 | 139.39 |
The hyperparameters corresponding to model sizes mentioned above are as follows:
| Model Size | L | AH | HS | FFN | P |
|------------|----|----|-----|------|------|
| BASE | 12 | 12 | 768 | 3072 | 125M |
| MED-SMALL | 6 | 8 | 512 | 2048 | 45M |
(AH = number of attention heads; HS = hidden size; FFN = feedforward network dimension; P = number of parameters.)
For other hyperparameters, we select:
- Peak Learning rate: 5e-4
- Warmup Steps: 6% of max steps
- Dropout: 0.1
[link-roberta-med-small-1M-1]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-med-small-1M-1
[link-roberta-med-small-1M-2]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-med-small-1M-2
[link-roberta-med-small-1M-3]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-med-small-1M-3
[link-roberta-base-10M-1]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-base-10M-1
[link-roberta-base-10M-2]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-base-10M-2
[link-roberta-base-10M-3]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-base-10M-3
[link-roberta-base-100M-1]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-base-100M-1
[link-roberta-base-100M-2]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-base-100M-2
[link-roberta-base-100M-3]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-base-100M-3
[link-roberta-base-1B-1]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-base-1B-1
[link-roberta-base-1B-2]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-base-1B-2
[link-roberta-base-1B-3]: https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-base-1B-3
|
mudes/en-large
|
mudes
| 2021-05-20T18:36:06Z | 5 | 0 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"jax",
"roberta",
"token-classification",
"mudes",
"en",
"arxiv:2102.09665",
"arxiv:2104.04630",
"license:apache-2.0",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
token-classification
| 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
---
language: en
tags:
- mudes
license: apache-2.0
---
# MUDES - {Mu}ltilingual {De}tection of Offensive {S}pans
We provide state-of-the-art models to detect toxic spans in social media texts. We introduce our framework in [this paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2102.09665). We have evaluated our models on Toxic Spans task at SemEval 2021 (Task 5). Our participation in the task is detailed in [this paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2104.04630).
## Usage
You can use this model when you have [MUDES](https://github.com/TharinduDR/MUDES) installed:
```bash
pip install mudes
```
Then you can use the model like this:
```python
from mudes.app.mudes_app import MUDESApp
app = MUDESApp("en-large", use_cuda=False)
print(app.predict_toxic_spans("You motherfucking cunt", spans=True))
```
## System Demonstration
An experimental demonstration interface called MUDES-UI has been released on [GitHub](https://github.com/TharinduDR/MUDES-UI) and can be checked out in [here](http://rgcl.wlv.ac.uk/mudes/).
## Citing & Authors
If you find this model helpful, feel free to cite our publications
```bibtex
@inproceedings{ranasinghemudes,
title={{MUDES: Multilingual Detection of Offensive Spans}},
author={Tharindu Ranasinghe and Marcos Zampieri},
booktitle={Proceedings of NAACL},
year={2021}
}
```
```bibtex
@inproceedings{ranasinghe2021semeval,
title={{WLV-RIT at SemEval-2021 Task 5: A Neural Transformer Framework for Detecting Toxic Spans}},
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Sarkar, Diptanu and Zampieri, Marcos and Ororbia, Alex},
booktitle={Proceedings of SemEval},
year={2021}
}
```
|
mrm8488/roberta-base-1B-1-finetuned-squadv2
|
mrm8488
| 2021-05-20T18:27:20Z | 13 | 0 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"jax",
"roberta",
"question-answering",
"en",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
question-answering
| 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
---
language: en
---
# RoBERTa-base (1B-1) + SQuAD v2 ❓
[roberta-base-1B-1](https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-base-1B-1) fine-tuned on [SQUAD v2 dataset](https://rajpurkar.github.io/SQuAD-explorer/explore/v2.0/dev/) for **Q&A** downstream task.
## Details of the downstream task (Q&A) - Model 🧠
RoBERTa Pretrained on Smaller Datasets
[NYU Machine Learning for Language](https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll) pretrained RoBERTa on smaller datasets (1M, 10M, 100M, 1B tokens). They released 3 models with lowest perplexities for each pretraining data size out of 25 runs (or 10 in the case of 1B tokens). The pretraining data reproduces that of BERT: They combine English Wikipedia and a reproduction of BookCorpus using texts from smashwords in a ratio of approximately 3:1.
## Details of the downstream task (Q&A) - Dataset 📚
**S**tanford **Q**uestion **A**nswering **D**ataset (SQuAD) is a reading comprehension dataset, consisting of questions posed by crowdworkers on a set of Wikipedia articles, where the answer to every question is a segment of text, or span, from the corresponding reading passage, or the question might be unanswerable.
**SQuAD2.0** combines the 100,000 questions in SQuAD1.1 with over 50,000 unanswerable questions written adversarially by crowdworkers to look similar to answerable ones. To do well on SQuAD2.0, systems must not only answer questions when possible, but also determine when no answer is supported by the paragraph and abstain from answering.
## Model training 🏋️
The model was trained on a Tesla P100 GPU and 25GB of RAM with the following command:
```bash
python transformers/examples/question-answering/run_squad.py \
--model_type roberta \
--model_name_or_path 'nyu-mll/roberta-base-1B-1' \
--do_eval \
--do_train \
--do_lower_case \
--train_file /content/dataset/train-v2.0.json \
--predict_file /content/dataset/dev-v2.0.json \
--per_gpu_train_batch_size 16 \
--learning_rate 3e-5 \
--num_train_epochs 10 \
--max_seq_length 384 \
--doc_stride 128 \
--output_dir /content/output \
--overwrite_output_dir \
--save_steps 1000 \
--version_2_with_negative
```
## Test set Results 🧾
| Metric | # Value |
| ------ | --------- |
| **EM** | **64.86** |
| **F1** | **68.99** |
```json
{
'exact': 64.86145034953255,
'f1': 68.9902640378272,
'total': 11873,
'HasAns_exact': 64.03508771929825,
'HasAns_f1': 72.3045554860189,
'HasAns_total': 5928,
'NoAns_exact': 65.68544995794785,
'NoAns_f1': 65.68544995794785,
'NoAns_total': 5945,
'best_exact': 64.86987282068559,
'best_exact_thresh': 0.0,
'best_f1': 68.99868650898054,
'best_f1_thresh': 0.0
}
```
### Model in action 🚀
Fast usage with **pipelines**:
```python
from transformers import pipeline
QnA_pipeline = pipeline('question-answering', model='mrm8488/roberta-base-1B-1-finetuned-squadv2')
QnA_pipeline({
'context': 'A new strain of flu that has the potential to become a pandemic has been identified in China by scientists.',
'question': 'What has been discovered by scientists from China ?'
})
# Output:
{'answer': 'A new strain of flu', 'end': 19, 'score': 0.7145650685380576,'start': 0}
```
> Created by [Manuel Romero/@mrm8488](https://twitter.com/mrm8488) | [LinkedIn](https://www.linkedin.com/in/manuel-romero-cs/)
> Made with <span style="color: #e25555;">♥</span> in Spain
|
mrm8488/roberta-base-1B-1-finetuned-squadv1
|
mrm8488
| 2021-05-20T18:26:13Z | 35 | 1 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"jax",
"roberta",
"question-answering",
"en",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
question-answering
| 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
---
language: en
---
# RoBERTa-base (1B-1) + SQuAD v1 ❓
[roberta-base-1B-1](https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll/roberta-base-1B-1) fine-tuned on [SQUAD v1.1 dataset](https://rajpurkar.github.io/SQuAD-explorer/explore/1.1/dev/) for **Q&A** downstream task.
## Details of the downstream task (Q&A) - Model 🧠
RoBERTa Pretrained on Smaller Datasets
[NYU Machine Learning for Language](https://huggingface.co/nyu-mll) pretrained RoBERTa on smaller datasets (1M, 10M, 100M, 1B tokens). They released 3 models with lowest perplexities for each pretraining data size out of 25 runs (or 10 in the case of 1B tokens). The pretraining data reproduces that of BERT: They combine English Wikipedia and a reproduction of BookCorpus using texts from smashwords in a ratio of approximately 3:1.
## Details of the downstream task (Q&A) - Dataset 📚
**S**tanford **Q**uestion **A**nswering **D**ataset (SQuAD) is a reading comprehension dataset, consisting of questions posed by crowdworkers on a set of Wikipedia articles, where the answer to every question is a segment of text, or span, from the corresponding reading passage, or the question might be unanswerable.
SQuAD v1.1 contains **100,000+** question-answer pairs on **500+** articles.
## Model training 🏋️
The model was trained on a Tesla P100 GPU and 25GB of RAM with the following command:
```bash
python transformers/examples/question-answering/run_squad.py \
--model_type roberta \
--model_name_or_path 'nyu-mll/roberta-base-1B-1' \
--do_eval \
--do_train \
--do_lower_case \
--train_file /content/dataset/train-v1.1.json \
--predict_file /content/dataset/dev-v1.1.json \
--per_gpu_train_batch_size 16 \
--learning_rate 3e-5 \
--num_train_epochs 10 \
--max_seq_length 384 \
--doc_stride 128 \
--output_dir /content/output \
--overwrite_output_dir \
--save_steps 1000
```
## Test set Results 🧾
| Metric | # Value |
| ------ | --------- |
| **EM** | **72.62** |
| **F1** | **82.19** |
```json
{
'exact': 72.62062440870388,
'f1': 82.19430877136834,
'total': 10570,
'HasAns_exact': 72.62062440870388,
'HasAns_f1': 82.19430877136834,
'HasAns_total': 10570,
'best_exact': 72.62062440870388,
'best_exact_thresh': 0.0,
'best_f1': 82.19430877136834,
'best_f1_thresh': 0.0
}
```
### Model in action 🚀
Fast usage with **pipelines**:
```python
from transformers import pipeline
QnA_pipeline = pipeline('question-answering', model='mrm8488/roberta-base-1B-1-finetuned-squadv1')
QnA_pipeline({
'context': 'A new strain of flu that has the potential to become a pandemic has been identified in China by scientists.',
'question': 'What has been discovered by scientists from China ?'
})
# Output:
{'answer': 'A new strain of flu', 'end': 19, 'score': 0.04702283976040074, 'start': 0}
```
> Created by [Manuel Romero/@mrm8488](https://twitter.com/mrm8488) | [LinkedIn](https://www.linkedin.com/in/manuel-romero-cs/)
> Made with <span style="color: #e25555;">♥</span> in Spain
|
mrm8488/distilroberta-finetuned-tweets-hate-speech
|
mrm8488
| 2021-05-20T18:25:15Z | 6 | 6 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"jax",
"roberta",
"text-classification",
"twitter",
"hate",
"speech",
"en",
"dataset:tweets_hate_speech_detection",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
text-classification
| 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
---
language: en
tags:
- twitter
- hate
- speech
datasets:
- tweets_hate_speech_detection
widget:
- text: "the fuck done with #mansplaining and other bullshit."
---
# distilroberta-base fine-tuned on tweets_hate_speech_detection dataset for hate speech detection
Validation accuray: 0.98
|
mrm8488/codeBERTaJS
|
mrm8488
| 2021-05-20T18:17:36Z | 10 | 6 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"jax",
"roberta",
"fill-mask",
"javascript",
"code",
"arxiv:1909.09436",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
fill-mask
| 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
---
language: code
thumbnail:
tags:
- javascript
- code
widget:
- text: "async function createUser(req, <mask>) { if (!validUser(req.body.user)) { return res.status(400); } user = userService.createUser(req.body.user); return res.json(user); }"
---
# CodeBERTaJS
CodeBERTaJS is a RoBERTa-like model trained on the [CodeSearchNet](https://github.blog/2019-09-26-introducing-the-codesearchnet-challenge/) dataset from GitHub for `javaScript` by [Manuel Romero](https://twitter.com/mrm8488)
The **tokenizer** is a Byte-level BPE tokenizer trained on the corpus using Hugging Face `tokenizers`.
Because it is trained on a corpus of code (vs. natural language), it encodes the corpus efficiently (the sequences are between 33% to 50% shorter, compared to the same corpus tokenized by gpt2/roberta).
The (small) **model** is a 6-layer, 84M parameters, RoBERTa-like Transformer model – that’s the same number of layers & heads as DistilBERT – initialized from the default initialization settings and trained from scratch on the full `javascript` corpus (120M after preproccessing) for 2 epochs.
## Quick start: masked language modeling prediction
```python
JS_CODE = """
async function createUser(req, <mask>) {
if (!validUser(req.body.user)) {
\t return res.status(400);
}
user = userService.createUser(req.body.user);
return res.json(user);
}
""".lstrip()
```
### Does the model know how to complete simple JS/express like code?
```python
from transformers import pipeline
fill_mask = pipeline(
"fill-mask",
model="mrm8488/codeBERTaJS",
tokenizer="mrm8488/codeBERTaJS"
)
fill_mask(JS_CODE)
## Top 5 predictions:
#
'res' # prob 0.069489665329
'next'
'req'
'user'
',req'
```
### Yes! That was easy 🎉 Let's try with another example
```python
JS_CODE_= """
function getKeys(obj) {
keys = [];
for (var [key, value] of Object.entries(obj)) {
keys.push(<mask>);
}
return keys
}
""".lstrip()
```
Results:
```python
'obj', 'key', ' value', 'keys', 'i'
```
> Not so bad! Right token was predicted as second option! 🎉
## This work is heavely inspired on [codeBERTa](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/master/model_cards/huggingface/CodeBERTa-small-v1/README.md) by huggingface team
<br>
## CodeSearchNet citation
<details>
```bibtex
@article{husain_codesearchnet_2019,
\ttitle = {{CodeSearchNet} {Challenge}: {Evaluating} the {State} of {Semantic} {Code} {Search}},
\tshorttitle = {{CodeSearchNet} {Challenge}},
\turl = {http://arxiv.org/abs/1909.09436},
\turldate = {2020-03-12},
\tjournal = {arXiv:1909.09436 [cs, stat]},
\tauthor = {Husain, Hamel and Wu, Ho-Hsiang and Gazit, Tiferet and Allamanis, Miltiadis and Brockschmidt, Marc},
\tmonth = sep,
\tyear = {2019},
\tnote = {arXiv: 1909.09436},
}
```
</details>
> Created by [Manuel Romero/@mrm8488](https://twitter.com/mrm8488)
> Made with <span style="color: #e25555;">♥</span> in Spain
|
mrm8488/chEMBL26_smiles_v2
|
mrm8488
| 2021-05-20T18:16:29Z | 20 | 0 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"jax",
"roberta",
"fill-mask",
"drugs",
"chemist",
"drug design",
"smile",
"en",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
fill-mask
| 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
---
language: en
tags:
- drugs
- chemist
- drug design
- smile
widget:
- text: "CC(C)CN(CC(OP(=O)(O)O)C(Cc1ccccc1)NC(=O)OC1CCOC1)S(=O)(=O)c1ccc(N)<mask>"
---
|
mrm8488/RuPERTa-base-finetuned-squadv1
|
mrm8488
| 2021-05-20T18:13:28Z | 14 | 0 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"jax",
"roberta",
"question-answering",
"es",
"dataset:squad",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
question-answering
| 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
---
language: es
datasets:
- squad
---
|
mrm8488/RuPERTa-base-finetuned-pos
|
mrm8488
| 2021-05-20T18:08:34Z | 17 | 0 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"jax",
"roberta",
"token-classification",
"es",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
token-classification
| 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
---
language: es
thumbnail:
---
# RuPERTa-base (Spanish RoBERTa) + POS 🎃🏷
This model is a fine-tuned on [CONLL CORPORA](https://www.kaggle.com/nltkdata/conll-corpora) version of [RuPERTa-base](https://huggingface.co/mrm8488/RuPERTa-base) for **POS** downstream task.
## Details of the downstream task (POS) - Dataset
- [Dataset: CONLL Corpora ES](https://www.kaggle.com/nltkdata/conll-corpora) 📚
| Dataset | # Examples |
| ---------------------- | ----- |
| Train | 445 K |
| Dev | 55 K |
- [Fine-tune on NER script provided by Huggingface](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/master/examples/token-classification/run_ner_old.py)
- Labels covered:
```
ADJ
ADP
ADV
AUX
CCONJ
DET
INTJ
NOUN
NUM
PART
PRON
PROPN
PUNCT
SCONJ
SYM
VERB
```
## Metrics on evaluation set 🧾
| Metric | # score |
| :------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: | :-------: |
| F1 | **97.39**
| Precision | **97.47** |
| Recall | **9732** |
## Model in action 🔨
Example of usage
```python
import torch
from transformers import AutoModelForTokenClassification, AutoTokenizer
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained('mrm8488/RuPERTa-base-finetuned-pos')
model = AutoModelForTokenClassification.from_pretrained('mrm8488/RuPERTa-base-finetuned-pos')
id2label = {
"0": "O",
"1": "ADJ",
"2": "ADP",
"3": "ADV",
"4": "AUX",
"5": "CCONJ",
"6": "DET",
"7": "INTJ",
"8": "NOUN",
"9": "NUM",
"10": "PART",
"11": "PRON",
"12": "PROPN",
"13": "PUNCT",
"14": "SCONJ",
"15": "SYM",
"16": "VERB"
}
text ="Mis amigos están pensando viajar a Londres este verano."
input_ids = torch.tensor(tokenizer.encode(text)).unsqueeze(0)
outputs = model(input_ids)
last_hidden_states = outputs[0]
for m in last_hidden_states:
for index, n in enumerate(m):
if(index > 0 and index <= len(text.split(" "))):
print(text.split(" ")[index-1] + ": " + id2label[str(torch.argmax(n).item())])
'''
Output:
--------
Mis: NUM
amigos: PRON
están: AUX
pensando: ADV
viajar: VERB
a: ADP
Londres: PROPN
este: DET
verano..: NOUN
'''
```
Yeah! Not too bad 🎉
> Created by [Manuel Romero/@mrm8488](https://twitter.com/mrm8488) | [LinkedIn](https://www.linkedin.com/in/manuel-romero-cs/)
> Made with <span style="color: #e25555;">♥</span> in Spain
|
jpcorb20/toxic-detector-distilroberta
|
jpcorb20
| 2021-05-20T17:25:58Z | 88 | 1 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"jax",
"roberta",
"text-classification",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
text-classification
| 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
# Distilroberta for toxic comment detection
See my GitHub repo [toxic-comment-server](https://github.com/jpcorb20/toxic-comment-server)
The model was trained from [DistilRoberta](https://huggingface.co/distilroberta-base) on [Kaggle Toxic Comments](https://www.kaggle.com/c/jigsaw-toxic-comment-classification-challenge) with the BCEWithLogits loss for Multi-Label prediction. Thus, please use the sigmoid activation on the logits (not made to use the softmax output, e.g. like the HF widget).
## Evaluation
F1 scores:
toxic: 0.72
severe_toxic: 0.38
obscene: 0.72
threat: 0.52
insult: 0.69
identity_hate: 0.60
Macro-F1: 0.61
|
softcatala/julibert
|
softcatala
| 2021-05-20T17:19:38Z | 8 | 2 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"jax",
"roberta",
"fill-mask",
"ca",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
fill-mask
| 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
---
language: ca
---
## Introduction
Download the model here:
* Catalan Roberta model: [julibert-2020-11-10.zip](https://www.softcatala.org/pub/softcatala/julibert/julibert-2020-11-10.zip)
## What's this?
Source code: https://github.com/Softcatala/julibert
* Corpus: Oscar Catalan Corpus (3,8G)
* Model type: Roberta
* Vocabulary size: 50265
* Steps: 500000
|
jason9693/SoongsilBERT-nsmc-base
|
jason9693
| 2021-05-20T17:08:31Z | 6 | 0 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"jax",
"roberta",
"text-classification",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
text-classification
| 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
# Finetuning
## Result
### Base Model
| | Size | **NSMC**<br/>(acc) | **Naver NER**<br/>(F1) | **PAWS**<br/>(acc) | **KorNLI**<br/>(acc) | **KorSTS**<br/>(spearman) | **Question Pair**<br/>(acc) | **KorQuaD (Dev)**<br/>(EM/F1) | **Korean-Hate-Speech (Dev)**<br/>(F1) |
| :-------------------- | :---: | :----------------: | :--------------------: | :----------------: | :------------------: | :-----------------------: | :-------------------------: | :---------------------------: | :-----------------------------------: |
| KoBERT | 351M | 89.59 | 87.92 | 81.25 | 79.62 | 81.59 | 94.85 | 51.75 / 79.15 | 66.21 |
| XLM-Roberta-Base | 1.03G | 89.03 | 86.65 | 82.80 | 80.23 | 78.45 | 93.80 | 64.70 / 88.94 | 64.06 |
| HanBERT | 614M | 90.06 | 87.70 | 82.95 | 80.32 | 82.73 | 94.72 | 78.74 / 92.02 | 68.32 |
| KoELECTRA-Base-v3 | 431M | 90.63 | 88.11 | 84.45 | 82.24 | 85.53 | 95.25 | 84.83 / 93.45 | 67.61 |
| Soongsil-BERT | 370M | **91.2** | - | - | - | 76 | 94 | - | **69** |
### Small Model
| | Size | **NSMC**<br/>(acc) | **Naver NER**<br/>(F1) | **PAWS**<br/>(acc) | **KorNLI**<br/>(acc) | **KorSTS**<br/>(spearman) | **Question Pair**<br/>(acc) | **KorQuaD (Dev)**<br/>(EM/F1) | **Korean-Hate-Speech (Dev)**<br/>(F1) |
| :--------------------- | :--: | :----------------: | :--------------------: | :----------------: | :------------------: | :-----------------------: | :-------------------------: | :---------------------------: | :-----------------------------------: |
| DistilKoBERT | 108M | 88.60 | 84.65 | 60.50 | 72.00 | 72.59 | 92.48 | 54.40 / 77.97 | 60.72 |
| KoELECTRA-Small-v3 | 54M | 89.36 | 85.40 | 77.45 | 78.60 | 80.79 | 94.85 | 82.11 / 91.13 | 63.07 |
| Soongsil-BERT | 213M | **90.7** | 84 | 69.1 | 76 | - | 92 | - | **66** |
## Reference
- [Transformers Examples](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/master/examples/README.md)
- [NSMC](https://github.com/e9t/nsmc)
- [Naver NER Dataset](https://github.com/naver/nlp-challenge)
- [PAWS](https://github.com/google-research-datasets/paws)
- [KorNLI/KorSTS](https://github.com/kakaobrain/KorNLUDatasets)
- [Question Pair](https://github.com/songys/Question_pair)
- [KorQuad](https://korquad.github.io/category/1.0_KOR.html)
- [Korean Hate Speech](https://github.com/kocohub/korean-hate-speech)
- [KoELECTRA](https://github.com/monologg/KoELECTRA)
- [KoBERT](https://github.com/SKTBrain/KoBERT)
- [HanBERT](https://github.com/tbai2019/HanBert-54k-N)
- [HanBert Transformers](https://github.com/monologg/HanBert-Transformers)
|
idjotherwise/autonlp-reading_prediction-172506
|
idjotherwise
| 2021-05-20T16:57:07Z | 6 | 0 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"jax",
"roberta",
"text-classification",
"autonlp",
"en",
"dataset:idjotherwise/autonlp-data-reading_prediction",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
text-classification
| 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
---
tags: autonlp
language: en
widget:
- text: "I love AutoNLP 🤗"
datasets:
- idjotherwise/autonlp-data-reading_prediction
---
# Model Trained Using AutoNLP
- Problem type: Single Column Regression
- Model ID: 172506
## Validation Metrics
- Loss: 0.03257797285914421
- MSE: 0.03257797285914421
- MAE: 0.14246532320976257
- R2: 0.9693824457290849
- RMSE: 0.18049369752407074
- Explained Variance: 0.9699198007583618
## Usage
You can use cURL to access this model:
```
$ curl -X POST -H "Authorization: Bearer YOUR_API_KEY" -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{"inputs": "I love AutoNLP"}' https://api-inference.huggingface.co/models/idjotherwise/autonlp-reading_prediction-172506
```
Or Python API:
```
from transformers import AutoModelForSequenceClassification, AutoTokenizer
model = AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained("idjotherwise/autonlp-reading_prediction-172506")
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("idjotherwise/autonlp-reading_prediction-172506")
inputs = tokenizer("I love AutoNLP", return_tensors="pt")
outputs = model(**inputs)
```
|
iarfmoose/roberta-small-bulgarian
|
iarfmoose
| 2021-05-20T16:54:01Z | 6 | 0 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"tf",
"jax",
"roberta",
"fill-mask",
"bg",
"arxiv:1907.11692",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
fill-mask
| 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
---
language: bg
---
# RoBERTa-small-bulgarian
The RoBERTa model was originally introduced in [this paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/1907.11692). This is a smaller version of [RoBERTa-base-bulgarian](https://huggingface.co/iarfmoose/roberta-small-bulgarian) with only 6 hidden layers, but similar performance.
## Intended uses
This model can be used for cloze tasks (masked language modeling) or finetuned on other tasks in Bulgarian.
## Limitations and bias
The training data is unfiltered text from the internet and may contain all sorts of biases.
## Training data
This model was trained on the following data:
- [bg_dedup from OSCAR](https://oscar-corpus.com/)
- [Newscrawl 1 million sentences 2017 from Leipzig Corpora Collection](https://wortschatz.uni-leipzig.de/en/download/bulgarian)
- [Wikipedia 1 million sentences 2016 from Leipzig Corpora Collection](https://wortschatz.uni-leipzig.de/en/download/bulgarian)
## Training procedure
The model was pretrained using a masked language-modeling objective with dynamic masking as described [here](https://huggingface.co/roberta-base#preprocessing)
It was trained for 160k steps. The batch size was limited to 8 due to GPU memory limitations.
|
iarfmoose/roberta-base-bulgarian
|
iarfmoose
| 2021-05-20T16:50:24Z | 29 | 1 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"tf",
"jax",
"roberta",
"fill-mask",
"bg",
"arxiv:1907.11692",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
fill-mask
| 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
---
language: bg
---
# RoBERTa-base-bulgarian
The RoBERTa model was originally introduced in [this paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/1907.11692). This is a version of [RoBERTa-base](https://huggingface.co/roberta-base) pretrained on Bulgarian text.
## Intended uses
This model can be used for cloze tasks (masked language modeling) or finetuned on other tasks in Bulgarian.
## Limitations and bias
The training data is unfiltered text from the internet and may contain all sorts of biases.
## Training data
This model was trained on the following data:
- [bg_dedup from OSCAR](https://oscar-corpus.com/)
- [Newscrawl 1 million sentences 2017 from Leipzig Corpora Collection](https://wortschatz.uni-leipzig.de/en/download/bulgarian)
- [Wikipedia 1 million sentences 2016 from Leipzig Corpora Collection](https://wortschatz.uni-leipzig.de/en/download/bulgarian)
## Training procedure
The model was pretrained using a masked language-modeling objective with dynamic masking as described [here](https://huggingface.co/roberta-base#preprocessing)
It was trained for 200k steps. The batch size was limited to 8 due to GPU memory limitations.
|
hashk1/EsperBERTo-malgranda
|
hashk1
| 2021-05-20T16:38:46Z | 4 | 0 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"jax",
"roberta",
"fill-mask",
"eo",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
fill-mask
| 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
---
language: eo
thumbnail: https://huggingface.co/blog/assets/01_how-to-train/EsperBERTo-thumbnail-v2.png
widget:
- text: "Ĉu vi paloras la <mask> Esperanto?"
---
## EsperBERTo: RoBERTa-like Language model trained on Esperanto
|
giganticode/StackOBERTflow-comments-small-v1
|
giganticode
| 2021-05-20T16:33:56Z | 10 | 1 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"jax",
"roberta",
"fill-mask",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
fill-mask
| 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
# StackOBERTflow-comments-small
StackOBERTflow is a RoBERTa model trained on StackOverflow comments.
A Byte-level BPE tokenizer with dropout was used (using the `tokenizers` package).
The model is *small*, i.e. has only 6-layers and the maximum sequence length was restricted to 256 tokens.
The model was trained for 6 epochs on several GBs of comments from the StackOverflow corpus.
## Quick start: masked language modeling prediction
```python
from transformers import pipeline
from pprint import pprint
COMMENT = "You really should not do it this way, I would use <mask> instead."
fill_mask = pipeline(
"fill-mask",
model="giganticode/StackOBERTflow-comments-small-v1",
tokenizer="giganticode/StackOBERTflow-comments-small-v1"
)
pprint(fill_mask(COMMENT))
# [{'score': 0.019997311756014824,
# 'sequence': '<s> You really should not do it this way, I would use jQuery instead.</s>',
# 'token': 1738},
# {'score': 0.01693696901202202,
# 'sequence': '<s> You really should not do it this way, I would use arrays instead.</s>',
# 'token': 2844},
# {'score': 0.013411642983555794,
# 'sequence': '<s> You really should not do it this way, I would use CSS instead.</s>',
# 'token': 2254},
# {'score': 0.013224546797573566,
# 'sequence': '<s> You really should not do it this way, I would use it instead.</s>',
# 'token': 300},
# {'score': 0.011984303593635559,
# 'sequence': '<s> You really should not do it this way, I would use classes instead.</s>',
# 'token': 1779}]
```
|
ghanashyamvtatti/roberta-fake-news
|
ghanashyamvtatti
| 2021-05-20T16:33:04Z | 11 | 3 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"tf",
"jax",
"roberta",
"text-classification",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
text-classification
| 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
A fake news detector using RoBERTa.
Dataset: https://www.kaggle.com/clmentbisaillon/fake-and-real-news-dataset
Training involved using hyperparameter search with 10 trials.
|
deepampatel/roberta-mlm-marathi
|
deepampatel
| 2021-05-20T15:58:32Z | 13 | 2 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"jax",
"roberta",
"fill-mask",
"mr",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
fill-mask
| 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
---
language: "mr"
---
# Welcome to Roberta-Marathi-MLM
## Model Description
> This is a small language model for [Marathi](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Marathi) language with 1M data samples taken from
[OSCAR page](https://oscar-public.huma-num.fr/shuffled/mr_dedup.txt.gz)
## Training params
- **Dataset** - 1M data samples are used to train this model from OSCAR page(https://oscar-corpus.com/) eventhough data set is of 2.7 GB due to resource constraint to train
I have picked only 1M data from the total 2.7GB data set. If you are interested in collaboration and have computational resources to train on you are most welcome to do so.
- **Preprocessing** - ByteLevelBPETokenizer is used to tokenize the sentences at character level and vocabulary size is set to 52k as per standard values given by 🤗
<!-- - **Hyperparameters** - __ByteLevelBPETokenizer__ : vocabulary size = 52_000 and min_frequency = 2
__Trainer__ : num_train_epochs=12 - trained for 12 epochs
per_gpu_train_batch_size=64 - batch size for the datasamples is 64
save_steps=10_000 - save model for every 10k steps
save_total_limit=2 - save limit is set for 2 -->
**Intended uses & limitations**
this is for anyone who wants to make use of marathi language models for various tasks like language generation, translation and many more use cases.
**Whatever else is helpful!**
If you are intersted in collaboration feel free to reach me [Deepam](mailto:deepam8155@gmail.com)
|
dbernsohn/roberta-python
|
dbernsohn
| 2021-05-20T15:57:13Z | 4 | 3 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"jax",
"roberta",
"fill-mask",
"arxiv:1907.11692",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
fill-mask
| 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
# roberta-python
---
language: python
datasets:
- code_search_net
---
This is a [roberta](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1907.11692.pdf) pre-trained version on the [CodeSearchNet dataset](https://github.com/github/CodeSearchNet) for **Python** Mask Language Model mission.
To load the model:
(necessary packages: !pip install transformers sentencepiece)
```python
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelWithLMHead, pipeline
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("dbernsohn/roberta-python")
model = AutoModelWithLMHead.from_pretrained("dbernsohn/roberta-python")
fill_mask = pipeline(
"fill-mask",
model=model,
tokenizer=tokenizer
)
```
You can then use this model to fill masked words in a Python code.
```python
code = """
new_dict = {}
for k, v in my_dict.<mask>():
new_dict[k] = v**2
""".lstrip()
pred = {x["token_str"].replace("Ġ", ""): x["score"] for x in fill_mask(code)}
sorted(pred.items(), key=lambda kv: kv[1], reverse=True)
# [('items', 0.7376779913902283),
# ('keys', 0.16238391399383545),
# ('values', 0.03965481370687485),
# ('iteritems', 0.03346433863043785),
# ('splitlines', 0.0032723243348300457)]
```
The whole training process and hyperparameters are in my [GitHub repo](https://github.com/DorBernsohn/CodeLM/tree/main/CodeMLM)
> Created by [Dor Bernsohn](https://www.linkedin.com/in/dor-bernsohn-70b2b1146/)
|
dbernsohn/roberta-php
|
dbernsohn
| 2021-05-20T15:56:10Z | 5 | 2 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"jax",
"roberta",
"fill-mask",
"arxiv:1907.11692",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
fill-mask
| 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
# roberta-php
---
language: php
datasets:
- code_search_net
---
This is a [roberta](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1907.11692.pdf) pre-trained version on the [CodeSearchNet dataset](https://github.com/github/CodeSearchNet) for **php** Mask Language Model mission.
To load the model:
(necessary packages: !pip install transformers sentencepiece)
```python
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelWithLMHead, pipeline
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("dbernsohn/roberta-php")
model = AutoModelWithLMHead.from_pretrained("dbernsohn/roberta-php")
fill_mask = pipeline(
"fill-mask",
model=model,
tokenizer=tokenizer
)
```
You can then use this model to fill masked words in a Java code.
```python
code = """
$people = array(
array('name' => 'Kalle', 'salt' => 856412),
array('name' => 'Pierre', 'salt' => 215863)
);
for($i = 0; $i < count($<mask>); ++$i) {
$people[$i]['salt'] = mt_rand(000000, 999999);
}
""".lstrip()
pred = {x["token_str"].replace("Ġ", ""): x["score"] for x in fill_mask(code)}
sorted(pred.items(), key=lambda kv: kv[1], reverse=True)
# [('people', 0.785636842250824),
# ('parts', 0.006270722020417452),
# ('id', 0.0035842324141412973),
# ('data', 0.0025512021966278553),
# ('config', 0.002258970635011792)]
```
The whole training process and hyperparameters are in my [GitHub repo](https://github.com/DorBernsohn/CodeLM/tree/main/CodeMLM)
> Created by [Dor Bernsohn](https://www.linkedin.com/in/dor-bernsohn-70b2b1146/)
|
dbernsohn/roberta-go
|
dbernsohn
| 2021-05-20T15:53:19Z | 13 | 0 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"jax",
"roberta",
"fill-mask",
"arxiv:1907.11692",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
fill-mask
| 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
# roberta-go
---
language: Go
datasets:
- code_search_net
---
This is a [roberta](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1907.11692.pdf) pre-trained version on the [CodeSearchNet dataset](https://github.com/github/CodeSearchNet) for **Golang** Mask Language Model mission.
To load the model:
(necessary packages: !pip install transformers sentencepiece)
```python
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelWithLMHead, pipeline
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("dbernsohn/roberta-go")
model = AutoModelWithLMHead.from_pretrained("dbernsohn/roberta-go")
fill_mask = pipeline(
"fill-mask",
model=model,
tokenizer=tokenizer
)
```
You can then use this model to fill masked words in a Java code.
```python
code = """
package main
import (
"fmt"
"runtime"
)
func main() {
fmt.Print("Go runs on ")
switch os := runtime.<mask>; os {
case "darwin":
fmt.Println("OS X.")
case "linux":
fmt.Println("Linux.")
default:
// freebsd, openbsd,
// plan9, windows...
fmt.Printf("%s.\n", os)
}
}
""".lstrip()
pred = {x["token_str"].replace("Ġ", ""): x["score"] for x in fill_mask(code)}
sorted(pred.items(), key=lambda kv: kv[1], reverse=True)
[('GOOS', 0.11810332536697388),
('FileInfo', 0.04276798665523529),
('Stdout', 0.03572738170623779),
('Getenv', 0.025064032524824142),
('FileMode', 0.01462600938975811)]
```
The whole training process and hyperparameters are in my [GitHub repo](https://github.com/DorBernsohn/CodeLM/tree/main/CodeMLM)
> Created by [Dor Bernsohn](https://www.linkedin.com/in/dor-bernsohn-70b2b1146/)
|
clue/roberta_chinese_base
|
clue
| 2021-05-20T15:23:58Z | 317 | 7 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"jax",
"roberta",
"zh",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] | null | 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
---
language: zh
---
## roberta_chinese_base
### Overview
**Language model:** roberta-base
**Model size:** 392M
**Language:** Chinese
**Training data:** [CLUECorpusSmall](https://github.com/CLUEbenchmark/CLUECorpus2020)
**Eval data:** [CLUE dataset](https://github.com/CLUEbenchmark/CLUE)
### Results
For results on downstream tasks like text classification, please refer to [this repository](https://github.com/CLUEbenchmark/CLUE).
### Usage
**NOTE:** You have to call **BertTokenizer** instead of RobertaTokenizer !!!
```
import torch
from transformers import BertTokenizer, BertModel
tokenizer = BertTokenizer.from_pretrained("clue/roberta_chinese_base")
roberta = BertModel.from_pretrained("clue/roberta_chinese_base")
```
### About CLUE benchmark
Organization of Language Understanding Evaluation benchmark for Chinese: tasks & datasets, baselines, pre-trained Chinese models, corpus and leaderboard.
Github: https://github.com/CLUEbenchmark
Website: https://www.cluebenchmarks.com/
|
clue/roberta_chinese_3L312_clue_tiny
|
clue
| 2021-05-20T15:22:48Z | 4 | 2 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"jax",
"roberta",
"zh",
"arxiv:2003.01355",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] | null | 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
---
language: zh
---
# Introduction
This model was trained on TPU and the details are as follows:
## Model
##
| Model_name | params | size | Training_corpus | Vocab |
| :------------------------------------------ | :----- | :------- | :----------------- | :-----------: |
| **`RoBERTa-tiny-clue`** <br/>Super_small_model | 7.5M | 28.3M | **CLUECorpus2020** | **CLUEVocab** |
| **`RoBERTa-tiny-pair`** <br/>Super_small_sentence_pair_model | 7.5M | 28.3M | **CLUECorpus2020** | **CLUEVocab** |
| **`RoBERTa-tiny3L768-clue`** <br/>small_model | 38M | 110M | **CLUECorpus2020** | **CLUEVocab** |
| **`RoBERTa-tiny3L312-clue`** <br/>small_model | <7.5M | 24M | **CLUECorpus2020** | **CLUEVocab** |
| **`RoBERTa-large-clue`** <br/> Large_model | 290M | 1.20G | **CLUECorpus2020** | **CLUEVocab** |
| **`RoBERTa-large-pair`** <br/>Large_sentence_pair_model | 290M | 1.20G | **CLUECorpus2020** | **CLUEVocab** |
### Usage
With the help of[Huggingface-Transformers 2.5.1](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers), you could use these model as follows
```
tokenizer = BertTokenizer.from_pretrained("MODEL_NAME")
model = BertModel.from_pretrained("MODEL_NAME")
```
`MODEL_NAME`:
| Model_NAME | MODEL_LINK |
| -------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------ |
| **RoBERTa-tiny-clue** | [`clue/roberta_chinese_clue_tiny`](https://huggingface.co/clue/roberta_chinese_clue_tiny) |
| **RoBERTa-tiny-pair** | [`clue/roberta_chinese_pair_tiny`](https://huggingface.co/clue/roberta_chinese_pair_tiny) |
| **RoBERTa-tiny3L768-clue** | [`clue/roberta_chinese_3L768_clue_tiny`](https://huggingface.co/clue/roberta_chinese_3L768_clue_tiny) |
| **RoBERTa-tiny3L312-clue** | [`clue/roberta_chinese_3L312_clue_tiny`](https://huggingface.co/clue/roberta_chinese_3L312_clue_tiny) |
| **RoBERTa-large-clue** | [`clue/roberta_chinese_clue_large`](https://huggingface.co/clue/roberta_chinese_clue_large) |
| **RoBERTa-large-pair** | [`clue/roberta_chinese_pair_large`](https://huggingface.co/clue/roberta_chinese_pair_large) |
## Details
Please read <a href='https://arxiv.org/pdf/2003.01355'>https://arxiv.org/pdf/2003.01355.
Please visit our repository: https://github.com/CLUEbenchmark/CLUEPretrainedModels.git
|
castorini/ance-msmarco-doc-maxp
|
castorini
| 2021-05-20T15:17:50Z | 11 | 2 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"roberta",
"arxiv:2007.00808",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] | null | 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
This model is converted from the original ANCE [repo](https://github.com/microsoft/ANCE) and fitted into Pyserini:
> Lee Xiong, Chenyan Xiong, Ye Li, Kwok-Fung Tang, Jialin Liu, Paul Bennett, Junaid Ahmed, Arnold Overwijk. [Approximate Nearest Neighbor Negative Contrastive Learning for Dense Text Retrieval](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2007.00808.pdf)
For more details on how to use it, check our experiments in [Pyserini](https://github.com/castorini/pyserini/blob/master/docs/experiments-ance.md)
|
castorini/ance-msmarco-doc-firstp
|
castorini
| 2021-05-20T15:17:20Z | 7 | 1 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"roberta",
"arxiv:2007.00808",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] | null | 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
This model is converted from the original ANCE [repo](https://github.com/microsoft/ANCE) and fitted into Pyserini:
> Lee Xiong, Chenyan Xiong, Ye Li, Kwok-Fung Tang, Jialin Liu, Paul Bennett, Junaid Ahmed, Arnold Overwijk. [Approximate Nearest Neighbor Negative Contrastive Learning for Dense Text Retrieval](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2007.00808.pdf)
For more details on how to use it, check our experiments in [Pyserini](https://github.com/castorini/pyserini/blob/master/docs/experiments-ance.md)
|
cahya/roberta-base-indonesian-522M
|
cahya
| 2021-05-20T14:41:00Z | 338 | 6 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"tf",
"jax",
"roberta",
"fill-mask",
"id",
"license:mit",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
fill-mask
| 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
---
language: "id"
license: "mit"
datasets:
- Indonesian Wikipedia
widget:
- text: "Ibu ku sedang bekerja <mask> supermarket."
---
# Indonesian RoBERTa base model (uncased)
## Model description
It is RoBERTa-base model pre-trained with indonesian Wikipedia using a masked language modeling (MLM) objective. This
model is uncased: it does not make a difference between indonesia and Indonesia.
This is one of several other language models that have been pre-trained with indonesian datasets. More detail about
its usage on downstream tasks (text classification, text generation, etc) is available at [Transformer based Indonesian Language Models](https://github.com/cahya-wirawan/indonesian-language-models/tree/master/Transformers)
## Intended uses & limitations
### How to use
You can use this model directly with a pipeline for masked language modeling:
```python
>>> from transformers import pipeline
>>> unmasker = pipeline('fill-mask', model='cahya/roberta-base-indonesian-522M')
>>> unmasker("Ibu ku sedang bekerja <mask> supermarket")
```
Here is how to use this model to get the features of a given text in PyTorch:
```python
from transformers import RobertaTokenizer, RobertaModel
model_name='cahya/roberta-base-indonesian-522M'
tokenizer = RobertaTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
model = RobertaModel.from_pretrained(model_name)
text = "Silakan diganti dengan text apa saja."
encoded_input = tokenizer(text, return_tensors='pt')
output = model(**encoded_input)
```
and in Tensorflow:
```python
from transformers import RobertaTokenizer, TFRobertaModel
model_name='cahya/roberta-base-indonesian-522M'
tokenizer = RobertaTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
model = TFRobertaModel.from_pretrained(model_name)
text = "Silakan diganti dengan text apa saja."
encoded_input = tokenizer(text, return_tensors='tf')
output = model(encoded_input)
```
## Training data
This model was pre-trained with 522MB of indonesian Wikipedia.
The texts are lowercased and tokenized using WordPiece and a vocabulary size of 32,000. The inputs of the model are
then of the form:
```<s> Sentence A </s> Sentence B </s>```
|
aychang/roberta-base-imdb
|
aychang
| 2021-05-20T14:25:56Z | 1,446 | 5 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"jax",
"roberta",
"text-classification",
"en",
"dataset:imdb",
"license:mit",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
text-classification
| 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
---
language:
- en
thumbnail:
tags:
- text-classification
license: mit
datasets:
- imdb
metrics:
---
# IMDB Sentiment Task: roberta-base
## Model description
A simple base roBERTa model trained on the "imdb" dataset.
## Intended uses & limitations
#### How to use
##### Transformers
```python
# Load model and tokenizer
from transformers import AutoModelForSequenceClassification, AutoTokenizer
model = AutoModelForQuestionAnswering.from_pretrained(model_name)
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
# Use pipeline
from transformers import pipeline
model_name = "aychang/roberta-base-imdb"
nlp = pipeline("sentiment-analysis", model=model_name, tokenizer=model_name)
results = nlp(["I didn't really like it because it was so terrible.", "I love how easy it is to watch and get good results."])
```
##### AdaptNLP
```python
from adaptnlp import EasySequenceClassifier
model_name = "aychang/roberta-base-imdb"
texts = ["I didn't really like it because it was so terrible.", "I love how easy it is to watch and get good results."]
classifer = EasySequenceClassifier
results = classifier.tag_text(text=texts, model_name_or_path=model_name, mini_batch_size=2)
```
#### Limitations and bias
This is minimal language model trained on a benchmark dataset.
## Training data
IMDB https://huggingface.co/datasets/imdb
## Training procedure
#### Hardware
One V100
#### Hyperparameters and Training Args
```python
from transformers import TrainingArguments
training_args = TrainingArguments(
output_dir='./models',
overwrite_output_dir=False,
num_train_epochs=2,
per_device_train_batch_size=8,
per_device_eval_batch_size=8,
warmup_steps=500,
weight_decay=0.01,
evaluation_strategy="steps",
logging_dir='./logs',
fp16=False,
eval_steps=800,
save_steps=300000
)
```
## Eval results
```
{'epoch': 2.0,
'eval_accuracy': 0.94668,
'eval_f1': array([0.94603457, 0.94731017]),
'eval_loss': 0.2578844428062439,
'eval_precision': array([0.95762642, 0.93624502]),
'eval_recall': array([0.93472, 0.95864]),
'eval_runtime': 244.7522,
'eval_samples_per_second': 102.144}
```
|
aravind-812/roberta-train-json
|
aravind-812
| 2021-05-20T14:12:53Z | 9 | 0 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"jax",
"roberta",
"question-answering",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
question-answering
| 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
---
datasets:
- squad
widget:
- text: "Which name is also used to describe the Amazon rainforest in English?"
context: "The Amazon rainforest (Portuguese: Floresta Amazônica or Amazônia; Spanish: Selva Amazónica, Amazonía or usually Amazonia; French: Forêt amazonienne; Dutch: Amazoneregenwoud), also known in English as Amazonia or the Amazon Jungle, is a moist broadleaf forest that covers most of the Amazon basin of South America. This basin encompasses 7,000,000 square kilometres (2,700,000 sq mi), of which 5,500,000 square kilometres (2,100,000 sq mi) are covered by the rainforest. This region includes territory belonging to nine nations. The majority of the forest is contained within Brazil, with 60% of the rainforest, followed by Peru with 13%, Colombia with 10%, and with minor amounts in Venezuela, Ecuador, Bolivia, Guyana, Suriname and French Guiana. States or departments in four nations contain \"Amazonas\" in their names. The Amazon represents over half of the planet's remaining rainforests, and comprises the largest and most biodiverse tract of tropical rainforest in the world, with an estimated 390 billion individual trees divided into 16,000 species."
- text: "How many square kilometers of rainforest is covered in the basin?"
context: "The Amazon rainforest (Portuguese: Floresta Amazônica or Amazônia; Spanish: Selva Amazónica, Amazonía or usually Amazonia; French: Forêt amazonienne; Dutch: Amazoneregenwoud), also known in English as Amazonia or the Amazon Jungle, is a moist broadleaf forest that covers most of the Amazon basin of South America. This basin encompasses 7,000,000 square kilometres (2,700,000 sq mi), of which 5,500,000 square kilometres (2,100,000 sq mi) are covered by the rainforest. This region includes territory belonging to nine nations. The majority of the forest is contained within Brazil, with 60% of the rainforest, followed by Peru with 13%, Colombia with 10%, and with minor amounts in Venezuela, Ecuador, Bolivia, Guyana, Suriname and French Guiana. States or departments in four nations contain \"Amazonas\" in their names. The Amazon represents over half of the planet's remaining rainforests, and comprises the largest and most biodiverse tract of tropical rainforest in the world, with an estimated 390 billion individual trees divided into 16,000 species."
|
pchanda/pretrained-smiles-pubchem10m
|
pchanda
| 2021-05-20T13:01:15Z | 729 | 1 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"roberta",
"fill-mask",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
fill-mask
| 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
model pretrained on 10m smiles from pubchem.
|
abhishek/autonlp-imdb_sentiment_classification-31154
|
abhishek
| 2021-05-20T12:46:38Z | 6 | 0 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"jax",
"roberta",
"text-classification",
"autonlp",
"en",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
text-classification
| 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
---
tags: autonlp
language: en
widget:
- text: "I love AutoNLP 🤗"
---
# Model Trained Using AutoNLP
- Problem type: Binary Classification
- Model ID: 31154
## Validation Metrics
- Loss: 0.19292379915714264
- Accuracy: 0.9395
- Precision: 0.9569557080474111
- Recall: 0.9204
- AUC: 0.9851040399999998
- F1: 0.9383219492302988
## Usage
You can use cURL to access this model:
```
$ curl -X POST -H "Authorization: Bearer YOUR_API_KEY" -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{"inputs": "I love AutoNLP"}' https://api-inference.huggingface.co/models/abhishek/autonlp-imdb_sentiment_classification-31154
```
Or Python API:
```
from transformers import AutoModelForSequenceClassification, AutoTokenizer
model = AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained("abhishek/autonlp-imdb_sentiment_classification-31154", use_auth_token=True)
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("abhishek/autonlp-imdb_sentiment_classification-31154", use_auth_token=True)
inputs = tokenizer("I love AutoNLP", return_tensors="pt")
outputs = model(**inputs)
```
|
SparkBeyond/roberta-large-sts-b
|
SparkBeyond
| 2021-05-20T12:26:47Z | 6 | 0 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"jax",
"roberta",
"text-classification",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
text-classification
| 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
# Roberta Large STS-B
This model is a fine tuned RoBERTA model over STS-B.
It was trained with these params:
!python /content/transformers/examples/text-classification/run_glue.py \
--model_type roberta \
--model_name_or_path roberta-large \
--task_name STS-B \
--do_train \
--do_eval \
--do_lower_case \
--data_dir /content/glue_data/STS-B/ \
--max_seq_length 128 \
--per_gpu_eval_batch_size=8 \
--per_gpu_train_batch_size=8 \
--learning_rate 2e-5 \
--num_train_epochs 3.0 \
--output_dir /content/roberta-sts-b
## How to run
```python
import toolz
import torch
batch_size = 6
def roberta_similarity_batches(to_predict):
batches = toolz.partition(batch_size, to_predict)
similarity_scores = []
for batch in batches:
sentences = [(sentence_similarity["sent1"], sentence_similarity["sent2"]) for sentence_similarity in batch]
batch_scores = similarity_roberta(model, tokenizer,sentences)
similarity_scores = similarity_scores + batch_scores[0].cpu().squeeze(axis=1).tolist()
return similarity_scores
def similarity_roberta(model, tokenizer, sent_pairs):
batch_token = tokenizer(sent_pairs, padding='max_length', truncation=True, max_length=500)
res = model(torch.tensor(batch_token['input_ids']).cuda(), attention_mask=torch.tensor(batch_token["attention_mask"]).cuda())
return res
similarity_roberta(model, tokenizer, [('NEW YORK--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Rosen Law Firm, a global investor rights law firm, announces it is investigating potential securities claims on behalf of shareholders of Vale S.A. ( VALE ) resulting from allegations that Vale may have issued materially misleading business information to the investing public',
'EQUITY ALERT: Rosen Law Firm Announces Investigation of Securities Claims Against Vale S.A. – VALE')])
```
|
MoseliMotsoehli/zuBERTa
|
MoseliMotsoehli
| 2021-05-20T12:14:07Z | 6 | 1 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"tf",
"jax",
"roberta",
"fill-mask",
"zu",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
fill-mask
| 2022-03-02T23:29:04Z |
---
language: zu
---
# zuBERTa
zuBERTa is a RoBERTa style transformer language model trained on zulu text.
## Intended uses & limitations
The model can be used for getting embeddings to use on a down-stream task such as question answering.
#### How to use
```python
>>> from transformers import pipeline
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelWithLMHead
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("MoseliMotsoehli/zuBERTa")
>>> model = AutoModelWithLMHead.from_pretrained("MoseliMotsoehli/zuBERTa")
>>> unmasker = pipeline('fill-mask', model=model, tokenizer=tokenizer)
>>> unmasker("Abafika eNkandla bafika sebeholwa <mask> uMpongo kaZingelwayo.")
[
{
"sequence": "<s>Abafika eNkandla bafika sebeholwa khona uMpongo kaZingelwayo.</s>",
"score": 0.050459690392017365,
"token": 555,
"token_str": "Ġkhona"
},
{
"sequence": "<s>Abafika eNkandla bafika sebeholwa inkosi uMpongo kaZingelwayo.</s>",
"score": 0.03668094798922539,
"token": 2321,
"token_str": "Ġinkosi"
},
{
"sequence": "<s>Abafika eNkandla bafika sebeholwa ubukhosi uMpongo kaZingelwayo.</s>",
"score": 0.028774697333574295,
"token": 5101,
"token_str": "Ġubukhosi"
}
]
```
## Training data
1. 30k sentences of text, came from the [Leipzig Corpora Collection](https://wortschatz.uni-leipzig.de/en/download) of zulu 2018. These were collected from news articles and creative writtings.
2. ~7500 articles of human generated translations were scraped from the zulu [wikipedia](https://zu.wikipedia.org/wiki/Special:AllPages).
### BibTeX entry and citation info
```bibtex
@inproceedings{author = {Moseli Motsoehli},
title = {Towards transformation of Southern African language models through transformers.},
year={2020}
}
```
|
zanelim/singbert
|
zanelim
| 2021-05-20T09:38:41Z | 6 | 4 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"tf",
"jax",
"bert",
"pretraining",
"singapore",
"sg",
"singlish",
"malaysia",
"ms",
"manglish",
"bert-base-uncased",
"en",
"license:mit",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] | null | 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
---
language: en
tags:
- singapore
- sg
- singlish
- malaysia
- ms
- manglish
- bert-base-uncased
license: mit
datasets:
- reddit singapore, malaysia
- hardwarezone
widget:
- text: "kopi c siew [MASK]"
- text: "die [MASK] must try"
---
# Model name
SingBert - Bert for Singlish (SG) and Manglish (MY).
## Model description
[BERT base uncased](https://github.com/google-research/bert#pre-trained-models), with pre-training finetuned on
[singlish](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Singlish) and [manglish](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Manglish) data.
## Intended uses & limitations
#### How to use
```python
>>> from transformers import pipeline
>>> nlp = pipeline('fill-mask', model='zanelim/singbert')
>>> nlp("kopi c siew [MASK]")
[{'sequence': '[CLS] kopi c siew dai [SEP]',
'score': 0.5092713236808777,
'token': 18765,
'token_str': 'dai'},
{'sequence': '[CLS] kopi c siew mai [SEP]',
'score': 0.3515934646129608,
'token': 14736,
'token_str': 'mai'},
{'sequence': '[CLS] kopi c siew bao [SEP]',
'score': 0.05576375499367714,
'token': 25945,
'token_str': 'bao'},
{'sequence': '[CLS] kopi c siew. [SEP]',
'score': 0.006019321270287037,
'token': 1012,
'token_str': '.'},
{'sequence': '[CLS] kopi c siew sai [SEP]',
'score': 0.0038361591286957264,
'token': 18952,
'token_str': 'sai'}]
>>> nlp("one teh c siew dai, and one kopi [MASK].")
[{'sequence': '[CLS] one teh c siew dai, and one kopi c [SEP]',
'score': 0.6176503300666809,
'token': 1039,
'token_str': 'c'},
{'sequence': '[CLS] one teh c siew dai, and one kopi o [SEP]',
'score': 0.21094971895217896,
'token': 1051,
'token_str': 'o'},
{'sequence': '[CLS] one teh c siew dai, and one kopi. [SEP]',
'score': 0.13027705252170563,
'token': 1012,
'token_str': '.'},
{'sequence': '[CLS] one teh c siew dai, and one kopi! [SEP]',
'score': 0.004680239595472813,
'token': 999,
'token_str': '!'},
{'sequence': '[CLS] one teh c siew dai, and one kopi w [SEP]',
'score': 0.002034128177911043,
'token': 1059,
'token_str': 'w'}]
>>> nlp("dont play [MASK] leh")
[{'sequence': '[CLS] dont play play leh [SEP]',
'score': 0.9281464219093323,
'token': 2377,
'token_str': 'play'},
{'sequence': '[CLS] dont play politics leh [SEP]',
'score': 0.010990909300744534,
'token': 4331,
'token_str': 'politics'},
{'sequence': '[CLS] dont play punk leh [SEP]',
'score': 0.005583590362221003,
'token': 7196,
'token_str': 'punk'},
{'sequence': '[CLS] dont play dirty leh [SEP]',
'score': 0.0025784350000321865,
'token': 6530,
'token_str': 'dirty'},
{'sequence': '[CLS] dont play cheat leh [SEP]',
'score': 0.0025066907983273268,
'token': 21910,
'token_str': 'cheat'}]
>>> nlp("catch no [MASK]")
[{'sequence': '[CLS] catch no ball [SEP]',
'score': 0.7922210693359375,
'token': 3608,
'token_str': 'ball'},
{'sequence': '[CLS] catch no balls [SEP]',
'score': 0.20503675937652588,
'token': 7395,
'token_str': 'balls'},
{'sequence': '[CLS] catch no tail [SEP]',
'score': 0.0006608376861549914,
'token': 5725,
'token_str': 'tail'},
{'sequence': '[CLS] catch no talent [SEP]',
'score': 0.0002158183924620971,
'token': 5848,
'token_str': 'talent'},
{'sequence': '[CLS] catch no prisoners [SEP]',
'score': 5.3481446229852736e-05,
'token': 5895,
'token_str': 'prisoners'}]
>>> nlp("confirm plus [MASK]")
[{'sequence': '[CLS] confirm plus chop [SEP]',
'score': 0.992355227470398,
'token': 24494,
'token_str': 'chop'},
{'sequence': '[CLS] confirm plus one [SEP]',
'score': 0.0037301010452210903,
'token': 2028,
'token_str': 'one'},
{'sequence': '[CLS] confirm plus minus [SEP]',
'score': 0.0014284878270700574,
'token': 15718,
'token_str': 'minus'},
{'sequence': '[CLS] confirm plus 1 [SEP]',
'score': 0.0011354683665558696,
'token': 1015,
'token_str': '1'},
{'sequence': '[CLS] confirm plus chopped [SEP]',
'score': 0.0003804611915256828,
'token': 24881,
'token_str': 'chopped'}]
>>> nlp("die [MASK] must try")
[{'sequence': '[CLS] die die must try [SEP]',
'score': 0.9552758932113647,
'token': 3280,
'token_str': 'die'},
{'sequence': '[CLS] die also must try [SEP]',
'score': 0.03644804656505585,
'token': 2036,
'token_str': 'also'},
{'sequence': '[CLS] die liao must try [SEP]',
'score': 0.003282855963334441,
'token': 727,
'token_str': 'liao'},
{'sequence': '[CLS] die already must try [SEP]',
'score': 0.0004937972989864647,
'token': 2525,
'token_str': 'already'},
{'sequence': '[CLS] die hard must try [SEP]',
'score': 0.0003659659414552152,
'token': 2524,
'token_str': 'hard'}]
```
Here is how to use this model to get the features of a given text in PyTorch:
```python
from transformers import BertTokenizer, BertModel
tokenizer = BertTokenizer.from_pretrained('zanelim/singbert')
model = BertModel.from_pretrained("zanelim/singbert")
text = "Replace me by any text you'd like."
encoded_input = tokenizer(text, return_tensors='pt')
output = model(**encoded_input)
```
and in TensorFlow:
```python
from transformers import BertTokenizer, TFBertModel
tokenizer = BertTokenizer.from_pretrained("zanelim/singbert")
model = TFBertModel.from_pretrained("zanelim/singbert")
text = "Replace me by any text you'd like."
encoded_input = tokenizer(text, return_tensors='tf')
output = model(encoded_input)
```
#### Limitations and bias
This model was finetuned on colloquial Singlish and Manglish corpus, hence it is best applied on downstream tasks involving the main
constituent languages- english, mandarin, malay. Also, as the training data is mainly from forums, beware of existing inherent bias.
## Training data
Colloquial singlish and manglish (both are a mixture of English, Mandarin, Tamil, Malay, and other local dialects like Hokkien, Cantonese or Teochew)
corpus. The corpus is collected from subreddits- `r/singapore` and `r/malaysia`, and forums such as `hardwarezone`.
## Training procedure
Initialized with [bert base uncased](https://github.com/google-research/bert#pre-trained-models) vocab and checkpoints (pre-trained weights).
Top 1000 custom vocab tokens (non-overlapped with original bert vocab) were further extracted from training data and filled into unused tokens in original bert vocab.
Pre-training was further finetuned on training data with the following hyperparameters
* train_batch_size: 512
* max_seq_length: 128
* num_train_steps: 300000
* num_warmup_steps: 5000
* learning_rate: 2e-5
* hardware: TPU v3-8
|
zanelim/singbert-large-sg
|
zanelim
| 2021-05-20T09:36:17Z | 9 | 4 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"tf",
"jax",
"bert",
"pretraining",
"singapore",
"sg",
"singlish",
"malaysia",
"ms",
"manglish",
"bert-large-uncased",
"en",
"license:mit",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] | null | 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
---
language: en
tags:
- singapore
- sg
- singlish
- malaysia
- ms
- manglish
- bert-large-uncased
license: mit
datasets:
- reddit singapore, malaysia
- hardwarezone
widget:
- text: "kopi c siew [MASK]"
- text: "die [MASK] must try"
---
# Model name
SingBert Large - Bert for Singlish (SG) and Manglish (MY).
## Model description
Similar to [SingBert](https://huggingface.co/zanelim/singbert) but the large version, which was initialized from [BERT large uncased (whole word masking)](https://github.com/google-research/bert#pre-trained-models), with pre-training finetuned on
[singlish](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Singlish) and [manglish](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Manglish) data.
## Intended uses & limitations
#### How to use
```python
>>> from transformers import pipeline
>>> nlp = pipeline('fill-mask', model='zanelim/singbert-large-sg')
>>> nlp("kopi c siew [MASK]")
[{'sequence': '[CLS] kopi c siew dai [SEP]',
'score': 0.9003700017929077,
'token': 18765,
'token_str': 'dai'},
{'sequence': '[CLS] kopi c siew mai [SEP]',
'score': 0.0779474675655365,
'token': 14736,
'token_str': 'mai'},
{'sequence': '[CLS] kopi c siew. [SEP]',
'score': 0.0032227332703769207,
'token': 1012,
'token_str': '.'},
{'sequence': '[CLS] kopi c siew bao [SEP]',
'score': 0.0017727474914863706,
'token': 25945,
'token_str': 'bao'},
{'sequence': '[CLS] kopi c siew peng [SEP]',
'score': 0.0012526646023616195,
'token': 26473,
'token_str': 'peng'}]
>>> nlp("one teh c siew dai, and one kopi [MASK]")
[{'sequence': '[CLS] one teh c siew dai, and one kopi. [SEP]',
'score': 0.5249741077423096,
'token': 1012,
'token_str': '.'},
{'sequence': '[CLS] one teh c siew dai, and one kopi o [SEP]',
'score': 0.27349168062210083,
'token': 1051,
'token_str': 'o'},
{'sequence': '[CLS] one teh c siew dai, and one kopi peng [SEP]',
'score': 0.057190295308828354,
'token': 26473,
'token_str': 'peng'},
{'sequence': '[CLS] one teh c siew dai, and one kopi c [SEP]',
'score': 0.04022320732474327,
'token': 1039,
'token_str': 'c'},
{'sequence': '[CLS] one teh c siew dai, and one kopi? [SEP]',
'score': 0.01191170234233141,
'token': 1029,
'token_str': '?'}]
>>> nlp("die [MASK] must try")
[{'sequence': '[CLS] die die must try [SEP]',
'score': 0.9921030402183533,
'token': 3280,
'token_str': 'die'},
{'sequence': '[CLS] die also must try [SEP]',
'score': 0.004993876442313194,
'token': 2036,
'token_str': 'also'},
{'sequence': '[CLS] die liao must try [SEP]',
'score': 0.000317625846946612,
'token': 727,
'token_str': 'liao'},
{'sequence': '[CLS] die still must try [SEP]',
'score': 0.0002260878391098231,
'token': 2145,
'token_str': 'still'},
{'sequence': '[CLS] die i must try [SEP]',
'score': 0.00016935862367972732,
'token': 1045,
'token_str': 'i'}]
>>> nlp("dont play [MASK] leh")
[{'sequence': '[CLS] dont play play leh [SEP]',
'score': 0.9079819321632385,
'token': 2377,
'token_str': 'play'},
{'sequence': '[CLS] dont play punk leh [SEP]',
'score': 0.006846973206847906,
'token': 7196,
'token_str': 'punk'},
{'sequence': '[CLS] dont play games leh [SEP]',
'score': 0.004041737411171198,
'token': 2399,
'token_str': 'games'},
{'sequence': '[CLS] dont play politics leh [SEP]',
'score': 0.003728888463228941,
'token': 4331,
'token_str': 'politics'},
{'sequence': '[CLS] dont play cheat leh [SEP]',
'score': 0.0032805048394948244,
'token': 21910,
'token_str': 'cheat'}]
>>> nlp("confirm plus [MASK]")
{'sequence': '[CLS] confirm plus chop [SEP]',
'score': 0.9749826192855835,
'token': 24494,
'token_str': 'chop'},
{'sequence': '[CLS] confirm plus chopped [SEP]',
'score': 0.017554156482219696,
'token': 24881,
'token_str': 'chopped'},
{'sequence': '[CLS] confirm plus minus [SEP]',
'score': 0.002725469646975398,
'token': 15718,
'token_str': 'minus'},
{'sequence': '[CLS] confirm plus guarantee [SEP]',
'score': 0.000900257145985961,
'token': 11302,
'token_str': 'guarantee'},
{'sequence': '[CLS] confirm plus one [SEP]',
'score': 0.0004384620988275856,
'token': 2028,
'token_str': 'one'}]
>>> nlp("catch no [MASK]")
[{'sequence': '[CLS] catch no ball [SEP]',
'score': 0.9381157159805298,
'token': 3608,
'token_str': 'ball'},
{'sequence': '[CLS] catch no balls [SEP]',
'score': 0.060842301696538925,
'token': 7395,
'token_str': 'balls'},
{'sequence': '[CLS] catch no fish [SEP]',
'score': 0.00030917322146706283,
'token': 3869,
'token_str': 'fish'},
{'sequence': '[CLS] catch no breath [SEP]',
'score': 7.552534952992573e-05,
'token': 3052,
'token_str': 'breath'},
{'sequence': '[CLS] catch no tail [SEP]',
'score': 4.208395694149658e-05,
'token': 5725,
'token_str': 'tail'}]
```
Here is how to use this model to get the features of a given text in PyTorch:
```python
from transformers import BertTokenizer, BertModel
tokenizer = BertTokenizer.from_pretrained('zanelim/singbert-large-sg')
model = BertModel.from_pretrained("zanelim/singbert-large-sg")
text = "Replace me by any text you'd like."
encoded_input = tokenizer(text, return_tensors='pt')
output = model(**encoded_input)
```
and in TensorFlow:
```python
from transformers import BertTokenizer, TFBertModel
tokenizer = BertTokenizer.from_pretrained("zanelim/singbert-large-sg")
model = TFBertModel.from_pretrained("zanelim/singbert-large-sg")
text = "Replace me by any text you'd like."
encoded_input = tokenizer(text, return_tensors='tf')
output = model(encoded_input)
```
#### Limitations and bias
This model was finetuned on colloquial Singlish and Manglish corpus, hence it is best applied on downstream tasks involving the main
constituent languages- english, mandarin, malay. Also, as the training data is mainly from forums, beware of existing inherent bias.
## Training data
Colloquial singlish and manglish (both are a mixture of English, Mandarin, Tamil, Malay, and other local dialects like Hokkien, Cantonese or Teochew)
corpus. The corpus is collected from subreddits- `r/singapore` and `r/malaysia`, and forums such as `hardwarezone`.
## Training procedure
Initialized with [bert large uncased (whole word masking)](https://github.com/google-research/bert#pre-trained-models) vocab and checkpoints (pre-trained weights).
Top 1000 custom vocab tokens (non-overlapped with original bert vocab) were further extracted from training data and filled into unused tokens in original bert vocab.
Pre-training was further finetuned on training data with the following hyperparameters
* train_batch_size: 512
* max_seq_length: 128
* num_train_steps: 300000
* num_warmup_steps: 5000
* learning_rate: 2e-5
* hardware: TPU v3-8
|
ykacer/bert-base-cased-imdb-sequence-classification
|
ykacer
| 2021-05-20T09:31:37Z | 6 | 0 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"jax",
"bert",
"text-classification",
"sequence",
"classification",
"en",
"dataset:imdb",
"license:apache-2.0",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
text-classification
| 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
---
language:
- en
thumbnail: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/JetRunner/BERT-of-Theseus/master/bert-of-theseus.png
tags:
- sequence
- classification
license: apache-2.0
datasets:
- imdb
metrics:
- accuracy
---
|
twmkn9/bert-base-uncased-squad2
|
twmkn9
| 2021-05-20T08:21:23Z | 245 | 2 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"jax",
"bert",
"question-answering",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
question-answering
| 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
This model is [BERT base uncased](https://huggingface.co/bert-base-uncased) trained on SQuAD v2 as:
```
export SQUAD_DIR=../../squad2
python3 run_squad.py
--model_type bert
--model_name_or_path bert-base-uncased
--do_train
--do_eval
--overwrite_cache
--do_lower_case
--version_2_with_negative
--save_steps 100000
--train_file $SQUAD_DIR/train-v2.0.json
--predict_file $SQUAD_DIR/dev-v2.0.json
--per_gpu_train_batch_size 8
--num_train_epochs 3
--learning_rate 3e-5
--max_seq_length 384
--doc_stride 128
--output_dir ./tmp/bert_fine_tuned/
```
Performance on a dev subset is close to the original paper:
```
Results:
{
'exact': 72.35932872655479,
'f1': 75.75355132564763,
'total': 6078,
'HasAns_exact': 74.29553264604812,
'HasAns_f1': 81.38490892002987,
'HasAns_total': 2910,
'NoAns_exact': 70.58080808080808,
'NoAns_f1': 70.58080808080808,
'NoAns_total': 3168,
'best_exact': 72.35932872655479,
'best_exact_thresh': 0.0,
'best_f1': 75.75355132564766,
'best_f1_thresh': 0.0
}
```
We are hopeful this might save you time, energy, and compute. Cheers!
|
tugstugi/bert-large-mongolian-cased
|
tugstugi
| 2021-05-20T08:16:24Z | 28 | 0 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"tf",
"jax",
"bert",
"fill-mask",
"mongolian",
"cased",
"mn",
"arxiv:1810.04805",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
fill-mask
| 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
---
language: "mn"
tags:
- bert
- mongolian
- cased
---
# BERT-LARGE-MONGOLIAN-CASED
[Link to Official Mongolian-BERT repo](https://github.com/tugstugi/mongolian-bert)
## Model description
This repository contains pre-trained Mongolian [BERT](https://arxiv.org/abs/1810.04805) models trained by [tugstugi](https://github.com/tugstugi), [enod](https://github.com/enod) and [sharavsambuu](https://github.com/sharavsambuu).
Special thanks to [nabar](https://github.com/nabar) who provided 5x TPUs.
This repository is based on the following open source projects: [google-research/bert](https://github.com/google-research/bert/),
[huggingface/pytorch-pretrained-BERT](https://github.com/huggingface/pytorch-pretrained-BERT) and [yoheikikuta/bert-japanese](https://github.com/yoheikikuta/bert-japanese).
#### How to use
```python
from transformers import pipeline, AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForMaskedLM
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained('tugstugi/bert-large-mongolian-cased', use_fast=False)
model = AutoModelForMaskedLM.from_pretrained('tugstugi/bert-large-mongolian-cased')
## declare task ##
pipe = pipeline(task="fill-mask", model=model, tokenizer=tokenizer)
## example ##
input_ = 'Монгол улсын [MASK] Улаанбаатар хотоос ярьж байна.'
output_ = pipe(input_)
for i in range(len(output_)):
print(output_[i])
## output ##
# {'sequence': 'Монгол улсын нийслэл Улаанбаатар хотоос ярьж байна.', 'score': 0.9779232740402222, 'token': 1176, 'token_str': 'нийслэл'}
# {'sequence': 'Монгол улсын Нийслэл Улаанбаатар хотоос ярьж байна.', 'score': 0.015034765936434269, 'token': 4059, 'token_str': 'Нийслэл'}
# {'sequence': 'Монгол улсын Ерөнхийлөгч Улаанбаатар хотоос ярьж байна.', 'score': 0.0021413620561361313, 'token': 325, 'token_str': 'Ерөнхийлөгч'}
# {'sequence': 'Монгол улсын ерөнхийлөгч Улаанбаатар хотоос ярьж байна.', 'score': 0.0008035294013097882, 'token': 1215, 'token_str': 'ерөнхийлөгч'}
# {'sequence': 'Монгол улсын нийслэлийн Улаанбаатар хотоос ярьж байна.', 'score': 0.0006434018723666668, 'token': 356, 'token_str': 'нийслэлийн'}
```
## Training data
Mongolian Wikipedia and the 700 million word Mongolian news data set [[Pretraining Procedure](https://github.com/tugstugi/mongolian-bert#pre-training)]
### BibTeX entry and citation info
```bibtex
@misc{mongolian-bert,
author = {Tuguldur, Erdene-Ochir and Gunchinish, Sharavsambuu and Bataa, Enkhbold},
title = {BERT Pretrained Models on Mongolian Datasets},
year = {2019},
publisher = {GitHub},
journal = {GitHub repository},
howpublished = {\url{https://github.com/tugstugi/mongolian-bert/}}
}
```
|
trueto/medbert-kd-chinese
|
trueto
| 2021-05-20T08:10:57Z | 9 | 10 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"jax",
"bert",
"pretraining",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] | null | 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
# [medbert](https://github.com/trueto/medbert)
本项目开源硕士毕业论文“BERT模型在中文临床自然语言处理中的应用探索与研究”相关模型
## 评估基准
构建了中文电子病历命名实体识别数据集(CEMRNER)、中文医学文本命名实体识别数据集(CMTNER)、
中文医学问句-问句识别数据集(CMedQQ)和中文临床文本分类数据集(CCTC)。
| **数据集** | **训练集** | **验证集** | **测试集** | **任务类型** | **语料来源** |
| ---- | ---- | ---- |---- |---- |:----:|
| CEMRNER | 965 | 138 | 276 | 命名实体识别 | 医渡云 |
| CMTNER | 14000 | 2000 | 4000 | 命名实体识别 | CHIP2020 |
| CMedQQ | 14000 | 2000 | 4000 | 句对识别 | 平安医疗 |
| CCTC | 26837 | 3834 | 7669 | 句子分类 | CHIP2019 |
## 开源模型
在6.5亿字符中文临床自然语言文本语料上基于BERT模型和Albert模型预训练获得了MedBERT和MedAlbert模型。
## 性能表现
在同等实验环境,相同训练参数和脚本下,各模型的性能表现
| **模型** | **CEMRNER** | **CMTNER** | **CMedQQ** | **CCTC** |
| :---- | :----: | :----: | :----: | :----: |
| [BERT](https://huggingface.co/bert-base-chinese) | 81.17% | 65.67% | 87.77% | 81.62% |
| [MC-BERT](https://github.com/alibaba-research/ChineseBLUE) | 80.93% | 66.15% | 89.04% | 80.65% |
| [PCL-BERT](https://code.ihub.org.cn/projects/1775) | 81.58% | 67.02% | 88.81% | 80.27% |
| MedBERT | 82.29% | 66.49% | 88.32% | **81.77%** |
|MedBERT-wwm| **82.60%** | 67.11% | 88.02% | 81.72% |
|MedBERT-kd | 82.58% | **67.27%** | **89.34%** | 80.73% |
|- | - | - | - | - |
| [Albert](https://huggingface.co/voidful/albert_chinese_base) | 79.98% | 62.42% | 86.81% | 79.83% |
| MedAlbert | 81.03% | 63.81% | 87.56% | 80.05% |
|MedAlbert-wwm| **81.28%** | **64.12%** | **87.71%** | **80.46%** |
## 引用格式
```
杨飞洪,王序文,李姣.BERT模型在中文临床自然语言处理中的应用探索与研究[EB/OL].https://github.com/trueto/medbert, 2021-03.
```
|
trueto/medbert-base-wwm-chinese
|
trueto
| 2021-05-20T08:09:44Z | 8 | 9 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"jax",
"bert",
"pretraining",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] | null | 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
# [medbert](https://github.com/trueto/medbert)
本项目开源硕士毕业论文“BERT模型在中文临床自然语言处理中的应用探索与研究”相关模型
## 评估基准
构建了中文电子病历命名实体识别数据集(CEMRNER)、中文医学文本命名实体识别数据集(CMTNER)、
中文医学问句-问句识别数据集(CMedQQ)和中文临床文本分类数据集(CCTC)。
| **数据集** | **训练集** | **验证集** | **测试集** | **任务类型** | **语料来源** |
| ---- | ---- | ---- |---- |---- |:----:|
| CEMRNER | 965 | 138 | 276 | 命名实体识别 | 医渡云 |
| CMTNER | 14000 | 2000 | 4000 | 命名实体识别 | CHIP2020 |
| CMedQQ | 14000 | 2000 | 4000 | 句对识别 | 平安医疗 |
| CCTC | 26837 | 3834 | 7669 | 句子分类 | CHIP2019 |
## 开源模型
在6.5亿字符中文临床自然语言文本语料上基于BERT模型和Albert模型预训练获得了MedBERT和MedAlbert模型。
## 性能表现
在同等实验环境,相同训练参数和脚本下,各模型的性能表现
| **模型** | **CEMRNER** | **CMTNER** | **CMedQQ** | **CCTC** |
| :---- | :----: | :----: | :----: | :----: |
| [BERT](https://huggingface.co/bert-base-chinese) | 81.17% | 65.67% | 87.77% | 81.62% |
| [MC-BERT](https://github.com/alibaba-research/ChineseBLUE) | 80.93% | 66.15% | 89.04% | 80.65% |
| [PCL-BERT](https://code.ihub.org.cn/projects/1775) | 81.58% | 67.02% | 88.81% | 80.27% |
| MedBERT | 82.29% | 66.49% | 88.32% | **81.77%** |
|MedBERT-wwm| **82.60%** | 67.11% | 88.02% | 81.72% |
|MedBERT-kd | 82.58% | **67.27%** | **89.34%** | 80.73% |
|- | - | - | - | - |
| [Albert](https://huggingface.co/voidful/albert_chinese_base) | 79.98% | 62.42% | 86.81% | 79.83% |
| MedAlbert | 81.03% | 63.81% | 87.56% | 80.05% |
|MedAlbert-wwm| **81.28%** | **64.12%** | **87.71%** | **80.46%** |
## 引用格式
```
杨飞洪,王序文,李姣.BERT模型在中文临床自然语言处理中的应用探索与研究[EB/OL].https://github.com/trueto/medbert, 2021-03.
```
|
trtd56/autonlp-wrime_joy_only-117396
|
trtd56
| 2021-05-20T08:07:48Z | 4 | 1 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"jax",
"bert",
"text-classification",
"autonlp",
"ja",
"dataset:trtd56/autonlp-data-wrime_joy_only",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
text-classification
| 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
---
tags: autonlp
language: ja
widget:
- text: "I love AutoNLP 🤗"
datasets:
- trtd56/autonlp-data-wrime_joy_only
---
# Model Trained Using AutoNLP
- Problem type: Binary Classification
- Model ID: 117396
## Validation Metrics
- Loss: 0.4094310998916626
- Accuracy: 0.8201678240740741
- Precision: 0.6750303520841765
- Recall: 0.7912713472485768
- AUC: 0.8927167943538512
- F1: 0.728543350076436
## Usage
You can use cURL to access this model:
```
$ curl -X POST -H "Authorization: Bearer YOUR_API_KEY" -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{"inputs": "I love AutoNLP"}' https://api-inference.huggingface.co/models/trtd56/autonlp-wrime_joy_only-117396
```
Or Python API:
```
from transformers import AutoModelForSequenceClassification, AutoTokenizer
model = AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained("trtd56/autonlp-wrime_joy_only-117396", use_auth_token=True)
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("trtd56/autonlp-wrime_joy_only-117396", use_auth_token=True)
inputs = tokenizer("I love AutoNLP", return_tensors="pt")
outputs = model(**inputs)
```
|
textattack/bert-base-uncased-yelp-polarity
|
textattack
| 2021-05-20T07:49:07Z | 16,043 | 4 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"jax",
"bert",
"text-classification",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
text-classification
| 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
## TextAttack Model Card
This `bert-base-uncased` model was fine-tuned for sequence classification using TextAttack
and the yelp_polarity dataset loaded using the `nlp` library. The model was fine-tuned
for 5 epochs with a batch size of 16, a learning
rate of 5e-05, and a maximum sequence length of 256.
Since this was a classification task, the model was trained with a cross-entropy loss function.
The best score the model achieved on this task was 0.9699473684210527, as measured by the
eval set accuracy, found after 4 epochs.
For more information, check out [TextAttack on Github](https://github.com/QData/TextAttack).
|
textattack/bert-base-uncased-rotten-tomatoes
|
textattack
| 2021-05-20T07:46:20Z | 422 | 1 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"jax",
"bert",
"text-classification",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
text-classification
| 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
## TextAttack Model Card
This `bert-base-uncased` model was fine-tuned for sequence classificationusing TextAttack
and the rotten_tomatoes dataset loaded using the `nlp` library. The model was fine-tuned
for 10 epochs with a batch size of 16, a learning
rate of 2e-05, and a maximum sequence length of 128.
Since this was a classification task, the model was trained with a cross-entropy loss function.
The best score the model achieved on this task was 0.875234521575985, as measured by the
eval set accuracy, found after 4 epochs.
For more information, check out [TextAttack on Github](https://github.com/QData/TextAttack).
|
textattack/bert-base-uncased-WNLI
|
textattack
| 2021-05-20T07:39:22Z | 44 | 1 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"jax",
"bert",
"text-classification",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
text-classification
| 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
## TextAttack Model Card
This `bert-base-uncased` model was fine-tuned for sequence classification using TextAttack
and the glue dataset loaded using the `nlp` library. The model was fine-tuned
for 5 epochs with a batch size of 64, a learning
rate of 5e-05, and a maximum sequence length of 256.
Since this was a classification task, the model was trained with a cross-entropy loss function.
The best score the model achieved on this task was 0.5633802816901409, as measured by the
eval set accuracy, found after 1 epoch.
For more information, check out [TextAttack on Github](https://github.com/QData/TextAttack).
|
textattack/bert-base-uncased-RTE
|
textattack
| 2021-05-20T07:36:18Z | 81 | 3 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"jax",
"bert",
"text-classification",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
text-classification
| 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
## TextAttack Model Card
This `bert-base-uncased` model was fine-tuned for sequence classification using TextAttack
and the glue dataset loaded using the `nlp` library. The model was fine-tuned
for 5 epochs with a batch size of 8, a learning
rate of 2e-05, and a maximum sequence length of 128.
Since this was a classification task, the model was trained with a cross-entropy loss function.
The best score the model achieved on this task was 0.7256317689530686, as measured by the
eval set accuracy, found after 2 epochs.
For more information, check out [TextAttack on Github](https://github.com/QData/TextAttack).
|
soniakris/Sonia_model
|
soniakris
| 2021-05-20T07:09:49Z | 4 | 0 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"tf",
"bert",
"fill-mask",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
fill-mask
| 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
Tensor-Flow Model using MASK token
|
socialmediaie/TRAC2020_ENG_C_bert-base-uncased
|
socialmediaie
| 2021-05-20T06:57:39Z | 6 | 0 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"jax",
"bert",
"text-classification",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
text-classification
| 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
# Multilingual Joint Fine-tuning of Transformer models for identifying Trolling, Aggression and Cyberbullying at TRAC 2020
Models and predictions for submission to TRAC - 2020 Second Workshop on Trolling, Aggression and Cyberbullying.
Our trained models as well as evaluation metrics during traing are available at: https://databank.illinois.edu/datasets/IDB-8882752#
We also make a few of our models available in HuggingFace's models repository at https://huggingface.co/socialmediaie/, these models can be further fine-tuned on your dataset of choice.
Our approach is described in our paper titled:
> Mishra, Sudhanshu, Shivangi Prasad, and Shubhanshu Mishra. 2020. "Multilingual Joint Fine-Tuning of Transformer Models for Identifying Trolling, Aggression and Cyberbullying at TRAC 2020." In Proceedings of the Second Workshop on Trolling, Aggression and Cyberbullying (TRAC-2020).
The source code for training this model and more details can be found on our code repository: https://github.com/socialmediaie/TRAC2020
NOTE: These models are retrained for uploading here after our submission so the evaluation measures may be slightly different from the ones reported in the paper.
If you plan to use the dataset please cite the following resources:
* Mishra, Sudhanshu, Shivangi Prasad, and Shubhanshu Mishra. 2020. "Multilingual Joint Fine-Tuning of Transformer Models for Identifying Trolling, Aggression and Cyberbullying at TRAC 2020." In Proceedings of the Second Workshop on Trolling, Aggression and Cyberbullying (TRAC-2020).
* Mishra, Shubhanshu, Shivangi Prasad, and Shubhanshu Mishra. 2020. “Trained Models for Multilingual Joint Fine-Tuning of Transformer Models for Identifying Trolling, Aggression and Cyberbullying at TRAC 2020.” University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. https://doi.org/10.13012/B2IDB-8882752_V1.
```
@inproceedings{Mishra2020TRAC,
author = {Mishra, Sudhanshu and Prasad, Shivangi and Mishra, Shubhanshu},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the Second Workshop on Trolling, Aggression and Cyberbullying (TRAC-2020)},
title = {{Multilingual Joint Fine-tuning of Transformer models for identifying Trolling, Aggression and Cyberbullying at TRAC 2020}},
year = {2020}
}
@data{illinoisdatabankIDB-8882752,
author = {Mishra, Shubhanshu and Prasad, Shivangi and Mishra, Shubhanshu},
doi = {10.13012/B2IDB-8882752_V1},
publisher = {University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign},
title = {{Trained models for Multilingual Joint Fine-tuning of Transformer models for identifying Trolling, Aggression and Cyberbullying at TRAC 2020}},
url = {https://doi.org/10.13012/B2IDB-8882752{\_}V1},
year = {2020}
}
```
## Usage
The models can be used via the following code:
```python
from transformers import AutoModel, AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForSequenceClassification
import torch
from pathlib import Path
from scipy.special import softmax
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
TASK_LABEL_IDS = {
"Sub-task A": ["OAG", "NAG", "CAG"],
"Sub-task B": ["GEN", "NGEN"],
"Sub-task C": ["OAG-GEN", "OAG-NGEN", "NAG-GEN", "NAG-NGEN", "CAG-GEN", "CAG-NGEN"]
}
model_version="databank" # other option is hugging face library
if model_version == "databank":
# Make sure you have downloaded the required model file from https://databank.illinois.edu/datasets/IDB-8882752
# Unzip the file at some model_path (we are using: "databank_model")
model_path = next(Path("databank_model").glob("./*/output/*/model"))
# Assuming you get the following type of structure inside "databank_model"
# 'databank_model/ALL/Sub-task C/output/bert-base-multilingual-uncased/model'
lang, task, _, base_model, _ = model_path.parts
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(base_model)
model = AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained(model_path)
else:
lang, task, base_model = "ALL", "Sub-task C", "bert-base-multilingual-uncased"
base_model = f"socialmediaie/TRAC2020_{lang}_{lang.split()[-1]}_{base_model}"
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(base_model)
model = AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained(base_model)
# For doing inference set model in eval mode
model.eval()
# If you want to further fine-tune the model you can reset the model to model.train()
task_labels = TASK_LABEL_IDS[task]
sentence = "This is a good cat and this is a bad dog."
processed_sentence = f"{tokenizer.cls_token} {sentence}"
tokens = tokenizer.tokenize(sentence)
indexed_tokens = tokenizer.convert_tokens_to_ids(tokens)
tokens_tensor = torch.tensor([indexed_tokens])
with torch.no_grad():
logits, = model(tokens_tensor, labels=None)
logits
preds = logits.detach().cpu().numpy()
preds_probs = softmax(preds, axis=1)
preds = np.argmax(preds_probs, axis=1)
preds_labels = np.array(task_labels)[preds]
print(dict(zip(task_labels, preds_probs[0])), preds_labels)
"""You should get an output as follows:
({'CAG-GEN': 0.06762535,
'CAG-NGEN': 0.03244293,
'NAG-GEN': 0.6897794,
'NAG-NGEN': 0.15498641,
'OAG-GEN': 0.034373745,
'OAG-NGEN': 0.020792078},
array(['NAG-GEN'], dtype='<U8'))
"""
```
|
smeylan/childes-bert
|
smeylan
| 2021-05-20T06:49:00Z | 34 | 0 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"jax",
"bert",
"fill-mask",
"language-modeling",
"en",
"dataset:childes",
"license:cc-by-sa-4.0",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
fill-mask
| 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
---
language: "en"
tags:
- language-modeling
license: "cc-by-sa-4.0"
datasets:
- childes
---
|
sismetanin/sbert-ru-sentiment-rusentiment
|
sismetanin
| 2021-05-20T06:38:36Z | 367 | 0 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"jax",
"bert",
"text-classification",
"sentiment analysis",
"Russian",
"ru",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
text-classification
| 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
---
language:
- ru
tags:
- sentiment analysis
- Russian
---
## SBERT-Large-Base-ru-sentiment-RuSentiment
SBERT-Large-ru-sentiment-RuSentiment is a [SBERT-Large](https://huggingface.co/sberbank-ai/sbert_large_nlu_ru) model fine-tuned on [RuSentiment dataset](https://github.com/text-machine-lab/rusentiment) of general-domain Russian-language posts from the largest Russian social network, VKontakte.
<table>
<thead>
<tr>
<th rowspan="4">Model</th>
<th rowspan="4">Score<br></th>
<th rowspan="4">Rank</th>
<th colspan="12">Dataset</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td colspan="6">SentiRuEval-2016<br></td>
<td colspan="2" rowspan="2">RuSentiment</td>
<td rowspan="2">KRND</td>
<td rowspan="2">LINIS Crowd</td>
<td rowspan="2">RuTweetCorp</td>
<td rowspan="2">RuReviews</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td colspan="3">TC</td>
<td colspan="3">Banks</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>micro F1</td>
<td>macro F1</td>
<td>F1</td>
<td>micro F1</td>
<td>macro F1</td>
<td>F1</td>
<td>wighted</td>
<td>F1</td>
<td>F1</td>
<td>F1</td>
<td>F1</td>
<td>F1</td>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr>
<td>SOTA</td>
<td>n/s</td>
<td></td>
<td>76.71</td>
<td>66.40</td>
<td>70.68</td>
<td>67.51</td>
<td>69.53</td>
<td>74.06</td>
<td>78.50</td>
<td>n/s</td>
<td>73.63</td>
<td>60.51</td>
<td>83.68</td>
<td>77.44</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>XLM-RoBERTa-Large</td>
<td>76.37</td>
<td>1</td>
<td>82.26</td>
<td>76.36</td>
<td>79.42</td>
<td>76.35</td>
<td>76.08</td>
<td>80.89</td>
<td>78.31</td>
<td>75.27</td>
<td>75.17</td>
<td>60.03</td>
<td>88.91</td>
<td>78.81</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>SBERT-Large</td>
<td>75.43</td>
<td>2</td>
<td>78.40</td>
<td>71.36</td>
<td>75.14</td>
<td>72.39</td>
<td>71.87</td>
<td>77.72</td>
<td>78.58</td>
<td>75.85</td>
<td>74.20</td>
<td>60.64</td>
<td>88.66</td>
<td>77.41</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>MBARTRuSumGazeta</td>
<td>74.70</td>
<td>3</td>
<td>76.06</td>
<td>68.95</td>
<td>73.04</td>
<td>72.34</td>
<td>71.93</td>
<td>77.83</td>
<td>76.71</td>
<td>73.56</td>
<td>74.18</td>
<td>60.54</td>
<td>87.22</td>
<td>77.51</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Conversational RuBERT</td>
<td>74.44</td>
<td>4</td>
<td>76.69</td>
<td>69.09</td>
<td>73.11</td>
<td>69.44</td>
<td>68.68</td>
<td>75.56</td>
<td>77.31</td>
<td>74.40</td>
<td>73.10</td>
<td>59.95</td>
<td>87.86</td>
<td>77.78</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>LaBSE</td>
<td>74.11</td>
<td>5</td>
<td>77.00</td>
<td>69.19</td>
<td>73.55</td>
<td>70.34</td>
<td>69.83</td>
<td>76.38</td>
<td>74.94</td>
<td>70.84</td>
<td>73.20</td>
<td>59.52</td>
<td>87.89</td>
<td>78.47</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>XLM-RoBERTa-Base</td>
<td>73.60</td>
<td>6</td>
<td>76.35</td>
<td>69.37</td>
<td>73.42</td>
<td>68.45</td>
<td>67.45</td>
<td>74.05</td>
<td>74.26</td>
<td>70.44</td>
<td>71.40</td>
<td>60.19</td>
<td>87.90</td>
<td>78.28</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>RuBERT</td>
<td>73.45</td>
<td>7</td>
<td>74.03</td>
<td>66.14</td>
<td>70.75</td>
<td>66.46</td>
<td>66.40</td>
<td>73.37</td>
<td>75.49</td>
<td>71.86</td>
<td>72.15</td>
<td>60.55</td>
<td>86.99</td>
<td>77.41</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>MBART-50-Large-Many-to-Many</td>
<td>73.15</td>
<td>8</td>
<td>75.38</td>
<td>67.81</td>
<td>72.26</td>
<td>67.13</td>
<td>66.97</td>
<td>73.85</td>
<td>74.78</td>
<td>70.98</td>
<td>71.98</td>
<td>59.20</td>
<td>87.05</td>
<td>77.24</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>SlavicBERT</td>
<td>71.96</td>
<td>9</td>
<td>71.45</td>
<td>63.03</td>
<td>68.44</td>
<td>64.32</td>
<td>63.99</td>
<td>71.31</td>
<td>72.13</td>
<td>67.57</td>
<td>72.54</td>
<td>58.70</td>
<td>86.43</td>
<td>77.16</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>EnRuDR-BERT</td>
<td>71.51</td>
<td>10</td>
<td>72.56</td>
<td>64.74</td>
<td>69.07</td>
<td>61.44</td>
<td>60.21</td>
<td>68.34</td>
<td>74.19</td>
<td>69.94</td>
<td>69.33</td>
<td>56.55</td>
<td>87.12</td>
<td>77.95</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>RuDR-BERT</td>
<td>71.14</td>
<td>11</td>
<td>72.79</td>
<td>64.23</td>
<td>68.36</td>
<td>61.86</td>
<td>60.92</td>
<td>68.48</td>
<td>74.65</td>
<td>70.63</td>
<td>68.74</td>
<td>54.45</td>
<td>87.04</td>
<td>77.91</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>MBART-50-Large</td>
<td>69.46</td>
<td>12</td>
<td>70.91</td>
<td>62.67</td>
<td>67.24</td>
<td>61.12</td>
<td>60.25</td>
<td>68.41</td>
<td>72.88</td>
<td>68.63</td>
<td>70.52</td>
<td>46.39</td>
<td>86.48</td>
<td>77.52</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
The table shows per-task scores and a macro-average of those scores to determine a models’s position on the leaderboard. For datasets with multiple evaluation metrics (e.g., macro F1 and weighted F1 for RuSentiment), we use an unweighted average of the metrics as the score for the task when computing the overall macro-average. The same strategy for comparing models’ results was applied in the GLUE benchmark.
## Citation
If you find this repository helpful, feel free to cite our publication:
```
@article{Smetanin2021Deep,
author = {Sergey Smetanin and Mikhail Komarov},
title = {Deep transfer learning baselines for sentiment analysis in Russian},
journal = {Information Processing & Management},
volume = {58},
number = {3},
pages = {102484},
year = {2021},
issn = {0306-4573},
doi = {0.1016/j.ipm.2020.102484}
}
```
Dataset:
```
@inproceedings{rogers2018rusentiment,
title={RuSentiment: An enriched sentiment analysis dataset for social media in Russian},
author={Rogers, Anna and Romanov, Alexey and Rumshisky, Anna and Volkova, Svitlana and Gronas, Mikhail and Gribov, Alex},
booktitle={Proceedings of the 27th international conference on computational linguistics},
pages={755--763},
year={2018}
}
```
|
sismetanin/sbert-ru-sentiment-krnd
|
sismetanin
| 2021-05-20T06:27:51Z | 16 | 0 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"jax",
"bert",
"text-classification",
"sentiment analysis",
"Russian",
"SBERT-Large",
"ru",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
text-classification
| 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
---
language:
- ru
tags:
- sentiment analysis
- Russian
- SBERT-Large
---
## SBERT-Large on Kaggle Russian News Dataset
<table>
<thead>
<tr>
<th rowspan="4">Model</th>
<th rowspan="4">Score<br></th>
<th rowspan="4">Rank</th>
<th colspan="12">Dataset</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td colspan="6">SentiRuEval-2016<br></td>
<td colspan="2" rowspan="2">RuSentiment</td>
<td rowspan="2">KRND</td>
<td rowspan="2">LINIS Crowd</td>
<td rowspan="2">RuTweetCorp</td>
<td rowspan="2">RuReviews</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td colspan="3">TC</td>
<td colspan="3">Banks</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>micro F<sub>1</sub></td>
<td>macro F<sub>1</sub></td>
<td>F<sub>1</sub></td>
<td>micro F<sub>1</sub></td>
<td>macro F<sub>1</sub></td>
<td>F<sub>1</sub></td>
<td>wighted F<sub>1</sub></td>
<td>F<sub>1</sub></td>
<td>F<sub>1</sub></td>
<td>F<sub>1</sub></td>
<td>F<sub>1</sub></td>
<td>F<sub>1</sub></td>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr>
<td>SOTA</td>
<td>n/s</td>
<td></td>
<td>76.71</td>
<td>66.40</td>
<td>70.68</td>
<td>67.51</td>
<td>69.53</td>
<td>74.06</td>
<td>78.50</td>
<td>n/s</td>
<td>73.63</td>
<td>60.51</td>
<td>83.68</td>
<td>77.44</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>XLM-RoBERTa-Large</td>
<td>76.37</td>
<td>1</td>
<td>82.26</td>
<td>76.36</td>
<td>79.42</td>
<td>76.35</td>
<td>76.08</td>
<td>80.89</td>
<td>78.31</td>
<td>75.27</td>
<td>75.17</td>
<td>60.03</td>
<td>88.91</td>
<td>78.81</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>SBERT-Large</td>
<td>75.43</td>
<td>2</td>
<td>78.40</td>
<td>71.36</td>
<td>75.14</td>
<td>72.39</td>
<td>71.87</td>
<td>77.72</td>
<td>78.58</td>
<td>75.85</td>
<td>74.20</td>
<td>60.64</td>
<td>88.66</td>
<td>77.41</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>MBARTRuSumGazeta</td>
<td>74.70</td>
<td>3</td>
<td>76.06</td>
<td>68.95</td>
<td>73.04</td>
<td>72.34</td>
<td>71.93</td>
<td>77.83</td>
<td>76.71</td>
<td>73.56</td>
<td>74.18</td>
<td>60.54</td>
<td>87.22</td>
<td>77.51</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Conversational RuBERT</td>
<td>74.44</td>
<td>4</td>
<td>76.69</td>
<td>69.09</td>
<td>73.11</td>
<td>69.44</td>
<td>68.68</td>
<td>75.56</td>
<td>77.31</td>
<td>74.40</td>
<td>73.10</td>
<td>59.95</td>
<td>87.86</td>
<td>77.78</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>LaBSE</td>
<td>74.11</td>
<td>5</td>
<td>77.00</td>
<td>69.19</td>
<td>73.55</td>
<td>70.34</td>
<td>69.83</td>
<td>76.38</td>
<td>74.94</td>
<td>70.84</td>
<td>73.20</td>
<td>59.52</td>
<td>87.89</td>
<td>78.47</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>XLM-RoBERTa-Base</td>
<td>73.60</td>
<td>6</td>
<td>76.35</td>
<td>69.37</td>
<td>73.42</td>
<td>68.45</td>
<td>67.45</td>
<td>74.05</td>
<td>74.26</td>
<td>70.44</td>
<td>71.40</td>
<td>60.19</td>
<td>87.90</td>
<td>78.28</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>RuBERT</td>
<td>73.45</td>
<td>7</td>
<td>74.03</td>
<td>66.14</td>
<td>70.75</td>
<td>66.46</td>
<td>66.40</td>
<td>73.37</td>
<td>75.49</td>
<td>71.86</td>
<td>72.15</td>
<td>60.55</td>
<td>86.99</td>
<td>77.41</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>MBART-50-Large-Many-to-Many</td>
<td>73.15</td>
<td>8</td>
<td>75.38</td>
<td>67.81</td>
<td>72.26</td>
<td>67.13</td>
<td>66.97</td>
<td>73.85</td>
<td>74.78</td>
<td>70.98</td>
<td>71.98</td>
<td>59.20</td>
<td>87.05</td>
<td>77.24</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>SlavicBERT</td>
<td>71.96</td>
<td>9</td>
<td>71.45</td>
<td>63.03</td>
<td>68.44</td>
<td>64.32</td>
<td>63.99</td>
<td>71.31</td>
<td>72.13</td>
<td>67.57</td>
<td>72.54</td>
<td>58.70</td>
<td>86.43</td>
<td>77.16</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>EnRuDR-BERT</td>
<td>71.51</td>
<td>10</td>
<td>72.56</td>
<td>64.74</td>
<td>69.07</td>
<td>61.44</td>
<td>60.21</td>
<td>68.34</td>
<td>74.19</td>
<td>69.94</td>
<td>69.33</td>
<td>56.55</td>
<td>87.12</td>
<td>77.95</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>RuDR-BERT</td>
<td>71.14</td>
<td>11</td>
<td>72.79</td>
<td>64.23</td>
<td>68.36</td>
<td>61.86</td>
<td>60.92</td>
<td>68.48</td>
<td>74.65</td>
<td>70.63</td>
<td>68.74</td>
<td>54.45</td>
<td>87.04</td>
<td>77.91</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>MBART-50-Large</td>
<td>69.46</td>
<td>12</td>
<td>70.91</td>
<td>62.67</td>
<td>67.24</td>
<td>61.12</td>
<td>60.25</td>
<td>68.41</td>
<td>72.88</td>
<td>68.63</td>
<td>70.52</td>
<td>46.39</td>
<td>86.48</td>
<td>77.52</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
|
sismetanin/rubert-toxic-pikabu-2ch
|
sismetanin
| 2021-05-20T06:16:03Z | 305 | 8 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"jax",
"bert",
"text-classification",
"toxic comments classification",
"ru",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
text-classification
| 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
---
language:
- ru
tags:
- toxic comments classification
---
## RuBERT-Toxic
RuBERT-Toxic is a [RuBERT](https://huggingface.co/DeepPavlov/rubert-base-cased) model fine-tuned on [Kaggle Russian Language Toxic Comments Dataset](https://www.kaggle.com/blackmoon/russian-language-toxic-comments). You can find a detailed description of the data used and the fine-tuning process in [this article](http://doi.org/10.28995/2075-7182-2020-19-1149-1159). You can also find this information at [GitHub](https://github.com/sismetanin/toxic-comments-detection-in-russian).
| System | P | R | F<sub>1</sub> |
| ------------- | ------------- | ------------- | ------------- |
| MNB-Toxic | 87.01% | 81.22% | 83.21% |
| M-BERT<sub>Base</sub>-Toxic | 91.19% | 91.10% | 91.15% |
| <b>RuBERT-Toxic</b> | <b>91.91%</b> | <b>92.51%</b> | <b>92.20%</b> |
| M-USE<sub>CNN</sub>-Toxic | 89.69% | 90.14% | 89.91% |
| M-USE<sub>Trans</sub>-Toxic | 90.85% | 91.92% | 91.35% |
We fine-tuned two versions of Multilingual Universal Sentence Encoder (M-USE), Multilingual Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (M-BERT) and RuBERT for toxic comments detection in Russian. Fine-tuned RuBERT-Toxic achieved F<sub>1</sub> = 92.20%, demonstrating the best classification score.
## Toxic Comments Dataset
[Kaggle Russian Language Toxic Comments Dataset](https://www.kaggle.com/blackmoon/russian-language-toxic-comments) is the collection of Russian-language annotated comments from [2ch](https://2ch.hk/) and [Pikabu](https://pikabu.ru/), which was published on Kaggle in 2019. It consists of 14412 comments, where 4826 texts were labelled as toxic, and 9586 were labelled as non-toxic. The average length of comments is ~175 characters; the minimum length is 21, and the maximum is 7403.
## Citation
If you find this repository helpful, feel free to cite our publication:
```
@INPROCEEDINGS{Smetanin2020Toxic,
author={Sergey Smetanin},
booktitle={Computational Linguistics and Intellectual Technologies: Proceedings of the International Conference “Dialogue 2020”},
title={Toxic Comments Detection in Russian},
year={2020},
doi={10.28995/2075-7182-2020-19-1149-1159}
}
```
|
sismetanin/rubert-ru-sentiment-rusentiment
|
sismetanin
| 2021-05-20T06:11:34Z | 416 | 6 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"jax",
"bert",
"text-classification",
"sentiment analysis",
"Russian",
"ru",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
text-classification
| 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
---
language:
- ru
tags:
- sentiment analysis
- Russian
---
## RuBERT-Base-ru-sentiment-RuSentiment
RuBERT-ru-sentiment-RuSentiment is a [RuBERT](https://huggingface.co/DeepPavlov/rubert-base-cased) model fine-tuned on [RuSentiment dataset](https://github.com/text-machine-lab/rusentiment) of general-domain Russian-language posts from the largest Russian social network, VKontakte.
<table>
<thead>
<tr>
<th rowspan="4">Model</th>
<th rowspan="4">Score<br></th>
<th rowspan="4">Rank</th>
<th colspan="12">Dataset</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td colspan="6">SentiRuEval-2016<br></td>
<td colspan="2" rowspan="2">RuSentiment</td>
<td rowspan="2">KRND</td>
<td rowspan="2">LINIS Crowd</td>
<td rowspan="2">RuTweetCorp</td>
<td rowspan="2">RuReviews</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td colspan="3">TC</td>
<td colspan="3">Banks</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>micro F1</td>
<td>macro F1</td>
<td>F1</td>
<td>micro F1</td>
<td>macro F1</td>
<td>F1</td>
<td>wighted</td>
<td>F1</td>
<td>F1</td>
<td>F1</td>
<td>F1</td>
<td>F1</td>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr>
<td>SOTA</td>
<td>n/s</td>
<td></td>
<td>76.71</td>
<td>66.40</td>
<td>70.68</td>
<td>67.51</td>
<td>69.53</td>
<td>74.06</td>
<td>78.50</td>
<td>n/s</td>
<td>73.63</td>
<td>60.51</td>
<td>83.68</td>
<td>77.44</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>XLM-RoBERTa-Large</td>
<td>76.37</td>
<td>1</td>
<td>82.26</td>
<td>76.36</td>
<td>79.42</td>
<td>76.35</td>
<td>76.08</td>
<td>80.89</td>
<td>78.31</td>
<td>75.27</td>
<td>75.17</td>
<td>60.03</td>
<td>88.91</td>
<td>78.81</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>SBERT-Large</td>
<td>75.43</td>
<td>2</td>
<td>78.40</td>
<td>71.36</td>
<td>75.14</td>
<td>72.39</td>
<td>71.87</td>
<td>77.72</td>
<td>78.58</td>
<td>75.85</td>
<td>74.20</td>
<td>60.64</td>
<td>88.66</td>
<td>77.41</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>MBARTRuSumGazeta</td>
<td>74.70</td>
<td>3</td>
<td>76.06</td>
<td>68.95</td>
<td>73.04</td>
<td>72.34</td>
<td>71.93</td>
<td>77.83</td>
<td>76.71</td>
<td>73.56</td>
<td>74.18</td>
<td>60.54</td>
<td>87.22</td>
<td>77.51</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Conversational RuBERT</td>
<td>74.44</td>
<td>4</td>
<td>76.69</td>
<td>69.09</td>
<td>73.11</td>
<td>69.44</td>
<td>68.68</td>
<td>75.56</td>
<td>77.31</td>
<td>74.40</td>
<td>73.10</td>
<td>59.95</td>
<td>87.86</td>
<td>77.78</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>LaBSE</td>
<td>74.11</td>
<td>5</td>
<td>77.00</td>
<td>69.19</td>
<td>73.55</td>
<td>70.34</td>
<td>69.83</td>
<td>76.38</td>
<td>74.94</td>
<td>70.84</td>
<td>73.20</td>
<td>59.52</td>
<td>87.89</td>
<td>78.47</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>XLM-RoBERTa-Base</td>
<td>73.60</td>
<td>6</td>
<td>76.35</td>
<td>69.37</td>
<td>73.42</td>
<td>68.45</td>
<td>67.45</td>
<td>74.05</td>
<td>74.26</td>
<td>70.44</td>
<td>71.40</td>
<td>60.19</td>
<td>87.90</td>
<td>78.28</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>RuBERT</td>
<td>73.45</td>
<td>7</td>
<td>74.03</td>
<td>66.14</td>
<td>70.75</td>
<td>66.46</td>
<td>66.40</td>
<td>73.37</td>
<td>75.49</td>
<td>71.86</td>
<td>72.15</td>
<td>60.55</td>
<td>86.99</td>
<td>77.41</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>MBART-50-Large-Many-to-Many</td>
<td>73.15</td>
<td>8</td>
<td>75.38</td>
<td>67.81</td>
<td>72.26</td>
<td>67.13</td>
<td>66.97</td>
<td>73.85</td>
<td>74.78</td>
<td>70.98</td>
<td>71.98</td>
<td>59.20</td>
<td>87.05</td>
<td>77.24</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>SlavicBERT</td>
<td>71.96</td>
<td>9</td>
<td>71.45</td>
<td>63.03</td>
<td>68.44</td>
<td>64.32</td>
<td>63.99</td>
<td>71.31</td>
<td>72.13</td>
<td>67.57</td>
<td>72.54</td>
<td>58.70</td>
<td>86.43</td>
<td>77.16</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>EnRuDR-BERT</td>
<td>71.51</td>
<td>10</td>
<td>72.56</td>
<td>64.74</td>
<td>69.07</td>
<td>61.44</td>
<td>60.21</td>
<td>68.34</td>
<td>74.19</td>
<td>69.94</td>
<td>69.33</td>
<td>56.55</td>
<td>87.12</td>
<td>77.95</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>RuDR-BERT</td>
<td>71.14</td>
<td>11</td>
<td>72.79</td>
<td>64.23</td>
<td>68.36</td>
<td>61.86</td>
<td>60.92</td>
<td>68.48</td>
<td>74.65</td>
<td>70.63</td>
<td>68.74</td>
<td>54.45</td>
<td>87.04</td>
<td>77.91</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>MBART-50-Large</td>
<td>69.46</td>
<td>12</td>
<td>70.91</td>
<td>62.67</td>
<td>67.24</td>
<td>61.12</td>
<td>60.25</td>
<td>68.41</td>
<td>72.88</td>
<td>68.63</td>
<td>70.52</td>
<td>46.39</td>
<td>86.48</td>
<td>77.52</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
The table shows per-task scores and a macro-average of those scores to determine a models’s position on the leaderboard. For datasets with multiple evaluation metrics (e.g., macro F1 and weighted F1 for RuSentiment), we use an unweighted average of the metrics as the score for the task when computing the overall macro-average. The same strategy for comparing models’ results was applied in the GLUE benchmark.
## Citation
If you find this repository helpful, feel free to cite our publication:
```
@article{Smetanin2021Deep,
author = {Sergey Smetanin and Mikhail Komarov},
title = {Deep transfer learning baselines for sentiment analysis in Russian},
journal = {Information Processing & Management},
volume = {58},
number = {3},
pages = {102484},
year = {2021},
issn = {0306-4573},
doi = {0.1016/j.ipm.2020.102484}
}
```
Dataset:
```
@inproceedings{rogers2018rusentiment,
title={RuSentiment: An enriched sentiment analysis dataset for social media in Russian},
author={Rogers, Anna and Romanov, Alexey and Rumshisky, Anna and Volkova, Svitlana and Gronas, Mikhail and Gribov, Alex},
booktitle={Proceedings of the 27th international conference on computational linguistics},
pages={755--763},
year={2018}
}
```
|
sismetanin/rubert-ru-sentiment-rureviews
|
sismetanin
| 2021-05-20T06:09:59Z | 116 | 2 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"jax",
"bert",
"text-classification",
"sentiment analysis",
"Russian",
"ru",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
text-classification
| 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
---
language:
- ru
tags:
- sentiment analysis
- Russian
---
## RuBERT-ru-sentiment-RuReviews
RuBERT-ru-sentiment-RuReviews is a [RuBERT](https://huggingface.co/DeepPavlov/rubert-base-cased) model fine-tuned on [RuReviews dataset](https://github.com/sismetanin/rureviews) of Russian-language reviews from the ”Women’s Clothes and Accessories” product category on the primary e-commerce site in Russia.
<table>
<thead>
<tr>
<th rowspan="4">Model</th>
<th rowspan="4">Score<br></th>
<th rowspan="4">Rank</th>
<th colspan="12">Dataset</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td colspan="6">SentiRuEval-2016<br></td>
<td colspan="2" rowspan="2">RuSentiment</td>
<td rowspan="2">KRND</td>
<td rowspan="2">LINIS Crowd</td>
<td rowspan="2">RuTweetCorp</td>
<td rowspan="2">RuReviews</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td colspan="3">TC</td>
<td colspan="3">Banks</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>micro F1</td>
<td>macro F1</td>
<td>F1</td>
<td>micro F1</td>
<td>macro F1</td>
<td>F1</td>
<td>wighted</td>
<td>F1</td>
<td>F1</td>
<td>F1</td>
<td>F1</td>
<td>F1</td>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr>
<td>SOTA</td>
<td>n/s</td>
<td></td>
<td>76.71</td>
<td>66.40</td>
<td>70.68</td>
<td>67.51</td>
<td>69.53</td>
<td>74.06</td>
<td>78.50</td>
<td>n/s</td>
<td>73.63</td>
<td>60.51</td>
<td>83.68</td>
<td>77.44</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>XLM-RoBERTa-Large</td>
<td>76.37</td>
<td>1</td>
<td>82.26</td>
<td>76.36</td>
<td>79.42</td>
<td>76.35</td>
<td>76.08</td>
<td>80.89</td>
<td>78.31</td>
<td>75.27</td>
<td>75.17</td>
<td>60.03</td>
<td>88.91</td>
<td>78.81</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>SBERT-Large</td>
<td>75.43</td>
<td>2</td>
<td>78.40</td>
<td>71.36</td>
<td>75.14</td>
<td>72.39</td>
<td>71.87</td>
<td>77.72</td>
<td>78.58</td>
<td>75.85</td>
<td>74.20</td>
<td>60.64</td>
<td>88.66</td>
<td>77.41</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>MBARTRuSumGazeta</td>
<td>74.70</td>
<td>3</td>
<td>76.06</td>
<td>68.95</td>
<td>73.04</td>
<td>72.34</td>
<td>71.93</td>
<td>77.83</td>
<td>76.71</td>
<td>73.56</td>
<td>74.18</td>
<td>60.54</td>
<td>87.22</td>
<td>77.51</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Conversational RuBERT</td>
<td>74.44</td>
<td>4</td>
<td>76.69</td>
<td>69.09</td>
<td>73.11</td>
<td>69.44</td>
<td>68.68</td>
<td>75.56</td>
<td>77.31</td>
<td>74.40</td>
<td>73.10</td>
<td>59.95</td>
<td>87.86</td>
<td>77.78</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>LaBSE</td>
<td>74.11</td>
<td>5</td>
<td>77.00</td>
<td>69.19</td>
<td>73.55</td>
<td>70.34</td>
<td>69.83</td>
<td>76.38</td>
<td>74.94</td>
<td>70.84</td>
<td>73.20</td>
<td>59.52</td>
<td>87.89</td>
<td>78.47</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>XLM-RoBERTa-Base</td>
<td>73.60</td>
<td>6</td>
<td>76.35</td>
<td>69.37</td>
<td>73.42</td>
<td>68.45</td>
<td>67.45</td>
<td>74.05</td>
<td>74.26</td>
<td>70.44</td>
<td>71.40</td>
<td>60.19</td>
<td>87.90</td>
<td>78.28</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>RuBERT</td>
<td>73.45</td>
<td>7</td>
<td>74.03</td>
<td>66.14</td>
<td>70.75</td>
<td>66.46</td>
<td>66.40</td>
<td>73.37</td>
<td>75.49</td>
<td>71.86</td>
<td>72.15</td>
<td>60.55</td>
<td>86.99</td>
<td>77.41</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>MBART-50-Large-Many-to-Many</td>
<td>73.15</td>
<td>8</td>
<td>75.38</td>
<td>67.81</td>
<td>72.26</td>
<td>67.13</td>
<td>66.97</td>
<td>73.85</td>
<td>74.78</td>
<td>70.98</td>
<td>71.98</td>
<td>59.20</td>
<td>87.05</td>
<td>77.24</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>SlavicBERT</td>
<td>71.96</td>
<td>9</td>
<td>71.45</td>
<td>63.03</td>
<td>68.44</td>
<td>64.32</td>
<td>63.99</td>
<td>71.31</td>
<td>72.13</td>
<td>67.57</td>
<td>72.54</td>
<td>58.70</td>
<td>86.43</td>
<td>77.16</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>EnRuDR-BERT</td>
<td>71.51</td>
<td>10</td>
<td>72.56</td>
<td>64.74</td>
<td>69.07</td>
<td>61.44</td>
<td>60.21</td>
<td>68.34</td>
<td>74.19</td>
<td>69.94</td>
<td>69.33</td>
<td>56.55</td>
<td>87.12</td>
<td>77.95</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>RuDR-BERT</td>
<td>71.14</td>
<td>11</td>
<td>72.79</td>
<td>64.23</td>
<td>68.36</td>
<td>61.86</td>
<td>60.92</td>
<td>68.48</td>
<td>74.65</td>
<td>70.63</td>
<td>68.74</td>
<td>54.45</td>
<td>87.04</td>
<td>77.91</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>MBART-50-Large</td>
<td>69.46</td>
<td>12</td>
<td>70.91</td>
<td>62.67</td>
<td>67.24</td>
<td>61.12</td>
<td>60.25</td>
<td>68.41</td>
<td>72.88</td>
<td>68.63</td>
<td>70.52</td>
<td>46.39</td>
<td>86.48</td>
<td>77.52</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
The table shows per-task scores and a macro-average of those scores to determine a models’s position on the leaderboard. For datasets with multiple evaluation metrics (e.g., macro F1 and weighted F1 for RuSentiment), we use an unweighted average of the metrics as the score for the task when computing the overall macro-average. The same strategy for comparing models’ results was applied in the GLUE benchmark.
## Citation
If you find this repository helpful, feel free to cite our publication:
```
@article{Smetanin2021Deep,
author = {Sergey Smetanin and Mikhail Komarov},
title = {Deep transfer learning baselines for sentiment analysis in Russian},
journal = {Information Processing & Management},
volume = {58},
number = {3},
pages = {102484},
year = {2021},
issn = {0306-4573},
doi = {0.1016/j.ipm.2020.102484}
}
```
Dataset:
```
@INPROCEEDINGS{Smetanin2019Sentiment,
author={Sergey Smetanin and Michail Komarov},
booktitle={2019 IEEE 21st Conference on Business Informatics (CBI)},
title={Sentiment Analysis of Product Reviews in Russian using Convolutional Neural Networks},
year={2019},
volume={01},
pages={482-486},
doi={10.1109/CBI.2019.00062},
ISSN={2378-1963},
month={July}
}
```
|
shoarora/electra-small-owt
|
shoarora
| 2021-05-20T05:54:08Z | 4 | 0 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"jax",
"bert",
"feature-extraction",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
feature-extraction
| 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
# ELECTRA-small-OWT
This is an unnoficial implementation of an
[ELECTRA](https://openreview.net/forum?id=r1xMH1BtvB) small model, trained on the
[OpenWebText corpus](https://skylion007.github.io/OpenWebTextCorpus/).
Differences from official ELECTRA models:
- we use a `BertForMaskedLM` as the generator and `BertForTokenClassification` as the discriminator
- they use an embedding projection layer, but Bert doesn't have one
## Pretraining ttask

(figure from [Clark et al. 2020](https://openreview.net/pdf?id=r1xMH1BtvB))
ELECTRA uses discriminative LM / replaced-token-detection for pretraining.
This involves a generator (a Masked LM model) creating examples for a discriminator
to classify as original or replaced for each token.
## Usage
```python
from transformers import BertForSequenceClassification, BertTokenizer
tokenizer = BertTokenizer.from_pretrained('bert-base-uncased')
electra = BertForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained('shoarora/electra-small-owt')
```
## Code
The pytorch module that implements this task is available [here](https://github.com/shoarora/lmtuners/blob/master/lmtuners/lightning_modules/discriminative_lm.py).
Further implementation information [here](https://github.com/shoarora/lmtuners/tree/master/experiments/disc_lm_small),
and [here](https://github.com/shoarora/lmtuners/blob/master/experiments/disc_lm_small/train_electra_small.py) is the script that created this model.
This specific model was trained with the following params:
- `batch_size: 512`
- `training_steps: 5e5`
- `warmup_steps: 4e4`
- `learning_rate: 2e-3`
## Downstream tasks
#### GLUE Dev results
| Model | # Params | CoLA | SST | MRPC | STS | QQP | MNLI | QNLI | RTE |
| --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- |
| ELECTRA-Small++ | 14M | 57.0 | 91. | 88.0 | 87.5 | 89.0 | 81.3 | 88.4 | 66.7|
| ELECTRA-Small-OWT | 14M | 56.8 | 88.3| 87.4 | 86.8 | 88.3 | 78.9 | 87.9 | 68.5|
| ELECTRA-Small-OWT (ours) | 17M | 56.3 | 88.4| 75.0 | 86.1 | 89.1 | 77.9 | 83.0 | 67.1|
| ALECTRA-Small-OWT (ours) | 4M | 50.6 | 89.1| 86.3 | 87.2 | 89.1 | 78.2 | 85.9 | 69.6|
- Table initialized from [ELECTRA github repo](https://github.com/google-research/electra)
#### GLUE Test results
| Model | # Params | CoLA | SST | MRPC | STS | QQP | MNLI | QNLI | RTE |
| --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- |
| BERT-Base | 110M | 52.1 | 93.5| 84.8 | 85.9 | 89.2 | 84.6 | 90.5 | 66.4|
| GPT | 117M | 45.4 | 91.3| 75.7 | 80.0 | 88.5 | 82.1 | 88.1 | 56.0|
| ELECTRA-Small++ | 14M | 57.0 | 91.2| 88.0 | 87.5 | 89.0 | 81.3 | 88.4 | 66.7|
| ELECTRA-Small-OWT (ours) | 17M | 57.4 | 89.3| 76.2 | 81.9 | 87.5 | 78.1 | 82.4 | 68.1|
| ALECTRA-Small-OWT (ours) | 4M | 43.9 | 87.9| 82.1 | 82.0 | 87.6 | 77.9 | 85.8 | 67.5|
|
junnyu/bert_chinese_mc_base
|
junnyu
| 2021-05-20T05:28:56Z | 8 | 3 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"jax",
"bert",
"fill-mask",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] |
fill-mask
| 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
https://github.com/alibaba-research/ChineseBLUE
|
seiya/oubiobert-base-uncased
|
seiya
| 2021-05-20T05:10:40Z | 55 | 3 |
transformers
|
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"jax",
"bert",
"pretraining",
"exbert",
"arxiv:2005.07202",
"license:apache-2.0",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] | null | 2022-03-02T23:29:05Z |
---
tags:
- exbert
license: apache-2.0
---
# ouBioBERT-Base, Uncased
Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers for Biomedical Text Mining by Osaka University (ouBioBERT) is a language model based on the BERT-Base (Devlin, et al., 2019) architecture. We pre-trained ouBioBERT on PubMed abstracts from the PubMed baseline (ftp://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/baseline) via our method.
The details of the pre-training procedure can be found in Wada, et al. (2020).
## Evaluation
We evaluated the performance of ouBioBERT in terms of the biomedical language understanding evaluation (BLUE) benchmark (Peng, et al., 2019). The numbers are mean (standard deviation) on five different random seeds.
| Dataset | Task Type | Score |
|:----------------|:-----------------------------|-------------:|
| MedSTS | Sentence similarity | 84.9 (0.6) |
| BIOSSES | Sentence similarity | 92.3 (0.8) |
| BC5CDR-disease | Named-entity recognition | 87.4 (0.1) |
| BC5CDR-chemical | Named-entity recognition | 93.7 (0.2) |
| ShARe/CLEFE | Named-entity recognition | 80.1 (0.4) |
| DDI | Relation extraction | 81.1 (1.5) |
| ChemProt | Relation extraction | 75.0 (0.3) |
| i2b2 2010 | Relation extraction | 74.0 (0.8) |
| HoC | Document classification | 86.4 (0.5) |
| MedNLI | Inference | 83.6 (0.7) |
| **Total** | Macro average of the scores |**83.8 (0.3)**|
## Code for Fine-tuning
We made the source code for fine-tuning freely available at [our repository](https://github.com/sy-wada/blue_benchmark_with_transformers).
## Citation
If you use our work in your research, please kindly cite the following paper:
```bibtex
@misc{2005.07202,
Author = {Shoya Wada and Toshihiro Takeda and Shiro Manabe and Shozo Konishi and Jun Kamohara and Yasushi Matsumura},
Title = {A pre-training technique to localize medical BERT and enhance BioBERT},
Year = {2020},
Eprint = {arXiv:2005.07202},
}
```
<a href="https://huggingface.co/exbert/?model=seiya/oubiobert-base-uncased&sentence=Coronavirus%20disease%20(COVID-19)%20is%20caused%20by%20SARS-COV2%20and%20represents%20the%20causative%20agent%20of%20a%20potentially%20fatal%20disease%20that%20is%20of%20great%20global%20public%20health%20concern.">
<img width="300px" src="https://cdn-media.huggingface.co/exbert/button.png">
</a>
|
Subsets and Splits
Filtered Qwen2.5 Distill Models
Identifies specific configurations of models by filtering cards that contain 'distill', 'qwen2.5', '7b' while excluding certain base models and incorrect model ID patterns, uncovering unique model variants.
Filtered Model Cards Count
Finds the count of entries with specific card details that include 'distill', 'qwen2.5', '7b' but exclude certain base models, revealing valuable insights about the dataset's content distribution.
Filtered Distill Qwen 7B Models
Filters for specific card entries containing 'distill', 'qwen', and '7b', excluding certain strings and patterns, to identify relevant model configurations.
Filtered Qwen-7b Model Cards
The query performs a detailed filtering based on specific keywords and excludes certain entries, which could be useful for identifying a specific subset of cards but does not provide deeper insights or trends.
Filtered Qwen 7B Model Cards
The query filters for specific terms related to "distilled" or "distill", "qwen", and "7b" in the 'card' column but excludes certain base models, providing a limited set of entries for further inspection.
Qwen 7B Distilled Models
The query provides a basic filtering of records to find specific card names that include keywords related to distilled Qwen 7b models, excluding a particular base model, which gives limited insight but helps in focusing on relevant entries.
Qwen 7B Distilled Model Cards
The query filters data based on specific keywords in the modelId and card fields, providing limited insight primarily useful for locating specific entries rather than revealing broad patterns or trends.
Qwen 7B Distilled Models
Finds all entries containing the terms 'distilled', 'qwen', and '7b' in a case-insensitive manner, providing a filtered set of records but without deeper analysis.
Distilled Qwen 7B Models
The query filters for specific model IDs containing 'distilled', 'qwen', and '7b', providing a basic retrieval of relevant entries but without deeper analysis or insight.
Filtered Model Cards with Distill Qwen2.
Filters and retrieves records containing specific keywords in the card description while excluding certain phrases, providing a basic count of relevant entries.
Filtered Model Cards with Distill Qwen 7
The query filters specific variations of card descriptions containing 'distill', 'qwen', and '7b' while excluding a particular base model, providing limited but specific data retrieval.
Distill Qwen 7B Model Cards
The query filters and retrieves rows where the 'card' column contains specific keywords ('distill', 'qwen', and '7b'), providing a basic filter result that can help in identifying specific entries.