pipeline_tag
stringclasses 48
values | library_name
stringclasses 198
values | text
stringlengths 1
900k
| metadata
stringlengths 2
438k
| id
stringlengths 5
122
| last_modified
null | tags
listlengths 1
1.84k
| sha
null | created_at
stringlengths 25
25
| arxiv
listlengths 0
201
| languages
listlengths 0
1.83k
| tags_str
stringlengths 17
9.34k
| text_str
stringlengths 0
389k
| text_lists
listlengths 0
722
| processed_texts
listlengths 1
723
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
text2text-generation
|
transformers
|
# t5-qa_webnlg_synth-en
## Model description
This model is a *Data Question Answering* model based on T5-small, that answers questions given a structured table as input.
It is actually a component of [QuestEval](https://github.com/ThomasScialom/QuestEval) metric but can be used independently as it is, for QA only.
## How to use
```python
from transformers import T5Tokenizer, T5ForConditionalGeneration
tokenizer = T5Tokenizer.from_pretrained("ThomasNLG/t5-qa_webnlg_synth-en")
model = T5ForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained("ThomasNLG/t5-qa_webnlg_synth-en")
```
You can play with the model using the inference API, the text input format should follow this template (accordingly to the training stage of the model):
`text_input = "{QUESTION} </s> {CONTEXT}"`
where `CONTEXT` is a structured table that is linearised this way:
`CONTEXT = "name [ The Eagle ] , eatType [ coffee shop ] , food [ French ] , priceRange [ £ 2 0 - 2 5 ]"`
## Training data
The model was trained on synthetic data as described in [Data-QuestEval: A Referenceless Metric for Data to Text Semantic Evaluation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2104.07555).
### Citation info
```bibtex
@article{rebuffel2021data,
title={Data-QuestEval: A Referenceless Metric for Data to Text Semantic Evaluation},
author={Rebuffel, Cl{\'e}ment and Scialom, Thomas and Soulier, Laure and Piwowarski, Benjamin and Lamprier, Sylvain and Staiano, Jacopo and Scoutheeten, Geoffrey and Gallinari, Patrick},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2104.07555},
year={2021}
}
```
|
{"language": "en", "license": "mit", "tags": ["qa", "question", "answering", "SQuAD", "data2text", "metric", "nlg", "t5-small"], "datasets": ["squad_v2"], "widget": [{"text": "What is the food type at The Eagle? </s> name [ The Eagle ] , eatType [ coffee shop ] , food [ French ] , priceRange [ \u00c2\u00a3 2 0 - 2 5 ]"}]}
|
ThomasNLG/t5-qa_webnlg_synth-en
| null |
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"jax",
"t5",
"text2text-generation",
"qa",
"question",
"answering",
"SQuAD",
"data2text",
"metric",
"nlg",
"t5-small",
"en",
"dataset:squad_v2",
"arxiv:2104.07555",
"license:mit",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"text-generation-inference",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[
"2104.07555"
] |
[
"en"
] |
TAGS
#transformers #pytorch #jax #t5 #text2text-generation #qa #question #answering #SQuAD #data2text #metric #nlg #t5-small #en #dataset-squad_v2 #arxiv-2104.07555 #license-mit #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #text-generation-inference #region-us
|
# t5-qa_webnlg_synth-en
## Model description
This model is a *Data Question Answering* model based on T5-small, that answers questions given a structured table as input.
It is actually a component of QuestEval metric but can be used independently as it is, for QA only.
## How to use
You can play with the model using the inference API, the text input format should follow this template (accordingly to the training stage of the model):
'text_input = "{QUESTION} </s> {CONTEXT}"'
where 'CONTEXT' is a structured table that is linearised this way:
'CONTEXT = "name [ The Eagle ] , eatType [ coffee shop ] , food [ French ] , priceRange [ £ 2 0 - 2 5 ]"'
## Training data
The model was trained on synthetic data as described in Data-QuestEval: A Referenceless Metric for Data to Text Semantic Evaluation.
info
|
[
"# t5-qa_webnlg_synth-en",
"## Model description\nThis model is a *Data Question Answering* model based on T5-small, that answers questions given a structured table as input.\nIt is actually a component of QuestEval metric but can be used independently as it is, for QA only.",
"## How to use\n\n\nYou can play with the model using the inference API, the text input format should follow this template (accordingly to the training stage of the model):\n\n'text_input = \"{QUESTION} </s> {CONTEXT}\"'\n\nwhere 'CONTEXT' is a structured table that is linearised this way:\n\n'CONTEXT = \"name [ The Eagle ] , eatType [ coffee shop ] , food [ French ] , priceRange [ £ 2 0 - 2 5 ]\"'",
"## Training data\nThe model was trained on synthetic data as described in Data-QuestEval: A Referenceless Metric for Data to Text Semantic Evaluation.\n\ninfo"
] |
[
"TAGS\n#transformers #pytorch #jax #t5 #text2text-generation #qa #question #answering #SQuAD #data2text #metric #nlg #t5-small #en #dataset-squad_v2 #arxiv-2104.07555 #license-mit #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #text-generation-inference #region-us \n",
"# t5-qa_webnlg_synth-en",
"## Model description\nThis model is a *Data Question Answering* model based on T5-small, that answers questions given a structured table as input.\nIt is actually a component of QuestEval metric but can be used independently as it is, for QA only.",
"## How to use\n\n\nYou can play with the model using the inference API, the text input format should follow this template (accordingly to the training stage of the model):\n\n'text_input = \"{QUESTION} </s> {CONTEXT}\"'\n\nwhere 'CONTEXT' is a structured table that is linearised this way:\n\n'CONTEXT = \"name [ The Eagle ] , eatType [ coffee shop ] , food [ French ] , priceRange [ £ 2 0 - 2 5 ]\"'",
"## Training data\nThe model was trained on synthetic data as described in Data-QuestEval: A Referenceless Metric for Data to Text Semantic Evaluation.\n\ninfo"
] |
text2text-generation
|
transformers
|
# t5-qg_squad1-en
## Model description
This model is a *Question Generation* model based on T5-small.
It is actually a component of [QuestEval](https://github.com/ThomasScialom/QuestEval) metric but can be used independently as it is, for QG only.
## How to use
```python
from transformers import T5Tokenizer, T5ForConditionalGeneration
tokenizer = T5Tokenizer.from_pretrained("ThomasNLG/t5-qg_squad1-en")
model = T5ForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained("ThomasNLG/t5-qg_squad1-en")
```
You can play with the model using the inference API, the text input format should follow this template (accordingly to the training stage of the model):
`text_input = "sv1 </s> {ANSWER} </s> {CONTEXT}"`
## Training data
The model was trained on SQuAD.
### Citation info
```bibtex
@article{scialom2020QuestEval,
title={QuestEval: Summarization Asks for Fact-based Evaluation},
author={Scialom, Thomas and Dray, Paul-Alexis and Gallinari, Patrick and Lamprier, Sylvain and Piwowarski, Benjamin and Staiano, Jacopo and Wang, Alex},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2103.12693},
year={2021}
}
```
|
{"language": "en", "license": "mit", "tags": ["qg", "question", "generation", "SQuAD", "metric", "nlg", "t5-small"], "datasets": ["squad"], "widget": [{"text": "sv1 </s> Louis 14 </s> Louis 14 was a French King."}]}
|
ThomasNLG/t5-qg_squad1-en
| null |
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"jax",
"t5",
"text2text-generation",
"qg",
"question",
"generation",
"SQuAD",
"metric",
"nlg",
"t5-small",
"en",
"dataset:squad",
"license:mit",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"has_space",
"text-generation-inference",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[
"en"
] |
TAGS
#transformers #pytorch #jax #t5 #text2text-generation #qg #question #generation #SQuAD #metric #nlg #t5-small #en #dataset-squad #license-mit #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #has_space #text-generation-inference #region-us
|
# t5-qg_squad1-en
## Model description
This model is a *Question Generation* model based on T5-small.
It is actually a component of QuestEval metric but can be used independently as it is, for QG only.
## How to use
You can play with the model using the inference API, the text input format should follow this template (accordingly to the training stage of the model):
'text_input = "sv1 </s> {ANSWER} </s> {CONTEXT}"'
## Training data
The model was trained on SQuAD.
info
|
[
"# t5-qg_squad1-en",
"## Model description\nThis model is a *Question Generation* model based on T5-small.\nIt is actually a component of QuestEval metric but can be used independently as it is, for QG only.",
"## How to use\n\n\nYou can play with the model using the inference API, the text input format should follow this template (accordingly to the training stage of the model):\n\n'text_input = \"sv1 </s> {ANSWER} </s> {CONTEXT}\"'",
"## Training data\nThe model was trained on SQuAD.\n\n\ninfo"
] |
[
"TAGS\n#transformers #pytorch #jax #t5 #text2text-generation #qg #question #generation #SQuAD #metric #nlg #t5-small #en #dataset-squad #license-mit #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #has_space #text-generation-inference #region-us \n",
"# t5-qg_squad1-en",
"## Model description\nThis model is a *Question Generation* model based on T5-small.\nIt is actually a component of QuestEval metric but can be used independently as it is, for QG only.",
"## How to use\n\n\nYou can play with the model using the inference API, the text input format should follow this template (accordingly to the training stage of the model):\n\n'text_input = \"sv1 </s> {ANSWER} </s> {CONTEXT}\"'",
"## Training data\nThe model was trained on SQuAD.\n\n\ninfo"
] |
text2text-generation
|
transformers
|
# t5-qg_webnlg_synth-en
## Model description
This model is a *Data Question Generation* model based on T5-small, that generates questions, given a structured table as input and the conditioned answer.
It is actually a component of [QuestEval](https://github.com/ThomasScialom/QuestEval) metric but can be used independently as it is, for QG only.
## How to use
```python
from transformers import T5Tokenizer, T5ForConditionalGeneration
tokenizer = T5Tokenizer.from_pretrained("ThomasNLG/t5-qg_webnlg_synth-en")
model = T5ForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained("ThomasNLG/t5-qg_webnlg_synth-en")
```
You can play with the model using the inference API, the text input format should follow this template (accordingly to the training stage of the model):
`text_input = "{ANSWER} </s> {CONTEXT}"`
where `CONTEXT is a structured table that is linearised this way:
`CONTEXT = "name [ The Eagle ] , eatType [ coffee shop ] , food [ French ] , priceRange [ £ 2 0 - 2 5 ]"`
## Training data
The model was trained on synthetic data as described in [Data-QuestEval: A Referenceless Metric for Data to Text Semantic Evaluation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2104.07555).
### Citation info
```bibtex
@article{rebuffel2021data,
title={Data-QuestEval: A Referenceless Metric for Data to Text Semantic Evaluation},
author={Rebuffel, Cl{\'e}ment and Scialom, Thomas and Soulier, Laure and Piwowarski, Benjamin and Lamprier, Sylvain and Staiano, Jacopo and Scoutheeten, Geoffrey and Gallinari, Patrick},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2104.07555},
year={2021}
}
```
|
{"language": "en", "license": "mit", "tags": ["qa", "question", "generation", "SQuAD", "data2text", "metric", "nlg", "t5-small"], "datasets": ["squad_v2"], "widget": [{"text": "The Eagle </s> name [ The Eagle ] , eatType [ coffee shop ] , food [ French ] , priceRange [ \u00c2\u00a3 2 0 - 2 5 ]"}]}
|
ThomasNLG/t5-qg_webnlg_synth-en
| null |
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"jax",
"t5",
"text2text-generation",
"qa",
"question",
"generation",
"SQuAD",
"data2text",
"metric",
"nlg",
"t5-small",
"en",
"dataset:squad_v2",
"arxiv:2104.07555",
"license:mit",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"text-generation-inference",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[
"2104.07555"
] |
[
"en"
] |
TAGS
#transformers #pytorch #jax #t5 #text2text-generation #qa #question #generation #SQuAD #data2text #metric #nlg #t5-small #en #dataset-squad_v2 #arxiv-2104.07555 #license-mit #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #text-generation-inference #region-us
|
# t5-qg_webnlg_synth-en
## Model description
This model is a *Data Question Generation* model based on T5-small, that generates questions, given a structured table as input and the conditioned answer.
It is actually a component of QuestEval metric but can be used independently as it is, for QG only.
## How to use
You can play with the model using the inference API, the text input format should follow this template (accordingly to the training stage of the model):
'text_input = "{ANSWER} </s> {CONTEXT}"'
where 'CONTEXT is a structured table that is linearised this way:
'CONTEXT = "name [ The Eagle ] , eatType [ coffee shop ] , food [ French ] , priceRange [ £ 2 0 - 2 5 ]"'
## Training data
The model was trained on synthetic data as described in Data-QuestEval: A Referenceless Metric for Data to Text Semantic Evaluation.
info
|
[
"# t5-qg_webnlg_synth-en",
"## Model description\nThis model is a *Data Question Generation* model based on T5-small, that generates questions, given a structured table as input and the conditioned answer. \nIt is actually a component of QuestEval metric but can be used independently as it is, for QG only.",
"## How to use\n\n\nYou can play with the model using the inference API, the text input format should follow this template (accordingly to the training stage of the model):\n\n'text_input = \"{ANSWER} </s> {CONTEXT}\"'\n\nwhere 'CONTEXT is a structured table that is linearised this way:\n\n'CONTEXT = \"name [ The Eagle ] , eatType [ coffee shop ] , food [ French ] , priceRange [ £ 2 0 - 2 5 ]\"'",
"## Training data\nThe model was trained on synthetic data as described in Data-QuestEval: A Referenceless Metric for Data to Text Semantic Evaluation.\n\ninfo"
] |
[
"TAGS\n#transformers #pytorch #jax #t5 #text2text-generation #qa #question #generation #SQuAD #data2text #metric #nlg #t5-small #en #dataset-squad_v2 #arxiv-2104.07555 #license-mit #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #text-generation-inference #region-us \n",
"# t5-qg_webnlg_synth-en",
"## Model description\nThis model is a *Data Question Generation* model based on T5-small, that generates questions, given a structured table as input and the conditioned answer. \nIt is actually a component of QuestEval metric but can be used independently as it is, for QG only.",
"## How to use\n\n\nYou can play with the model using the inference API, the text input format should follow this template (accordingly to the training stage of the model):\n\n'text_input = \"{ANSWER} </s> {CONTEXT}\"'\n\nwhere 'CONTEXT is a structured table that is linearised this way:\n\n'CONTEXT = \"name [ The Eagle ] , eatType [ coffee shop ] , food [ French ] , priceRange [ £ 2 0 - 2 5 ]\"'",
"## Training data\nThe model was trained on synthetic data as described in Data-QuestEval: A Referenceless Metric for Data to Text Semantic Evaluation.\n\ninfo"
] |
text2text-generation
|
transformers
|
# t5-weighter_cnndm-en
## Model description
This model is a *Classifier* model based on T5-small, that predicts if a answer / question couple is considered as important fact or not (Is this answer enough relevant to appear in a plausible summary?).
It is actually a component of [QuestEval](https://github.com/ThomasScialom/QuestEval) metric but can be used independently as it is.
## How to use
```python
from transformers import T5Tokenizer, T5ForConditionalGeneration
tokenizer = T5Tokenizer.from_pretrained("ThomasNLG/t5-weighter_cnndm-en")
model = T5ForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained("ThomasNLG/t5-weighter_cnndm-en")
```
You can play with the model using the inference API, the text input format should follow this template (accordingly to the training stage of the model):
`text_input = "{ANSWER} </s> {QUESTION} </s> {CONTEXT}"`
## Training data
The model was trained on synthetic data as described in [Questeval: Summarization asks for fact-based evaluation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.12693).
### Citation info
```bibtex
@article{scialom2021questeval,
title={Questeval: Summarization asks for fact-based evaluation},
author={Scialom, Thomas and Dray, Paul-Alexis and Gallinari, Patrick and Lamprier, Sylvain and Piwowarski, Benjamin and Staiano, Jacopo and Wang, Alex},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2103.12693},
year={2021}
}
```
|
{"language": "en", "license": "mit", "tags": ["qa", "classification", "question", "answering", "SQuAD", "metric", "nlg", "t5-small"], "datasets": ["squad", "cnndm"], "widget": [{"text": "a Buckingham Palace guard </s> Who felt on a manhole? </s> This is the embarrassing moment a Buckingham Palace guard slipped and fell on a manhole cover in front of hundreds of shocked tourists as he took up position in his sentry box. [...] The Guard comprises two detachments, one each for Buckingham Palace and St James\u2019s Palace, under the command of the Captain of The Queen\u2019s Guard."}]}
|
ThomasNLG/t5-weighter_cnndm-en
| null |
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"jax",
"t5",
"text2text-generation",
"qa",
"classification",
"question",
"answering",
"SQuAD",
"metric",
"nlg",
"t5-small",
"en",
"dataset:squad",
"dataset:cnndm",
"arxiv:2103.12693",
"license:mit",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"text-generation-inference",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[
"2103.12693"
] |
[
"en"
] |
TAGS
#transformers #pytorch #jax #t5 #text2text-generation #qa #classification #question #answering #SQuAD #metric #nlg #t5-small #en #dataset-squad #dataset-cnndm #arxiv-2103.12693 #license-mit #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #text-generation-inference #region-us
|
# t5-weighter_cnndm-en
## Model description
This model is a *Classifier* model based on T5-small, that predicts if a answer / question couple is considered as important fact or not (Is this answer enough relevant to appear in a plausible summary?).
It is actually a component of QuestEval metric but can be used independently as it is.
## How to use
You can play with the model using the inference API, the text input format should follow this template (accordingly to the training stage of the model):
'text_input = "{ANSWER} </s> {QUESTION} </s> {CONTEXT}"'
## Training data
The model was trained on synthetic data as described in Questeval: Summarization asks for fact-based evaluation.
info
|
[
"# t5-weighter_cnndm-en",
"## Model description\nThis model is a *Classifier* model based on T5-small, that predicts if a answer / question couple is considered as important fact or not (Is this answer enough relevant to appear in a plausible summary?).\nIt is actually a component of QuestEval metric but can be used independently as it is.",
"## How to use\n\n\nYou can play with the model using the inference API, the text input format should follow this template (accordingly to the training stage of the model):\n\n'text_input = \"{ANSWER} </s> {QUESTION} </s> {CONTEXT}\"'",
"## Training data\nThe model was trained on synthetic data as described in Questeval: Summarization asks for fact-based evaluation.\n\ninfo"
] |
[
"TAGS\n#transformers #pytorch #jax #t5 #text2text-generation #qa #classification #question #answering #SQuAD #metric #nlg #t5-small #en #dataset-squad #dataset-cnndm #arxiv-2103.12693 #license-mit #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #text-generation-inference #region-us \n",
"# t5-weighter_cnndm-en",
"## Model description\nThis model is a *Classifier* model based on T5-small, that predicts if a answer / question couple is considered as important fact or not (Is this answer enough relevant to appear in a plausible summary?).\nIt is actually a component of QuestEval metric but can be used independently as it is.",
"## How to use\n\n\nYou can play with the model using the inference API, the text input format should follow this template (accordingly to the training stage of the model):\n\n'text_input = \"{ANSWER} </s> {QUESTION} </s> {CONTEXT}\"'",
"## Training data\nThe model was trained on synthetic data as described in Questeval: Summarization asks for fact-based evaluation.\n\ninfo"
] |
reinforcement-learning
|
ml-agents
|
# Snowball Fight ☃️, a multi-agent environment for ML-Agents made by Hugging Face
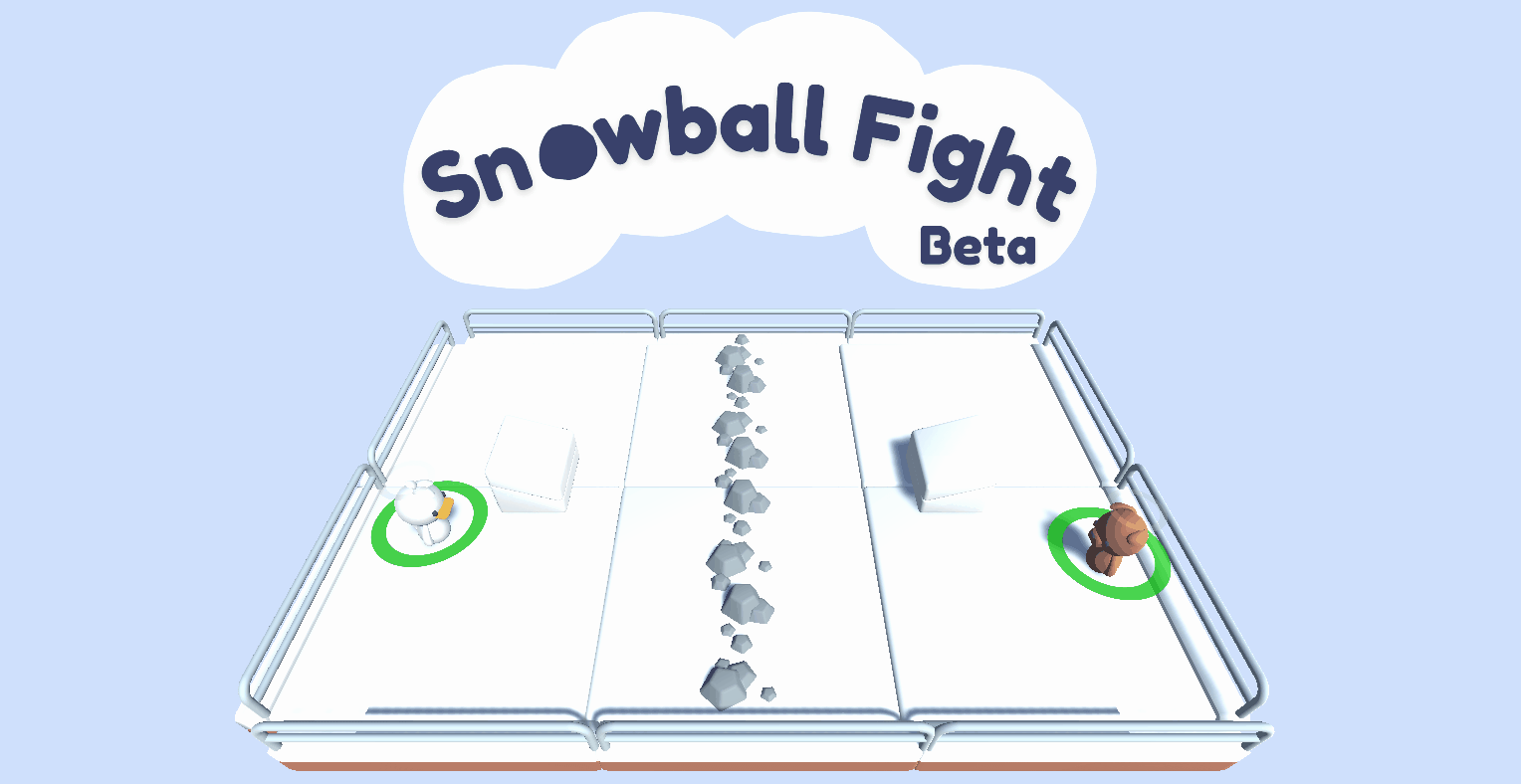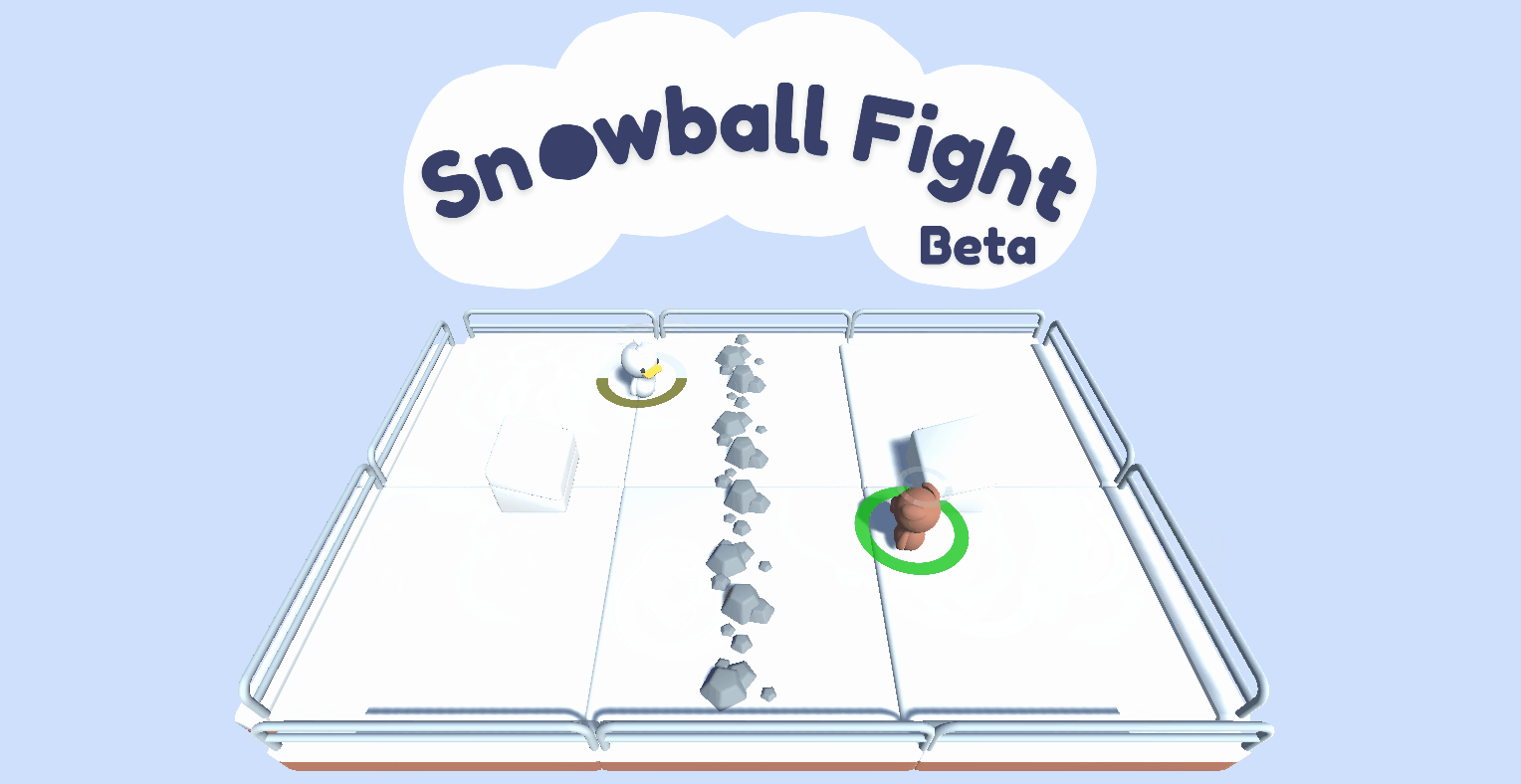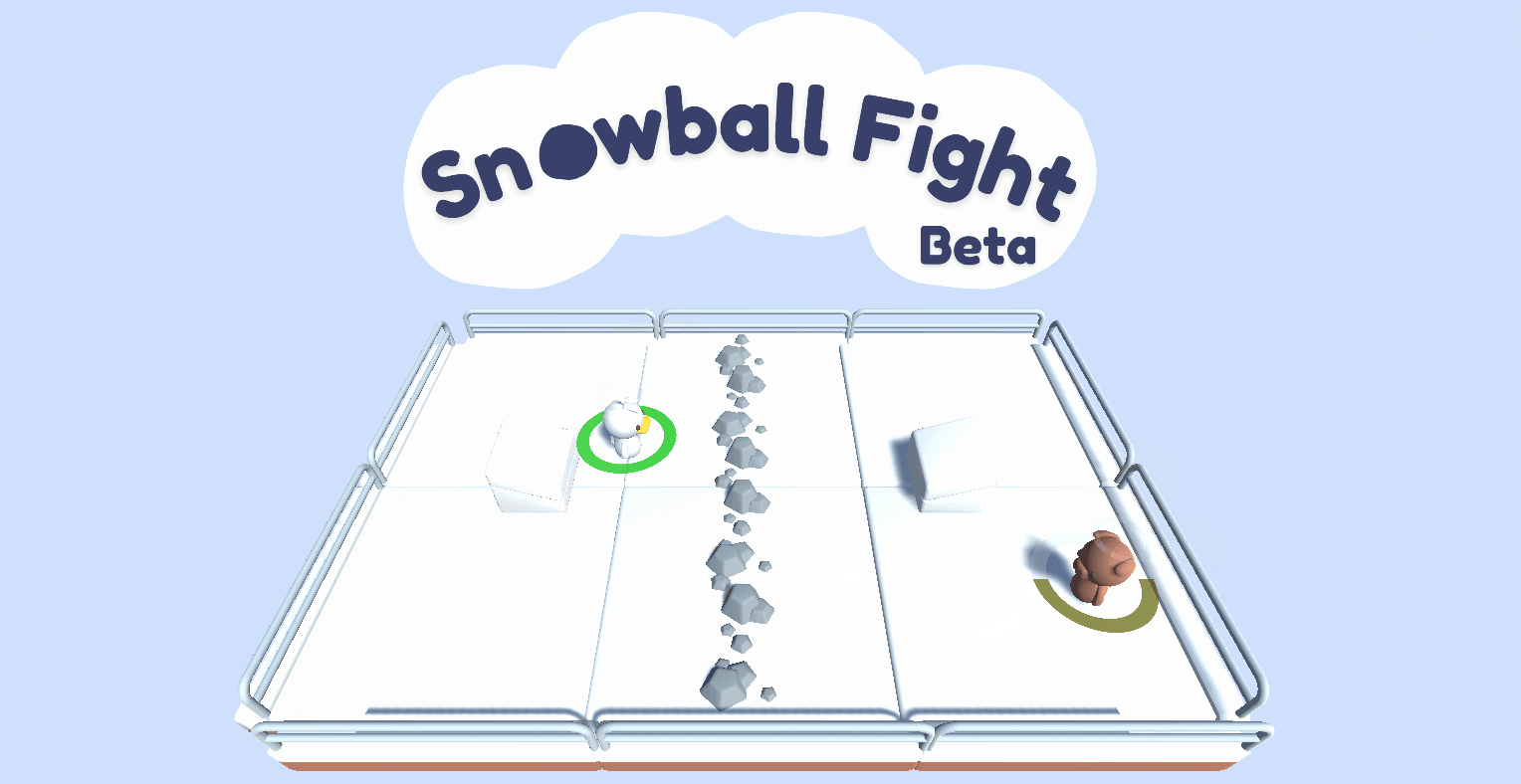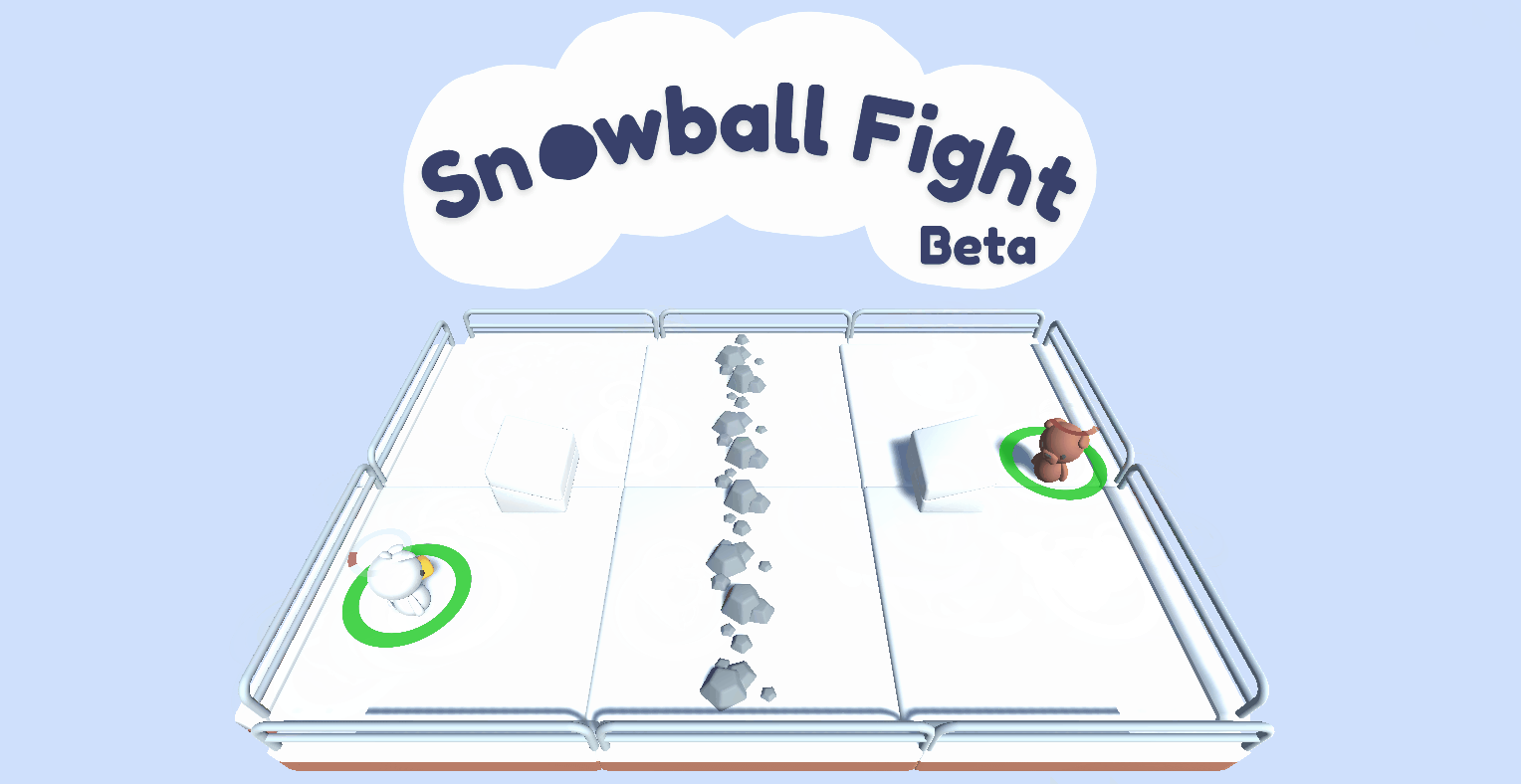
A multi-agent environment using Unity ML-Agents Toolkit where two agents compete in a 1vs1 snowball fight game.
👉 You can [play it online at this link](https://huggingface.co/spaces/ThomasSimonini/SnowballFight).
⚠️ You need to have some skills in ML-Agents if you want to use it if it's not the case [check the documentation](https://github.com/Unity-Technologies/ml-agents/tree/main/docs)
## The Environment
- Two agents compete **in a 1 vs 1 snowball fight game**.
- The goal is to **hit the opponent team while avoiding the opponent's snowballs ❄️**.
### Observation Space
- Ray-casts:
- **10 ray-casts forward** distributed over 100 degrees: detecting opponent.
- **10 ray-casts forward** distributed over 100 degrees: detecting walls, shelter and frontier.
- **10 ray-casts forward** distributed over 100 degrees: detecting snowballs.
- **3 ray-casts backward** distributed over 45 degrees: detecting wall and shelter.
- Vector Observations:
- **Bool canShoot** (you can only shoot a snowball every 2 seconds).
- **Float currentHealth**: normalized [0, 1]
- **Vector3 vertical speed**
- **Vector3 horizontal speed**
- **Vector3 "home" position**
### Action Space (Discrete)
- Vector Action space:
- **Four branched actions** corresponding to forward, backward, sideways movement, rotation, and snowball shoot.
### Agent Reward Function (dependant):
- If the team is **injured**:
- 0.1 to the shooter.
- If the team is **dead**:
- (1 - accumulated time penalty): when a snowball hits the
opponent, the accumulated time penalty decreases by (1 / MaxStep) every fixed update and is reset to 0 at the beginning of an episode.
- (-1) When a snowball hit our team.
### Addendum
- There **is no friendly fire**, which means that an agent can't shoot himself, or in the future, in a 2vs2 game can't shoot a teammate.
## How to use it
### Set-up the environment
1. Clone this project `git clone https://huggingface.co/ThomasSimonini/ML-Agents-SnowballFight-1vs1`
2. Open Unity Hub and create a new 3D Project
3. In the cloned project folder, open `.\ML-Agents-SnowballFight-1vs1\packages` and copy manifest.json and package.lock.json
4. Paste these two files in `Your Unity Project\Packages` => this will install the required packages.
5. Drop the SnowballFight-1vs1 unity package to your Unity Project.
### Watch the trained agents
6. If you want to watch the trained agents, open `Assets\1vs1\Scenes\1vs1_v2_Training.` place the `\ML-Agents-SnowballFight-1vs1\saved_model\SnowballFight1vs1-4999988.onnx` into BlueAgent and PurpleAgent Model.
### Train, the agent
6. If you want to train it again, the scene is `Assets\1vs1\Scenes\1vs1_v2_Training.`
## Training info
- SnowballFight1vs1 was trained with 5100000 steps.
- The final ELO score was 1766.452.
### Config File
`behaviors:
SnowballFight1vs1:
trainer_type: ppo
hyperparameters:
batch_size: 2048
buffer_size: 20480
learning_rate: 0.0003
beta: 0.005
epsilon: 0.2
lambd: 0.95
num_epoch: 3
learning_rate_schedule: constant
network_settings:
normalize: false
hidden_units: 512
num_layers: 2
vis_encode_type: simple
reward_signals:
extrinsic:
gamma: 0.99
strength: 1.0
keep_checkpoints: 40
checkpoint_interval: 200000
max_steps: 50000000
time_horizon: 1000
summary_freq: 50000
self_play:
save_steps: 50000
team_change: 200000
swap_steps: 2000
window: 10
play_against_latest_model_ratio: 0.5
initial_elo: 1200.0
`
|
{"license": "apache-2.0", "tags": ["deep-reinforcement-learning", "reinforcement-learning", "ml-agents"], "environment": ["SnowballFight-1vs1"]}
|
ThomasSimonini/ML-Agents-SnowballFight-1vs1
| null |
[
"ml-agents",
"onnx",
"deep-reinforcement-learning",
"reinforcement-learning",
"license:apache-2.0",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[] |
TAGS
#ml-agents #onnx #deep-reinforcement-learning #reinforcement-learning #license-apache-2.0 #region-us
|
# Snowball Fight ️, a multi-agent environment for ML-Agents made by Hugging Face
!Snowball Fight 1vs1
A multi-agent environment using Unity ML-Agents Toolkit where two agents compete in a 1vs1 snowball fight game.
You can play it online at this link.
️ You need to have some skills in ML-Agents if you want to use it if it's not the case check the documentation
## The Environment
- Two agents compete in a 1 vs 1 snowball fight game.
- The goal is to hit the opponent team while avoiding the opponent's snowballs ️.
### Observation Space
- Ray-casts:
- 10 ray-casts forward distributed over 100 degrees: detecting opponent.
- 10 ray-casts forward distributed over 100 degrees: detecting walls, shelter and frontier.
- 10 ray-casts forward distributed over 100 degrees: detecting snowballs.
- 3 ray-casts backward distributed over 45 degrees: detecting wall and shelter.
- Vector Observations:
- Bool canShoot (you can only shoot a snowball every 2 seconds).
- Float currentHealth: normalized [0, 1]
- Vector3 vertical speed
- Vector3 horizontal speed
- Vector3 "home" position
### Action Space (Discrete)
- Vector Action space:
- Four branched actions corresponding to forward, backward, sideways movement, rotation, and snowball shoot.
### Agent Reward Function (dependant):
- If the team is injured:
- 0.1 to the shooter.
- If the team is dead:
- (1 - accumulated time penalty): when a snowball hits the
opponent, the accumulated time penalty decreases by (1 / MaxStep) every fixed update and is reset to 0 at the beginning of an episode.
- (-1) When a snowball hit our team.
### Addendum
- There is no friendly fire, which means that an agent can't shoot himself, or in the future, in a 2vs2 game can't shoot a teammate.
## How to use it
### Set-up the environment
1. Clone this project 'git clone URL
2. Open Unity Hub and create a new 3D Project
3. In the cloned project folder, open '.\ML-Agents-SnowballFight-1vs1\packages' and copy URL and URL
4. Paste these two files in 'Your Unity Project\Packages' => this will install the required packages.
5. Drop the SnowballFight-1vs1 unity package to your Unity Project.
### Watch the trained agents
6. If you want to watch the trained agents, open 'Assets\1vs1\Scenes\1vs1_v2_Training.' place the '\ML-Agents-SnowballFight-1vs1\saved_model\URL' into BlueAgent and PurpleAgent Model.
### Train, the agent
6. If you want to train it again, the scene is 'Assets\1vs1\Scenes\1vs1_v2_Training.'
## Training info
- SnowballFight1vs1 was trained with 5100000 steps.
- The final ELO score was 1766.452.
### Config File
'behaviors:
SnowballFight1vs1:
trainer_type: ppo
hyperparameters:
batch_size: 2048
buffer_size: 20480
learning_rate: 0.0003
beta: 0.005
epsilon: 0.2
lambd: 0.95
num_epoch: 3
learning_rate_schedule: constant
network_settings:
normalize: false
hidden_units: 512
num_layers: 2
vis_encode_type: simple
reward_signals:
extrinsic:
gamma: 0.99
strength: 1.0
keep_checkpoints: 40
checkpoint_interval: 200000
max_steps: 50000000
time_horizon: 1000
summary_freq: 50000
self_play:
save_steps: 50000
team_change: 200000
swap_steps: 2000
window: 10
play_against_latest_model_ratio: 0.5
initial_elo: 1200.0
'
|
[
"# Snowball Fight ️, a multi-agent environment for ML-Agents made by Hugging Face \n!Snowball Fight 1vs1\nA multi-agent environment using Unity ML-Agents Toolkit where two agents compete in a 1vs1 snowball fight game.\n\n You can play it online at this link.\n\n️ You need to have some skills in ML-Agents if you want to use it if it's not the case check the documentation",
"## The Environment\n- Two agents compete in a 1 vs 1 snowball fight game.\n- The goal is to hit the opponent team while avoiding the opponent's snowballs ️.",
"### Observation Space\n- Ray-casts:\n\t- 10 ray-casts forward distributed over 100 degrees: detecting opponent.\n\t- 10 ray-casts forward distributed over 100 degrees: detecting walls, shelter and frontier.\n\t- 10 ray-casts forward distributed over 100 degrees: detecting snowballs.\n\t- 3 ray-casts backward distributed over 45 degrees: detecting wall and shelter.\n\n- Vector Observations:\n\t- Bool canShoot (you can only shoot a snowball every 2 seconds).\n\t- Float currentHealth: normalized [0, 1]\n\t- Vector3 vertical speed\n\t- Vector3 horizontal speed\n\t- Vector3 \"home\" position",
"### Action Space (Discrete) \n- Vector Action space:\n - Four branched actions corresponding to forward, backward, sideways movement, rotation, and snowball shoot.",
"### Agent Reward Function (dependant):\n- If the team is injured:\n - 0.1 to the shooter.\n- If the team is dead:\n - (1 - accumulated time penalty): when a snowball hits the\n opponent, the accumulated time penalty decreases by (1 / MaxStep) every fixed update and is reset to 0 at the beginning of an episode.\n - (-1) When a snowball hit our team.",
"### Addendum\n- There is no friendly fire, which means that an agent can't shoot himself, or in the future, in a 2vs2 game can't shoot a teammate.",
"## How to use it",
"### Set-up the environment\n1. Clone this project 'git clone URL\n2. Open Unity Hub and create a new 3D Project\n3. In the cloned project folder, open '.\\ML-Agents-SnowballFight-1vs1\\packages' and copy URL and URL\n4. Paste these two files in 'Your Unity Project\\Packages' => this will install the required packages.\n5. Drop the SnowballFight-1vs1 unity package to your Unity Project.",
"### Watch the trained agents\n6. If you want to watch the trained agents, open 'Assets\\1vs1\\Scenes\\1vs1_v2_Training.' place the '\\ML-Agents-SnowballFight-1vs1\\saved_model\\URL' into BlueAgent and PurpleAgent Model.",
"### Train, the agent\n6. If you want to train it again, the scene is 'Assets\\1vs1\\Scenes\\1vs1_v2_Training.'",
"## Training info\n- SnowballFight1vs1 was trained with 5100000 steps.\n- The final ELO score was 1766.452.",
"### Config File\n'behaviors:\n SnowballFight1vs1:\n trainer_type: ppo\n hyperparameters:\n batch_size: 2048\n buffer_size: 20480\n learning_rate: 0.0003\n beta: 0.005\n epsilon: 0.2\n lambd: 0.95\n num_epoch: 3\n learning_rate_schedule: constant\n network_settings:\n normalize: false\n hidden_units: 512\n num_layers: 2\n vis_encode_type: simple\n reward_signals:\n extrinsic:\n gamma: 0.99\n strength: 1.0\n keep_checkpoints: 40\n checkpoint_interval: 200000\n max_steps: 50000000\n time_horizon: 1000\n summary_freq: 50000\n self_play:\n save_steps: 50000\n team_change: 200000\n swap_steps: 2000\n window: 10\n play_against_latest_model_ratio: 0.5\n initial_elo: 1200.0\n'"
] |
[
"TAGS\n#ml-agents #onnx #deep-reinforcement-learning #reinforcement-learning #license-apache-2.0 #region-us \n",
"# Snowball Fight ️, a multi-agent environment for ML-Agents made by Hugging Face \n!Snowball Fight 1vs1\nA multi-agent environment using Unity ML-Agents Toolkit where two agents compete in a 1vs1 snowball fight game.\n\n You can play it online at this link.\n\n️ You need to have some skills in ML-Agents if you want to use it if it's not the case check the documentation",
"## The Environment\n- Two agents compete in a 1 vs 1 snowball fight game.\n- The goal is to hit the opponent team while avoiding the opponent's snowballs ️.",
"### Observation Space\n- Ray-casts:\n\t- 10 ray-casts forward distributed over 100 degrees: detecting opponent.\n\t- 10 ray-casts forward distributed over 100 degrees: detecting walls, shelter and frontier.\n\t- 10 ray-casts forward distributed over 100 degrees: detecting snowballs.\n\t- 3 ray-casts backward distributed over 45 degrees: detecting wall and shelter.\n\n- Vector Observations:\n\t- Bool canShoot (you can only shoot a snowball every 2 seconds).\n\t- Float currentHealth: normalized [0, 1]\n\t- Vector3 vertical speed\n\t- Vector3 horizontal speed\n\t- Vector3 \"home\" position",
"### Action Space (Discrete) \n- Vector Action space:\n - Four branched actions corresponding to forward, backward, sideways movement, rotation, and snowball shoot.",
"### Agent Reward Function (dependant):\n- If the team is injured:\n - 0.1 to the shooter.\n- If the team is dead:\n - (1 - accumulated time penalty): when a snowball hits the\n opponent, the accumulated time penalty decreases by (1 / MaxStep) every fixed update and is reset to 0 at the beginning of an episode.\n - (-1) When a snowball hit our team.",
"### Addendum\n- There is no friendly fire, which means that an agent can't shoot himself, or in the future, in a 2vs2 game can't shoot a teammate.",
"## How to use it",
"### Set-up the environment\n1. Clone this project 'git clone URL\n2. Open Unity Hub and create a new 3D Project\n3. In the cloned project folder, open '.\\ML-Agents-SnowballFight-1vs1\\packages' and copy URL and URL\n4. Paste these two files in 'Your Unity Project\\Packages' => this will install the required packages.\n5. Drop the SnowballFight-1vs1 unity package to your Unity Project.",
"### Watch the trained agents\n6. If you want to watch the trained agents, open 'Assets\\1vs1\\Scenes\\1vs1_v2_Training.' place the '\\ML-Agents-SnowballFight-1vs1\\saved_model\\URL' into BlueAgent and PurpleAgent Model.",
"### Train, the agent\n6. If you want to train it again, the scene is 'Assets\\1vs1\\Scenes\\1vs1_v2_Training.'",
"## Training info\n- SnowballFight1vs1 was trained with 5100000 steps.\n- The final ELO score was 1766.452.",
"### Config File\n'behaviors:\n SnowballFight1vs1:\n trainer_type: ppo\n hyperparameters:\n batch_size: 2048\n buffer_size: 20480\n learning_rate: 0.0003\n beta: 0.005\n epsilon: 0.2\n lambd: 0.95\n num_epoch: 3\n learning_rate_schedule: constant\n network_settings:\n normalize: false\n hidden_units: 512\n num_layers: 2\n vis_encode_type: simple\n reward_signals:\n extrinsic:\n gamma: 0.99\n strength: 1.0\n keep_checkpoints: 40\n checkpoint_interval: 200000\n max_steps: 50000000\n time_horizon: 1000\n summary_freq: 50000\n self_play:\n save_steps: 50000\n team_change: 200000\n swap_steps: 2000\n window: 10\n play_against_latest_model_ratio: 0.5\n initial_elo: 1200.0\n'"
] |
reinforcement-learning
|
stable-baselines3
|
# **PPO** Agent playing **CartPole-v1**
This is a trained model of a **PPO** agent playing **CartPole-v1**
using the [stable-baselines3 library](https://github.com/DLR-RM/stable-baselines3).
## Usage (with Stable-baselines3)
TODO: Add your code
```python
from stable_baselines3 import ...
from huggingface_sb3 import load_from_hub
...
```
|
{"library_name": "stable-baselines3", "tags": ["CartPole-v1", "deep-reinforcement-learning", "reinforcement-learning", "stable-baselines3"], "model-index": [{"name": "PPO", "results": [{"task": {"type": "reinforcement-learning", "name": "reinforcement-learning"}, "dataset": {"name": "CartPole-v1", "type": "CartPole-v1"}, "metrics": [{"type": "mean_reward", "value": "236.70 +/- 117.42", "name": "mean_reward", "verified": false}]}]}]}
|
ThomasSimonini/demo-hf-CartPole-v1
| null |
[
"stable-baselines3",
"CartPole-v1",
"deep-reinforcement-learning",
"reinforcement-learning",
"model-index",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[] |
TAGS
#stable-baselines3 #CartPole-v1 #deep-reinforcement-learning #reinforcement-learning #model-index #region-us
|
# PPO Agent playing CartPole-v1
This is a trained model of a PPO agent playing CartPole-v1
using the stable-baselines3 library.
## Usage (with Stable-baselines3)
TODO: Add your code
|
[
"# PPO Agent playing CartPole-v1\nThis is a trained model of a PPO agent playing CartPole-v1\nusing the stable-baselines3 library.",
"## Usage (with Stable-baselines3)\nTODO: Add your code"
] |
[
"TAGS\n#stable-baselines3 #CartPole-v1 #deep-reinforcement-learning #reinforcement-learning #model-index #region-us \n",
"# PPO Agent playing CartPole-v1\nThis is a trained model of a PPO agent playing CartPole-v1\nusing the stable-baselines3 library.",
"## Usage (with Stable-baselines3)\nTODO: Add your code"
] |
reinforcement-learning
| null |
# mlagents-snowballfight-1vs1-ppo ☃️
This is a saved model of a PPO 1vs1 agent playing Snowball Fight.
|
{"license": "apache-2.0", "tags": ["deep-reinforcement-learning", "reinforcement-learning", "mlagents"], "environment": [{"MLAgents": "Snowballfight-1vs1-ppo"}]}
|
ThomasSimonini/mlagents-snowballfight-1vs1-ppo
| null |
[
"deep-reinforcement-learning",
"reinforcement-learning",
"mlagents",
"license:apache-2.0",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[] |
TAGS
#deep-reinforcement-learning #reinforcement-learning #mlagents #license-apache-2.0 #region-us
|
# mlagents-snowballfight-1vs1-ppo ️
This is a saved model of a PPO 1vs1 agent playing Snowball Fight.
|
[
"# mlagents-snowballfight-1vs1-ppo ️\nThis is a saved model of a PPO 1vs1 agent playing Snowball Fight."
] |
[
"TAGS\n#deep-reinforcement-learning #reinforcement-learning #mlagents #license-apache-2.0 #region-us \n",
"# mlagents-snowballfight-1vs1-ppo ️\nThis is a saved model of a PPO 1vs1 agent playing Snowball Fight."
] |
reinforcement-learning
|
stable-baselines3
|
# ppo-Walker2DBulletEnv-v0
This is a pre-trained model of a PPO agent playing AntBulletEnv-v0 using the [stable-baselines3](https://github.com/DLR-RM/stable-baselines3) library.
### Usage (with Stable-baselines3)
Using this model becomes easy when you have stable-baselines3 and huggingface_sb3 installed:
```
pip install stable-baselines3
pip install huggingface_sb3
```
Then, you can use the model like this:
```python
import gym
import pybullet_envs
from huggingface_sb3 import load_from_hub
from stable_baselines3 import PPO
from stable_baselines3.common.vec_env import DummyVecEnv, VecNormalize
from stable_baselines3.common.evaluation import evaluate_policy
# Retrieve the model from the hub
## repo_id = id of the model repository from the Hugging Face Hub (repo_id = {organization}/{repo_name})
## filename = name of the model zip file from the repository
repo_id = "ThomasSimonini/ppo-AntBulletEnv-v0"
checkpoint = load_from_hub(repo_id = repo_id, filename="ppo-AntBulletEnv-v0.zip")
model = PPO.load(checkpoint)
# Load the saved statistics
stats_path = load_from_hub(repo_id = repo_id, filename="vec_normalize.pkl")
eval_env = DummyVecEnv([lambda: gym.make("AntBulletEnv-v0")])
eval_env = VecNormalize.load(stats_path, eval_env)
# do not update them at test time
eval_env.training = False
# reward normalization is not needed at test time
eval_env.norm_reward = False
from stable_baselines3.common.evaluation import evaluate_policy
mean_reward, std_reward = evaluate_policy(model, eval_env)
print(f"Mean reward = {mean_reward:.2f} +/- {std_reward:.2f}")
```
### Evaluation Results
Mean_reward: 3547.01 +/- 33.32
|
{"tags": ["deep-reinforcement-learning", "reinforcement-learning", "stable-baselines3"]}
|
ThomasSimonini/ppo-AntBulletEnv-v0
| null |
[
"stable-baselines3",
"deep-reinforcement-learning",
"reinforcement-learning",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[] |
TAGS
#stable-baselines3 #deep-reinforcement-learning #reinforcement-learning #region-us
|
# ppo-Walker2DBulletEnv-v0
This is a pre-trained model of a PPO agent playing AntBulletEnv-v0 using the stable-baselines3 library.
### Usage (with Stable-baselines3)
Using this model becomes easy when you have stable-baselines3 and huggingface_sb3 installed:
Then, you can use the model like this:
### Evaluation Results
Mean_reward: 3547.01 +/- 33.32
|
[
"# ppo-Walker2DBulletEnv-v0\n\nThis is a pre-trained model of a PPO agent playing AntBulletEnv-v0 using the stable-baselines3 library.",
"### Usage (with Stable-baselines3)\nUsing this model becomes easy when you have stable-baselines3 and huggingface_sb3 installed:\n\n\nThen, you can use the model like this:",
"### Evaluation Results\nMean_reward: 3547.01 +/- 33.32"
] |
[
"TAGS\n#stable-baselines3 #deep-reinforcement-learning #reinforcement-learning #region-us \n",
"# ppo-Walker2DBulletEnv-v0\n\nThis is a pre-trained model of a PPO agent playing AntBulletEnv-v0 using the stable-baselines3 library.",
"### Usage (with Stable-baselines3)\nUsing this model becomes easy when you have stable-baselines3 and huggingface_sb3 installed:\n\n\nThen, you can use the model like this:",
"### Evaluation Results\nMean_reward: 3547.01 +/- 33.32"
] |
reinforcement-learning
|
stable-baselines3
|
# PPO Agent playing BreakoutNoFrameskip-v4
This is a trained model of a **PPO agent playing BreakoutNoFrameskip-v4 using the [stable-baselines3 library](https://stable-baselines3.readthedocs.io/en/master/index.html)**.
The training report: https://wandb.ai/simoninithomas/HFxSB3/reports/Atari-HFxSB3-Benchmark--VmlldzoxNjI3NTIy
## Evaluation Results
Mean_reward: `339.0`
# Usage (with Stable-baselines3)
- You need to use `gym==0.19` since it **includes Atari Roms**.
- The Action Space is 6 since we use only **possible actions in this game**.
Watch your agent interacts :
```python
# Import the libraries
import os
import gym
from stable_baselines3 import PPO
from stable_baselines3.common.vec_env import VecNormalize
from stable_baselines3.common.env_util import make_atari_env
from stable_baselines3.common.vec_env import VecFrameStack
from huggingface_sb3 import load_from_hub, push_to_hub
# Load the model
checkpoint = load_from_hub("ThomasSimonini/ppo-BreakoutNoFrameskip-v4", "ppo-BreakoutNoFrameskip-v4.zip")
# Because we using 3.7 on Colab and this agent was trained with 3.8 to avoid Pickle errors:
custom_objects = {
"learning_rate": 0.0,
"lr_schedule": lambda _: 0.0,
"clip_range": lambda _: 0.0,
}
model= PPO.load(checkpoint, custom_objects=custom_objects)
env = make_atari_env('BreakoutNoFrameskip-v4', n_envs=1)
env = VecFrameStack(env, n_stack=4)
obs = env.reset()
while True:
action, _states = model.predict(obs)
obs, rewards, dones, info = env.step(action)
env.render()
```
## Training Code
```python
import wandb
import gym
from stable_baselines3 import PPO
from stable_baselines3.common.env_util import make_atari_env
from stable_baselines3.common.vec_env import VecFrameStack, VecVideoRecorder
from stable_baselines3.common.callbacks import CheckpointCallback
from wandb.integration.sb3 import WandbCallback
from huggingface_sb3 import load_from_hub, push_to_hub
config = {
"env_name": "BreakoutNoFrameskip-v4",
"num_envs": 8,
"total_timesteps": int(10e6),
"seed": 661550378,
}
run = wandb.init(
project="HFxSB3",
config = config,
sync_tensorboard = True, # Auto-upload sb3's tensorboard metrics
monitor_gym = True, # Auto-upload the videos of agents playing the game
save_code = True, # Save the code to W&B
)
# There already exists an environment generator
# that will make and wrap atari environments correctly.
# Here we are also multi-worker training (n_envs=8 => 8 environments)
env = make_atari_env(config["env_name"], n_envs=config["num_envs"], seed=config["seed"]) #BreakoutNoFrameskip-v4
print("ENV ACTION SPACE: ", env.action_space.n)
# Frame-stacking with 4 frames
env = VecFrameStack(env, n_stack=4)
# Video recorder
env = VecVideoRecorder(env, "videos", record_video_trigger=lambda x: x % 100000 == 0, video_length=2000)
model = PPO(policy = "CnnPolicy",
env = env,
batch_size = 256,
clip_range = 0.1,
ent_coef = 0.01,
gae_lambda = 0.9,
gamma = 0.99,
learning_rate = 2.5e-4,
max_grad_norm = 0.5,
n_epochs = 4,
n_steps = 128,
vf_coef = 0.5,
tensorboard_log = f"runs",
verbose=1,
)
model.learn(
total_timesteps = config["total_timesteps"],
callback = [
WandbCallback(
gradient_save_freq = 1000,
model_save_path = f"models/{run.id}",
),
CheckpointCallback(save_freq=10000, save_path='./breakout',
name_prefix=config["env_name"]),
]
)
model.save("ppo-BreakoutNoFrameskip-v4.zip")
push_to_hub(repo_id="ThomasSimonini/ppo-BreakoutNoFrameskip-v4",
filename="ppo-BreakoutNoFrameskip-v4.zip",
commit_message="Added Breakout trained agent")
```
|
{"tags": ["deep-reinforcement-learning", "reinforcement-learning", "stable-baselines3", "atari"], "model-index": [{"name": "PPO Agent", "results": [{"task": {"type": "reinforcement-learning"}, "dataset": {"name": "BreakoutNoFrameskip-v4", "type": "BreakoutNoFrameskip-v4"}, "metrics": [{"type": "mean_reward", "value": 339}]}]}]}
|
ThomasSimonini/ppo-BreakoutNoFrameskip-v4
| null |
[
"stable-baselines3",
"deep-reinforcement-learning",
"reinforcement-learning",
"atari",
"model-index",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[] |
TAGS
#stable-baselines3 #deep-reinforcement-learning #reinforcement-learning #atari #model-index #region-us
|
# PPO Agent playing BreakoutNoFrameskip-v4
This is a trained model of a PPO agent playing BreakoutNoFrameskip-v4 using the stable-baselines3 library.
The training report: URL
## Evaluation Results
Mean_reward: '339.0'
# Usage (with Stable-baselines3)
- You need to use 'gym==0.19' since it includes Atari Roms.
- The Action Space is 6 since we use only possible actions in this game.
Watch your agent interacts :
## Training Code
|
[
"# PPO Agent playing BreakoutNoFrameskip-v4\nThis is a trained model of a PPO agent playing BreakoutNoFrameskip-v4 using the stable-baselines3 library.\n\nThe training report: URL",
"## Evaluation Results\nMean_reward: '339.0'",
"# Usage (with Stable-baselines3)\n- You need to use 'gym==0.19' since it includes Atari Roms.\n- The Action Space is 6 since we use only possible actions in this game.\n\n\nWatch your agent interacts :",
"## Training Code"
] |
[
"TAGS\n#stable-baselines3 #deep-reinforcement-learning #reinforcement-learning #atari #model-index #region-us \n",
"# PPO Agent playing BreakoutNoFrameskip-v4\nThis is a trained model of a PPO agent playing BreakoutNoFrameskip-v4 using the stable-baselines3 library.\n\nThe training report: URL",
"## Evaluation Results\nMean_reward: '339.0'",
"# Usage (with Stable-baselines3)\n- You need to use 'gym==0.19' since it includes Atari Roms.\n- The Action Space is 6 since we use only possible actions in this game.\n\n\nWatch your agent interacts :",
"## Training Code"
] |
reinforcement-learning
|
stable-baselines3
|
# **PPO** Agent playing **LunarLander-v2**
This is a trained model of a **PPO** agent playing **LunarLander-v2**
using the [stable-baselines3 library](https://github.com/DLR-RM/stable-baselines3).
## Usage (with Stable-baselines3)
TODO: Add your code
```python
from stable_baselines3 import ...
from huggingface_sb3 import load_from_hub
...
```
|
{"library_name": "stable-baselines3", "tags": ["LunarLander-v2", "deep-reinforcement-learning", "reinforcement-learning", "stable-baselines3"], "model-index": [{"name": "PPO", "results": [{"task": {"type": "reinforcement-learning", "name": "reinforcement-learning"}, "dataset": {"name": "LunarLander-v2", "type": "LunarLander-v2"}, "metrics": [{"type": "mean_reward", "value": "-273.72 +/- 71.58", "name": "mean_reward", "verified": false}]}]}]}
|
ThomasSimonini/ppo-LunarLander-v2
| null |
[
"stable-baselines3",
"LunarLander-v2",
"deep-reinforcement-learning",
"reinforcement-learning",
"model-index",
"has_space",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[] |
TAGS
#stable-baselines3 #LunarLander-v2 #deep-reinforcement-learning #reinforcement-learning #model-index #has_space #region-us
|
# PPO Agent playing LunarLander-v2
This is a trained model of a PPO agent playing LunarLander-v2
using the stable-baselines3 library.
## Usage (with Stable-baselines3)
TODO: Add your code
|
[
"# PPO Agent playing LunarLander-v2\nThis is a trained model of a PPO agent playing LunarLander-v2\nusing the stable-baselines3 library.",
"## Usage (with Stable-baselines3)\nTODO: Add your code"
] |
[
"TAGS\n#stable-baselines3 #LunarLander-v2 #deep-reinforcement-learning #reinforcement-learning #model-index #has_space #region-us \n",
"# PPO Agent playing LunarLander-v2\nThis is a trained model of a PPO agent playing LunarLander-v2\nusing the stable-baselines3 library.",
"## Usage (with Stable-baselines3)\nTODO: Add your code"
] |
reinforcement-learning
|
stable-baselines3
|
# PPO Agent playing PongNoFrameskip-v4
This is a trained model of a **PPO agent playing PongNoFrameskip-v4 using the [stable-baselines3 library](https://stable-baselines3.readthedocs.io/en/master/index.html)** (our agent is the 🟢 one).
The training report: https://wandb.ai/simoninithomas/HFxSB3/reports/Atari-HFxSB3-Benchmark--VmlldzoxNjI3NTIy
## Evaluation Results
Mean_reward: `21.00 +/- 0.0`
# Usage (with Stable-baselines3)
- You need to use `gym==0.19` since it **includes Atari Roms**.
- The Action Space is 6 since we use only **possible actions in this game**.
Watch your agent interacts :
```python
# Import the libraries
import os
import gym
from stable_baselines3 import PPO
from stable_baselines3.common.vec_env import VecNormalize
from stable_baselines3.common.env_util import make_atari_env
from stable_baselines3.common.vec_env import VecFrameStack
from huggingface_sb3 import load_from_hub, push_to_hub
# Load the model
checkpoint = load_from_hub("ThomasSimonini/ppo-PongNoFrameskip-v4", "ppo-PongNoFrameskip-v4.zip")
# Because we using 3.7 on Colab and this agent was trained with 3.8 to avoid Pickle errors:
custom_objects = {
"learning_rate": 0.0,
"lr_schedule": lambda _: 0.0,
"clip_range": lambda _: 0.0,
}
model= PPO.load(checkpoint, custom_objects=custom_objects)
env = make_atari_env('PongNoFrameskip-v4', n_envs=1)
env = VecFrameStack(env, n_stack=4)
obs = env.reset()
while True:
action, _states = model.predict(obs)
obs, rewards, dones, info = env.step(action)
env.render()
```
## Training Code
```python
import wandb
import gym
from stable_baselines3 import PPO
from stable_baselines3.common.env_util import make_atari_env
from stable_baselines3.common.vec_env import VecFrameStack, VecVideoRecorder
from stable_baselines3.common.callbacks import CheckpointCallback
from wandb.integration.sb3 import WandbCallback
from huggingface_sb3 import load_from_hub, push_to_hub
config = {
"env_name": "PongNoFrameskip-v4",
"num_envs": 8,
"total_timesteps": int(10e6),
"seed": 4089164106,
}
run = wandb.init(
project="HFxSB3",
config = config,
sync_tensorboard = True, # Auto-upload sb3's tensorboard metrics
monitor_gym = True, # Auto-upload the videos of agents playing the game
save_code = True, # Save the code to W&B
)
# There already exists an environment generator
# that will make and wrap atari environments correctly.
# Here we are also multi-worker training (n_envs=8 => 8 environments)
env = make_atari_env(config["env_name"], n_envs=config["num_envs"], seed=config["seed"]) #PongNoFrameskip-v4
print("ENV ACTION SPACE: ", env.action_space.n)
# Frame-stacking with 4 frames
env = VecFrameStack(env, n_stack=4)
# Video recorder
env = VecVideoRecorder(env, "videos", record_video_trigger=lambda x: x % 100000 == 0, video_length=2000)
# https://github.com/DLR-RM/rl-trained-agents/blob/10a9c31e806820d59b20d8b85ca67090338ea912/ppo/PongNoFrameskip-v4_1/PongNoFrameskip-v4/config.yml
model = PPO(policy = "CnnPolicy",
env = env,
batch_size = 256,
clip_range = 0.1,
ent_coef = 0.01,
gae_lambda = 0.9,
gamma = 0.99,
learning_rate = 2.5e-4,
max_grad_norm = 0.5,
n_epochs = 4,
n_steps = 128,
vf_coef = 0.5,
tensorboard_log = f"runs",
verbose=1,
)
model.learn(
total_timesteps = config["total_timesteps"],
callback = [
WandbCallback(
gradient_save_freq = 1000,
model_save_path = f"models/{run.id}",
),
CheckpointCallback(save_freq=10000, save_path='./pong',
name_prefix=config["env_name"]),
]
)
model.save("ppo-PongNoFrameskip-v4.zip")
push_to_hub(repo_id="ThomasSimonini/ppo-PongNoFrameskip-v4",
filename="ppo-PongNoFrameskip-v4.zip",
commit_message="Added Pong trained agent")
```
|
{"tags": ["deep-reinforcement-learning", "reinforcement-learning", "stable-baselines3", "atari"], "model-index": [{"name": "PPO Agent", "results": [{"task": {"type": "reinforcement-learning"}, "dataset": {"name": "PongNoFrameskip-v4", "type": "PongNoFrameskip-v4"}, "metrics": [{"type": "mean_reward", "value": 21}]}]}]}
|
ThomasSimonini/ppo-PongNoFrameskip-v4
| null |
[
"stable-baselines3",
"deep-reinforcement-learning",
"reinforcement-learning",
"atari",
"model-index",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[] |
TAGS
#stable-baselines3 #deep-reinforcement-learning #reinforcement-learning #atari #model-index #region-us
|
# PPO Agent playing PongNoFrameskip-v4
This is a trained model of a PPO agent playing PongNoFrameskip-v4 using the stable-baselines3 library (our agent is the 🟢 one).
The training report: URL
## Evaluation Results
Mean_reward: '21.00 +/- 0.0'
# Usage (with Stable-baselines3)
- You need to use 'gym==0.19' since it includes Atari Roms.
- The Action Space is 6 since we use only possible actions in this game.
Watch your agent interacts :
## Training Code
|
[
"# PPO Agent playing PongNoFrameskip-v4\nThis is a trained model of a PPO agent playing PongNoFrameskip-v4 using the stable-baselines3 library (our agent is the 🟢 one).\n\nThe training report: URL",
"## Evaluation Results\nMean_reward: '21.00 +/- 0.0'",
"# Usage (with Stable-baselines3)\n- You need to use 'gym==0.19' since it includes Atari Roms.\n- The Action Space is 6 since we use only possible actions in this game.\n\n\nWatch your agent interacts :",
"## Training Code"
] |
[
"TAGS\n#stable-baselines3 #deep-reinforcement-learning #reinforcement-learning #atari #model-index #region-us \n",
"# PPO Agent playing PongNoFrameskip-v4\nThis is a trained model of a PPO agent playing PongNoFrameskip-v4 using the stable-baselines3 library (our agent is the 🟢 one).\n\nThe training report: URL",
"## Evaluation Results\nMean_reward: '21.00 +/- 0.0'",
"# Usage (with Stable-baselines3)\n- You need to use 'gym==0.19' since it includes Atari Roms.\n- The Action Space is 6 since we use only possible actions in this game.\n\n\nWatch your agent interacts :",
"## Training Code"
] |
reinforcement-learning
|
stable-baselines3
|
# PPO Agent playing QbertNoFrameskip-v4
This is a trained model of a **PPO agent playing QbertNoFrameskip-v4 using the [stable-baselines3 library](https://stable-baselines3.readthedocs.io/en/master/index.html)**.
The training report: https://wandb.ai/simoninithomas/HFxSB3/reports/Atari-HFxSB3-Benchmark--VmlldzoxNjI3NTIy
## Evaluation Results
Mean_reward: `15685.00 +/- 115.217`
# Usage (with Stable-baselines3)
- You need to use `gym==0.19` since it **includes Atari Roms**.
- The Action Space is 6 since we use only **possible actions in this game**.
Watch your agent interacts :
```python
# Import the libraries
import os
import gym
from stable_baselines3 import PPO
from stable_baselines3.common.vec_env import VecNormalize
from stable_baselines3.common.env_util import make_atari_env
from stable_baselines3.common.vec_env import VecFrameStack
from huggingface_sb3 import load_from_hub, push_to_hub
# Load the model
checkpoint = load_from_hub("ThomasSimonini/ppo-QbertNoFrameskip-v4", "ppo-QbertNoFrameskip-v4.zip")
# Because we using 3.7 on Colab and this agent was trained with 3.8 to avoid Pickle errors:
custom_objects = {
"learning_rate": 0.0,
"lr_schedule": lambda _: 0.0,
"clip_range": lambda _: 0.0,
}
model= PPO.load(checkpoint, custom_objects=custom_objects)
env = make_atari_env('QbertNoFrameskip-v4', n_envs=1)
env = VecFrameStack(env, n_stack=4)
obs = env.reset()
while True:
action, _states = model.predict(obs)
obs, rewards, dones, info = env.step(action)
env.render()
```
## Training Code
```python
import wandb
import gym
from stable_baselines3 import PPO
from stable_baselines3.common.env_util import make_atari_env
from stable_baselines3.common.vec_env import VecFrameStack, VecVideoRecorder
from stable_baselines3.common.callbacks import CheckpointCallback
from wandb.integration.sb3 import WandbCallback
from huggingface_sb3 import load_from_hub, push_to_hub
config = {
"env_name": "QbertNoFrameskip-v4",
"num_envs": 8,
"total_timesteps": int(10e6),
"seed": 1194709219,
}
run = wandb.init(
project="HFxSB3",
config = config,
sync_tensorboard = True, # Auto-upload sb3's tensorboard metrics
monitor_gym = True, # Auto-upload the videos of agents playing the game
save_code = True, # Save the code to W&B
)
# There already exists an environment generator
# that will make and wrap atari environments correctly.
# Here we are also multi-worker training (n_envs=8 => 8 environments)
env = make_atari_env(config["env_name"], n_envs=config["num_envs"], seed=config["seed"]) #QbertNoFrameskip-v4
print("ENV ACTION SPACE: ", env.action_space.n)
# Frame-stacking with 4 frames
env = VecFrameStack(env, n_stack=4)
# Video recorder
env = VecVideoRecorder(env, "videos", record_video_trigger=lambda x: x % 100000 == 0, video_length=2000)
model = PPO(policy = "CnnPolicy",
env = env,
batch_size = 256,
clip_range = 0.1,
ent_coef = 0.01,
gae_lambda = 0.9,
gamma = 0.99,
learning_rate = 2.5e-4,
max_grad_norm = 0.5,
n_epochs = 4,
n_steps = 128,
vf_coef = 0.5,
tensorboard_log = f"runs",
verbose=1,
)
model.learn(
total_timesteps = config["total_timesteps"],
callback = [
WandbCallback(
gradient_save_freq = 1000,
model_save_path = f"models/{run.id}",
),
CheckpointCallback(save_freq=10000, save_path='./qbert',
name_prefix=config["env_name"]),
]
)
model.save("ppo-QbertNoFrameskip-v4.zip")
push_to_hub(repo_id="ThomasSimonini/ppo-QbertNoFrameskip-v4",
filename="ppo-QbertNoFrameskip-v4.zip",
commit_message="Added Qbert trained agent")
```
|
{"tags": ["deep-reinforcement-learning", "reinforcement-learning", "stable-baselines3", "atari"], "model-index": [{"name": "PPO Agent", "results": [{"task": {"type": "reinforcement-learning"}, "dataset": {"name": "QbertNoFrameskip-v4", "type": "QbertNoFrameskip-v4"}, "metrics": [{"type": "mean_reward", "value": "15685.00 +/- 115.217"}]}]}]}
|
ThomasSimonini/ppo-QbertNoFrameskip-v4
| null |
[
"stable-baselines3",
"deep-reinforcement-learning",
"reinforcement-learning",
"atari",
"model-index",
"has_space",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[] |
TAGS
#stable-baselines3 #deep-reinforcement-learning #reinforcement-learning #atari #model-index #has_space #region-us
|
# PPO Agent playing QbertNoFrameskip-v4
This is a trained model of a PPO agent playing QbertNoFrameskip-v4 using the stable-baselines3 library.
The training report: URL
## Evaluation Results
Mean_reward: '15685.00 +/- 115.217'
# Usage (with Stable-baselines3)
- You need to use 'gym==0.19' since it includes Atari Roms.
- The Action Space is 6 since we use only possible actions in this game.
Watch your agent interacts :
## Training Code
|
[
"# PPO Agent playing QbertNoFrameskip-v4\nThis is a trained model of a PPO agent playing QbertNoFrameskip-v4 using the stable-baselines3 library.\n\nThe training report: URL",
"## Evaluation Results\nMean_reward: '15685.00 +/- 115.217'",
"# Usage (with Stable-baselines3)\n- You need to use 'gym==0.19' since it includes Atari Roms.\n- The Action Space is 6 since we use only possible actions in this game.\n\n\nWatch your agent interacts :",
"## Training Code"
] |
[
"TAGS\n#stable-baselines3 #deep-reinforcement-learning #reinforcement-learning #atari #model-index #has_space #region-us \n",
"# PPO Agent playing QbertNoFrameskip-v4\nThis is a trained model of a PPO agent playing QbertNoFrameskip-v4 using the stable-baselines3 library.\n\nThe training report: URL",
"## Evaluation Results\nMean_reward: '15685.00 +/- 115.217'",
"# Usage (with Stable-baselines3)\n- You need to use 'gym==0.19' since it includes Atari Roms.\n- The Action Space is 6 since we use only possible actions in this game.\n\n\nWatch your agent interacts :",
"## Training Code"
] |
reinforcement-learning
|
stable-baselines3
|
# PPO Agent playing SeaquestNoFrameskip-v4
This is a trained model of a **PPO agent playing SeaquestNoFrameskip-v4 using the [stable-baselines3 library](https://stable-baselines3.readthedocs.io/en/master/index.html)**.
The training report: https://wandb.ai/simoninithomas/HFxSB3/reports/Atari-HFxSB3-Benchmark--VmlldzoxNjI3NTIy
## Evaluation Results
Mean_reward: `1820.00 +/- 20.0`
# Usage (with Stable-baselines3)
- You need to use `gym==0.19` since it **includes Atari Roms**.
- The Action Space is 6 since we use only **possible actions in this game**.
Watch your agent interacts :
```python
# Import the libraries
import os
import gym
from stable_baselines3 import PPO
from stable_baselines3.common.vec_env import VecNormalize
from stable_baselines3.common.env_util import make_atari_env
from stable_baselines3.common.vec_env import VecFrameStack
from huggingface_sb3 import load_from_hub, push_to_hub
# Load the model
checkpoint = load_from_hub("ThomasSimonini/ppo-SeaquestNoFrameskip-v4", "ppo-SeaquestNoFrameskip-v4.zip")
# Because we using 3.7 on Colab and this agent was trained with 3.8 to avoid Pickle errors:
custom_objects = {
"learning_rate": 0.0,
"lr_schedule": lambda _: 0.0,
"clip_range": lambda _: 0.0,
}
model= PPO.load(checkpoint, custom_objects=custom_objects)
env = make_atari_env('SeaquestNoFrameskip-v4', n_envs=1)
env = VecFrameStack(env, n_stack=4)
obs = env.reset()
while True:
action, _states = model.predict(obs)
obs, rewards, dones, info = env.step(action)
env.render()
```
## Training Code
```python
import wandb
import gym
from stable_baselines3 import PPO
from stable_baselines3.common.env_util import make_atari_env
from stable_baselines3.common.vec_env import VecFrameStack, VecVideoRecorder
from stable_baselines3.common.callbacks import CheckpointCallback
from wandb.integration.sb3 import WandbCallback
from huggingface_sb3 import load_from_hub, push_to_hub
config = {
"env_name": "SeaquestNoFrameskip-v4",
"num_envs": 8,
"total_timesteps": int(10e6),
"seed": 2862830927,
}
run = wandb.init(
project="HFxSB3",
config = config,
sync_tensorboard = True, # Auto-upload sb3's tensorboard metrics
monitor_gym = True, # Auto-upload the videos of agents playing the game
save_code = True, # Save the code to W&B
)
# There already exists an environment generator
# that will make and wrap atari environments correctly.
# Here we are also multi-worker training (n_envs=8 => 8 environments)
env = make_atari_env(config["env_name"], n_envs=config["num_envs"], seed=config["seed"]) #SeaquestNoFrameskip-v4
print("ENV ACTION SPACE: ", env.action_space.n)
# Frame-stacking with 4 frames
env = VecFrameStack(env, n_stack=4)
# Video recorder
env = VecVideoRecorder(env, "videos", record_video_trigger=lambda x: x % 100000 == 0, video_length=2000)
model = PPO(policy = "CnnPolicy",
env = env,
batch_size = 256,
clip_range = 0.1,
ent_coef = 0.01,
gae_lambda = 0.9,
gamma = 0.99,
learning_rate = 2.5e-4,
max_grad_norm = 0.5,
n_epochs = 4,
n_steps = 128,
vf_coef = 0.5,
tensorboard_log = f"runs",
verbose=1,
)
model.learn(
total_timesteps = config["total_timesteps"],
callback = [
WandbCallback(
gradient_save_freq = 1000,
model_save_path = f"models/{run.id}",
),
CheckpointCallback(save_freq=10000, save_path='./seaquest',
name_prefix=config["env_name"]),
]
)
model.save("ppo-SeaquestNoFrameskip-v4.zip")
push_to_hub(repo_id="ThomasSimonini/ppo-SeaquestNoFrameskip-v4",
filename="ppo-SeaquestNoFrameskip-v4.zip",
commit_message="Added Seaquest trained agent")
```
|
{"tags": ["deep-reinforcement-learning", "reinforcement-learning", "stable-baselines3", "atari"], "model-index": [{"name": "PPO Agent", "results": [{"task": {"type": "reinforcement-learning"}, "dataset": {"name": "SeaquestNoFrameskip-v4", "type": "SeaquestNoFrameskip-v4"}, "metrics": [{"type": "mean_reward", "value": "1820.00 +/- 20.0"}]}]}]}
|
ThomasSimonini/ppo-SeaquestNoFrameskip-v4
| null |
[
"stable-baselines3",
"deep-reinforcement-learning",
"reinforcement-learning",
"atari",
"model-index",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[] |
TAGS
#stable-baselines3 #deep-reinforcement-learning #reinforcement-learning #atari #model-index #region-us
|
# PPO Agent playing SeaquestNoFrameskip-v4
This is a trained model of a PPO agent playing SeaquestNoFrameskip-v4 using the stable-baselines3 library.
The training report: URL
## Evaluation Results
Mean_reward: '1820.00 +/- 20.0'
# Usage (with Stable-baselines3)
- You need to use 'gym==0.19' since it includes Atari Roms.
- The Action Space is 6 since we use only possible actions in this game.
Watch your agent interacts :
## Training Code
|
[
"# PPO Agent playing SeaquestNoFrameskip-v4\nThis is a trained model of a PPO agent playing SeaquestNoFrameskip-v4 using the stable-baselines3 library.\n\nThe training report: URL",
"## Evaluation Results\nMean_reward: '1820.00 +/- 20.0'",
"# Usage (with Stable-baselines3)\n- You need to use 'gym==0.19' since it includes Atari Roms.\n- The Action Space is 6 since we use only possible actions in this game.\n\n\nWatch your agent interacts :",
"## Training Code"
] |
[
"TAGS\n#stable-baselines3 #deep-reinforcement-learning #reinforcement-learning #atari #model-index #region-us \n",
"# PPO Agent playing SeaquestNoFrameskip-v4\nThis is a trained model of a PPO agent playing SeaquestNoFrameskip-v4 using the stable-baselines3 library.\n\nThe training report: URL",
"## Evaluation Results\nMean_reward: '1820.00 +/- 20.0'",
"# Usage (with Stable-baselines3)\n- You need to use 'gym==0.19' since it includes Atari Roms.\n- The Action Space is 6 since we use only possible actions in this game.\n\n\nWatch your agent interacts :",
"## Training Code"
] |
reinforcement-learning
|
stable-baselines3
|
# ThomasSimonini/ppo-SpaceInvadersNoFrameskip-v4
This is a pre-trained model of a PPO agent playing SpaceInvadersNoFrameskip using the [stable-baselines3](https://github.com/DLR-RM/stable-baselines3) library. It is taken from [RL-trained-agents](https://github.com/DLR-RM/rl-trained-agents)
### Usage (with Stable-baselines3)
Using this model becomes easy when you have stable-baselines3 and huggingface_sb3 installed:
```
pip install stable-baselines3
pip install huggingface_sb3
```
Then, you can use the model like this:
```python
import gym
from huggingface_sb3 import load_from_hub
from stable_baselines3 import PPO
from stable_baselines3.common.evaluation import evaluate_policy
from stable_baselines3.common.env_util import make_atari_env
from stable_baselines3.common.vec_env import VecFrameStack
# Retrieve the model from the hub
## repo_id = id of the model repository from the Hugging Face Hub (repo_id = {organization}/{repo_name})
## filename = name of the model zip file from the repository
checkpoint = load_from_hub(repo_id="ThomasSimonini/ppo-SpaceInvadersNoFrameskip-v4", filename="ppo-SpaceInvadersNoFrameskip-v4.zip")
model = PPO.load(checkpoint)
```
### Evaluation Results
Mean_reward: 627.160 (162 eval episodes)
|
{"tags": ["deep-reinforcement-learning", "reinforcement-learning", "stable-baselines3"]}
|
ThomasSimonini/ppo-SpaceInvadersNoFrameskip-v4
| null |
[
"stable-baselines3",
"deep-reinforcement-learning",
"reinforcement-learning",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[] |
TAGS
#stable-baselines3 #deep-reinforcement-learning #reinforcement-learning #region-us
|
# ThomasSimonini/ppo-SpaceInvadersNoFrameskip-v4
This is a pre-trained model of a PPO agent playing SpaceInvadersNoFrameskip using the stable-baselines3 library. It is taken from RL-trained-agents
### Usage (with Stable-baselines3)
Using this model becomes easy when you have stable-baselines3 and huggingface_sb3 installed:
Then, you can use the model like this:
### Evaluation Results
Mean_reward: 627.160 (162 eval episodes)
|
[
"# ThomasSimonini/ppo-SpaceInvadersNoFrameskip-v4\n\nThis is a pre-trained model of a PPO agent playing SpaceInvadersNoFrameskip using the stable-baselines3 library. It is taken from RL-trained-agents",
"### Usage (with Stable-baselines3)\nUsing this model becomes easy when you have stable-baselines3 and huggingface_sb3 installed:\n\n\nThen, you can use the model like this:",
"### Evaluation Results\nMean_reward: 627.160 (162 eval episodes)"
] |
[
"TAGS\n#stable-baselines3 #deep-reinforcement-learning #reinforcement-learning #region-us \n",
"# ThomasSimonini/ppo-SpaceInvadersNoFrameskip-v4\n\nThis is a pre-trained model of a PPO agent playing SpaceInvadersNoFrameskip using the stable-baselines3 library. It is taken from RL-trained-agents",
"### Usage (with Stable-baselines3)\nUsing this model becomes easy when you have stable-baselines3 and huggingface_sb3 installed:\n\n\nThen, you can use the model like this:",
"### Evaluation Results\nMean_reward: 627.160 (162 eval episodes)"
] |
reinforcement-learning
|
stable-baselines3
|
# **PPO** Agent playing **Walker2DBulletEnv-v0**
This is a trained model of a **PPO** agent playing **Walker2DBulletEnv-v0**
using the [stable-baselines3 library](https://github.com/DLR-RM/stable-baselines3).
## Usage (with Stable-baselines3)
TODO: Add your code
```python
from stable_baselines3 import ...
from huggingface_sb3 import load_from_hub
...
```
|
{"library_name": "stable-baselines3", "tags": ["Walker2DBulletEnv-v0", "deep-reinforcement-learning", "reinforcement-learning", "stable-baselines3"], "model-index": [{"name": "PPO", "results": [{"task": {"type": "reinforcement-learning", "name": "reinforcement-learning"}, "dataset": {"name": "Walker2DBulletEnv-v0", "type": "Walker2DBulletEnv-v0"}, "metrics": [{"type": "mean_reward", "value": "29.51 +/- 2.93", "name": "mean_reward"}]}]}]}
|
ThomasSimonini/ppo-Walker2DBulletEnv-v0
| null |
[
"stable-baselines3",
"Walker2DBulletEnv-v0",
"deep-reinforcement-learning",
"reinforcement-learning",
"model-index",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[] |
TAGS
#stable-baselines3 #Walker2DBulletEnv-v0 #deep-reinforcement-learning #reinforcement-learning #model-index #region-us
|
# PPO Agent playing Walker2DBulletEnv-v0
This is a trained model of a PPO agent playing Walker2DBulletEnv-v0
using the stable-baselines3 library.
## Usage (with Stable-baselines3)
TODO: Add your code
|
[
"# PPO Agent playing Walker2DBulletEnv-v0\nThis is a trained model of a PPO agent playing Walker2DBulletEnv-v0\nusing the stable-baselines3 library.",
"## Usage (with Stable-baselines3)\nTODO: Add your code"
] |
[
"TAGS\n#stable-baselines3 #Walker2DBulletEnv-v0 #deep-reinforcement-learning #reinforcement-learning #model-index #region-us \n",
"# PPO Agent playing Walker2DBulletEnv-v0\nThis is a trained model of a PPO agent playing Walker2DBulletEnv-v0\nusing the stable-baselines3 library.",
"## Usage (with Stable-baselines3)\nTODO: Add your code"
] |
reinforcement-learning
| null |
model-index:
- name: stable-baselines3-ppo-LunarLander-v2
---
# ARCHIVED MODEL, DO NOT USE IT
# stable-baselines3-ppo-LunarLander-v2 🚀👩🚀
This is a saved model of a PPO agent playing [LunarLander-v2](https://gym.openai.com/envs/LunarLander-v2/). The model is taken from [rl-baselines3-zoo](https://github.com/DLR-RM/rl-trained-agents)
The goal is to correctly land the lander by controlling firing engines (fire left orientation engine, fire main engine and fire right orientation engine).
<iframe width="560" height="315" src="https://www.youtube.com/embed/kE-Fvht81I0" title="YouTube video player" frameborder="0" allow="accelerometer; autoplay; clipboard-write; encrypted-media; gyroscope; picture-in-picture" allowfullscreen></iframe>
👉 You can watch the agent playing by using this [notebook](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/19OonMRkMyCH6Dg0ECFQi7evxMRqkW3U0?usp=sharing)
## Use the Model
### Install the dependencies
You need to use the [Stable Baselines 3 Hugging Face version](https://github.com/simoninithomas/stable-baselines3) of the library (this version contains the function to load saved models directly from the Hugging Face Hub):
```
pip install git+https://github.com/simoninithomas/stable-baselines3.git
```
### Evaluate the agent
⚠️You need to have Linux or MacOS to be able to use this environment. If it's not the case you can use the [colab notebook](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/19OonMRkMyCH6Dg0ECFQi7evxMRqkW3U0#scrollTo=Qbzj9quh0FsP)
```
# Import the libraries
import gym
from stable_baselines3 import PPO
from stable_baselines3.common.evaluation import evaluate_policy
# Load the environment
env = gym.make('LunarLander-v2')
model = PPO.load_from_huggingface(hf_model_id="ThomasSimonini/stable-baselines3-ppo-LunarLander-v2",hf_model_filename="LunarLander-v2")
# Evaluate the agent
eval_env = gym.make('LunarLander-v2')
mean_reward, std_reward = evaluate_policy(model, eval_env, n_eval_episodes=10, deterministic=True)
print(f"mean_reward={mean_reward:.2f} +/- {std_reward}")
# Watch the agent play
obs = env.reset()
for i in range(1000):
action, _state = model.predict(obs)
obs, reward, done, info = env.step(action)
env.render()
if done:
obs = env.reset()
```
## Results
Mean Reward (10 evaluation episodes): 245.63 +/- 10.02
|
{"license": "apache-2.0", "tags": ["deep-reinforcement-learning", "reinforcement-learning"]}
|
ThomasSimonini/stable-baselines3-ppo-LunarLander-v2
| null |
[
"deep-reinforcement-learning",
"reinforcement-learning",
"license:apache-2.0",
"has_space",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[] |
TAGS
#deep-reinforcement-learning #reinforcement-learning #license-apache-2.0 #has_space #region-us
|
model-index:
- name: stable-baselines3-ppo-LunarLander-v2
---
# ARCHIVED MODEL, DO NOT USE IT
# stable-baselines3-ppo-LunarLander-v2
This is a saved model of a PPO agent playing LunarLander-v2. The model is taken from rl-baselines3-zoo
The goal is to correctly land the lander by controlling firing engines (fire left orientation engine, fire main engine and fire right orientation engine).
<iframe width="560" height="315" src="URL title="YouTube video player" frameborder="0" allow="accelerometer; autoplay; clipboard-write; encrypted-media; gyroscope; picture-in-picture" allowfullscreen></iframe>
You can watch the agent playing by using this notebook
## Use the Model
### Install the dependencies
You need to use the Stable Baselines 3 Hugging Face version of the library (this version contains the function to load saved models directly from the Hugging Face Hub):
### Evaluate the agent
️You need to have Linux or MacOS to be able to use this environment. If it's not the case you can use the colab notebook
## Results
Mean Reward (10 evaluation episodes): 245.63 +/- 10.02
|
[
"# ARCHIVED MODEL, DO NOT USE IT",
"# stable-baselines3-ppo-LunarLander-v2 \nThis is a saved model of a PPO agent playing LunarLander-v2. The model is taken from rl-baselines3-zoo\n\nThe goal is to correctly land the lander by controlling firing engines (fire left orientation engine, fire main engine and fire right orientation engine).\n\n<iframe width=\"560\" height=\"315\" src=\"URL title=\"YouTube video player\" frameborder=\"0\" allow=\"accelerometer; autoplay; clipboard-write; encrypted-media; gyroscope; picture-in-picture\" allowfullscreen></iframe>\n\n You can watch the agent playing by using this notebook",
"## Use the Model",
"### Install the dependencies\nYou need to use the Stable Baselines 3 Hugging Face version of the library (this version contains the function to load saved models directly from the Hugging Face Hub):",
"### Evaluate the agent\n️You need to have Linux or MacOS to be able to use this environment. If it's not the case you can use the colab notebook",
"## Results\nMean Reward (10 evaluation episodes): 245.63 +/- 10.02"
] |
[
"TAGS\n#deep-reinforcement-learning #reinforcement-learning #license-apache-2.0 #has_space #region-us \n",
"# ARCHIVED MODEL, DO NOT USE IT",
"# stable-baselines3-ppo-LunarLander-v2 \nThis is a saved model of a PPO agent playing LunarLander-v2. The model is taken from rl-baselines3-zoo\n\nThe goal is to correctly land the lander by controlling firing engines (fire left orientation engine, fire main engine and fire right orientation engine).\n\n<iframe width=\"560\" height=\"315\" src=\"URL title=\"YouTube video player\" frameborder=\"0\" allow=\"accelerometer; autoplay; clipboard-write; encrypted-media; gyroscope; picture-in-picture\" allowfullscreen></iframe>\n\n You can watch the agent playing by using this notebook",
"## Use the Model",
"### Install the dependencies\nYou need to use the Stable Baselines 3 Hugging Face version of the library (this version contains the function to load saved models directly from the Hugging Face Hub):",
"### Evaluate the agent\n️You need to have Linux or MacOS to be able to use this environment. If it's not the case you can use the colab notebook",
"## Results\nMean Reward (10 evaluation episodes): 245.63 +/- 10.02"
] |
text2text-generation
|
transformers
|
# t5-end2end-question-generation
This model is a fine-tuned version of [t5-base](https://huggingface.co/t5-base) on the squad dataset to generate questions based on a context.
👉 If you want to learn how to fine-tune the t5 model to do the same, you can follow this [tutorial](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1z-Zl2hftMrFXabYfmz8o9YZpgYx6sGeW?usp=sharing)
For instance:
```
Context: "Python is an interpreted, high-level, general-purpose programming language. Created by Guido van Rossum and first released in 1991, Python's design philosophy emphasizes code readability with its notable use of significant whitespace."
```
```
Questions:
Who created Python?,
When was Python first released?
What is Python's design philosophy?
```
It achieves the following results on the evaluation set:
- Loss: 1.5691
## Use the Model
```
from transformers import T5ForConditionalGeneration, T5TokenizerFast
hfmodel = T5ForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained("ThomasSimonini/t5-end2end-question-generation")
text= "The abolition of feudal privileges by the National Constituent Assembly on 4 August 1789 and the Declaration \\nof the Rights of Man and of the Citizen (La Déclaration des Droits de l'Homme et du Citoyen), drafted by Lafayette \\nwith the help of Thomas Jefferson and adopted on 26 August, paved the way to a Constitutional Monarchy \\n(4 September 1791 – 21 September 1792). Despite these dramatic changes, life at the court continued, while the situation \\nin Paris was becoming critical because of bread shortages in September. On 5 October 1789, a crowd from Paris descended upon Versailles \\nand forced the royal family to move to the Tuileries Palace in Paris, where they lived under a form of house arrest under \\nthe watch of Lafayette's Garde Nationale, while the Comte de Provence and his wife were allowed to reside in the \\nPetit Luxembourg, where they remained until they went into exile on 20 June 1791."
def run_model(input_string, **generator_args):
generator_args = {
"max_length": 256,
"num_beams": 4,
"length_penalty": 1.5,
"no_repeat_ngram_size": 3,
"early_stopping": True,
}
input_string = "generate questions: " + input_string + " </s>"
input_ids = tokenizer.encode(input_string, return_tensors="pt")
res = hfmodel.generate(input_ids, **generator_args)
output = tokenizer.batch_decode(res, skip_special_tokens=True)
output = [item.split("<sep>") for item in output]
return output
run_model(text)
=> [['When did the National Constituent Assembly abolish feudal privileges?',
' Who drafted the Declaration of the Rights of Man and of the Citizen?',
' When was the Constitutional Monarchy established?',
' What was the name of the Declaration that paved the way to a constitutional monarchy?',
'']]
```
### Training hyperparameters
The following hyperparameters were used during training:
- learning_rate: 0.0001
- train_batch_size: 4
- eval_batch_size: 4
- seed: 42
- gradient_accumulation_steps: 16
- total_train_batch_size: 64
- optimizer: Adam with betas=(0.9,0.999) and epsilon=1e-08
- lr_scheduler_type: linear
- num_epochs: 7
### Training results
| Training Loss | Epoch | Step | Validation Loss |
|:-------------:|:-----:|:----:|:---------------:|
| 2.5834 | 0.34 | 100 | 1.9107 |
| 1.9642 | 0.68 | 200 | 1.7227 |
| 1.8526 | 1.02 | 300 | 1.6627 |
| 1.7383 | 1.36 | 400 | 1.6354 |
| 1.7223 | 1.69 | 500 | 1.6154 |
| 1.6871 | 2.03 | 600 | 1.6096 |
| 1.6309 | 2.37 | 700 | 1.6048 |
| 1.6242 | 2.71 | 800 | 1.5923 |
| 1.6226 | 3.05 | 900 | 1.5855 |
| 1.5645 | 3.39 | 1000 | 1.5874 |
| 1.5705 | 3.73 | 1100 | 1.5822 |
| 1.5543 | 4.07 | 1200 | 1.5817 |
| 1.5284 | 4.41 | 1300 | 1.5841 |
| 1.5275 | 4.75 | 1400 | 1.5741 |
| 1.5269 | 5.08 | 1500 | 1.5715 |
| 1.5079 | 5.42 | 1600 | 1.5701 |
| 1.4876 | 5.76 | 1700 | 1.5754 |
| 1.498 | 6.1 | 1800 | 1.5699 |
| 1.4852 | 6.44 | 1900 | 1.5693 |
| 1.4776 | 6.78 | 2000 | 1.5691 |
### Framework versions
- Transformers 4.10.3
- Pytorch 1.9.0+cu102
- Datasets 1.12.1
- Tokenizers 0.10.3
|
{"license": "apache-2.0", "tags": ["generated_from_trainer"], "datasets": ["squad"]}
|
ThomasSimonini/t5-end2end-question-generation
| null |
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"t5",
"text2text-generation",
"generated_from_trainer",
"dataset:squad",
"license:apache-2.0",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"has_space",
"text-generation-inference",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[] |
TAGS
#transformers #pytorch #t5 #text2text-generation #generated_from_trainer #dataset-squad #license-apache-2.0 #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #has_space #text-generation-inference #region-us
|
t5-end2end-question-generation
==============================
This model is a fine-tuned version of t5-base on the squad dataset to generate questions based on a context.
If you want to learn how to fine-tune the t5 model to do the same, you can follow this tutorial
For instance:
It achieves the following results on the evaluation set:
* Loss: 1.5691
Use the Model
-------------
### Training hyperparameters
The following hyperparameters were used during training:
* learning\_rate: 0.0001
* train\_batch\_size: 4
* eval\_batch\_size: 4
* seed: 42
* gradient\_accumulation\_steps: 16
* total\_train\_batch\_size: 64
* optimizer: Adam with betas=(0.9,0.999) and epsilon=1e-08
* lr\_scheduler\_type: linear
* num\_epochs: 7
### Training results
### Framework versions
* Transformers 4.10.3
* Pytorch 1.9.0+cu102
* Datasets 1.12.1
* Tokenizers 0.10.3
|
[
"### Training hyperparameters\n\n\nThe following hyperparameters were used during training:\n\n\n* learning\\_rate: 0.0001\n* train\\_batch\\_size: 4\n* eval\\_batch\\_size: 4\n* seed: 42\n* gradient\\_accumulation\\_steps: 16\n* total\\_train\\_batch\\_size: 64\n* optimizer: Adam with betas=(0.9,0.999) and epsilon=1e-08\n* lr\\_scheduler\\_type: linear\n* num\\_epochs: 7",
"### Training results",
"### Framework versions\n\n\n* Transformers 4.10.3\n* Pytorch 1.9.0+cu102\n* Datasets 1.12.1\n* Tokenizers 0.10.3"
] |
[
"TAGS\n#transformers #pytorch #t5 #text2text-generation #generated_from_trainer #dataset-squad #license-apache-2.0 #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #has_space #text-generation-inference #region-us \n",
"### Training hyperparameters\n\n\nThe following hyperparameters were used during training:\n\n\n* learning\\_rate: 0.0001\n* train\\_batch\\_size: 4\n* eval\\_batch\\_size: 4\n* seed: 42\n* gradient\\_accumulation\\_steps: 16\n* total\\_train\\_batch\\_size: 64\n* optimizer: Adam with betas=(0.9,0.999) and epsilon=1e-08\n* lr\\_scheduler\\_type: linear\n* num\\_epochs: 7",
"### Training results",
"### Framework versions\n\n\n* Transformers 4.10.3\n* Pytorch 1.9.0+cu102\n* Datasets 1.12.1\n* Tokenizers 0.10.3"
] |
text-generation
|
transformers
|
# Harry Potter DialoGPT Model
|
{"tags": ["conversational"]}
|
ThoracicCosine/DialoGPT-small-harrypotter
| null |
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"gpt2",
"text-generation",
"conversational",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"text-generation-inference",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[] |
TAGS
#transformers #pytorch #gpt2 #text-generation #conversational #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #text-generation-inference #region-us
|
# Harry Potter DialoGPT Model
|
[
"# Harry Potter DialoGPT Model"
] |
[
"TAGS\n#transformers #pytorch #gpt2 #text-generation #conversational #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #text-generation-inference #region-us \n",
"# Harry Potter DialoGPT Model"
] |
text-generation
|
transformers
|
#Michael DialoGPT Model
|
{"tags": ["conversational"]}
|
Tidum/DialoGPT-large-Michael
| null |
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"gpt2",
"text-generation",
"conversational",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"text-generation-inference",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[] |
TAGS
#transformers #pytorch #gpt2 #text-generation #conversational #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #text-generation-inference #region-us
|
#Michael DialoGPT Model
|
[] |
[
"TAGS\n#transformers #pytorch #gpt2 #text-generation #conversational #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #text-generation-inference #region-us \n"
] |
token-classification
|
transformers
|
<!-- This model card has been generated automatically according to the information the Trainer had access to. You
should probably proofread and complete it, then remove this comment. -->
# IceBERT-finetuned-ner
This model is a fine-tuned version of [vesteinn/IceBERT](https://huggingface.co/vesteinn/IceBERT) on the mim_gold_ner dataset.
It achieves the following results on the evaluation set:
- Loss: 0.0772
- Precision: 0.8920
- Recall: 0.8656
- F1: 0.8786
- Accuracy: 0.9855
## Model description
More information needed
## Intended uses & limitations
More information needed
## Training and evaluation data
More information needed
## Training procedure
### Training hyperparameters
The following hyperparameters were used during training:
- learning_rate: 2e-05
- train_batch_size: 16
- eval_batch_size: 16
- seed: 42
- optimizer: Adam with betas=(0.9,0.999) and epsilon=1e-08
- lr_scheduler_type: linear
- num_epochs: 3
### Training results
| Training Loss | Epoch | Step | Validation Loss | Precision | Recall | F1 | Accuracy |
|:-------------:|:-----:|:----:|:---------------:|:---------:|:------:|:------:|:--------:|
| 0.0519 | 1.0 | 2904 | 0.0731 | 0.8700 | 0.8564 | 0.8631 | 0.9832 |
| 0.026 | 2.0 | 5808 | 0.0749 | 0.8771 | 0.8540 | 0.8654 | 0.9840 |
| 0.0159 | 3.0 | 8712 | 0.0772 | 0.8920 | 0.8656 | 0.8786 | 0.9855 |
### Framework versions
- Transformers 4.11.2
- Pytorch 1.9.0+cu102
- Datasets 1.12.1
- Tokenizers 0.10.3
|
{"license": "gpl-3.0", "tags": ["generated_from_trainer"], "datasets": ["mim_gold_ner"], "metrics": ["precision", "recall", "f1", "accuracy"], "model-index": [{"name": "IceBERT-finetuned-ner", "results": [{"task": {"type": "token-classification", "name": "Token Classification"}, "dataset": {"name": "mim_gold_ner", "type": "mim_gold_ner", "args": "mim-gold-ner"}, "metrics": [{"type": "precision", "value": 0.8920083733530353, "name": "Precision"}, {"type": "recall", "value": 0.8655753375552635, "name": "Recall"}, {"type": "f1", "value": 0.8785930867192238, "name": "F1"}, {"type": "accuracy", "value": 0.9855436530476731, "name": "Accuracy"}]}]}]}
|
Titantoe/IceBERT-finetuned-ner
| null |
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"tensorboard",
"roberta",
"token-classification",
"generated_from_trainer",
"dataset:mim_gold_ner",
"license:gpl-3.0",
"model-index",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[] |
TAGS
#transformers #pytorch #tensorboard #roberta #token-classification #generated_from_trainer #dataset-mim_gold_ner #license-gpl-3.0 #model-index #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #region-us
|
IceBERT-finetuned-ner
=====================
This model is a fine-tuned version of vesteinn/IceBERT on the mim\_gold\_ner dataset.
It achieves the following results on the evaluation set:
* Loss: 0.0772
* Precision: 0.8920
* Recall: 0.8656
* F1: 0.8786
* Accuracy: 0.9855
Model description
-----------------
More information needed
Intended uses & limitations
---------------------------
More information needed
Training and evaluation data
----------------------------
More information needed
Training procedure
------------------
### Training hyperparameters
The following hyperparameters were used during training:
* learning\_rate: 2e-05
* train\_batch\_size: 16
* eval\_batch\_size: 16
* seed: 42
* optimizer: Adam with betas=(0.9,0.999) and epsilon=1e-08
* lr\_scheduler\_type: linear
* num\_epochs: 3
### Training results
### Framework versions
* Transformers 4.11.2
* Pytorch 1.9.0+cu102
* Datasets 1.12.1
* Tokenizers 0.10.3
|
[
"### Training hyperparameters\n\n\nThe following hyperparameters were used during training:\n\n\n* learning\\_rate: 2e-05\n* train\\_batch\\_size: 16\n* eval\\_batch\\_size: 16\n* seed: 42\n* optimizer: Adam with betas=(0.9,0.999) and epsilon=1e-08\n* lr\\_scheduler\\_type: linear\n* num\\_epochs: 3",
"### Training results",
"### Framework versions\n\n\n* Transformers 4.11.2\n* Pytorch 1.9.0+cu102\n* Datasets 1.12.1\n* Tokenizers 0.10.3"
] |
[
"TAGS\n#transformers #pytorch #tensorboard #roberta #token-classification #generated_from_trainer #dataset-mim_gold_ner #license-gpl-3.0 #model-index #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #region-us \n",
"### Training hyperparameters\n\n\nThe following hyperparameters were used during training:\n\n\n* learning\\_rate: 2e-05\n* train\\_batch\\_size: 16\n* eval\\_batch\\_size: 16\n* seed: 42\n* optimizer: Adam with betas=(0.9,0.999) and epsilon=1e-08\n* lr\\_scheduler\\_type: linear\n* num\\_epochs: 3",
"### Training results",
"### Framework versions\n\n\n* Transformers 4.11.2\n* Pytorch 1.9.0+cu102\n* Datasets 1.12.1\n* Tokenizers 0.10.3"
] |
token-classification
|
transformers
|
<!-- This model card has been generated automatically according to the information the Trainer had access to. You
should probably proofread and complete it, then remove this comment. -->
# XLMR-ENIS-finetuned-ner
This model is a fine-tuned version of [vesteinn/XLMR-ENIS](https://huggingface.co/vesteinn/XLMR-ENIS) on the mim_gold_ner dataset.
It achieves the following results on the evaluation set:
- Loss: 0.0941
- Precision: 0.8714
- Recall: 0.8450
- F1: 0.8580
- Accuracy: 0.9827
## Model description
More information needed
## Intended uses & limitations
More information needed
## Training and evaluation data
More information needed
## Training procedure
### Training hyperparameters
The following hyperparameters were used during training:
- learning_rate: 2e-05
- train_batch_size: 16
- eval_batch_size: 16
- seed: 42
- optimizer: Adam with betas=(0.9,0.999) and epsilon=1e-08
- lr_scheduler_type: linear
- num_epochs: 3
### Training results
| Training Loss | Epoch | Step | Validation Loss | Precision | Recall | F1 | Accuracy |
|:-------------:|:-----:|:----:|:---------------:|:---------:|:------:|:------:|:--------:|
| 0.0572 | 1.0 | 2904 | 0.0998 | 0.8586 | 0.8171 | 0.8373 | 0.9802 |
| 0.0313 | 2.0 | 5808 | 0.0868 | 0.8666 | 0.8288 | 0.8473 | 0.9822 |
| 0.0199 | 3.0 | 8712 | 0.0941 | 0.8714 | 0.8450 | 0.8580 | 0.9827 |
### Framework versions
- Transformers 4.11.2
- Pytorch 1.9.0+cu102
- Datasets 1.12.1
- Tokenizers 0.10.3
|
{"license": "agpl-3.0", "tags": ["generated_from_trainer"], "datasets": ["mim_gold_ner"], "metrics": ["precision", "recall", "f1", "accuracy"], "model-index": [{"name": "XLMR-ENIS-finetuned-ner", "results": [{"task": {"type": "token-classification", "name": "Token Classification"}, "dataset": {"name": "mim_gold_ner", "type": "mim_gold_ner", "args": "mim-gold-ner"}, "metrics": [{"type": "precision", "value": 0.8713799976550592, "name": "Precision"}, {"type": "recall", "value": 0.8450255827174531, "name": "Recall"}, {"type": "f1", "value": 0.8580004617871162, "name": "F1"}, {"type": "accuracy", "value": 0.9827265378338392, "name": "Accuracy"}]}]}]}
|
Titantoe/XLMR-ENIS-finetuned-ner
| null |
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"tensorboard",
"xlm-roberta",
"token-classification",
"generated_from_trainer",
"dataset:mim_gold_ner",
"license:agpl-3.0",
"model-index",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[] |
TAGS
#transformers #pytorch #tensorboard #xlm-roberta #token-classification #generated_from_trainer #dataset-mim_gold_ner #license-agpl-3.0 #model-index #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #region-us
|
XLMR-ENIS-finetuned-ner
=======================
This model is a fine-tuned version of vesteinn/XLMR-ENIS on the mim\_gold\_ner dataset.
It achieves the following results on the evaluation set:
* Loss: 0.0941
* Precision: 0.8714
* Recall: 0.8450
* F1: 0.8580
* Accuracy: 0.9827
Model description
-----------------
More information needed
Intended uses & limitations
---------------------------
More information needed
Training and evaluation data
----------------------------
More information needed
Training procedure
------------------
### Training hyperparameters
The following hyperparameters were used during training:
* learning\_rate: 2e-05
* train\_batch\_size: 16
* eval\_batch\_size: 16
* seed: 42
* optimizer: Adam with betas=(0.9,0.999) and epsilon=1e-08
* lr\_scheduler\_type: linear
* num\_epochs: 3
### Training results
### Framework versions
* Transformers 4.11.2
* Pytorch 1.9.0+cu102
* Datasets 1.12.1
* Tokenizers 0.10.3
|
[
"### Training hyperparameters\n\n\nThe following hyperparameters were used during training:\n\n\n* learning\\_rate: 2e-05\n* train\\_batch\\_size: 16\n* eval\\_batch\\_size: 16\n* seed: 42\n* optimizer: Adam with betas=(0.9,0.999) and epsilon=1e-08\n* lr\\_scheduler\\_type: linear\n* num\\_epochs: 3",
"### Training results",
"### Framework versions\n\n\n* Transformers 4.11.2\n* Pytorch 1.9.0+cu102\n* Datasets 1.12.1\n* Tokenizers 0.10.3"
] |
[
"TAGS\n#transformers #pytorch #tensorboard #xlm-roberta #token-classification #generated_from_trainer #dataset-mim_gold_ner #license-agpl-3.0 #model-index #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #region-us \n",
"### Training hyperparameters\n\n\nThe following hyperparameters were used during training:\n\n\n* learning\\_rate: 2e-05\n* train\\_batch\\_size: 16\n* eval\\_batch\\_size: 16\n* seed: 42\n* optimizer: Adam with betas=(0.9,0.999) and epsilon=1e-08\n* lr\\_scheduler\\_type: linear\n* num\\_epochs: 3",
"### Training results",
"### Framework versions\n\n\n* Transformers 4.11.2\n* Pytorch 1.9.0+cu102\n* Datasets 1.12.1\n* Tokenizers 0.10.3"
] |
text-generation
|
transformers
|
# Mast DialoGPT Model
|
{"tags": ["conversational"]}
|
Toadally/DialoGPT-small-david_mast
| null |
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"gpt2",
"text-generation",
"conversational",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"text-generation-inference",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[] |
TAGS
#transformers #pytorch #gpt2 #text-generation #conversational #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #text-generation-inference #region-us
|
# Mast DialoGPT Model
|
[
"# Mast DialoGPT Model"
] |
[
"TAGS\n#transformers #pytorch #gpt2 #text-generation #conversational #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #text-generation-inference #region-us \n",
"# Mast DialoGPT Model"
] |
text-generation
|
transformers
|
# Boon 2 DialoGPT Model
|
{"tags": ["conversational"]}
|
Tofu05/DialoGPT-large-boon2
| null |
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"gpt2",
"text-generation",
"conversational",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"text-generation-inference",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[] |
TAGS
#transformers #pytorch #gpt2 #text-generation #conversational #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #text-generation-inference #region-us
|
# Boon 2 DialoGPT Model
|
[
"# Boon 2 DialoGPT Model"
] |
[
"TAGS\n#transformers #pytorch #gpt2 #text-generation #conversational #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #text-generation-inference #region-us \n",
"# Boon 2 DialoGPT Model"
] |
text-generation
|
transformers
|
# Boon Bot DialoGPT Model
|
{"tags": ["conversational"]}
|
Tofu05/DialoGPT-med-boon3
| null |
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"gpt2",
"text-generation",
"conversational",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"text-generation-inference",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[] |
TAGS
#transformers #pytorch #gpt2 #text-generation #conversational #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #text-generation-inference #region-us
|
# Boon Bot DialoGPT Model
|
[
"# Boon Bot DialoGPT Model"
] |
[
"TAGS\n#transformers #pytorch #gpt2 #text-generation #conversational #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #text-generation-inference #region-us \n",
"# Boon Bot DialoGPT Model"
] |
text-generation
|
transformers
|
# DialoGPT Model
|
{"tags": ["conversational"]}
|
TofuBoy/DialoGPT-medium-Yubin2
| null |
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"gpt2",
"text-generation",
"conversational",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"text-generation-inference",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[] |
TAGS
#transformers #pytorch #gpt2 #text-generation #conversational #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #text-generation-inference #region-us
|
# DialoGPT Model
|
[
"# DialoGPT Model"
] |
[
"TAGS\n#transformers #pytorch #gpt2 #text-generation #conversational #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #text-generation-inference #region-us \n",
"# DialoGPT Model"
] |
text-generation
|
transformers
|
# Boon Bot DialoGPT Model
|
{"tags": ["conversational"]}
|
TofuBoy/DialoGPT-medium-boon
| null |
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"gpt2",
"text-generation",
"conversational",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"text-generation-inference",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[] |
TAGS
#transformers #pytorch #gpt2 #text-generation #conversational #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #text-generation-inference #region-us
|
# Boon Bot DialoGPT Model
|
[
"# Boon Bot DialoGPT Model"
] |
[
"TAGS\n#transformers #pytorch #gpt2 #text-generation #conversational #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #text-generation-inference #region-us \n",
"# Boon Bot DialoGPT Model"
] |
text-classification
|
transformers
|
<!-- This model card has been generated automatically according to the information the Trainer had access to. You
should probably proofread and complete it, then remove this comment. -->
# xlm-roberta-base-finetuned-marc-en
This model is a fine-tuned version of [xlm-roberta-base](https://huggingface.co/xlm-roberta-base) on the amazon_reviews_multi dataset.
It achieves the following results on the evaluation set:
- Loss: 0.9237
- Mae: 0.5122
## Model description
More information needed
## Intended uses & limitations
More information needed
## Training and evaluation data
More information needed
## Training procedure
### Training hyperparameters
The following hyperparameters were used during training:
- learning_rate: 2e-05
- train_batch_size: 16
- eval_batch_size: 16
- seed: 42
- optimizer: Adam with betas=(0.9,0.999) and epsilon=1e-08
- lr_scheduler_type: linear
- num_epochs: 2
### Training results
| Training Loss | Epoch | Step | Validation Loss | Mae |
|:-------------:|:-----:|:----:|:---------------:|:------:|
| 1.1089 | 1.0 | 235 | 0.9380 | 0.4878 |
| 0.9546 | 2.0 | 470 | 0.9237 | 0.5122 |
### Framework versions
- Transformers 4.14.1
- Pytorch 1.10.0+cu111
- Datasets 1.16.1
- Tokenizers 0.10.3
|
{"license": "mit", "tags": ["generated_from_trainer"], "datasets": ["amazon_reviews_multi"], "model-index": [{"name": "xlm-roberta-base-finetuned-marc-en", "results": []}]}
|
TomO/xlm-roberta-base-finetuned-marc-en
| null |
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"tensorboard",
"xlm-roberta",
"text-classification",
"generated_from_trainer",
"dataset:amazon_reviews_multi",
"license:mit",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[] |
TAGS
#transformers #pytorch #tensorboard #xlm-roberta #text-classification #generated_from_trainer #dataset-amazon_reviews_multi #license-mit #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #region-us
|
xlm-roberta-base-finetuned-marc-en
==================================
This model is a fine-tuned version of xlm-roberta-base on the amazon\_reviews\_multi dataset.
It achieves the following results on the evaluation set:
* Loss: 0.9237
* Mae: 0.5122
Model description
-----------------
More information needed
Intended uses & limitations
---------------------------
More information needed
Training and evaluation data
----------------------------
More information needed
Training procedure
------------------
### Training hyperparameters
The following hyperparameters were used during training:
* learning\_rate: 2e-05
* train\_batch\_size: 16
* eval\_batch\_size: 16
* seed: 42
* optimizer: Adam with betas=(0.9,0.999) and epsilon=1e-08
* lr\_scheduler\_type: linear
* num\_epochs: 2
### Training results
### Framework versions
* Transformers 4.14.1
* Pytorch 1.10.0+cu111
* Datasets 1.16.1
* Tokenizers 0.10.3
|
[
"### Training hyperparameters\n\n\nThe following hyperparameters were used during training:\n\n\n* learning\\_rate: 2e-05\n* train\\_batch\\_size: 16\n* eval\\_batch\\_size: 16\n* seed: 42\n* optimizer: Adam with betas=(0.9,0.999) and epsilon=1e-08\n* lr\\_scheduler\\_type: linear\n* num\\_epochs: 2",
"### Training results",
"### Framework versions\n\n\n* Transformers 4.14.1\n* Pytorch 1.10.0+cu111\n* Datasets 1.16.1\n* Tokenizers 0.10.3"
] |
[
"TAGS\n#transformers #pytorch #tensorboard #xlm-roberta #text-classification #generated_from_trainer #dataset-amazon_reviews_multi #license-mit #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #region-us \n",
"### Training hyperparameters\n\n\nThe following hyperparameters were used during training:\n\n\n* learning\\_rate: 2e-05\n* train\\_batch\\_size: 16\n* eval\\_batch\\_size: 16\n* seed: 42\n* optimizer: Adam with betas=(0.9,0.999) and epsilon=1e-08\n* lr\\_scheduler\\_type: linear\n* num\\_epochs: 2",
"### Training results",
"### Framework versions\n\n\n* Transformers 4.14.1\n* Pytorch 1.10.0+cu111\n* Datasets 1.16.1\n* Tokenizers 0.10.3"
] |
text-classification
|
transformers
|
<!-- This model card has been generated automatically according to the information the Trainer had access to. You
should probably proofread and complete it, then remove this comment. -->
# TOMFINSEN
This model is a fine-tuned version of [deepmind/language-perceiver](https://huggingface.co/deepmind/language-perceiver) on the financial_phrasebank dataset.
It achieves the following results on the evaluation set:
- Loss: 0.3642
- Recall: 0.8986
- Accuracy: 0.8742
- Precision: 0.8510
## Model description
More information needed
## Intended uses & limitations
More information needed
## Training and evaluation data
More information needed
## Training procedure
### Training hyperparameters
The following hyperparameters were used during training:
- learning_rate: 2e-05
- train_batch_size: 16
- eval_batch_size: 16
- seed: 42
- distributed_type: tpu
- optimizer: Adam with betas=(0.9,0.999) and epsilon=1e-08
- lr_scheduler_type: linear
- num_epochs: 4
### Training results
| Training Loss | Epoch | Step | Validation Loss | Recall | Accuracy | Precision |
|:-------------:|:-----:|:----:|:---------------:|:------:|:--------:|:---------:|
| 0.5403 | 1.0 | 273 | 0.4207 | 0.8358 | 0.8619 | 0.8534 |
| 0.3939 | 2.0 | 546 | 0.3750 | 0.8943 | 0.8577 | 0.8225 |
| 0.1993 | 3.0 | 819 | 0.3113 | 0.8882 | 0.8660 | 0.8367 |
| 0.301 | 4.0 | 1092 | 0.3642 | 0.8986 | 0.8742 | 0.8510 |
### Framework versions
- Transformers 4.15.0
- Pytorch 1.9.0+cu102
- Datasets 1.17.0
- Tokenizers 0.10.3
|
{"license": "apache-2.0", "tags": ["generated_from_trainer"], "datasets": ["financial_phrasebank"], "metrics": ["recall", "accuracy", "precision"], "model-index": [{"name": "TOMFINSEN", "results": [{"task": {"type": "text-classification", "name": "Text Classification"}, "dataset": {"name": "financial_phrasebank", "type": "financial_phrasebank", "args": "sentences_50agree"}, "metrics": [{"type": "recall", "value": 0.8985861629736692, "name": "Recall"}, {"type": "accuracy", "value": 0.8742268041237113, "name": "Accuracy"}, {"type": "precision", "value": 0.8509995913451198, "name": "Precision"}]}]}]}
|
tomwetherell/TOMFINSEN
| null |
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"tensorboard",
"perceiver",
"text-classification",
"generated_from_trainer",
"dataset:financial_phrasebank",
"license:apache-2.0",
"model-index",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[] |
TAGS
#transformers #pytorch #tensorboard #perceiver #text-classification #generated_from_trainer #dataset-financial_phrasebank #license-apache-2.0 #model-index #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #region-us
|
TOMFINSEN
=========
This model is a fine-tuned version of deepmind/language-perceiver on the financial\_phrasebank dataset.
It achieves the following results on the evaluation set:
* Loss: 0.3642
* Recall: 0.8986
* Accuracy: 0.8742
* Precision: 0.8510
Model description
-----------------
More information needed
Intended uses & limitations
---------------------------
More information needed
Training and evaluation data
----------------------------
More information needed
Training procedure
------------------
### Training hyperparameters
The following hyperparameters were used during training:
* learning\_rate: 2e-05
* train\_batch\_size: 16
* eval\_batch\_size: 16
* seed: 42
* distributed\_type: tpu
* optimizer: Adam with betas=(0.9,0.999) and epsilon=1e-08
* lr\_scheduler\_type: linear
* num\_epochs: 4
### Training results
### Framework versions
* Transformers 4.15.0
* Pytorch 1.9.0+cu102
* Datasets 1.17.0
* Tokenizers 0.10.3
|
[
"### Training hyperparameters\n\n\nThe following hyperparameters were used during training:\n\n\n* learning\\_rate: 2e-05\n* train\\_batch\\_size: 16\n* eval\\_batch\\_size: 16\n* seed: 42\n* distributed\\_type: tpu\n* optimizer: Adam with betas=(0.9,0.999) and epsilon=1e-08\n* lr\\_scheduler\\_type: linear\n* num\\_epochs: 4",
"### Training results",
"### Framework versions\n\n\n* Transformers 4.15.0\n* Pytorch 1.9.0+cu102\n* Datasets 1.17.0\n* Tokenizers 0.10.3"
] |
[
"TAGS\n#transformers #pytorch #tensorboard #perceiver #text-classification #generated_from_trainer #dataset-financial_phrasebank #license-apache-2.0 #model-index #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #region-us \n",
"### Training hyperparameters\n\n\nThe following hyperparameters were used during training:\n\n\n* learning\\_rate: 2e-05\n* train\\_batch\\_size: 16\n* eval\\_batch\\_size: 16\n* seed: 42\n* distributed\\_type: tpu\n* optimizer: Adam with betas=(0.9,0.999) and epsilon=1e-08\n* lr\\_scheduler\\_type: linear\n* num\\_epochs: 4",
"### Training results",
"### Framework versions\n\n\n* Transformers 4.15.0\n* Pytorch 1.9.0+cu102\n* Datasets 1.17.0\n* Tokenizers 0.10.3"
] |
automatic-speech-recognition
|
transformers
|
# Wav2Vec2-Large-XLSR-53-Finnish
Fine-tuned [facebook/wav2vec2-large-xlsr-53](https://huggingface.co/facebook/wav2vec2-large-xlsr-53) on Finnish using the [Common Voice](https://huggingface.co/datasets/common_voice), [CSS10](https://www.kaggle.com/bryanpark/finnish-single-speaker-speech-dataset) and [Finnish parliament session 2](https://b2share.eudat.eu/records/4df422d631544ce682d6af1d4714b2d4) datasets.
When using this model, make sure that your speech input is sampled at 16kHz.
## Usage
The model can be used directly (without a language model) as follows:
```python
import numpy as np
import torch
import torchaudio
from datasets import load_dataset
from transformers import Wav2Vec2ForCTC, Wav2Vec2Processor
test_dataset = load_dataset("common_voice", "fi", split="test[:2%]")
processor = Wav2Vec2Processor.from_pretrained("Tommi/wav2vec2-large-xlsr-53-finnish")
model = Wav2Vec2ForCTC.from_pretrained("Tommi/wav2vec2-large-xlsr-53-finnish")
resampler = lambda sr, y: librosa.resample(y.squeeze(), sr, 16_000)
# Preprocessing the datasets.
# We need to read the aduio files as arrays
def speech_file_to_array_fn(batch):
speech_array, sampling_rate = torchaudio.load(batch["path"])
batch["speech"] = resampler(sampling_rate, speech_array.numpy()).squeeze()
return batch
test_dataset = test_dataset.map(speech_file_to_array_fn)
inputs = processor(test_dataset["speech"][:2], sampling_rate=16_000, return_tensors="pt", padding=True)
with torch.no_grad():
logits = model(inputs.input_values, attention_mask=inputs.attention_mask).logits
predicted_ids = torch.argmax(logits, dim=-1)
print("Prediction:", processor.batch_decode(predicted_ids))
print("Reference:", test_dataset["sentence"][:2])
```
## Evaluation
The model can be evaluated as follows on the Finnish test data of Common Voice.
```python
import librosa
import torch
import torchaudio
from datasets import load_dataset, load_metric
from transformers import Wav2Vec2ForCTC, Wav2Vec2Processor
import re
test_dataset = load_dataset("common_voice", "fi", split="test")
wer = load_metric("wer")
processor = Wav2Vec2Processor.from_pretrained("Tommi/wav2vec2-large-xlsr-53-finnish")
model = Wav2Vec2ForCTC.from_pretrained("Tommi/wav2vec2-large-xlsr-53-finnish")
model.to("cuda")
chars_to_ignore_regex = '[\,\?\.\!\-\;\:\"\"\%\'\"\�\'\...\…\–\é]'
resampler = lambda sr, y: librosa.resample(y.numpy().squeeze(), sr, 16_000)
# Preprocessing the datasets.
# We need to read the audio files as arrays
def speech_file_to_array_fn(batch):
batch["sentence"] = re.sub(chars_to_ignore_regex, '', batch["sentence"]).lower()
speech_array, sampling_rate = torchaudio.load(batch["path"])
batch["speech"] = resampler(sampling_rate, speech_array).squeeze()
return batch
test_dataset = test_dataset.map(speech_file_to_array_fn)
# Preprocessing the datasets.
# We need to read the audio files as arrays
def evaluate(batch):
inputs = processor(batch["speech"], sampling_rate=16_000, return_tensors="pt", padding=True)
with torch.no_grad():
logits = model(inputs.input_values.to("cuda"), attention_mask=inputs.attention_mask.to("cuda")).logits
pred_ids = torch.argmax(logits, dim=-1)
batch["pred_strings"] = processor.batch_decode(pred_ids)
return batch
result = test_dataset.map(evaluate, batched=True, batch_size=8)
print("WER: {:2f}".format(100 * wer.compute(predictions=result["pred_strings"], references=result["sentence"])))
```
**Test Result**: 35.43 %
## Training
The Common Voice `train`, `validation`, and `other` datasets were used for training as well as CSS10 and Finnish parliament session 2
The script used for training can be found [here](...) # TODO: fill in a link to your training script here. If you trained your model in a colab, simply fill in the link here. If you trained the model locally, it would be great if you could upload the training script on github and paste the link here.
|
{"language": "fi", "license": "apache-2.0", "tags": ["audio", "automatic-speech-recognition", "speech", "xlsr-fine-tuning-week"], "datasets": ["common_voice", "CSS10", "Finnish parliament session 2"], "metrics": ["wer"], "model-index": [{"name": "Finnish XLSR Wav2Vec2 Large 53", "results": [{"task": {"type": "automatic-speech-recognition", "name": "Speech Recognition"}, "dataset": {"name": "Common Voice fi", "type": "common_voice", "args": "fi"}, "metrics": [{"type": "wer", "value": 35.43, "name": "Test WER"}]}]}]}
|
Tommi/wav2vec2-large-xlsr-53-finnish
| null |
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"jax",
"wav2vec2",
"automatic-speech-recognition",
"audio",
"speech",
"xlsr-fine-tuning-week",
"fi",
"license:apache-2.0",
"model-index",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[
"fi"
] |
TAGS
#transformers #pytorch #jax #wav2vec2 #automatic-speech-recognition #audio #speech #xlsr-fine-tuning-week #fi #license-apache-2.0 #model-index #endpoints_compatible #region-us
|
# Wav2Vec2-Large-XLSR-53-Finnish
Fine-tuned facebook/wav2vec2-large-xlsr-53 on Finnish using the Common Voice, CSS10 and Finnish parliament session 2 datasets.
When using this model, make sure that your speech input is sampled at 16kHz.
## Usage
The model can be used directly (without a language model) as follows:
## Evaluation
The model can be evaluated as follows on the Finnish test data of Common Voice.
Test Result: 35.43 %
## Training
The Common Voice 'train', 'validation', and 'other' datasets were used for training as well as CSS10 and Finnish parliament session 2
The script used for training can be found here # TODO: fill in a link to your training script here. If you trained your model in a colab, simply fill in the link here. If you trained the model locally, it would be great if you could upload the training script on github and paste the link here.
|
[
"# Wav2Vec2-Large-XLSR-53-Finnish\n\nFine-tuned facebook/wav2vec2-large-xlsr-53 on Finnish using the Common Voice, CSS10 and Finnish parliament session 2 datasets.\n\nWhen using this model, make sure that your speech input is sampled at 16kHz.",
"## Usage\n\nThe model can be used directly (without a language model) as follows:",
"## Evaluation\n\nThe model can be evaluated as follows on the Finnish test data of Common Voice.\n\n\n\n\nTest Result: 35.43 %",
"## Training\n\nThe Common Voice 'train', 'validation', and 'other' datasets were used for training as well as CSS10 and Finnish parliament session 2\n\nThe script used for training can be found here # TODO: fill in a link to your training script here. If you trained your model in a colab, simply fill in the link here. If you trained the model locally, it would be great if you could upload the training script on github and paste the link here."
] |
[
"TAGS\n#transformers #pytorch #jax #wav2vec2 #automatic-speech-recognition #audio #speech #xlsr-fine-tuning-week #fi #license-apache-2.0 #model-index #endpoints_compatible #region-us \n",
"# Wav2Vec2-Large-XLSR-53-Finnish\n\nFine-tuned facebook/wav2vec2-large-xlsr-53 on Finnish using the Common Voice, CSS10 and Finnish parliament session 2 datasets.\n\nWhen using this model, make sure that your speech input is sampled at 16kHz.",
"## Usage\n\nThe model can be used directly (without a language model) as follows:",
"## Evaluation\n\nThe model can be evaluated as follows on the Finnish test data of Common Voice.\n\n\n\n\nTest Result: 35.43 %",
"## Training\n\nThe Common Voice 'train', 'validation', and 'other' datasets were used for training as well as CSS10 and Finnish parliament session 2\n\nThe script used for training can be found here # TODO: fill in a link to your training script here. If you trained your model in a colab, simply fill in the link here. If you trained the model locally, it would be great if you could upload the training script on github and paste the link here."
] |
text-generation
|
transformers
|
# Rick DialoGPT Model
|
{"tags": ["conversational"]}
|
Tr1ex/DialoGPT-small-rick
| null |
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"gpt2",
"text-generation",
"conversational",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"text-generation-inference",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[] |
TAGS
#transformers #pytorch #gpt2 #text-generation #conversational #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #text-generation-inference #region-us
|
# Rick DialoGPT Model
|
[
"# Rick DialoGPT Model"
] |
[
"TAGS\n#transformers #pytorch #gpt2 #text-generation #conversational #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #text-generation-inference #region-us \n",
"# Rick DialoGPT Model"
] |
text-generation
|
transformers
|
<!-- This model card has been generated automatically according to the information the Trainer had access to. You
should probably proofread and complete it, then remove this comment. -->
# dgpt
This model is a fine-tuned version of [distilgpt2](https://huggingface.co/distilgpt2) on an unknown dataset.
## Model description
More information needed
## Intended uses & limitations
More information needed
## Training and evaluation data
More information needed
## Training procedure
### Training hyperparameters
The following hyperparameters were used during training:
- learning_rate: 5e-05
- train_batch_size: 2
- eval_batch_size: 8
- seed: 42
- distributed_type: tpu
- num_devices: 8
- total_train_batch_size: 16
- total_eval_batch_size: 64
- optimizer: Adam with betas=(0.9,0.999) and epsilon=1e-08
- lr_scheduler_type: linear
- num_epochs: 10.0
### Training results
### Framework versions
- Transformers 4.14.0.dev0
- Pytorch 1.9.0+cu102
- Datasets 1.16.2.dev0
- Tokenizers 0.10.3
hello
hello
|
{"license": "apache-2.0", "tags": ["generated_from_trainer"], "model-index": [{"name": "dgpt", "results": []}]}
|
TrLOX/gpt2-tdk
| null |
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"gpt2",
"text-generation",
"generated_from_trainer",
"license:apache-2.0",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"has_space",
"text-generation-inference",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[] |
TAGS
#transformers #pytorch #gpt2 #text-generation #generated_from_trainer #license-apache-2.0 #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #has_space #text-generation-inference #region-us
|
# dgpt
This model is a fine-tuned version of distilgpt2 on an unknown dataset.
## Model description
More information needed
## Intended uses & limitations
More information needed
## Training and evaluation data
More information needed
## Training procedure
### Training hyperparameters
The following hyperparameters were used during training:
- learning_rate: 5e-05
- train_batch_size: 2
- eval_batch_size: 8
- seed: 42
- distributed_type: tpu
- num_devices: 8
- total_train_batch_size: 16
- total_eval_batch_size: 64
- optimizer: Adam with betas=(0.9,0.999) and epsilon=1e-08
- lr_scheduler_type: linear
- num_epochs: 10.0
### Training results
### Framework versions
- Transformers 4.14.0.dev0
- Pytorch 1.9.0+cu102
- Datasets 1.16.2.dev0
- Tokenizers 0.10.3
hello
hello
|
[
"# dgpt\n\nThis model is a fine-tuned version of distilgpt2 on an unknown dataset.",
"## Model description\n\nMore information needed",
"## Intended uses & limitations\n\nMore information needed",
"## Training and evaluation data\n\nMore information needed",
"## Training procedure",
"### Training hyperparameters\n\nThe following hyperparameters were used during training:\n- learning_rate: 5e-05\n- train_batch_size: 2\n- eval_batch_size: 8\n- seed: 42\n- distributed_type: tpu\n- num_devices: 8\n- total_train_batch_size: 16\n- total_eval_batch_size: 64\n- optimizer: Adam with betas=(0.9,0.999) and epsilon=1e-08\n- lr_scheduler_type: linear\n- num_epochs: 10.0",
"### Training results",
"### Framework versions\n\n- Transformers 4.14.0.dev0\n- Pytorch 1.9.0+cu102\n- Datasets 1.16.2.dev0\n- Tokenizers 0.10.3\nhello\nhello"
] |
[
"TAGS\n#transformers #pytorch #gpt2 #text-generation #generated_from_trainer #license-apache-2.0 #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #has_space #text-generation-inference #region-us \n",
"# dgpt\n\nThis model is a fine-tuned version of distilgpt2 on an unknown dataset.",
"## Model description\n\nMore information needed",
"## Intended uses & limitations\n\nMore information needed",
"## Training and evaluation data\n\nMore information needed",
"## Training procedure",
"### Training hyperparameters\n\nThe following hyperparameters were used during training:\n- learning_rate: 5e-05\n- train_batch_size: 2\n- eval_batch_size: 8\n- seed: 42\n- distributed_type: tpu\n- num_devices: 8\n- total_train_batch_size: 16\n- total_eval_batch_size: 64\n- optimizer: Adam with betas=(0.9,0.999) and epsilon=1e-08\n- lr_scheduler_type: linear\n- num_epochs: 10.0",
"### Training results",
"### Framework versions\n\n- Transformers 4.14.0.dev0\n- Pytorch 1.9.0+cu102\n- Datasets 1.16.2.dev0\n- Tokenizers 0.10.3\nhello\nhello"
] |
token-classification
|
transformers
|
# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers
The goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.
With TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in [WMT 2020](http://www.statmt.org/wmt20/quality-estimation-task.html). TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as [OpenKiwi](https://github.com/Unbabel/OpenKiwi) and [DeepQuest](https://github.com/sheffieldnlp/deepQuest).
## Features
- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.
- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.
- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented.
- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in [HuggingFace.](https://huggingface.co/TransQuest)
## Installation
### From pip
```bash
pip install transquest
```
### From Source
```bash
git clone https://github.com/TharinduDR/TransQuest.git
cd TransQuest
pip install -r requirements.txt
```
## Using Pre-trained Models
```python
from transquest.algo.word_level.microtransquest.run_model import MicroTransQuestModel
import torch
model = MicroTransQuestModel("xlmroberta", "TransQuest/microtransquest-de_en-pharmaceutical-smt", labels=["OK", "BAD"], use_cuda=torch.cuda.is_available())
source_tags, target_tags = model.predict([["if not , you may not be protected against the diseases . ", "ja tā nav , Jūs varat nepasargāt no slimībām . "]])
```
## Documentation
For more details follow the documentation.
1. **[Installation](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/install/)** - Install TransQuest locally using pip.
2. **Architectures** - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest
1. [Sentence-level Architectures](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/architectures/sentence_level_architectures/) - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.
2. [Word-level Architecture](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/architectures/word_level_architecture/) - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation.
3. **Examples** - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.
1. [Sentence-level Examples](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/examples/sentence_level_examples/)
2. [Word-level Examples](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/examples/word_level_examples/)
4. **Pre-trained Models** - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level
1. [Sentence-level Models](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/models/sentence_level_pretrained/)
2. [Word-level Models](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/models/word_level_pretrained/)
5. **[Contact](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/contact/)** - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest
## Citations
If you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to [ACL 2021](https://2021.aclweb.org/).
```bash
@InProceedings{ranasinghe2021,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {An Exploratory Analysis of Multilingual Word Level Quality Estimation with Cross-Lingual Transformers},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics},
year = {2021}
}
```
If you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in [COLING 2020](https://coling2020.org/) and in [WMT 2020](http://www.statmt.org/wmt20/) at EMNLP 2020.
```bash
@InProceedings{transquest:2020a,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Computational Linguistics},
year = {2020}
}
```
```bash
@InProceedings{transquest:2020b,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {TransQuest at WMT2020: Sentence-Level Direct Assessment},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the Fifth Conference on Machine Translation},
year = {2020}
}
```
|
{"language": "de-en", "license": "apache-2.0", "tags": ["Quality Estimation", "microtransquest"]}
|
TransQuest/microtransquest-de_en-pharmaceutical-smt
| null |
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"xlm-roberta",
"token-classification",
"Quality Estimation",
"microtransquest",
"license:apache-2.0",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[
"de-en"
] |
TAGS
#transformers #pytorch #xlm-roberta #token-classification #Quality Estimation #microtransquest #license-apache-2.0 #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #region-us
|
# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers
The goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.
With TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.
## Features
- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.
- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.
- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented.
- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.
## Installation
### From pip
### From Source
## Using Pre-trained Models
## Documentation
For more details follow the documentation.
1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip.
2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest
1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.
2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation.
3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.
1. Sentence-level Examples
2. Word-level Examples
4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level
1. Sentence-level Models
2. Word-level Models
5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest
s
If you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.
If you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020.
|
[
"# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers\nThe goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.\n\nWith TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.",
"## Features\n- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.\n- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.\n- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented. \n- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.",
"## Installation",
"### From pip",
"### From Source",
"## Using Pre-trained Models",
"## Documentation\nFor more details follow the documentation.\n\n1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip. \n2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest\n 1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.\n 2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation. \n3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.\n 1. Sentence-level Examples\n 2. Word-level Examples\n4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level\n 1. Sentence-level Models\n 2. Word-level Models\n5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest\n\n\ns\nIf you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.\n\n\n\nIf you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020."
] |
[
"TAGS\n#transformers #pytorch #xlm-roberta #token-classification #Quality Estimation #microtransquest #license-apache-2.0 #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #region-us \n",
"# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers\nThe goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.\n\nWith TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.",
"## Features\n- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.\n- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.\n- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented. \n- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.",
"## Installation",
"### From pip",
"### From Source",
"## Using Pre-trained Models",
"## Documentation\nFor more details follow the documentation.\n\n1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip. \n2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest\n 1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.\n 2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation. \n3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.\n 1. Sentence-level Examples\n 2. Word-level Examples\n4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level\n 1. Sentence-level Models\n 2. Word-level Models\n5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest\n\n\ns\nIf you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.\n\n\n\nIf you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020."
] |
token-classification
|
transformers
|
# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers
The goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.
With TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in [WMT 2020](http://www.statmt.org/wmt20/quality-estimation-task.html). TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as [OpenKiwi](https://github.com/Unbabel/OpenKiwi) and [DeepQuest](https://github.com/sheffieldnlp/deepQuest).
## Features
- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.
- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.
- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented.
- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in [HuggingFace.](https://huggingface.co/TransQuest)
## Installation
### From pip
```bash
pip install transquest
```
### From Source
```bash
git clone https://github.com/TharinduDR/TransQuest.git
cd TransQuest
pip install -r requirements.txt
```
## Using Pre-trained Models
```python
from transquest.algo.word_level.microtransquest.run_model import MicroTransQuestModel
import torch
model = MicroTransQuestModel("xlmroberta", "TransQuest/microtransquest-en_cs-it-smt", labels=["OK", "BAD"], use_cuda=torch.cuda.is_available())
source_tags, target_tags = model.predict([["if not , you may not be protected against the diseases . ", "ja tā nav , Jūs varat nepasargāt no slimībām . "]])
```
## Documentation
For more details follow the documentation.
1. **[Installation](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/install/)** - Install TransQuest locally using pip.
2. **Architectures** - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest
1. [Sentence-level Architectures](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/architectures/sentence_level_architectures/) - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.
2. [Word-level Architecture](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/architectures/word_level_architecture/) - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation.
3. **Examples** - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.
1. [Sentence-level Examples](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/examples/sentence_level_examples/)
2. [Word-level Examples](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/examples/word_level_examples/)
4. **Pre-trained Models** - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level
1. [Sentence-level Models](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/models/sentence_level_pretrained/)
2. [Word-level Models](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/models/word_level_pretrained/)
5. **[Contact](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/contact/)** - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest
## Citations
If you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to [ACL 2021](https://2021.aclweb.org/).
```bash
@InProceedings{ranasinghe2021,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {An Exploratory Analysis of Multilingual Word Level Quality Estimation with Cross-Lingual Transformers},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics},
year = {2021}
}
```
If you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in [COLING 2020](https://coling2020.org/) and in [WMT 2020](http://www.statmt.org/wmt20/) at EMNLP 2020.
```bash
@InProceedings{transquest:2020a,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Computational Linguistics},
year = {2020}
}
```
```bash
@InProceedings{transquest:2020b,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {TransQuest at WMT2020: Sentence-Level Direct Assessment},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the Fifth Conference on Machine Translation},
year = {2020}
}
```
|
{"language": "en-cs", "license": "apache-2.0", "tags": ["Quality Estimation", "microtransquest"]}
|
TransQuest/microtransquest-en_cs-it-smt
| null |
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"xlm-roberta",
"token-classification",
"Quality Estimation",
"microtransquest",
"license:apache-2.0",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[
"en-cs"
] |
TAGS
#transformers #pytorch #xlm-roberta #token-classification #Quality Estimation #microtransquest #license-apache-2.0 #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #region-us
|
# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers
The goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.
With TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.
## Features
- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.
- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.
- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented.
- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.
## Installation
### From pip
### From Source
## Using Pre-trained Models
## Documentation
For more details follow the documentation.
1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip.
2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest
1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.
2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation.
3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.
1. Sentence-level Examples
2. Word-level Examples
4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level
1. Sentence-level Models
2. Word-level Models
5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest
s
If you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.
If you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020.
|
[
"# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers\nThe goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.\n\nWith TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.",
"## Features\n- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.\n- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.\n- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented. \n- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.",
"## Installation",
"### From pip",
"### From Source",
"## Using Pre-trained Models",
"## Documentation\nFor more details follow the documentation.\n\n1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip. \n2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest\n 1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.\n 2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation. \n3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.\n 1. Sentence-level Examples\n 2. Word-level Examples\n4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level\n 1. Sentence-level Models\n 2. Word-level Models\n5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest\n\n\ns\nIf you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.\n\n\n\nIf you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020."
] |
[
"TAGS\n#transformers #pytorch #xlm-roberta #token-classification #Quality Estimation #microtransquest #license-apache-2.0 #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #region-us \n",
"# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers\nThe goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.\n\nWith TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.",
"## Features\n- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.\n- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.\n- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented. \n- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.",
"## Installation",
"### From pip",
"### From Source",
"## Using Pre-trained Models",
"## Documentation\nFor more details follow the documentation.\n\n1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip. \n2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest\n 1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.\n 2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation. \n3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.\n 1. Sentence-level Examples\n 2. Word-level Examples\n4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level\n 1. Sentence-level Models\n 2. Word-level Models\n5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest\n\n\ns\nIf you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.\n\n\n\nIf you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020."
] |
token-classification
|
transformers
|
# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers
The goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.
With TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in [WMT 2020](http://www.statmt.org/wmt20/quality-estimation-task.html). TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as [OpenKiwi](https://github.com/Unbabel/OpenKiwi) and [DeepQuest](https://github.com/sheffieldnlp/deepQuest).
## Features
- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.
- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.
- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented.
- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in [HuggingFace.](https://huggingface.co/TransQuest)
## Installation
### From pip
```bash
pip install transquest
```
### From Source
```bash
git clone https://github.com/TharinduDR/TransQuest.git
cd TransQuest
pip install -r requirements.txt
```
## Using Pre-trained Models
```python
from transquest.algo.word_level.microtransquest.run_model import MicroTransQuestModel
import torch
model = MicroTransQuestModel("xlmroberta", "TransQuest/microtransquest-en_de-it-nmt", labels=["OK", "BAD"], use_cuda=torch.cuda.is_available())
source_tags, target_tags = model.predict([["if not , you may not be protected against the diseases . ", "ja tā nav , Jūs varat nepasargāt no slimībām . "]])
```
## Documentation
For more details follow the documentation.
1. **[Installation](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/install/)** - Install TransQuest locally using pip.
2. **Architectures** - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest
1. [Sentence-level Architectures](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/architectures/sentence_level_architectures/) - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.
2. [Word-level Architecture](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/architectures/word_level_architecture/) - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation.
3. **Examples** - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.
1. [Sentence-level Examples](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/examples/sentence_level_examples/)
2. [Word-level Examples](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/examples/word_level_examples/)
4. **Pre-trained Models** - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level
1. [Sentence-level Models](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/models/sentence_level_pretrained/)
2. [Word-level Models](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/models/word_level_pretrained/)
5. **[Contact](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/contact/)** - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest
## Citations
If you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to [ACL 2021](https://2021.aclweb.org/).
```bash
@InProceedings{ranasinghe2021,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {An Exploratory Analysis of Multilingual Word Level Quality Estimation with Cross-Lingual Transformers},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics},
year = {2021}
}
```
If you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in [COLING 2020](https://coling2020.org/) and in [WMT 2020](http://www.statmt.org/wmt20/) at EMNLP 2020.
```bash
@InProceedings{transquest:2020a,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Computational Linguistics},
year = {2020}
}
```
```bash
@InProceedings{transquest:2020b,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {TransQuest at WMT2020: Sentence-Level Direct Assessment},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the Fifth Conference on Machine Translation},
year = {2020}
}
```
|
{"language": "en-de", "license": "apache-2.0", "tags": ["Quality Estimation", "microtransquest"]}
|
TransQuest/microtransquest-en_de-it-nmt
| null |
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"xlm-roberta",
"token-classification",
"Quality Estimation",
"microtransquest",
"license:apache-2.0",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[
"en-de"
] |
TAGS
#transformers #pytorch #xlm-roberta #token-classification #Quality Estimation #microtransquest #license-apache-2.0 #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #region-us
|
# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers
The goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.
With TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.
## Features
- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.
- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.
- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented.
- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.
## Installation
### From pip
### From Source
## Using Pre-trained Models
## Documentation
For more details follow the documentation.
1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip.
2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest
1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.
2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation.
3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.
1. Sentence-level Examples
2. Word-level Examples
4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level
1. Sentence-level Models
2. Word-level Models
5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest
s
If you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.
If you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020.
|
[
"# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers\nThe goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.\n\nWith TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.",
"## Features\n- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.\n- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.\n- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented. \n- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.",
"## Installation",
"### From pip",
"### From Source",
"## Using Pre-trained Models",
"## Documentation\nFor more details follow the documentation.\n\n1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip. \n2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest\n 1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.\n 2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation. \n3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.\n 1. Sentence-level Examples\n 2. Word-level Examples\n4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level\n 1. Sentence-level Models\n 2. Word-level Models\n5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest\n\n\ns\nIf you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.\n\n\n\nIf you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020."
] |
[
"TAGS\n#transformers #pytorch #xlm-roberta #token-classification #Quality Estimation #microtransquest #license-apache-2.0 #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #region-us \n",
"# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers\nThe goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.\n\nWith TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.",
"## Features\n- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.\n- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.\n- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented. \n- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.",
"## Installation",
"### From pip",
"### From Source",
"## Using Pre-trained Models",
"## Documentation\nFor more details follow the documentation.\n\n1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip. \n2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest\n 1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.\n 2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation. \n3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.\n 1. Sentence-level Examples\n 2. Word-level Examples\n4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level\n 1. Sentence-level Models\n 2. Word-level Models\n5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest\n\n\ns\nIf you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.\n\n\n\nIf you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020."
] |
null | null |
# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers
The goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.
With TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in [WMT 2020](http://www.statmt.org/wmt20/quality-estimation-task.html). TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as [OpenKiwi](https://github.com/Unbabel/OpenKiwi) and [DeepQuest](https://github.com/sheffieldnlp/deepQuest).
## Features
- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.
- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.
- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented.
- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in [HuggingFace.](https://huggingface.co/TransQuest)
## Installation
### From pip
```bash
pip install transquest
```
### From Source
```bash
git clone https://github.com/TharinduDR/TransQuest.git
cd TransQuest
pip install -r requirements.txt
```
## Using Pre-trained Models
```python
from transquest.algo.word_level.microtransquest.run_model import MicroTransQuestModel
import torch
model = MicroTransQuestModel("xlmroberta", "TransQuest/microtransquest-en_de-it-smt", labels=["OK", "BAD"], use_cuda=torch.cuda.is_available())
source_tags, target_tags = model.predict([["if not , you may not be protected against the diseases . ", "ja tā nav , Jūs varat nepasargāt no slimībām . "]])
```
## Documentation
For more details follow the documentation.
1. **[Installation](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/install/)** - Install TransQuest locally using pip.
2. **Architectures** - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest
1. [Sentence-level Architectures](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/architectures/sentence_level_architectures/) - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.
2. [Word-level Architecture](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/architectures/word_level_architecture/) - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation.
3. **Examples** - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.
1. [Sentence-level Examples](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/examples/sentence_level_examples/)
2. [Word-level Examples](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/examples/word_level_examples/)
4. **Pre-trained Models** - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level
1. [Sentence-level Models](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/models/sentence_level_pretrained/)
2. [Word-level Models](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/models/word_level_pretrained/)
5. **[Contact](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/contact/)** - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest
## Citations
If you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to [ACL 2021](https://2021.aclweb.org/).
```bash
@InProceedings{ranasinghe2021,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {An Exploratory Analysis of Multilingual Word Level Quality Estimation with Cross-Lingual Transformers},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics},
year = {2021}
}
```
If you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in [COLING 2020](https://coling2020.org/) and in [WMT 2020](http://www.statmt.org/wmt20/) at EMNLP 2020.
```bash
@InProceedings{transquest:2020a,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Computational Linguistics},
year = {2020}
}
```
```bash
@InProceedings{transquest:2020b,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {TransQuest at WMT2020: Sentence-Level Direct Assessment},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the Fifth Conference on Machine Translation},
year = {2020}
}
```
|
{"language": "en-de", "license": "apache-2.0", "tags": ["Quality Estimation", "microtransquest"]}
|
TransQuest/microtransquest-en_de-it-smt
| null |
[
"Quality Estimation",
"microtransquest",
"license:apache-2.0",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[
"en-de"
] |
TAGS
#Quality Estimation #microtransquest #license-apache-2.0 #region-us
|
# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers
The goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.
With TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.
## Features
- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.
- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.
- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented.
- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.
## Installation
### From pip
### From Source
## Using Pre-trained Models
## Documentation
For more details follow the documentation.
1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip.
2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest
1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.
2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation.
3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.
1. Sentence-level Examples
2. Word-level Examples
4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level
1. Sentence-level Models
2. Word-level Models
5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest
s
If you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.
If you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020.
|
[
"# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers\nThe goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.\n\nWith TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.",
"## Features\n- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.\n- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.\n- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented. \n- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.",
"## Installation",
"### From pip",
"### From Source",
"## Using Pre-trained Models",
"## Documentation\nFor more details follow the documentation.\n\n1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip. \n2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest\n 1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.\n 2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation. \n3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.\n 1. Sentence-level Examples\n 2. Word-level Examples\n4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level\n 1. Sentence-level Models\n 2. Word-level Models\n5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest\n\n\ns\nIf you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.\n\n\n\nIf you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020."
] |
[
"TAGS\n#Quality Estimation #microtransquest #license-apache-2.0 #region-us \n",
"# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers\nThe goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.\n\nWith TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.",
"## Features\n- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.\n- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.\n- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented. \n- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.",
"## Installation",
"### From pip",
"### From Source",
"## Using Pre-trained Models",
"## Documentation\nFor more details follow the documentation.\n\n1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip. \n2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest\n 1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.\n 2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation. \n3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.\n 1. Sentence-level Examples\n 2. Word-level Examples\n4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level\n 1. Sentence-level Models\n 2. Word-level Models\n5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest\n\n\ns\nIf you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.\n\n\n\nIf you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020."
] |
token-classification
|
transformers
|
# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers
The goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.
With TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in [WMT 2020](http://www.statmt.org/wmt20/quality-estimation-task.html). TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as [OpenKiwi](https://github.com/Unbabel/OpenKiwi) and [DeepQuest](https://github.com/sheffieldnlp/deepQuest).
## Features
- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.
- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.
- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented.
- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in [HuggingFace.](https://huggingface.co/TransQuest)
## Installation
### From pip
```bash
pip install transquest
```
### From Source
```bash
git clone https://github.com/TharinduDR/TransQuest.git
cd TransQuest
pip install -r requirements.txt
```
## Using Pre-trained Models
```python
from transquest.algo.word_level.microtransquest.run_model import MicroTransQuestModel
import torch
model = MicroTransQuestModel("xlmroberta", "TransQuest/microtransquest-en_de-wiki", labels=["OK", "BAD"], use_cuda=torch.cuda.is_available())
source_tags, target_tags = model.predict([["if not , you may not be protected against the diseases . ", "ja tā nav , Jūs varat nepasargāt no slimībām . "]])
```
## Documentation
For more details follow the documentation.
1. **[Installation](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/install/)** - Install TransQuest locally using pip.
2. **Architectures** - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest
1. [Sentence-level Architectures](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/architectures/sentence_level_architectures/) - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.
2. [Word-level Architecture](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/architectures/word_level_architecture/) - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation.
3. **Examples** - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.
1. [Sentence-level Examples](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/examples/sentence_level_examples/)
2. [Word-level Examples](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/examples/word_level_examples/)
4. **Pre-trained Models** - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level
1. [Sentence-level Models](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/models/sentence_level_pretrained/)
2. [Word-level Models](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/models/word_level_pretrained/)
5. **[Contact](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/contact/)** - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest
## Citations
If you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to [ACL 2021](https://2021.aclweb.org/).
```bash
@InProceedings{ranasinghe2021,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {An Exploratory Analysis of Multilingual Word Level Quality Estimation with Cross-Lingual Transformers},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics},
year = {2021}
}
```
If you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in [COLING 2020](https://coling2020.org/) and in [WMT 2020](http://www.statmt.org/wmt20/) at EMNLP 2020.
```bash
@InProceedings{transquest:2020a,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Computational Linguistics},
year = {2020}
}
```
```bash
@InProceedings{transquest:2020b,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {TransQuest at WMT2020: Sentence-Level Direct Assessment},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the Fifth Conference on Machine Translation},
year = {2020}
}
```
|
{"language": "en-de", "license": "apache-2.0", "tags": ["Quality Estimation", "microtransquest"]}
|
TransQuest/microtransquest-en_de-wiki
| null |
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"xlm-roberta",
"token-classification",
"Quality Estimation",
"microtransquest",
"license:apache-2.0",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[
"en-de"
] |
TAGS
#transformers #pytorch #xlm-roberta #token-classification #Quality Estimation #microtransquest #license-apache-2.0 #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #region-us
|
# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers
The goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.
With TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.
## Features
- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.
- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.
- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented.
- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.
## Installation
### From pip
### From Source
## Using Pre-trained Models
## Documentation
For more details follow the documentation.
1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip.
2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest
1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.
2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation.
3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.
1. Sentence-level Examples
2. Word-level Examples
4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level
1. Sentence-level Models
2. Word-level Models
5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest
s
If you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.
If you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020.
|
[
"# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers\nThe goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.\n\nWith TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.",
"## Features\n- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.\n- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.\n- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented. \n- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.",
"## Installation",
"### From pip",
"### From Source",
"## Using Pre-trained Models",
"## Documentation\nFor more details follow the documentation.\n\n1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip. \n2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest\n 1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.\n 2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation. \n3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.\n 1. Sentence-level Examples\n 2. Word-level Examples\n4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level\n 1. Sentence-level Models\n 2. Word-level Models\n5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest\n\n\ns\nIf you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.\n\n\n\nIf you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020."
] |
[
"TAGS\n#transformers #pytorch #xlm-roberta #token-classification #Quality Estimation #microtransquest #license-apache-2.0 #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #region-us \n",
"# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers\nThe goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.\n\nWith TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.",
"## Features\n- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.\n- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.\n- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented. \n- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.",
"## Installation",
"### From pip",
"### From Source",
"## Using Pre-trained Models",
"## Documentation\nFor more details follow the documentation.\n\n1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip. \n2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest\n 1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.\n 2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation. \n3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.\n 1. Sentence-level Examples\n 2. Word-level Examples\n4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level\n 1. Sentence-level Models\n 2. Word-level Models\n5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest\n\n\ns\nIf you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.\n\n\n\nIf you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020."
] |
token-classification
|
transformers
|
# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers
The goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.
With TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in [WMT 2020](http://www.statmt.org/wmt20/quality-estimation-task.html). TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as [OpenKiwi](https://github.com/Unbabel/OpenKiwi) and [DeepQuest](https://github.com/sheffieldnlp/deepQuest).
## Features
- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.
- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.
- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented.
- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in [HuggingFace.](https://huggingface.co/TransQuest)
## Installation
### From pip
```bash
pip install transquest
```
### From Source
```bash
git clone https://github.com/TharinduDR/TransQuest.git
cd TransQuest
pip install -r requirements.txt
```
## Using Pre-trained Models
```python
from transquest.algo.word_level.microtransquest.run_model import MicroTransQuestModel
import torch
model = MicroTransQuestModel("xlmroberta", "TransQuest/microtransquest-en_lv-pharmaceutical-nmt", labels=["OK", "BAD"], use_cuda=torch.cuda.is_available())
source_tags, target_tags = model.predict([["if not , you may not be protected against the diseases . ", "ja tā nav , Jūs varat nepasargāt no slimībām . "]])
```
## Documentation
For more details follow the documentation.
1. **[Installation](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/install/)** - Install TransQuest locally using pip.
2. **Architectures** - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest
1. [Sentence-level Architectures](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/architectures/sentence_level_architectures/) - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.
2. [Word-level Architecture](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/architectures/word_level_architecture/) - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation.
3. **Examples** - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.
1. [Sentence-level Examples](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/examples/sentence_level_examples/)
2. [Word-level Examples](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/examples/word_level_examples/)
4. **Pre-trained Models** - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level
1. [Sentence-level Models](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/models/sentence_level_pretrained/)
2. [Word-level Models](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/models/word_level_pretrained/)
5. **[Contact](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/contact/)** - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest
## Citations
If you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to [ACL 2021](https://2021.aclweb.org/).
```bash
@InProceedings{ranasinghe2021,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {An Exploratory Analysis of Multilingual Word Level Quality Estimation with Cross-Lingual Transformers},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics},
year = {2021}
}
```
If you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in [COLING 2020](https://coling2020.org/) and in [WMT 2020](http://www.statmt.org/wmt20/) at EMNLP 2020.
```bash
@InProceedings{transquest:2020a,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Computational Linguistics},
year = {2020}
}
```
```bash
@InProceedings{transquest:2020b,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {TransQuest at WMT2020: Sentence-Level Direct Assessment},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the Fifth Conference on Machine Translation},
year = {2020}
}
```
|
{"language": "en-lv", "license": "apache-2.0", "tags": ["Quality Estimation", "microtransquest"]}
|
TransQuest/microtransquest-en_lv-pharmaceutical-nmt
| null |
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"xlm-roberta",
"token-classification",
"Quality Estimation",
"microtransquest",
"license:apache-2.0",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[
"en-lv"
] |
TAGS
#transformers #pytorch #xlm-roberta #token-classification #Quality Estimation #microtransquest #license-apache-2.0 #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #region-us
|
# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers
The goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.
With TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.
## Features
- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.
- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.
- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented.
- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.
## Installation
### From pip
### From Source
## Using Pre-trained Models
## Documentation
For more details follow the documentation.
1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip.
2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest
1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.
2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation.
3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.
1. Sentence-level Examples
2. Word-level Examples
4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level
1. Sentence-level Models
2. Word-level Models
5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest
s
If you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.
If you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020.
|
[
"# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers\nThe goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.\n\nWith TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.",
"## Features\n- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.\n- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.\n- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented. \n- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.",
"## Installation",
"### From pip",
"### From Source",
"## Using Pre-trained Models",
"## Documentation\nFor more details follow the documentation.\n\n1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip. \n2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest\n 1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.\n 2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation. \n3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.\n 1. Sentence-level Examples\n 2. Word-level Examples\n4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level\n 1. Sentence-level Models\n 2. Word-level Models\n5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest\n\n\ns\nIf you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.\n\n\n\nIf you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020."
] |
[
"TAGS\n#transformers #pytorch #xlm-roberta #token-classification #Quality Estimation #microtransquest #license-apache-2.0 #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #region-us \n",
"# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers\nThe goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.\n\nWith TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.",
"## Features\n- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.\n- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.\n- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented. \n- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.",
"## Installation",
"### From pip",
"### From Source",
"## Using Pre-trained Models",
"## Documentation\nFor more details follow the documentation.\n\n1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip. \n2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest\n 1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.\n 2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation. \n3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.\n 1. Sentence-level Examples\n 2. Word-level Examples\n4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level\n 1. Sentence-level Models\n 2. Word-level Models\n5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest\n\n\ns\nIf you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.\n\n\n\nIf you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020."
] |
token-classification
|
transformers
|
# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers
The goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.
With TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in [WMT 2020](http://www.statmt.org/wmt20/quality-estimation-task.html). TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as [OpenKiwi](https://github.com/Unbabel/OpenKiwi) and [DeepQuest](https://github.com/sheffieldnlp/deepQuest).
## Features
- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.
- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.
- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented.
- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in [HuggingFace.](https://huggingface.co/TransQuest)
## Installation
### From pip
```bash
pip install transquest
```
### From Source
```bash
git clone https://github.com/TharinduDR/TransQuest.git
cd TransQuest
pip install -r requirements.txt
```
## Using Pre-trained Models
```python
from transquest.algo.word_level.microtransquest.run_model import MicroTransQuestModel
import torch
model = MicroTransQuestModel("xlmroberta", "TransQuest/microtransquest-en_lv-pharmaceutical-smt", labels=["OK", "BAD"], use_cuda=torch.cuda.is_available())
source_tags, target_tags = model.predict([["if not , you may not be protected against the diseases . ", "ja tā nav , Jūs varat nepasargāt no slimībām . "]])
```
## Documentation
For more details follow the documentation.
1. **[Installation](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/install/)** - Install TransQuest locally using pip.
2. **Architectures** - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest
1. [Sentence-level Architectures](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/architectures/sentence_level_architectures/) - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.
2. [Word-level Architecture](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/architectures/word_level_architecture/) - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation.
3. **Examples** - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.
1. [Sentence-level Examples](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/examples/sentence_level_examples/)
2. [Word-level Examples](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/examples/word_level_examples/)
4. **Pre-trained Models** - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level
1. [Sentence-level Models](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/models/sentence_level_pretrained/)
2. [Word-level Models](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/models/word_level_pretrained/)
5. **[Contact](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/contact/)** - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest
## Citations
If you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to [ACL 2021](https://2021.aclweb.org/).
```bash
@InProceedings{ranasinghe2021,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {An Exploratory Analysis of Multilingual Word Level Quality Estimation with Cross-Lingual Transformers},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics},
year = {2021}
}
```
If you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in [COLING 2020](https://coling2020.org/) and in [WMT 2020](http://www.statmt.org/wmt20/) at EMNLP 2020.
```bash
@InProceedings{transquest:2020a,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Computational Linguistics},
year = {2020}
}
```
```bash
@InProceedings{transquest:2020b,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {TransQuest at WMT2020: Sentence-Level Direct Assessment},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the Fifth Conference on Machine Translation},
year = {2020}
}
```
|
{"language": "en-lv", "license": "apache-2.0", "tags": ["Quality Estimation", "microtransquest"]}
|
TransQuest/microtransquest-en_lv-pharmaceutical-smt
| null |
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"xlm-roberta",
"token-classification",
"Quality Estimation",
"microtransquest",
"license:apache-2.0",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[
"en-lv"
] |
TAGS
#transformers #pytorch #xlm-roberta #token-classification #Quality Estimation #microtransquest #license-apache-2.0 #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #region-us
|
# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers
The goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.
With TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.
## Features
- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.
- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.
- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented.
- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.
## Installation
### From pip
### From Source
## Using Pre-trained Models
## Documentation
For more details follow the documentation.
1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip.
2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest
1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.
2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation.
3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.
1. Sentence-level Examples
2. Word-level Examples
4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level
1. Sentence-level Models
2. Word-level Models
5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest
s
If you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.
If you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020.
|
[
"# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers\nThe goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.\n\nWith TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.",
"## Features\n- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.\n- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.\n- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented. \n- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.",
"## Installation",
"### From pip",
"### From Source",
"## Using Pre-trained Models",
"## Documentation\nFor more details follow the documentation.\n\n1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip. \n2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest\n 1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.\n 2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation. \n3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.\n 1. Sentence-level Examples\n 2. Word-level Examples\n4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level\n 1. Sentence-level Models\n 2. Word-level Models\n5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest\n\n\ns\nIf you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.\n\n\n\nIf you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020."
] |
[
"TAGS\n#transformers #pytorch #xlm-roberta #token-classification #Quality Estimation #microtransquest #license-apache-2.0 #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #region-us \n",
"# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers\nThe goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.\n\nWith TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.",
"## Features\n- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.\n- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.\n- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented. \n- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.",
"## Installation",
"### From pip",
"### From Source",
"## Using Pre-trained Models",
"## Documentation\nFor more details follow the documentation.\n\n1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip. \n2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest\n 1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.\n 2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation. \n3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.\n 1. Sentence-level Examples\n 2. Word-level Examples\n4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level\n 1. Sentence-level Models\n 2. Word-level Models\n5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest\n\n\ns\nIf you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.\n\n\n\nIf you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020."
] |
token-classification
|
transformers
|
# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers
The goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.
With TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in [WMT 2020](http://www.statmt.org/wmt20/quality-estimation-task.html). TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as [OpenKiwi](https://github.com/Unbabel/OpenKiwi) and [DeepQuest](https://github.com/sheffieldnlp/deepQuest).
## Features
- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.
- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.
- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented.
- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in [HuggingFace.](https://huggingface.co/TransQuest)
## Installation
### From pip
```bash
pip install transquest
```
### From Source
```bash
git clone https://github.com/TharinduDR/TransQuest.git
cd TransQuest
pip install -r requirements.txt
```
## Using Pre-trained Models
```python
from transquest.algo.word_level.microtransquest.run_model import MicroTransQuestModel
import torch
model = MicroTransQuestModel("xlmroberta", "TransQuest/microtransquest-en_zh-wiki", labels=["OK", "BAD"], use_cuda=torch.cuda.is_available())
source_tags, target_tags = model.predict([["if not , you may not be protected against the diseases . ", "ja tā nav , Jūs varat nepasargāt no slimībām . "]])
```
## Documentation
For more details follow the documentation.
1. **[Installation](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/install/)** - Install TransQuest locally using pip.
2. **Architectures** - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest
1. [Sentence-level Architectures](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/architectures/sentence_level_architectures/) - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.
2. [Word-level Architecture](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/architectures/word_level_architecture/) - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation.
3. **Examples** - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.
1. [Sentence-level Examples](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/examples/sentence_level_examples/)
2. [Word-level Examples](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/examples/word_level_examples/)
4. **Pre-trained Models** - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level
1. [Sentence-level Models](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/models/sentence_level_pretrained/)
2. [Word-level Models](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/models/word_level_pretrained/)
5. **[Contact](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/contact/)** - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest
## Citations
If you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to [ACL 2021](https://2021.aclweb.org/).
```bash
@InProceedings{ranasinghe2021,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {An Exploratory Analysis of Multilingual Word Level Quality Estimation with Cross-Lingual Transformers},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics},
year = {2021}
}
```
If you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in [COLING 2020](https://coling2020.org/) and in [WMT 2020](http://www.statmt.org/wmt20/) at EMNLP 2020.
```bash
@InProceedings{transquest:2020a,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Computational Linguistics},
year = {2020}
}
```
```bash
@InProceedings{transquest:2020b,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {TransQuest at WMT2020: Sentence-Level Direct Assessment},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the Fifth Conference on Machine Translation},
year = {2020}
}
```
|
{"language": "en-zh", "license": "apache-2.0", "tags": ["Quality Estimation", "microtransquest"]}
|
TransQuest/microtransquest-en_zh-wiki
| null |
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"xlm-roberta",
"token-classification",
"Quality Estimation",
"microtransquest",
"license:apache-2.0",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[
"en-zh"
] |
TAGS
#transformers #pytorch #xlm-roberta #token-classification #Quality Estimation #microtransquest #license-apache-2.0 #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #region-us
|
# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers
The goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.
With TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.
## Features
- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.
- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.
- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented.
- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.
## Installation
### From pip
### From Source
## Using Pre-trained Models
## Documentation
For more details follow the documentation.
1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip.
2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest
1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.
2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation.
3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.
1. Sentence-level Examples
2. Word-level Examples
4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level
1. Sentence-level Models
2. Word-level Models
5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest
s
If you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.
If you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020.
|
[
"# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers\nThe goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.\n\nWith TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.",
"## Features\n- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.\n- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.\n- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented. \n- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.",
"## Installation",
"### From pip",
"### From Source",
"## Using Pre-trained Models",
"## Documentation\nFor more details follow the documentation.\n\n1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip. \n2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest\n 1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.\n 2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation. \n3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.\n 1. Sentence-level Examples\n 2. Word-level Examples\n4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level\n 1. Sentence-level Models\n 2. Word-level Models\n5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest\n\n\ns\nIf you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.\n\n\n\nIf you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020."
] |
[
"TAGS\n#transformers #pytorch #xlm-roberta #token-classification #Quality Estimation #microtransquest #license-apache-2.0 #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #region-us \n",
"# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers\nThe goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.\n\nWith TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.",
"## Features\n- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.\n- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.\n- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented. \n- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.",
"## Installation",
"### From pip",
"### From Source",
"## Using Pre-trained Models",
"## Documentation\nFor more details follow the documentation.\n\n1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip. \n2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest\n 1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.\n 2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation. \n3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.\n 1. Sentence-level Examples\n 2. Word-level Examples\n4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level\n 1. Sentence-level Models\n 2. Word-level Models\n5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest\n\n\ns\nIf you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.\n\n\n\nIf you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020."
] |
text-classification
|
transformers
|
# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers
The goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.
With TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in [WMT 2020](http://www.statmt.org/wmt20/quality-estimation-task.html). TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as [OpenKiwi](https://github.com/Unbabel/OpenKiwi) and [DeepQuest](https://github.com/sheffieldnlp/deepQuest).
## Features
- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.
- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.
- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented.
- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in [HuggingFace.](https://huggingface.co/TransQuest)
## Installation
### From pip
```bash
pip install transquest
```
### From Source
```bash
git clone https://github.com/TharinduDR/TransQuest.git
cd TransQuest
pip install -r requirements.txt
```
## Using Pre-trained Models
```python
import torch
from transquest.algo.sentence_level.monotransquest.run_model import MonoTransQuestModel
model = MonoTransQuestModel("xlmroberta", "TransQuest/monotransquest-da-any_en", num_labels=1, use_cuda=torch.cuda.is_available())
predictions, raw_outputs = model.predict([["Reducerea acestor conflicte este importantă pentru conservare.", "Reducing these conflicts is not important for preservation."]])
print(predictions)
```
## Documentation
For more details follow the documentation.
1. **[Installation](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/install/)** - Install TransQuest locally using pip.
2. **Architectures** - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest
1. [Sentence-level Architectures](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/architectures/sentence_level_architectures/) - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.
2. [Word-level Architecture](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/architectures/word_level_architecture/) - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation.
3. **Examples** - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.
1. [Sentence-level Examples](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/examples/sentence_level_examples/)
2. [Word-level Examples](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/examples/word_level_examples/)
4. **Pre-trained Models** - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level
1. [Sentence-level Models](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/models/sentence_level_pretrained/)
2. [Word-level Models](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/models/word_level_pretrained/)
5. **[Contact](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/contact/)** - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest
## Citations
If you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to [ACL 2021](https://2021.aclweb.org/).
```bash
@InProceedings{ranasinghe2021,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {An Exploratory Analysis of Multilingual Word Level Quality Estimation with Cross-Lingual Transformers},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics},
year = {2021}
}
```
If you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in [COLING 2020](https://coling2020.org/) and in [WMT 2020](http://www.statmt.org/wmt20/) at EMNLP 2020.
```bash
@InProceedings{transquest:2020a,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Computational Linguistics},
year = {2020}
}
```
```bash
@InProceedings{transquest:2020b,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {TransQuest at WMT2020: Sentence-Level Direct Assessment},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the Fifth Conference on Machine Translation},
year = {2020}
}
```
|
{"language": "multilingual-en", "license": "apache-2.0", "tags": ["Quality Estimation", "monotransquest", "DA"]}
|
TransQuest/monotransquest-da-any_en
| null |
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"xlm-roberta",
"text-classification",
"Quality Estimation",
"monotransquest",
"DA",
"license:apache-2.0",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[
"multilingual-en"
] |
TAGS
#transformers #pytorch #xlm-roberta #text-classification #Quality Estimation #monotransquest #DA #license-apache-2.0 #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #region-us
|
# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers
The goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.
With TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.
## Features
- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.
- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.
- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented.
- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.
## Installation
### From pip
### From Source
## Using Pre-trained Models
## Documentation
For more details follow the documentation.
1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip.
2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest
1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.
2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation.
3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.
1. Sentence-level Examples
2. Word-level Examples
4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level
1. Sentence-level Models
2. Word-level Models
5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest
s
If you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.
If you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020.
|
[
"# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers\nThe goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.\n\nWith TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.",
"## Features\n- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.\n- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.\n- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented. \n- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.",
"## Installation",
"### From pip",
"### From Source",
"## Using Pre-trained Models",
"## Documentation\nFor more details follow the documentation.\n\n1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip. \n2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest\n 1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.\n 2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation. \n3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.\n 1. Sentence-level Examples\n 2. Word-level Examples\n4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level\n 1. Sentence-level Models\n 2. Word-level Models\n5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest\n\n\ns\nIf you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.\n\n\n\nIf you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020."
] |
[
"TAGS\n#transformers #pytorch #xlm-roberta #text-classification #Quality Estimation #monotransquest #DA #license-apache-2.0 #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #region-us \n",
"# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers\nThe goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.\n\nWith TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.",
"## Features\n- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.\n- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.\n- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented. \n- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.",
"## Installation",
"### From pip",
"### From Source",
"## Using Pre-trained Models",
"## Documentation\nFor more details follow the documentation.\n\n1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip. \n2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest\n 1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.\n 2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation. \n3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.\n 1. Sentence-level Examples\n 2. Word-level Examples\n4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level\n 1. Sentence-level Models\n 2. Word-level Models\n5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest\n\n\ns\nIf you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.\n\n\n\nIf you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020."
] |
text-classification
|
transformers
|
# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers
The goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.
With TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in [WMT 2020](http://www.statmt.org/wmt20/quality-estimation-task.html). TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as [OpenKiwi](https://github.com/Unbabel/OpenKiwi) and [DeepQuest](https://github.com/sheffieldnlp/deepQuest).
## Features
- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.
- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.
- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented.
- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in [HuggingFace.](https://huggingface.co/TransQuest)
## Installation
### From pip
```bash
pip install transquest
```
### From Source
```bash
git clone https://github.com/TharinduDR/TransQuest.git
cd TransQuest
pip install -r requirements.txt
```
## Using Pre-trained Models
```python
import torch
from transquest.algo.sentence_level.monotransquest.run_model import MonoTransQuestModel
model = MonoTransQuestModel("xlmroberta", "TransQuest/monotransquest-da-en_any", num_labels=1, use_cuda=torch.cuda.is_available())
predictions, raw_outputs = model.predict([["Reducerea acestor conflicte este importantă pentru conservare.", "Reducing these conflicts is not important for preservation."]])
print(predictions)
```
## Documentation
For more details follow the documentation.
1. **[Installation](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/install/)** - Install TransQuest locally using pip.
2. **Architectures** - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest
1. [Sentence-level Architectures](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/architectures/sentence_level_architectures/) - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.
2. [Word-level Architecture](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/architectures/word_level_architecture/) - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation.
3. **Examples** - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.
1. [Sentence-level Examples](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/examples/sentence_level_examples/)
2. [Word-level Examples](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/examples/word_level_examples/)
4. **Pre-trained Models** - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level
1. [Sentence-level Models](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/models/sentence_level_pretrained/)
2. [Word-level Models](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/models/word_level_pretrained/)
5. **[Contact](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/contact/)** - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest
## Citations
If you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to [ACL 2021](https://2021.aclweb.org/).
```bash
@InProceedings{ranasinghe2021,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {An Exploratory Analysis of Multilingual Word Level Quality Estimation with Cross-Lingual Transformers},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics},
year = {2021}
}
```
If you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in [COLING 2020](https://coling2020.org/) and in [WMT 2020](http://www.statmt.org/wmt20/) at EMNLP 2020.
```bash
@InProceedings{transquest:2020a,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Computational Linguistics},
year = {2020}
}
```
```bash
@InProceedings{transquest:2020b,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {TransQuest at WMT2020: Sentence-Level Direct Assessment},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the Fifth Conference on Machine Translation},
year = {2020}
}
```
|
{"language": "en-multilingual", "license": "apache-2.0", "tags": ["Quality Estimation", "monotransquest", "DA"]}
|
TransQuest/monotransquest-da-en_any
| null |
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"xlm-roberta",
"text-classification",
"Quality Estimation",
"monotransquest",
"DA",
"license:apache-2.0",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[
"en-multilingual"
] |
TAGS
#transformers #pytorch #xlm-roberta #text-classification #Quality Estimation #monotransquest #DA #license-apache-2.0 #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #region-us
|
# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers
The goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.
With TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.
## Features
- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.
- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.
- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented.
- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.
## Installation
### From pip
### From Source
## Using Pre-trained Models
## Documentation
For more details follow the documentation.
1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip.
2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest
1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.
2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation.
3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.
1. Sentence-level Examples
2. Word-level Examples
4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level
1. Sentence-level Models
2. Word-level Models
5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest
s
If you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.
If you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020.
|
[
"# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers\nThe goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.\n\nWith TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.",
"## Features\n- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.\n- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.\n- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented. \n- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.",
"## Installation",
"### From pip",
"### From Source",
"## Using Pre-trained Models",
"## Documentation\nFor more details follow the documentation.\n\n1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip. \n2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest\n 1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.\n 2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation. \n3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.\n 1. Sentence-level Examples\n 2. Word-level Examples\n4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level\n 1. Sentence-level Models\n 2. Word-level Models\n5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest\n\n\ns\nIf you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.\n\n\n\nIf you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020."
] |
[
"TAGS\n#transformers #pytorch #xlm-roberta #text-classification #Quality Estimation #monotransquest #DA #license-apache-2.0 #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #region-us \n",
"# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers\nThe goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.\n\nWith TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.",
"## Features\n- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.\n- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.\n- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented. \n- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.",
"## Installation",
"### From pip",
"### From Source",
"## Using Pre-trained Models",
"## Documentation\nFor more details follow the documentation.\n\n1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip. \n2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest\n 1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.\n 2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation. \n3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.\n 1. Sentence-level Examples\n 2. Word-level Examples\n4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level\n 1. Sentence-level Models\n 2. Word-level Models\n5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest\n\n\ns\nIf you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.\n\n\n\nIf you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020."
] |
text-classification
|
transformers
|
# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers
The goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.
With TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in [WMT 2020](http://www.statmt.org/wmt20/quality-estimation-task.html). TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as [OpenKiwi](https://github.com/Unbabel/OpenKiwi) and [DeepQuest](https://github.com/sheffieldnlp/deepQuest).
## Features
- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.
- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.
- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented.
- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in [HuggingFace.](https://huggingface.co/TransQuest)
## Installation
### From pip
```bash
pip install transquest
```
### From Source
```bash
git clone https://github.com/TharinduDR/TransQuest.git
cd TransQuest
pip install -r requirements.txt
```
## Using Pre-trained Models
```python
import torch
from transquest.algo.sentence_level.monotransquest.run_model import MonoTransQuestModel
model = MonoTransQuestModel("xlmroberta", "TransQuest/monotransquest-da-en_de-wiki", num_labels=1, use_cuda=torch.cuda.is_available())
predictions, raw_outputs = model.predict([["Reducerea acestor conflicte este importantă pentru conservare.", "Reducing these conflicts is not important for preservation."]])
print(predictions)
```
## Documentation
For more details follow the documentation.
1. **[Installation](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/install/)** - Install TransQuest locally using pip.
2. **Architectures** - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest
1. [Sentence-level Architectures](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/architectures/sentence_level_architectures/) - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.
2. [Word-level Architecture](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/architectures/word_level_architecture/) - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation.
3. **Examples** - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.
1. [Sentence-level Examples](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/examples/sentence_level_examples/)
2. [Word-level Examples](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/examples/word_level_examples/)
4. **Pre-trained Models** - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level
1. [Sentence-level Models](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/models/sentence_level_pretrained/)
2. [Word-level Models](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/models/word_level_pretrained/)
5. **[Contact](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/contact/)** - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest
## Citations
If you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to [ACL 2021](https://2021.aclweb.org/).
```bash
@InProceedings{ranasinghe2021,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {An Exploratory Analysis of Multilingual Word Level Quality Estimation with Cross-Lingual Transformers},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics},
year = {2021}
}
```
If you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in [COLING 2020](https://coling2020.org/) and in [WMT 2020](http://www.statmt.org/wmt20/) at EMNLP 2020.
```bash
@InProceedings{transquest:2020a,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Computational Linguistics},
year = {2020}
}
```
```bash
@InProceedings{transquest:2020b,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {TransQuest at WMT2020: Sentence-Level Direct Assessment},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the Fifth Conference on Machine Translation},
year = {2020}
}
```
|
{"language": "en-de", "license": "apache-2.0", "tags": ["Quality Estimation", "monotransquest", "DA"]}
|
TransQuest/monotransquest-da-en_de-wiki
| null |
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"xlm-roberta",
"text-classification",
"Quality Estimation",
"monotransquest",
"DA",
"license:apache-2.0",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[
"en-de"
] |
TAGS
#transformers #pytorch #xlm-roberta #text-classification #Quality Estimation #monotransquest #DA #license-apache-2.0 #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #region-us
|
# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers
The goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.
With TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.
## Features
- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.
- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.
- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented.
- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.
## Installation
### From pip
### From Source
## Using Pre-trained Models
## Documentation
For more details follow the documentation.
1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip.
2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest
1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.
2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation.
3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.
1. Sentence-level Examples
2. Word-level Examples
4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level
1. Sentence-level Models
2. Word-level Models
5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest
s
If you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.
If you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020.
|
[
"# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers\nThe goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.\n\nWith TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.",
"## Features\n- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.\n- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.\n- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented. \n- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.",
"## Installation",
"### From pip",
"### From Source",
"## Using Pre-trained Models",
"## Documentation\nFor more details follow the documentation.\n\n1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip. \n2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest\n 1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.\n 2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation. \n3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.\n 1. Sentence-level Examples\n 2. Word-level Examples\n4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level\n 1. Sentence-level Models\n 2. Word-level Models\n5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest\n\n\ns\nIf you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.\n\n\n\nIf you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020."
] |
[
"TAGS\n#transformers #pytorch #xlm-roberta #text-classification #Quality Estimation #monotransquest #DA #license-apache-2.0 #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #region-us \n",
"# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers\nThe goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.\n\nWith TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.",
"## Features\n- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.\n- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.\n- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented. \n- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.",
"## Installation",
"### From pip",
"### From Source",
"## Using Pre-trained Models",
"## Documentation\nFor more details follow the documentation.\n\n1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip. \n2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest\n 1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.\n 2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation. \n3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.\n 1. Sentence-level Examples\n 2. Word-level Examples\n4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level\n 1. Sentence-level Models\n 2. Word-level Models\n5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest\n\n\ns\nIf you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.\n\n\n\nIf you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020."
] |
text-classification
|
transformers
|
# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers
The goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.
With TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in [WMT 2020](http://www.statmt.org/wmt20/quality-estimation-task.html). TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as [OpenKiwi](https://github.com/Unbabel/OpenKiwi) and [DeepQuest](https://github.com/sheffieldnlp/deepQuest).
## Features
- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.
- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.
- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented.
- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in [HuggingFace.](https://huggingface.co/TransQuest)
## Installation
### From pip
```bash
pip install transquest
```
### From Source
```bash
git clone https://github.com/TharinduDR/TransQuest.git
cd TransQuest
pip install -r requirements.txt
```
## Using Pre-trained Models
```python
import torch
from transquest.algo.sentence_level.monotransquest.run_model import MonoTransQuestModel
model = MonoTransQuestModel("xlmroberta", "TransQuest/monotransquest-da-en_zh-wiki", num_labels=1, use_cuda=torch.cuda.is_available())
predictions, raw_outputs = model.predict([["Reducerea acestor conflicte este importantă pentru conservare.", "Reducing these conflicts is not important for preservation."]])
print(predictions)
```
## Documentation
For more details follow the documentation.
1. **[Installation](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/install/)** - Install TransQuest locally using pip.
2. **Architectures** - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest
1. [Sentence-level Architectures](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/architectures/sentence_level_architectures/) - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.
2. [Word-level Architecture](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/architectures/word_level_architecture/) - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation.
3. **Examples** - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.
1. [Sentence-level Examples](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/examples/sentence_level_examples/)
2. [Word-level Examples](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/examples/word_level_examples/)
4. **Pre-trained Models** - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level
1. [Sentence-level Models](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/models/sentence_level_pretrained/)
2. [Word-level Models](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/models/word_level_pretrained/)
5. **[Contact](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/contact/)** - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest
## Citations
If you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to [ACL 2021](https://2021.aclweb.org/).
```bash
@InProceedings{ranasinghe2021,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {An Exploratory Analysis of Multilingual Word Level Quality Estimation with Cross-Lingual Transformers},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics},
year = {2021}
}
```
If you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in [COLING 2020](https://coling2020.org/) and in [WMT 2020](http://www.statmt.org/wmt20/) at EMNLP 2020.
```bash
@InProceedings{transquest:2020a,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Computational Linguistics},
year = {2020}
}
```
```bash
@InProceedings{transquest:2020b,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {TransQuest at WMT2020: Sentence-Level Direct Assessment},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the Fifth Conference on Machine Translation},
year = {2020}
}
```
|
{"language": "en-zh", "license": "apache-2.0", "tags": ["Quality Estimation", "monotransquest", "DA"]}
|
TransQuest/monotransquest-da-en_zh-wiki
| null |
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"xlm-roberta",
"text-classification",
"Quality Estimation",
"monotransquest",
"DA",
"license:apache-2.0",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[
"en-zh"
] |
TAGS
#transformers #pytorch #xlm-roberta #text-classification #Quality Estimation #monotransquest #DA #license-apache-2.0 #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #region-us
|
# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers
The goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.
With TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.
## Features
- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.
- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.
- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented.
- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.
## Installation
### From pip
### From Source
## Using Pre-trained Models
## Documentation
For more details follow the documentation.
1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip.
2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest
1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.
2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation.
3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.
1. Sentence-level Examples
2. Word-level Examples
4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level
1. Sentence-level Models
2. Word-level Models
5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest
s
If you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.
If you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020.
|
[
"# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers\nThe goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.\n\nWith TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.",
"## Features\n- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.\n- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.\n- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented. \n- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.",
"## Installation",
"### From pip",
"### From Source",
"## Using Pre-trained Models",
"## Documentation\nFor more details follow the documentation.\n\n1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip. \n2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest\n 1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.\n 2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation. \n3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.\n 1. Sentence-level Examples\n 2. Word-level Examples\n4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level\n 1. Sentence-level Models\n 2. Word-level Models\n5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest\n\n\ns\nIf you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.\n\n\n\nIf you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020."
] |
[
"TAGS\n#transformers #pytorch #xlm-roberta #text-classification #Quality Estimation #monotransquest #DA #license-apache-2.0 #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #region-us \n",
"# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers\nThe goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.\n\nWith TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.",
"## Features\n- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.\n- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.\n- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented. \n- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.",
"## Installation",
"### From pip",
"### From Source",
"## Using Pre-trained Models",
"## Documentation\nFor more details follow the documentation.\n\n1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip. \n2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest\n 1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.\n 2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation. \n3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.\n 1. Sentence-level Examples\n 2. Word-level Examples\n4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level\n 1. Sentence-level Models\n 2. Word-level Models\n5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest\n\n\ns\nIf you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.\n\n\n\nIf you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020."
] |
text-classification
|
transformers
|
# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers
The goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.
With TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in [WMT 2020](http://www.statmt.org/wmt20/quality-estimation-task.html). TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as [OpenKiwi](https://github.com/Unbabel/OpenKiwi) and [DeepQuest](https://github.com/sheffieldnlp/deepQuest).
## Features
- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.
- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.
- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented.
- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in [HuggingFace.](https://huggingface.co/TransQuest)
## Installation
### From pip
```bash
pip install transquest
```
### From Source
```bash
git clone https://github.com/TharinduDR/TransQuest.git
cd TransQuest
pip install -r requirements.txt
```
## Using Pre-trained Models
```python
import torch
from transquest.algo.sentence_level.monotransquest.run_model import MonoTransQuestModel
model = MonoTransQuestModel("xlmroberta", "TransQuest/monotransquest-da-et_en-wiki", num_labels=1, use_cuda=torch.cuda.is_available())
predictions, raw_outputs = model.predict([["Reducerea acestor conflicte este importantă pentru conservare.", "Reducing these conflicts is not important for preservation."]])
print(predictions)
```
## Documentation
For more details follow the documentation.
1. **[Installation](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/install/)** - Install TransQuest locally using pip.
2. **Architectures** - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest
1. [Sentence-level Architectures](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/architectures/sentence_level_architectures/) - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.
2. [Word-level Architecture](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/architectures/word_level_architecture/) - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation.
3. **Examples** - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.
1. [Sentence-level Examples](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/examples/sentence_level_examples/)
2. [Word-level Examples](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/examples/word_level_examples/)
4. **Pre-trained Models** - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level
1. [Sentence-level Models](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/models/sentence_level_pretrained/)
2. [Word-level Models](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/models/word_level_pretrained/)
5. **[Contact](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/contact/)** - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest
## Citations
If you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to [ACL 2021](https://2021.aclweb.org/).
```bash
@InProceedings{ranasinghe2021,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {An Exploratory Analysis of Multilingual Word Level Quality Estimation with Cross-Lingual Transformers},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics},
year = {2021}
}
```
If you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in [COLING 2020](https://coling2020.org/) and in [WMT 2020](http://www.statmt.org/wmt20/) at EMNLP 2020.
```bash
@InProceedings{transquest:2020a,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Computational Linguistics},
year = {2020}
}
```
```bash
@InProceedings{transquest:2020b,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {TransQuest at WMT2020: Sentence-Level Direct Assessment},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the Fifth Conference on Machine Translation},
year = {2020}
}
```
|
{"language": "et-en", "license": "apache-2.0", "tags": ["Quality Estimation", "monotransquest", "DA"]}
|
TransQuest/monotransquest-da-et_en-wiki
| null |
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"xlm-roberta",
"text-classification",
"Quality Estimation",
"monotransquest",
"DA",
"license:apache-2.0",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[
"et-en"
] |
TAGS
#transformers #pytorch #xlm-roberta #text-classification #Quality Estimation #monotransquest #DA #license-apache-2.0 #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #region-us
|
# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers
The goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.
With TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.
## Features
- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.
- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.
- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented.
- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.
## Installation
### From pip
### From Source
## Using Pre-trained Models
## Documentation
For more details follow the documentation.
1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip.
2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest
1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.
2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation.
3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.
1. Sentence-level Examples
2. Word-level Examples
4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level
1. Sentence-level Models
2. Word-level Models
5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest
s
If you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.
If you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020.
|
[
"# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers\nThe goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.\n\nWith TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.",
"## Features\n- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.\n- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.\n- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented. \n- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.",
"## Installation",
"### From pip",
"### From Source",
"## Using Pre-trained Models",
"## Documentation\nFor more details follow the documentation.\n\n1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip. \n2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest\n 1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.\n 2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation. \n3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.\n 1. Sentence-level Examples\n 2. Word-level Examples\n4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level\n 1. Sentence-level Models\n 2. Word-level Models\n5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest\n\n\ns\nIf you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.\n\n\n\nIf you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020."
] |
[
"TAGS\n#transformers #pytorch #xlm-roberta #text-classification #Quality Estimation #monotransquest #DA #license-apache-2.0 #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #region-us \n",
"# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers\nThe goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.\n\nWith TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.",
"## Features\n- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.\n- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.\n- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented. \n- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.",
"## Installation",
"### From pip",
"### From Source",
"## Using Pre-trained Models",
"## Documentation\nFor more details follow the documentation.\n\n1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip. \n2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest\n 1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.\n 2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation. \n3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.\n 1. Sentence-level Examples\n 2. Word-level Examples\n4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level\n 1. Sentence-level Models\n 2. Word-level Models\n5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest\n\n\ns\nIf you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.\n\n\n\nIf you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020."
] |
text-classification
|
transformers
|
# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers
The goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.
With TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in [WMT 2020](http://www.statmt.org/wmt20/quality-estimation-task.html). TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as [OpenKiwi](https://github.com/Unbabel/OpenKiwi) and [DeepQuest](https://github.com/sheffieldnlp/deepQuest).
## Features
- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.
- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.
- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented.
- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in [HuggingFace.](https://huggingface.co/TransQuest)
## Installation
### From pip
```bash
pip install transquest
```
### From Source
```bash
git clone https://github.com/TharinduDR/TransQuest.git
cd TransQuest
pip install -r requirements.txt
```
## Using Pre-trained Models
```python
import torch
from transquest.algo.sentence_level.monotransquest.run_model import MonoTransQuestModel
model = MonoTransQuestModel("xlmroberta", "TransQuest/monotransquest-da-multilingual", num_labels=1, use_cuda=torch.cuda.is_available())
predictions, raw_outputs = model.predict([["Reducerea acestor conflicte este importantă pentru conservare.", "Reducing these conflicts is not important for preservation."]])
print(predictions)
```
## Documentation
For more details follow the documentation.
1. **[Installation](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/install/)** - Install TransQuest locally using pip.
2. **Architectures** - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest
1. [Sentence-level Architectures](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/architectures/sentence_level_architectures/) - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.
2. [Word-level Architecture](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/architectures/word_level_architecture/) - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation.
3. **Examples** - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.
1. [Sentence-level Examples](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/examples/sentence_level_examples/)
2. [Word-level Examples](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/examples/word_level_examples/)
4. **Pre-trained Models** - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level
1. [Sentence-level Models](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/models/sentence_level_pretrained/)
2. [Word-level Models](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/models/word_level_pretrained/)
5. **[Contact](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/contact/)** - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest
## Citations
If you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to [ACL 2021](https://2021.aclweb.org/).
```bash
@InProceedings{ranasinghe2021,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {An Exploratory Analysis of Multilingual Word Level Quality Estimation with Cross-Lingual Transformers},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics},
year = {2021}
}
```
If you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in [COLING 2020](https://coling2020.org/) and in [WMT 2020](http://www.statmt.org/wmt20/) at EMNLP 2020.
```bash
@InProceedings{transquest:2020a,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Computational Linguistics},
year = {2020}
}
```
```bash
@InProceedings{transquest:2020b,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {TransQuest at WMT2020: Sentence-Level Direct Assessment},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the Fifth Conference on Machine Translation},
year = {2020}
}
```
|
{"language": "multilingual-multilingual", "license": "apache-2.0", "tags": ["Quality Estimation", "monotransquest", "DA"]}
|
TransQuest/monotransquest-da-multilingual
| null |
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"xlm-roberta",
"text-classification",
"Quality Estimation",
"monotransquest",
"DA",
"license:apache-2.0",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[
"multilingual-multilingual"
] |
TAGS
#transformers #pytorch #xlm-roberta #text-classification #Quality Estimation #monotransquest #DA #license-apache-2.0 #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #region-us
|
# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers
The goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.
With TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.
## Features
- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.
- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.
- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented.
- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.
## Installation
### From pip
### From Source
## Using Pre-trained Models
## Documentation
For more details follow the documentation.
1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip.
2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest
1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.
2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation.
3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.
1. Sentence-level Examples
2. Word-level Examples
4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level
1. Sentence-level Models
2. Word-level Models
5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest
s
If you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.
If you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020.
|
[
"# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers\nThe goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.\n\nWith TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.",
"## Features\n- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.\n- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.\n- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented. \n- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.",
"## Installation",
"### From pip",
"### From Source",
"## Using Pre-trained Models",
"## Documentation\nFor more details follow the documentation.\n\n1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip. \n2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest\n 1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.\n 2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation. \n3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.\n 1. Sentence-level Examples\n 2. Word-level Examples\n4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level\n 1. Sentence-level Models\n 2. Word-level Models\n5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest\n\n\ns\nIf you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.\n\n\n\nIf you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020."
] |
[
"TAGS\n#transformers #pytorch #xlm-roberta #text-classification #Quality Estimation #monotransquest #DA #license-apache-2.0 #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #region-us \n",
"# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers\nThe goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.\n\nWith TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.",
"## Features\n- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.\n- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.\n- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented. \n- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.",
"## Installation",
"### From pip",
"### From Source",
"## Using Pre-trained Models",
"## Documentation\nFor more details follow the documentation.\n\n1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip. \n2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest\n 1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.\n 2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation. \n3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.\n 1. Sentence-level Examples\n 2. Word-level Examples\n4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level\n 1. Sentence-level Models\n 2. Word-level Models\n5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest\n\n\ns\nIf you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.\n\n\n\nIf you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020."
] |
text-classification
|
transformers
|
# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers
The goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.
With TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in [WMT 2020](http://www.statmt.org/wmt20/quality-estimation-task.html). TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as [OpenKiwi](https://github.com/Unbabel/OpenKiwi) and [DeepQuest](https://github.com/sheffieldnlp/deepQuest).
## Features
- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.
- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.
- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented.
- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in [HuggingFace.](https://huggingface.co/TransQuest)
## Installation
### From pip
```bash
pip install transquest
```
### From Source
```bash
git clone https://github.com/TharinduDR/TransQuest.git
cd TransQuest
pip install -r requirements.txt
```
## Using Pre-trained Models
```python
import torch
from transquest.algo.sentence_level.monotransquest.run_model import MonoTransQuestModel
model = MonoTransQuestModel("xlmroberta", "TransQuest/monotransquest-da-ne_en-wiki", num_labels=1, use_cuda=torch.cuda.is_available())
predictions, raw_outputs = model.predict([["Reducerea acestor conflicte este importantă pentru conservare.", "Reducing these conflicts is not important for preservation."]])
print(predictions)
```
## Documentation
For more details follow the documentation.
1. **[Installation](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/install/)** - Install TransQuest locally using pip.
2. **Architectures** - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest
1. [Sentence-level Architectures](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/architectures/sentence_level_architectures/) - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.
2. [Word-level Architecture](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/architectures/word_level_architecture/) - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation.
3. **Examples** - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.
1. [Sentence-level Examples](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/examples/sentence_level_examples/)
2. [Word-level Examples](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/examples/word_level_examples/)
4. **Pre-trained Models** - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level
1. [Sentence-level Models](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/models/sentence_level_pretrained/)
2. [Word-level Models](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/models/word_level_pretrained/)
5. **[Contact](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/contact/)** - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest
## Citations
If you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to [ACL 2021](https://2021.aclweb.org/).
```bash
@InProceedings{ranasinghe2021,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {An Exploratory Analysis of Multilingual Word Level Quality Estimation with Cross-Lingual Transformers},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics},
year = {2021}
}
```
If you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in [COLING 2020](https://coling2020.org/) and in [WMT 2020](http://www.statmt.org/wmt20/) at EMNLP 2020.
```bash
@InProceedings{transquest:2020a,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Computational Linguistics},
year = {2020}
}
```
```bash
@InProceedings{transquest:2020b,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {TransQuest at WMT2020: Sentence-Level Direct Assessment},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the Fifth Conference on Machine Translation},
year = {2020}
}
```
|
{"language": "ne-en", "license": "apache-2.0", "tags": ["Quality Estimation", "monotransquest", "DA"]}
|
TransQuest/monotransquest-da-ne_en-wiki
| null |
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"xlm-roberta",
"text-classification",
"Quality Estimation",
"monotransquest",
"DA",
"license:apache-2.0",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[
"ne-en"
] |
TAGS
#transformers #pytorch #xlm-roberta #text-classification #Quality Estimation #monotransquest #DA #license-apache-2.0 #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #region-us
|
# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers
The goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.
With TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.
## Features
- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.
- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.
- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented.
- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.
## Installation
### From pip
### From Source
## Using Pre-trained Models
## Documentation
For more details follow the documentation.
1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip.
2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest
1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.
2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation.
3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.
1. Sentence-level Examples
2. Word-level Examples
4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level
1. Sentence-level Models
2. Word-level Models
5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest
s
If you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.
If you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020.
|
[
"# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers\nThe goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.\n\nWith TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.",
"## Features\n- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.\n- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.\n- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented. \n- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.",
"## Installation",
"### From pip",
"### From Source",
"## Using Pre-trained Models",
"## Documentation\nFor more details follow the documentation.\n\n1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip. \n2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest\n 1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.\n 2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation. \n3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.\n 1. Sentence-level Examples\n 2. Word-level Examples\n4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level\n 1. Sentence-level Models\n 2. Word-level Models\n5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest\n\n\ns\nIf you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.\n\n\n\nIf you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020."
] |
[
"TAGS\n#transformers #pytorch #xlm-roberta #text-classification #Quality Estimation #monotransquest #DA #license-apache-2.0 #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #region-us \n",
"# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers\nThe goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.\n\nWith TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.",
"## Features\n- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.\n- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.\n- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented. \n- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.",
"## Installation",
"### From pip",
"### From Source",
"## Using Pre-trained Models",
"## Documentation\nFor more details follow the documentation.\n\n1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip. \n2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest\n 1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.\n 2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation. \n3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.\n 1. Sentence-level Examples\n 2. Word-level Examples\n4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level\n 1. Sentence-level Models\n 2. Word-level Models\n5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest\n\n\ns\nIf you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.\n\n\n\nIf you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020."
] |
text-classification
|
transformers
|
# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers
The goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.
With TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in [WMT 2020](http://www.statmt.org/wmt20/quality-estimation-task.html). TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as [OpenKiwi](https://github.com/Unbabel/OpenKiwi) and [DeepQuest](https://github.com/sheffieldnlp/deepQuest).
## Features
- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.
- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.
- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented.
- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in [HuggingFace.](https://huggingface.co/TransQuest)
## Installation
### From pip
```bash
pip install transquest
```
### From Source
```bash
git clone https://github.com/TharinduDR/TransQuest.git
cd TransQuest
pip install -r requirements.txt
```
## Using Pre-trained Models
```python
import torch
from transquest.algo.sentence_level.monotransquest.run_model import MonoTransQuestModel
model = MonoTransQuestModel("xlmroberta", "TransQuest/monotransquest-da-ro_en-wiki", num_labels=1, use_cuda=torch.cuda.is_available())
predictions, raw_outputs = model.predict([["Reducerea acestor conflicte este importantă pentru conservare.", "Reducing these conflicts is not important for preservation."]])
print(predictions)
```
## Documentation
For more details follow the documentation.
1. **[Installation](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/install/)** - Install TransQuest locally using pip.
2. **Architectures** - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest
1. [Sentence-level Architectures](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/architectures/sentence_level_architectures/) - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.
2. [Word-level Architecture](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/architectures/word_level_architecture/) - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation.
3. **Examples** - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.
1. [Sentence-level Examples](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/examples/sentence_level_examples/)
2. [Word-level Examples](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/examples/word_level_examples/)
4. **Pre-trained Models** - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level
1. [Sentence-level Models](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/models/sentence_level_pretrained/)
2. [Word-level Models](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/models/word_level_pretrained/)
5. **[Contact](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/contact/)** - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest
## Citations
If you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to [ACL 2021](https://2021.aclweb.org/).
```bash
@InProceedings{ranasinghe2021,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {An Exploratory Analysis of Multilingual Word Level Quality Estimation with Cross-Lingual Transformers},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics},
year = {2021}
}
```
If you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in [COLING 2020](https://coling2020.org/) and in [WMT 2020](http://www.statmt.org/wmt20/) at EMNLP 2020.
```bash
@InProceedings{transquest:2020a,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Computational Linguistics},
year = {2020}
}
```
```bash
@InProceedings{transquest:2020b,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {TransQuest at WMT2020: Sentence-Level Direct Assessment},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the Fifth Conference on Machine Translation},
year = {2020}
}
```
|
{"language": "ro-en", "license": "apache-2.0", "tags": ["Quality Estimation", "monotransquest", "DA"]}
|
TransQuest/monotransquest-da-ro_en-wiki
| null |
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"xlm-roberta",
"text-classification",
"Quality Estimation",
"monotransquest",
"DA",
"license:apache-2.0",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[
"ro-en"
] |
TAGS
#transformers #pytorch #xlm-roberta #text-classification #Quality Estimation #monotransquest #DA #license-apache-2.0 #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #region-us
|
# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers
The goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.
With TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.
## Features
- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.
- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.
- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented.
- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.
## Installation
### From pip
### From Source
## Using Pre-trained Models
## Documentation
For more details follow the documentation.
1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip.
2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest
1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.
2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation.
3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.
1. Sentence-level Examples
2. Word-level Examples
4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level
1. Sentence-level Models
2. Word-level Models
5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest
s
If you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.
If you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020.
|
[
"# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers\nThe goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.\n\nWith TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.",
"## Features\n- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.\n- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.\n- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented. \n- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.",
"## Installation",
"### From pip",
"### From Source",
"## Using Pre-trained Models",
"## Documentation\nFor more details follow the documentation.\n\n1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip. \n2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest\n 1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.\n 2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation. \n3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.\n 1. Sentence-level Examples\n 2. Word-level Examples\n4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level\n 1. Sentence-level Models\n 2. Word-level Models\n5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest\n\n\ns\nIf you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.\n\n\n\nIf you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020."
] |
[
"TAGS\n#transformers #pytorch #xlm-roberta #text-classification #Quality Estimation #monotransquest #DA #license-apache-2.0 #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #region-us \n",
"# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers\nThe goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.\n\nWith TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.",
"## Features\n- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.\n- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.\n- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented. \n- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.",
"## Installation",
"### From pip",
"### From Source",
"## Using Pre-trained Models",
"## Documentation\nFor more details follow the documentation.\n\n1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip. \n2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest\n 1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.\n 2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation. \n3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.\n 1. Sentence-level Examples\n 2. Word-level Examples\n4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level\n 1. Sentence-level Models\n 2. Word-level Models\n5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest\n\n\ns\nIf you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.\n\n\n\nIf you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020."
] |
text-classification
|
transformers
|
# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers
The goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.
With TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in [WMT 2020](http://www.statmt.org/wmt20/quality-estimation-task.html). TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as [OpenKiwi](https://github.com/Unbabel/OpenKiwi) and [DeepQuest](https://github.com/sheffieldnlp/deepQuest).
## Features
- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.
- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.
- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented.
- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in [HuggingFace.](https://huggingface.co/TransQuest)
## Installation
### From pip
```bash
pip install transquest
```
### From Source
```bash
git clone https://github.com/TharinduDR/TransQuest.git
cd TransQuest
pip install -r requirements.txt
```
## Using Pre-trained Models
```python
import torch
from transquest.algo.sentence_level.monotransquest.run_model import MonoTransQuestModel
model = MonoTransQuestModel("xlmroberta", "TransQuest/monotransquest-da-ru_en-reddit_wikiquotes", num_labels=1, use_cuda=torch.cuda.is_available())
predictions, raw_outputs = model.predict([["Reducerea acestor conflicte este importantă pentru conservare.", "Reducing these conflicts is not important for preservation."]])
print(predictions)
```
## Documentation
For more details follow the documentation.
1. **[Installation](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/install/)** - Install TransQuest locally using pip.
2. **Architectures** - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest
1. [Sentence-level Architectures](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/architectures/sentence_level_architectures/) - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.
2. [Word-level Architecture](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/architectures/word_level_architecture/) - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation.
3. **Examples** - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.
1. [Sentence-level Examples](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/examples/sentence_level_examples/)
2. [Word-level Examples](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/examples/word_level_examples/)
4. **Pre-trained Models** - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level
1. [Sentence-level Models](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/models/sentence_level_pretrained/)
2. [Word-level Models](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/models/word_level_pretrained/)
5. **[Contact](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/contact/)** - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest
## Citations
If you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to [ACL 2021](https://2021.aclweb.org/).
```bash
@InProceedings{ranasinghe2021,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {An Exploratory Analysis of Multilingual Word Level Quality Estimation with Cross-Lingual Transformers},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics},
year = {2021}
}
```
If you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in [COLING 2020](https://coling2020.org/) and in [WMT 2020](http://www.statmt.org/wmt20/) at EMNLP 2020.
```bash
@InProceedings{transquest:2020a,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Computational Linguistics},
year = {2020}
}
```
```bash
@InProceedings{transquest:2020b,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {TransQuest at WMT2020: Sentence-Level Direct Assessment},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the Fifth Conference on Machine Translation},
year = {2020}
}
```
|
{"language": "ru-en", "license": "apache-2.0", "tags": ["Quality Estimation", "monotransquest", "DA"]}
|
TransQuest/monotransquest-da-ru_en-reddit_wikiquotes
| null |
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"xlm-roberta",
"text-classification",
"Quality Estimation",
"monotransquest",
"DA",
"license:apache-2.0",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[
"ru-en"
] |
TAGS
#transformers #pytorch #xlm-roberta #text-classification #Quality Estimation #monotransquest #DA #license-apache-2.0 #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #region-us
|
# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers
The goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.
With TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.
## Features
- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.
- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.
- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented.
- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.
## Installation
### From pip
### From Source
## Using Pre-trained Models
## Documentation
For more details follow the documentation.
1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip.
2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest
1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.
2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation.
3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.
1. Sentence-level Examples
2. Word-level Examples
4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level
1. Sentence-level Models
2. Word-level Models
5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest
s
If you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.
If you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020.
|
[
"# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers\nThe goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.\n\nWith TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.",
"## Features\n- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.\n- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.\n- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented. \n- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.",
"## Installation",
"### From pip",
"### From Source",
"## Using Pre-trained Models",
"## Documentation\nFor more details follow the documentation.\n\n1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip. \n2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest\n 1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.\n 2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation. \n3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.\n 1. Sentence-level Examples\n 2. Word-level Examples\n4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level\n 1. Sentence-level Models\n 2. Word-level Models\n5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest\n\n\ns\nIf you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.\n\n\n\nIf you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020."
] |
[
"TAGS\n#transformers #pytorch #xlm-roberta #text-classification #Quality Estimation #monotransquest #DA #license-apache-2.0 #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #region-us \n",
"# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers\nThe goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.\n\nWith TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.",
"## Features\n- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.\n- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.\n- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented. \n- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.",
"## Installation",
"### From pip",
"### From Source",
"## Using Pre-trained Models",
"## Documentation\nFor more details follow the documentation.\n\n1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip. \n2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest\n 1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.\n 2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation. \n3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.\n 1. Sentence-level Examples\n 2. Word-level Examples\n4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level\n 1. Sentence-level Models\n 2. Word-level Models\n5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest\n\n\ns\nIf you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.\n\n\n\nIf you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020."
] |
text-classification
|
transformers
|
# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers
The goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.
With TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in [WMT 2020](http://www.statmt.org/wmt20/quality-estimation-task.html). TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as [OpenKiwi](https://github.com/Unbabel/OpenKiwi) and [DeepQuest](https://github.com/sheffieldnlp/deepQuest).
## Features
- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.
- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.
- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented.
- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in [HuggingFace.](https://huggingface.co/TransQuest)
## Installation
### From pip
```bash
pip install transquest
```
### From Source
```bash
git clone https://github.com/TharinduDR/TransQuest.git
cd TransQuest
pip install -r requirements.txt
```
## Using Pre-trained Models
```python
import torch
from transquest.algo.sentence_level.monotransquest.run_model import MonoTransQuestModel
model = MonoTransQuestModel("xlmroberta", "TransQuest/monotransquest-da-si_en-wiki", num_labels=1, use_cuda=torch.cuda.is_available())
predictions, raw_outputs = model.predict([["Reducerea acestor conflicte este importantă pentru conservare.", "Reducing these conflicts is not important for preservation."]])
print(predictions)
```
## Documentation
For more details follow the documentation.
1. **[Installation](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/install/)** - Install TransQuest locally using pip.
2. **Architectures** - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest
1. [Sentence-level Architectures](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/architectures/sentence_level_architectures/) - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.
2. [Word-level Architecture](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/architectures/word_level_architecture/) - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation.
3. **Examples** - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.
1. [Sentence-level Examples](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/examples/sentence_level_examples/)
2. [Word-level Examples](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/examples/word_level_examples/)
4. **Pre-trained Models** - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level
1. [Sentence-level Models](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/models/sentence_level_pretrained/)
2. [Word-level Models](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/models/word_level_pretrained/)
5. **[Contact](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/contact/)** - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest
## Citations
If you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to [ACL 2021](https://2021.aclweb.org/).
```bash
@InProceedings{ranasinghe2021,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {An Exploratory Analysis of Multilingual Word Level Quality Estimation with Cross-Lingual Transformers},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics},
year = {2021}
}
```
If you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in [COLING 2020](https://coling2020.org/) and in [WMT 2020](http://www.statmt.org/wmt20/) at EMNLP 2020.
```bash
@InProceedings{transquest:2020a,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Computational Linguistics},
year = {2020}
}
```
```bash
@InProceedings{transquest:2020b,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {TransQuest at WMT2020: Sentence-Level Direct Assessment},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the Fifth Conference on Machine Translation},
year = {2020}
}
```
|
{"language": "si-en", "license": "apache-2.0", "tags": ["Quality Estimation", "monotransquest", "DA"]}
|
TransQuest/monotransquest-da-si_en-wiki
| null |
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"xlm-roberta",
"text-classification",
"Quality Estimation",
"monotransquest",
"DA",
"license:apache-2.0",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[
"si-en"
] |
TAGS
#transformers #pytorch #xlm-roberta #text-classification #Quality Estimation #monotransquest #DA #license-apache-2.0 #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #region-us
|
# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers
The goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.
With TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.
## Features
- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.
- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.
- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented.
- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.
## Installation
### From pip
### From Source
## Using Pre-trained Models
## Documentation
For more details follow the documentation.
1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip.
2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest
1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.
2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation.
3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.
1. Sentence-level Examples
2. Word-level Examples
4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level
1. Sentence-level Models
2. Word-level Models
5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest
s
If you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.
If you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020.
|
[
"# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers\nThe goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.\n\nWith TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.",
"## Features\n- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.\n- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.\n- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented. \n- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.",
"## Installation",
"### From pip",
"### From Source",
"## Using Pre-trained Models",
"## Documentation\nFor more details follow the documentation.\n\n1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip. \n2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest\n 1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.\n 2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation. \n3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.\n 1. Sentence-level Examples\n 2. Word-level Examples\n4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level\n 1. Sentence-level Models\n 2. Word-level Models\n5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest\n\n\ns\nIf you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.\n\n\n\nIf you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020."
] |
[
"TAGS\n#transformers #pytorch #xlm-roberta #text-classification #Quality Estimation #monotransquest #DA #license-apache-2.0 #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #region-us \n",
"# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers\nThe goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.\n\nWith TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.",
"## Features\n- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.\n- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.\n- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented. \n- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.",
"## Installation",
"### From pip",
"### From Source",
"## Using Pre-trained Models",
"## Documentation\nFor more details follow the documentation.\n\n1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip. \n2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest\n 1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.\n 2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation. \n3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.\n 1. Sentence-level Examples\n 2. Word-level Examples\n4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level\n 1. Sentence-level Models\n 2. Word-level Models\n5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest\n\n\ns\nIf you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.\n\n\n\nIf you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020."
] |
text-classification
|
transformers
|
# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers
The goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.
With TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in [WMT 2020](http://www.statmt.org/wmt20/quality-estimation-task.html). TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as [OpenKiwi](https://github.com/Unbabel/OpenKiwi) and [DeepQuest](https://github.com/sheffieldnlp/deepQuest).
## Features
- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.
- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.
- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented.
- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in [HuggingFace.](https://huggingface.co/TransQuest)
## Installation
### From pip
```bash
pip install transquest
```
### From Source
```bash
git clone https://github.com/TharinduDR/TransQuest.git
cd TransQuest
pip install -r requirements.txt
```
## Using Pre-trained Models
```python
import torch
from transquest.algo.sentence_level.monotransquest.run_model import MonoTransQuestModel
model = MonoTransQuestModel("xlmroberta", "TransQuest/monotransquest-hter-de_en-pharmaceutical", num_labels=1, use_cuda=torch.cuda.is_available())
predictions, raw_outputs = model.predict([["Reducerea acestor conflicte este importantă pentru conservare.", "Reducing these conflicts is not important for preservation."]])
print(predictions)
```
## Documentation
For more details follow the documentation.
1. **[Installation](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/install/)** - Install TransQuest locally using pip.
2. **Architectures** - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest
1. [Sentence-level Architectures](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/architectures/sentence_level_architectures/) - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.
2. [Word-level Architecture](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/architectures/word_level_architecture/) - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation.
3. **Examples** - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.
1. [Sentence-level Examples](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/examples/sentence_level_examples/)
2. [Word-level Examples](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/examples/word_level_examples/)
4. **Pre-trained Models** - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level
1. [Sentence-level Models](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/models/sentence_level_pretrained/)
2. [Word-level Models](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/models/word_level_pretrained/)
5. **[Contact](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/contact/)** - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest
## Citations
If you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to [ACL 2021](https://2021.aclweb.org/).
```bash
@InProceedings{ranasinghe2021,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {An Exploratory Analysis of Multilingual Word Level Quality Estimation with Cross-Lingual Transformers},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics},
year = {2021}
}
```
If you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in [COLING 2020](https://coling2020.org/) and in [WMT 2020](http://www.statmt.org/wmt20/) at EMNLP 2020.
```bash
@InProceedings{transquest:2020a,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Computational Linguistics},
year = {2020}
}
```
```bash
@InProceedings{transquest:2020b,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {TransQuest at WMT2020: Sentence-Level Direct Assessment},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the Fifth Conference on Machine Translation},
year = {2020}
}
```
|
{"language": "de-en", "license": "apache-2.0", "tags": ["Quality Estimation", "monotransquest", "hter"]}
|
TransQuest/monotransquest-hter-de_en-pharmaceutical
| null |
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"xlm-roberta",
"text-classification",
"Quality Estimation",
"monotransquest",
"hter",
"license:apache-2.0",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[
"de-en"
] |
TAGS
#transformers #pytorch #xlm-roberta #text-classification #Quality Estimation #monotransquest #hter #license-apache-2.0 #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #region-us
|
# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers
The goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.
With TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.
## Features
- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.
- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.
- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented.
- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.
## Installation
### From pip
### From Source
## Using Pre-trained Models
## Documentation
For more details follow the documentation.
1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip.
2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest
1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.
2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation.
3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.
1. Sentence-level Examples
2. Word-level Examples
4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level
1. Sentence-level Models
2. Word-level Models
5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest
s
If you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.
If you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020.
|
[
"# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers\nThe goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.\n\nWith TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.",
"## Features\n- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.\n- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.\n- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented. \n- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.",
"## Installation",
"### From pip",
"### From Source",
"## Using Pre-trained Models",
"## Documentation\nFor more details follow the documentation.\n\n1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip. \n2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest\n 1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.\n 2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation. \n3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.\n 1. Sentence-level Examples\n 2. Word-level Examples\n4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level\n 1. Sentence-level Models\n 2. Word-level Models\n5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest\n\n\ns\nIf you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.\n\n\n\nIf you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020."
] |
[
"TAGS\n#transformers #pytorch #xlm-roberta #text-classification #Quality Estimation #monotransquest #hter #license-apache-2.0 #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #region-us \n",
"# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers\nThe goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.\n\nWith TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.",
"## Features\n- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.\n- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.\n- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented. \n- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.",
"## Installation",
"### From pip",
"### From Source",
"## Using Pre-trained Models",
"## Documentation\nFor more details follow the documentation.\n\n1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip. \n2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest\n 1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.\n 2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation. \n3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.\n 1. Sentence-level Examples\n 2. Word-level Examples\n4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level\n 1. Sentence-level Models\n 2. Word-level Models\n5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest\n\n\ns\nIf you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.\n\n\n\nIf you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020."
] |
text-classification
|
transformers
|
# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers
The goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.
With TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in [WMT 2020](http://www.statmt.org/wmt20/quality-estimation-task.html). TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as [OpenKiwi](https://github.com/Unbabel/OpenKiwi) and [DeepQuest](https://github.com/sheffieldnlp/deepQuest).
## Features
- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.
- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.
- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented.
- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in [HuggingFace.](https://huggingface.co/TransQuest)
## Installation
### From pip
```bash
pip install transquest
```
### From Source
```bash
git clone https://github.com/TharinduDR/TransQuest.git
cd TransQuest
pip install -r requirements.txt
```
## Using Pre-trained Models
```python
import torch
from transquest.algo.sentence_level.monotransquest.run_model import MonoTransQuestModel
model = MonoTransQuestModel("xlmroberta", "TransQuest/monotransquest-hter-en_any", num_labels=1, use_cuda=torch.cuda.is_available())
predictions, raw_outputs = model.predict([["Reducerea acestor conflicte este importantă pentru conservare.", "Reducing these conflicts is not important for preservation."]])
print(predictions)
```
## Documentation
For more details follow the documentation.
1. **[Installation](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/install/)** - Install TransQuest locally using pip.
2. **Architectures** - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest
1. [Sentence-level Architectures](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/architectures/sentence_level_architectures/) - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.
2. [Word-level Architecture](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/architectures/word_level_architecture/) - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation.
3. **Examples** - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.
1. [Sentence-level Examples](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/examples/sentence_level_examples/)
2. [Word-level Examples](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/examples/word_level_examples/)
4. **Pre-trained Models** - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level
1. [Sentence-level Models](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/models/sentence_level_pretrained/)
2. [Word-level Models](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/models/word_level_pretrained/)
5. **[Contact](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/contact/)** - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest
## Citations
If you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to [ACL 2021](https://2021.aclweb.org/).
```bash
@InProceedings{ranasinghe2021,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {An Exploratory Analysis of Multilingual Word Level Quality Estimation with Cross-Lingual Transformers},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics},
year = {2021}
}
```
If you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in [COLING 2020](https://coling2020.org/) and in [WMT 2020](http://www.statmt.org/wmt20/) at EMNLP 2020.
```bash
@InProceedings{transquest:2020a,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Computational Linguistics},
year = {2020}
}
```
```bash
@InProceedings{transquest:2020b,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {TransQuest at WMT2020: Sentence-Level Direct Assessment},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the Fifth Conference on Machine Translation},
year = {2020}
}
```
|
{"language": "en-multilingual", "license": "apache-2.0", "tags": ["Quality Estimation", "monotransquest", "HTER"]}
|
TransQuest/monotransquest-hter-en_any
| null |
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"xlm-roberta",
"text-classification",
"Quality Estimation",
"monotransquest",
"HTER",
"license:apache-2.0",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[
"en-multilingual"
] |
TAGS
#transformers #pytorch #xlm-roberta #text-classification #Quality Estimation #monotransquest #HTER #license-apache-2.0 #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #region-us
|
# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers
The goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.
With TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.
## Features
- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.
- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.
- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented.
- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.
## Installation
### From pip
### From Source
## Using Pre-trained Models
## Documentation
For more details follow the documentation.
1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip.
2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest
1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.
2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation.
3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.
1. Sentence-level Examples
2. Word-level Examples
4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level
1. Sentence-level Models
2. Word-level Models
5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest
s
If you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.
If you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020.
|
[
"# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers\nThe goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.\n\nWith TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.",
"## Features\n- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.\n- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.\n- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented. \n- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.",
"## Installation",
"### From pip",
"### From Source",
"## Using Pre-trained Models",
"## Documentation\nFor more details follow the documentation.\n\n1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip. \n2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest\n 1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.\n 2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation. \n3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.\n 1. Sentence-level Examples\n 2. Word-level Examples\n4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level\n 1. Sentence-level Models\n 2. Word-level Models\n5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest\n\n\ns\nIf you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.\n\n\n\nIf you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020."
] |
[
"TAGS\n#transformers #pytorch #xlm-roberta #text-classification #Quality Estimation #monotransquest #HTER #license-apache-2.0 #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #region-us \n",
"# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers\nThe goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.\n\nWith TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.",
"## Features\n- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.\n- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.\n- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented. \n- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.",
"## Installation",
"### From pip",
"### From Source",
"## Using Pre-trained Models",
"## Documentation\nFor more details follow the documentation.\n\n1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip. \n2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest\n 1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.\n 2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation. \n3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.\n 1. Sentence-level Examples\n 2. Word-level Examples\n4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level\n 1. Sentence-level Models\n 2. Word-level Models\n5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest\n\n\ns\nIf you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.\n\n\n\nIf you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020."
] |
text-classification
|
transformers
|
# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers
The goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.
With TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in [WMT 2020](http://www.statmt.org/wmt20/quality-estimation-task.html). TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as [OpenKiwi](https://github.com/Unbabel/OpenKiwi) and [DeepQuest](https://github.com/sheffieldnlp/deepQuest).
## Features
- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.
- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.
- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented.
- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in [HuggingFace.](https://huggingface.co/TransQuest)
## Installation
### From pip
```bash
pip install transquest
```
### From Source
```bash
git clone https://github.com/TharinduDR/TransQuest.git
cd TransQuest
pip install -r requirements.txt
```
## Using Pre-trained Models
```python
import torch
from transquest.algo.sentence_level.monotransquest.run_model import MonoTransQuestModel
model = MonoTransQuestModel("xlmroberta", "TransQuest/monotransquest-hter-en_cs-pharmaceutical", num_labels=1, use_cuda=torch.cuda.is_available())
predictions, raw_outputs = model.predict([["Reducerea acestor conflicte este importantă pentru conservare.", "Reducing these conflicts is not important for preservation."]])
print(predictions)
```
## Documentation
For more details follow the documentation.
1. **[Installation](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/install/)** - Install TransQuest locally using pip.
2. **Architectures** - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest
1. [Sentence-level Architectures](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/architectures/sentence_level_architectures/) - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.
2. [Word-level Architecture](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/architectures/word_level_architecture/) - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation.
3. **Examples** - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.
1. [Sentence-level Examples](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/examples/sentence_level_examples/)
2. [Word-level Examples](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/examples/word_level_examples/)
4. **Pre-trained Models** - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level
1. [Sentence-level Models](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/models/sentence_level_pretrained/)
2. [Word-level Models](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/models/word_level_pretrained/)
5. **[Contact](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/contact/)** - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest
## Citations
If you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to [ACL 2021](https://2021.aclweb.org/).
```bash
@InProceedings{ranasinghe2021,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {An Exploratory Analysis of Multilingual Word Level Quality Estimation with Cross-Lingual Transformers},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics},
year = {2021}
}
```
If you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in [COLING 2020](https://coling2020.org/) and in [WMT 2020](http://www.statmt.org/wmt20/) at EMNLP 2020.
```bash
@InProceedings{transquest:2020a,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Computational Linguistics},
year = {2020}
}
```
```bash
@InProceedings{transquest:2020b,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {TransQuest at WMT2020: Sentence-Level Direct Assessment},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the Fifth Conference on Machine Translation},
year = {2020}
}
```
|
{"language": "en-cs", "license": "apache-2.0", "tags": ["Quality Estimation", "monotransquest", "hter"]}
|
TransQuest/monotransquest-hter-en_cs-pharmaceutical
| null |
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"xlm-roberta",
"text-classification",
"Quality Estimation",
"monotransquest",
"hter",
"license:apache-2.0",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[
"en-cs"
] |
TAGS
#transformers #pytorch #xlm-roberta #text-classification #Quality Estimation #monotransquest #hter #license-apache-2.0 #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #region-us
|
# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers
The goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.
With TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.
## Features
- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.
- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.
- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented.
- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.
## Installation
### From pip
### From Source
## Using Pre-trained Models
## Documentation
For more details follow the documentation.
1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip.
2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest
1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.
2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation.
3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.
1. Sentence-level Examples
2. Word-level Examples
4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level
1. Sentence-level Models
2. Word-level Models
5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest
s
If you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.
If you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020.
|
[
"# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers\nThe goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.\n\nWith TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.",
"## Features\n- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.\n- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.\n- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented. \n- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.",
"## Installation",
"### From pip",
"### From Source",
"## Using Pre-trained Models",
"## Documentation\nFor more details follow the documentation.\n\n1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip. \n2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest\n 1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.\n 2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation. \n3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.\n 1. Sentence-level Examples\n 2. Word-level Examples\n4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level\n 1. Sentence-level Models\n 2. Word-level Models\n5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest\n\n\ns\nIf you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.\n\n\n\nIf you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020."
] |
[
"TAGS\n#transformers #pytorch #xlm-roberta #text-classification #Quality Estimation #monotransquest #hter #license-apache-2.0 #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #region-us \n",
"# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers\nThe goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.\n\nWith TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.",
"## Features\n- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.\n- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.\n- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented. \n- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.",
"## Installation",
"### From pip",
"### From Source",
"## Using Pre-trained Models",
"## Documentation\nFor more details follow the documentation.\n\n1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip. \n2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest\n 1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.\n 2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation. \n3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.\n 1. Sentence-level Examples\n 2. Word-level Examples\n4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level\n 1. Sentence-level Models\n 2. Word-level Models\n5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest\n\n\ns\nIf you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.\n\n\n\nIf you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020."
] |
text-classification
|
transformers
|
# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers
The goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.
With TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in [WMT 2020](http://www.statmt.org/wmt20/quality-estimation-task.html). TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as [OpenKiwi](https://github.com/Unbabel/OpenKiwi) and [DeepQuest](https://github.com/sheffieldnlp/deepQuest).
## Features
- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.
- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.
- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented.
- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in [HuggingFace.](https://huggingface.co/TransQuest)
## Installation
### From pip
```bash
pip install transquest
```
### From Source
```bash
git clone https://github.com/TharinduDR/TransQuest.git
cd TransQuest
pip install -r requirements.txt
```
## Using Pre-trained Models
```python
import torch
from transquest.algo.sentence_level.monotransquest.run_model import MonoTransQuestModel
model = MonoTransQuestModel("xlmroberta", "TransQuest/monotransquest-hter-en_de-it-nmt", num_labels=1, use_cuda=torch.cuda.is_available())
predictions, raw_outputs = model.predict([["Reducerea acestor conflicte este importantă pentru conservare.", "Reducing these conflicts is not important for preservation."]])
print(predictions)
```
## Documentation
For more details follow the documentation.
1. **[Installation](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/install/)** - Install TransQuest locally using pip.
2. **Architectures** - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest
1. [Sentence-level Architectures](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/architectures/sentence_level_architectures/) - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.
2. [Word-level Architecture](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/architectures/word_level_architecture/) - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation.
3. **Examples** - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.
1. [Sentence-level Examples](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/examples/sentence_level_examples/)
2. [Word-level Examples](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/examples/word_level_examples/)
4. **Pre-trained Models** - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level
1. [Sentence-level Models](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/models/sentence_level_pretrained/)
2. [Word-level Models](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/models/word_level_pretrained/)
5. **[Contact](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/contact/)** - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest
## Citations
If you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to [ACL 2021](https://2021.aclweb.org/).
```bash
@InProceedings{ranasinghe2021,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {An Exploratory Analysis of Multilingual Word Level Quality Estimation with Cross-Lingual Transformers},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics},
year = {2021}
}
```
If you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in [COLING 2020](https://coling2020.org/) and in [WMT 2020](http://www.statmt.org/wmt20/) at EMNLP 2020.
```bash
@InProceedings{transquest:2020a,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Computational Linguistics},
year = {2020}
}
```
```bash
@InProceedings{transquest:2020b,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {TransQuest at WMT2020: Sentence-Level Direct Assessment},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the Fifth Conference on Machine Translation},
year = {2020}
}
```
|
{"language": "en-de", "license": "apache-2.0", "tags": ["Quality Estimation", "monotransquest", "hter"]}
|
TransQuest/monotransquest-hter-en_de-it-nmt
| null |
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"xlm-roberta",
"text-classification",
"Quality Estimation",
"monotransquest",
"hter",
"license:apache-2.0",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[
"en-de"
] |
TAGS
#transformers #pytorch #xlm-roberta #text-classification #Quality Estimation #monotransquest #hter #license-apache-2.0 #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #region-us
|
# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers
The goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.
With TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.
## Features
- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.
- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.
- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented.
- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.
## Installation
### From pip
### From Source
## Using Pre-trained Models
## Documentation
For more details follow the documentation.
1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip.
2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest
1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.
2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation.
3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.
1. Sentence-level Examples
2. Word-level Examples
4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level
1. Sentence-level Models
2. Word-level Models
5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest
s
If you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.
If you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020.
|
[
"# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers\nThe goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.\n\nWith TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.",
"## Features\n- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.\n- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.\n- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented. \n- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.",
"## Installation",
"### From pip",
"### From Source",
"## Using Pre-trained Models",
"## Documentation\nFor more details follow the documentation.\n\n1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip. \n2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest\n 1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.\n 2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation. \n3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.\n 1. Sentence-level Examples\n 2. Word-level Examples\n4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level\n 1. Sentence-level Models\n 2. Word-level Models\n5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest\n\n\ns\nIf you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.\n\n\n\nIf you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020."
] |
[
"TAGS\n#transformers #pytorch #xlm-roberta #text-classification #Quality Estimation #monotransquest #hter #license-apache-2.0 #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #region-us \n",
"# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers\nThe goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.\n\nWith TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.",
"## Features\n- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.\n- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.\n- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented. \n- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.",
"## Installation",
"### From pip",
"### From Source",
"## Using Pre-trained Models",
"## Documentation\nFor more details follow the documentation.\n\n1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip. \n2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest\n 1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.\n 2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation. \n3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.\n 1. Sentence-level Examples\n 2. Word-level Examples\n4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level\n 1. Sentence-level Models\n 2. Word-level Models\n5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest\n\n\ns\nIf you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.\n\n\n\nIf you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020."
] |
text-classification
|
transformers
|
# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers
The goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.
With TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in [WMT 2020](http://www.statmt.org/wmt20/quality-estimation-task.html). TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as [OpenKiwi](https://github.com/Unbabel/OpenKiwi) and [DeepQuest](https://github.com/sheffieldnlp/deepQuest).
## Features
- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.
- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.
- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented.
- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in [HuggingFace.](https://huggingface.co/TransQuest)
## Installation
### From pip
```bash
pip install transquest
```
### From Source
```bash
git clone https://github.com/TharinduDR/TransQuest.git
cd TransQuest
pip install -r requirements.txt
```
## Using Pre-trained Models
```python
import torch
from transquest.algo.sentence_level.monotransquest.run_model import MonoTransQuestModel
model = MonoTransQuestModel("xlmroberta", "TransQuest/monotransquest-hter-en_de-it-smt", num_labels=1, use_cuda=torch.cuda.is_available())
predictions, raw_outputs = model.predict([["Reducerea acestor conflicte este importantă pentru conservare.", "Reducing these conflicts is not important for preservation."]])
print(predictions)
```
## Documentation
For more details follow the documentation.
1. **[Installation](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/install/)** - Install TransQuest locally using pip.
2. **Architectures** - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest
1. [Sentence-level Architectures](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/architectures/sentence_level_architectures/) - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.
2. [Word-level Architecture](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/architectures/word_level_architecture/) - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation.
3. **Examples** - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.
1. [Sentence-level Examples](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/examples/sentence_level_examples/)
2. [Word-level Examples](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/examples/word_level_examples/)
4. **Pre-trained Models** - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level
1. [Sentence-level Models](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/models/sentence_level_pretrained/)
2. [Word-level Models](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/models/word_level_pretrained/)
5. **[Contact](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/contact/)** - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest
## Citations
If you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to [ACL 2021](https://2021.aclweb.org/).
```bash
@InProceedings{ranasinghe2021,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {An Exploratory Analysis of Multilingual Word Level Quality Estimation with Cross-Lingual Transformers},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics},
year = {2021}
}
```
If you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in [COLING 2020](https://coling2020.org/) and in [WMT 2020](http://www.statmt.org/wmt20/) at EMNLP 2020.
```bash
@InProceedings{transquest:2020a,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Computational Linguistics},
year = {2020}
}
```
```bash
@InProceedings{transquest:2020b,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {TransQuest at WMT2020: Sentence-Level Direct Assessment},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the Fifth Conference on Machine Translation},
year = {2020}
}
```
|
{"language": "en-de", "license": "apache-2.0", "tags": ["Quality Estimation", "monotransquest", "hter"]}
|
TransQuest/monotransquest-hter-en_de-it-smt
| null |
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"xlm-roberta",
"text-classification",
"Quality Estimation",
"monotransquest",
"hter",
"license:apache-2.0",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[
"en-de"
] |
TAGS
#transformers #pytorch #xlm-roberta #text-classification #Quality Estimation #monotransquest #hter #license-apache-2.0 #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #region-us
|
# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers
The goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.
With TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.
## Features
- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.
- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.
- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented.
- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.
## Installation
### From pip
### From Source
## Using Pre-trained Models
## Documentation
For more details follow the documentation.
1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip.
2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest
1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.
2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation.
3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.
1. Sentence-level Examples
2. Word-level Examples
4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level
1. Sentence-level Models
2. Word-level Models
5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest
s
If you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.
If you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020.
|
[
"# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers\nThe goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.\n\nWith TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.",
"## Features\n- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.\n- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.\n- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented. \n- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.",
"## Installation",
"### From pip",
"### From Source",
"## Using Pre-trained Models",
"## Documentation\nFor more details follow the documentation.\n\n1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip. \n2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest\n 1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.\n 2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation. \n3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.\n 1. Sentence-level Examples\n 2. Word-level Examples\n4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level\n 1. Sentence-level Models\n 2. Word-level Models\n5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest\n\n\ns\nIf you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.\n\n\n\nIf you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020."
] |
[
"TAGS\n#transformers #pytorch #xlm-roberta #text-classification #Quality Estimation #monotransquest #hter #license-apache-2.0 #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #region-us \n",
"# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers\nThe goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.\n\nWith TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.",
"## Features\n- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.\n- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.\n- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented. \n- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.",
"## Installation",
"### From pip",
"### From Source",
"## Using Pre-trained Models",
"## Documentation\nFor more details follow the documentation.\n\n1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip. \n2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest\n 1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.\n 2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation. \n3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.\n 1. Sentence-level Examples\n 2. Word-level Examples\n4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level\n 1. Sentence-level Models\n 2. Word-level Models\n5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest\n\n\ns\nIf you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.\n\n\n\nIf you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020."
] |
text-classification
|
transformers
|
# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers
The goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.
With TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in [WMT 2020](http://www.statmt.org/wmt20/quality-estimation-task.html). TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as [OpenKiwi](https://github.com/Unbabel/OpenKiwi) and [DeepQuest](https://github.com/sheffieldnlp/deepQuest).
## Features
- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.
- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.
- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented.
- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in [HuggingFace.](https://huggingface.co/TransQuest)
## Installation
### From pip
```bash
pip install transquest
```
### From Source
```bash
git clone https://github.com/TharinduDR/TransQuest.git
cd TransQuest
pip install -r requirements.txt
```
## Using Pre-trained Models
```python
import torch
from transquest.algo.sentence_level.monotransquest.run_model import MonoTransQuestModel
model = MonoTransQuestModel("xlmroberta", "TransQuest/monotransquest-hter-en_de-wiki", num_labels=1, use_cuda=torch.cuda.is_available())
predictions, raw_outputs = model.predict([["Reducerea acestor conflicte este importantă pentru conservare.", "Reducing these conflicts is not important for preservation."]])
print(predictions)
```
## Documentation
For more details follow the documentation.
1. **[Installation](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/install/)** - Install TransQuest locally using pip.
2. **Architectures** - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest
1. [Sentence-level Architectures](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/architectures/sentence_level_architectures/) - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.
2. [Word-level Architecture](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/architectures/word_level_architecture/) - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation.
3. **Examples** - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.
1. [Sentence-level Examples](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/examples/sentence_level_examples/)
2. [Word-level Examples](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/examples/word_level_examples/)
4. **Pre-trained Models** - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level
1. [Sentence-level Models](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/models/sentence_level_pretrained/)
2. [Word-level Models](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/models/word_level_pretrained/)
5. **[Contact](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/contact/)** - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest
## Citations
If you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to [ACL 2021](https://2021.aclweb.org/).
```bash
@InProceedings{ranasinghe2021,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {An Exploratory Analysis of Multilingual Word Level Quality Estimation with Cross-Lingual Transformers},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics},
year = {2021}
}
```
If you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in [COLING 2020](https://coling2020.org/) and in [WMT 2020](http://www.statmt.org/wmt20/) at EMNLP 2020.
```bash
@InProceedings{transquest:2020a,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Computational Linguistics},
year = {2020}
}
```
```bash
@InProceedings{transquest:2020b,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {TransQuest at WMT2020: Sentence-Level Direct Assessment},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the Fifth Conference on Machine Translation},
year = {2020}
}
```
|
{"language": "en-de", "license": "apache-2.0", "tags": ["Quality Estimation", "monotransquest", "hter"]}
|
TransQuest/monotransquest-hter-en_de-wiki
| null |
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"xlm-roberta",
"text-classification",
"Quality Estimation",
"monotransquest",
"hter",
"license:apache-2.0",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[
"en-de"
] |
TAGS
#transformers #pytorch #xlm-roberta #text-classification #Quality Estimation #monotransquest #hter #license-apache-2.0 #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #region-us
|
# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers
The goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.
With TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.
## Features
- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.
- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.
- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented.
- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.
## Installation
### From pip
### From Source
## Using Pre-trained Models
## Documentation
For more details follow the documentation.
1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip.
2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest
1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.
2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation.
3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.
1. Sentence-level Examples
2. Word-level Examples
4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level
1. Sentence-level Models
2. Word-level Models
5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest
s
If you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.
If you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020.
|
[
"# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers\nThe goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.\n\nWith TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.",
"## Features\n- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.\n- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.\n- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented. \n- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.",
"## Installation",
"### From pip",
"### From Source",
"## Using Pre-trained Models",
"## Documentation\nFor more details follow the documentation.\n\n1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip. \n2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest\n 1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.\n 2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation. \n3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.\n 1. Sentence-level Examples\n 2. Word-level Examples\n4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level\n 1. Sentence-level Models\n 2. Word-level Models\n5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest\n\n\ns\nIf you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.\n\n\n\nIf you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020."
] |
[
"TAGS\n#transformers #pytorch #xlm-roberta #text-classification #Quality Estimation #monotransquest #hter #license-apache-2.0 #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #region-us \n",
"# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers\nThe goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.\n\nWith TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.",
"## Features\n- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.\n- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.\n- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented. \n- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.",
"## Installation",
"### From pip",
"### From Source",
"## Using Pre-trained Models",
"## Documentation\nFor more details follow the documentation.\n\n1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip. \n2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest\n 1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.\n 2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation. \n3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.\n 1. Sentence-level Examples\n 2. Word-level Examples\n4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level\n 1. Sentence-level Models\n 2. Word-level Models\n5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest\n\n\ns\nIf you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.\n\n\n\nIf you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020."
] |
text-classification
|
transformers
|
# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers
The goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.
With TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in [WMT 2020](http://www.statmt.org/wmt20/quality-estimation-task.html). TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as [OpenKiwi](https://github.com/Unbabel/OpenKiwi) and [DeepQuest](https://github.com/sheffieldnlp/deepQuest).
## Features
- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.
- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.
- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented.
- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in [HuggingFace.](https://huggingface.co/TransQuest)
## Installation
### From pip
```bash
pip install transquest
```
### From Source
```bash
git clone https://github.com/TharinduDR/TransQuest.git
cd TransQuest
pip install -r requirements.txt
```
## Using Pre-trained Models
```python
import torch
from transquest.algo.sentence_level.monotransquest.run_model import MonoTransQuestModel
model = MonoTransQuestModel("xlmroberta", "TransQuest/monotransquest-hter-en_lv-it-nmt", num_labels=1, use_cuda=torch.cuda.is_available())
predictions, raw_outputs = model.predict([["Reducerea acestor conflicte este importantă pentru conservare.", "Reducing these conflicts is not important for preservation."]])
print(predictions)
```
## Documentation
For more details follow the documentation.
1. **[Installation](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/install/)** - Install TransQuest locally using pip.
2. **Architectures** - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest
1. [Sentence-level Architectures](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/architectures/sentence_level_architectures/) - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.
2. [Word-level Architecture](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/architectures/word_level_architecture/) - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation.
3. **Examples** - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.
1. [Sentence-level Examples](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/examples/sentence_level_examples/)
2. [Word-level Examples](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/examples/word_level_examples/)
4. **Pre-trained Models** - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level
1. [Sentence-level Models](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/models/sentence_level_pretrained/)
2. [Word-level Models](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/models/word_level_pretrained/)
5. **[Contact](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/contact/)** - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest
## Citations
If you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to [ACL 2021](https://2021.aclweb.org/).
```bash
@InProceedings{ranasinghe2021,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {An Exploratory Analysis of Multilingual Word Level Quality Estimation with Cross-Lingual Transformers},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics},
year = {2021}
}
```
If you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in [COLING 2020](https://coling2020.org/) and in [WMT 2020](http://www.statmt.org/wmt20/) at EMNLP 2020.
```bash
@InProceedings{transquest:2020a,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Computational Linguistics},
year = {2020}
}
```
```bash
@InProceedings{transquest:2020b,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {TransQuest at WMT2020: Sentence-Level Direct Assessment},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the Fifth Conference on Machine Translation},
year = {2020}
}
```
|
{"language": "en-lv", "license": "apache-2.0", "tags": ["Quality Estimation", "monotransquest", "hter"]}
|
TransQuest/monotransquest-hter-en_lv-it-nmt
| null |
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"xlm-roberta",
"text-classification",
"Quality Estimation",
"monotransquest",
"hter",
"license:apache-2.0",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[
"en-lv"
] |
TAGS
#transformers #pytorch #xlm-roberta #text-classification #Quality Estimation #monotransquest #hter #license-apache-2.0 #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #region-us
|
# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers
The goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.
With TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.
## Features
- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.
- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.
- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented.
- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.
## Installation
### From pip
### From Source
## Using Pre-trained Models
## Documentation
For more details follow the documentation.
1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip.
2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest
1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.
2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation.
3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.
1. Sentence-level Examples
2. Word-level Examples
4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level
1. Sentence-level Models
2. Word-level Models
5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest
s
If you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.
If you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020.
|
[
"# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers\nThe goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.\n\nWith TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.",
"## Features\n- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.\n- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.\n- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented. \n- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.",
"## Installation",
"### From pip",
"### From Source",
"## Using Pre-trained Models",
"## Documentation\nFor more details follow the documentation.\n\n1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip. \n2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest\n 1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.\n 2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation. \n3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.\n 1. Sentence-level Examples\n 2. Word-level Examples\n4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level\n 1. Sentence-level Models\n 2. Word-level Models\n5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest\n\n\ns\nIf you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.\n\n\n\nIf you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020."
] |
[
"TAGS\n#transformers #pytorch #xlm-roberta #text-classification #Quality Estimation #monotransquest #hter #license-apache-2.0 #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #region-us \n",
"# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers\nThe goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.\n\nWith TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.",
"## Features\n- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.\n- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.\n- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented. \n- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.",
"## Installation",
"### From pip",
"### From Source",
"## Using Pre-trained Models",
"## Documentation\nFor more details follow the documentation.\n\n1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip. \n2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest\n 1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.\n 2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation. \n3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.\n 1. Sentence-level Examples\n 2. Word-level Examples\n4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level\n 1. Sentence-level Models\n 2. Word-level Models\n5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest\n\n\ns\nIf you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.\n\n\n\nIf you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020."
] |
text-classification
|
transformers
|
# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers
The goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.
With TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in [WMT 2020](http://www.statmt.org/wmt20/quality-estimation-task.html). TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as [OpenKiwi](https://github.com/Unbabel/OpenKiwi) and [DeepQuest](https://github.com/sheffieldnlp/deepQuest).
## Features
- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.
- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.
- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented.
- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in [HuggingFace.](https://huggingface.co/TransQuest)
## Installation
### From pip
```bash
pip install transquest
```
### From Source
```bash
git clone https://github.com/TharinduDR/TransQuest.git
cd TransQuest
pip install -r requirements.txt
```
## Using Pre-trained Models
```python
import torch
from transquest.algo.sentence_level.monotransquest.run_model import MonoTransQuestModel
model = MonoTransQuestModel("xlmroberta", "TransQuest/monotransquest-hter-en_lv-it-smt", num_labels=1, use_cuda=torch.cuda.is_available())
predictions, raw_outputs = model.predict([["Reducerea acestor conflicte este importantă pentru conservare.", "Reducing these conflicts is not important for preservation."]])
print(predictions)
```
## Documentation
For more details follow the documentation.
1. **[Installation](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/install/)** - Install TransQuest locally using pip.
2. **Architectures** - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest
1. [Sentence-level Architectures](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/architectures/sentence_level_architectures/) - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.
2. [Word-level Architecture](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/architectures/word_level_architecture/) - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation.
3. **Examples** - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.
1. [Sentence-level Examples](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/examples/sentence_level_examples/)
2. [Word-level Examples](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/examples/word_level_examples/)
4. **Pre-trained Models** - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level
1. [Sentence-level Models](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/models/sentence_level_pretrained/)
2. [Word-level Models](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/models/word_level_pretrained/)
5. **[Contact](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/contact/)** - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest
## Citations
If you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to [ACL 2021](https://2021.aclweb.org/).
```bash
@InProceedings{ranasinghe2021,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {An Exploratory Analysis of Multilingual Word Level Quality Estimation with Cross-Lingual Transformers},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics},
year = {2021}
}
```
If you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in [COLING 2020](https://coling2020.org/) and in [WMT 2020](http://www.statmt.org/wmt20/) at EMNLP 2020.
```bash
@InProceedings{transquest:2020a,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Computational Linguistics},
year = {2020}
}
```
```bash
@InProceedings{transquest:2020b,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {TransQuest at WMT2020: Sentence-Level Direct Assessment},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the Fifth Conference on Machine Translation},
year = {2020}
}
```
|
{"language": "en-lv", "license": "apache-2.0", "tags": ["Quality Estimation", "monotransquest", "hter"]}
|
TransQuest/monotransquest-hter-en_lv-it-smt
| null |
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"xlm-roberta",
"text-classification",
"Quality Estimation",
"monotransquest",
"hter",
"license:apache-2.0",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[
"en-lv"
] |
TAGS
#transformers #pytorch #xlm-roberta #text-classification #Quality Estimation #monotransquest #hter #license-apache-2.0 #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #region-us
|
# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers
The goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.
With TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.
## Features
- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.
- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.
- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented.
- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.
## Installation
### From pip
### From Source
## Using Pre-trained Models
## Documentation
For more details follow the documentation.
1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip.
2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest
1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.
2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation.
3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.
1. Sentence-level Examples
2. Word-level Examples
4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level
1. Sentence-level Models
2. Word-level Models
5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest
s
If you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.
If you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020.
|
[
"# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers\nThe goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.\n\nWith TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.",
"## Features\n- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.\n- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.\n- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented. \n- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.",
"## Installation",
"### From pip",
"### From Source",
"## Using Pre-trained Models",
"## Documentation\nFor more details follow the documentation.\n\n1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip. \n2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest\n 1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.\n 2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation. \n3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.\n 1. Sentence-level Examples\n 2. Word-level Examples\n4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level\n 1. Sentence-level Models\n 2. Word-level Models\n5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest\n\n\ns\nIf you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.\n\n\n\nIf you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020."
] |
[
"TAGS\n#transformers #pytorch #xlm-roberta #text-classification #Quality Estimation #monotransquest #hter #license-apache-2.0 #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #region-us \n",
"# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers\nThe goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.\n\nWith TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.",
"## Features\n- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.\n- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.\n- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented. \n- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.",
"## Installation",
"### From pip",
"### From Source",
"## Using Pre-trained Models",
"## Documentation\nFor more details follow the documentation.\n\n1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip. \n2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest\n 1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.\n 2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation. \n3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.\n 1. Sentence-level Examples\n 2. Word-level Examples\n4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level\n 1. Sentence-level Models\n 2. Word-level Models\n5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest\n\n\ns\nIf you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.\n\n\n\nIf you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020."
] |
text-classification
|
transformers
|
# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers
The goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.
With TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in [WMT 2020](http://www.statmt.org/wmt20/quality-estimation-task.html). TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as [OpenKiwi](https://github.com/Unbabel/OpenKiwi) and [DeepQuest](https://github.com/sheffieldnlp/deepQuest).
## Features
- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.
- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.
- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented.
- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in [HuggingFace.](https://huggingface.co/TransQuest)
## Installation
### From pip
```bash
pip install transquest
```
### From Source
```bash
git clone https://github.com/TharinduDR/TransQuest.git
cd TransQuest
pip install -r requirements.txt
```
## Using Pre-trained Models
```python
import torch
from transquest.algo.sentence_level.monotransquest.run_model import MonoTransQuestModel
model = MonoTransQuestModel("xlmroberta", "TransQuest/monotransquest-hter-en_zh-wiki", num_labels=1, use_cuda=torch.cuda.is_available())
predictions, raw_outputs = model.predict([["Reducerea acestor conflicte este importantă pentru conservare.", "Reducing these conflicts is not important for preservation."]])
print(predictions)
```
## Documentation
For more details follow the documentation.
## Table of Contents
1. **[Installation](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/install/)** - Install TransQuest locally using pip.
2. **Architectures** - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest
1. [Sentence-level Architectures](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/architectures/sentence_level_architectures/) - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.
2. [Word-level Architecture](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/architectures/word_level_architecture/) - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation.
3. **Examples** - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.
1. [Sentence-level Examples](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/examples/sentence_level_examples/)
2. [Word-level Examples](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/examples/word_level_examples/)
4. **Pre-trained Models** - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level
1. [Sentence-level Models](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/models/sentence_level_pretrained/)
2. [Word-level Models](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/models/word_level_pretrained/)
5. **[Contact](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/contact/)** - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest
## Citations
If you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to [ACL 2021](https://2021.aclweb.org/).
```bash
@InProceedings{ranasinghe2021,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {An Exploratory Analysis of Multilingual Word Level Quality Estimation with Cross-Lingual Transformers},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics},
year = {2021}
}
```
If you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in [COLING 2020](https://coling2020.org/) and in [WMT 2020](http://www.statmt.org/wmt20/) at EMNLP 2020.
```bash
@InProceedings{transquest:2020a,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Computational Linguistics},
year = {2020}
}
```
```bash
@InProceedings{transquest:2020b,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {TransQuest at WMT2020: Sentence-Level Direct Assessment},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the Fifth Conference on Machine Translation},
year = {2020}
}
```
|
{"language": "en-zh", "license": "apache-2.0", "tags": ["Quality Estimation", "monotransquest", "hter"]}
|
TransQuest/monotransquest-hter-en_zh-wiki
| null |
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"xlm-roberta",
"text-classification",
"Quality Estimation",
"monotransquest",
"hter",
"license:apache-2.0",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[
"en-zh"
] |
TAGS
#transformers #pytorch #xlm-roberta #text-classification #Quality Estimation #monotransquest #hter #license-apache-2.0 #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #region-us
|
# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers
The goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.
With TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.
## Features
- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.
- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.
- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented.
- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.
## Installation
### From pip
### From Source
## Using Pre-trained Models
## Documentation
For more details follow the documentation.
## Table of Contents
1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip.
2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest
1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.
2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation.
3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.
1. Sentence-level Examples
2. Word-level Examples
4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level
1. Sentence-level Models
2. Word-level Models
5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest
s
If you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.
If you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020.
|
[
"# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers\nThe goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.\n\nWith TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.",
"## Features\n- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.\n- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.\n- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented. \n- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.",
"## Installation",
"### From pip",
"### From Source",
"## Using Pre-trained Models",
"## Documentation\nFor more details follow the documentation.",
"## Table of Contents\n1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip. \n2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest\n 1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.\n 2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation. \n3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.\n 1. Sentence-level Examples\n 2. Word-level Examples\n4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level\n 1. Sentence-level Models\n 2. Word-level Models\n5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest\n\n\ns\nIf you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.\n\n\n\nIf you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020."
] |
[
"TAGS\n#transformers #pytorch #xlm-roberta #text-classification #Quality Estimation #monotransquest #hter #license-apache-2.0 #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #region-us \n",
"# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers\nThe goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.\n\nWith TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.",
"## Features\n- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.\n- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.\n- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented. \n- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.",
"## Installation",
"### From pip",
"### From Source",
"## Using Pre-trained Models",
"## Documentation\nFor more details follow the documentation.",
"## Table of Contents\n1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip. \n2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest\n 1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.\n 2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation. \n3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.\n 1. Sentence-level Examples\n 2. Word-level Examples\n4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level\n 1. Sentence-level Models\n 2. Word-level Models\n5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest\n\n\ns\nIf you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.\n\n\n\nIf you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020."
] |
feature-extraction
|
transformers
|
# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers
The goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.
With TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in [WMT 2020](http://www.statmt.org/wmt20/quality-estimation-task.html). TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as [OpenKiwi](https://github.com/Unbabel/OpenKiwi) and [DeepQuest](https://github.com/sheffieldnlp/deepQuest).
## Features
- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.
- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.
- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented.
- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in [HuggingFace.](https://huggingface.co/TransQuest)
## Installation
### From pip
```bash
pip install transquest
```
### From Source
```bash
git clone https://github.com/TharinduDR/TransQuest.git
cd TransQuest
pip install -r requirements.txt
```
## Using Pre-trained Models
```python
import torch
from transquest.algo.sentence_level.siamesetransquest.run_model import SiameseTransQuestModel
model = SiameseTransQuestModel("TransQuest/siamesetransquest-da-en_de-wiki")
predictions = model.predict([["Reducerea acestor conflicte este importantă pentru conservare.", "Reducing these conflicts is not important for preservation."]])
print(predictions)
```
## Documentation
For more details follow the documentation.
1. **[Installation](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/install/)** - Install TransQuest locally using pip.
2. **Architectures** - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest
1. [Sentence-level Architectures](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/architectures/sentence_level_architectures/) - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.
2. [Word-level Architecture](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/architectures/word_level_architecture/) - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation.
3. **Examples** - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.
1. [Sentence-level Examples](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/examples/sentence_level_examples/)
2. [Word-level Examples](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/examples/word_level_examples/)
4. **Pre-trained Models** - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level
1. [Sentence-level Models](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/models/sentence_level_pretrained/)
2. [Word-level Models](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/models/word_level_pretrained/)
5. **[Contact](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/contact/)** - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest
## Citations
If you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to [ACL 2021](https://2021.aclweb.org/).
```bash
@InProceedings{ranasinghe2021,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {An Exploratory Analysis of Multilingual Word Level Quality Estimation with Cross-Lingual Transformers},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics},
year = {2021}
}
```
If you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in [COLING 2020](https://coling2020.org/) and in [WMT 2020](http://www.statmt.org/wmt20/) at EMNLP 2020.
```bash
@InProceedings{transquest:2020a,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Computational Linguistics},
year = {2020}
}
```
```bash
@InProceedings{transquest:2020b,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {TransQuest at WMT2020: Sentence-Level Direct Assessment},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the Fifth Conference on Machine Translation},
year = {2020}
}
```
|
{"language": "en-de", "license": "apache-2.0", "tags": ["Quality Estimation", "siamesetransquest", "da"]}
|
TransQuest/siamesetransquest-da-en_de-wiki
| null |
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"xlm-roberta",
"feature-extraction",
"Quality Estimation",
"siamesetransquest",
"da",
"license:apache-2.0",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[
"en-de"
] |
TAGS
#transformers #pytorch #xlm-roberta #feature-extraction #Quality Estimation #siamesetransquest #da #license-apache-2.0 #endpoints_compatible #region-us
|
# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers
The goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.
With TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.
## Features
- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.
- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.
- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented.
- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.
## Installation
### From pip
### From Source
## Using Pre-trained Models
## Documentation
For more details follow the documentation.
1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip.
2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest
1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.
2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation.
3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.
1. Sentence-level Examples
2. Word-level Examples
4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level
1. Sentence-level Models
2. Word-level Models
5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest
s
If you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.
If you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020.
|
[
"# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers\nThe goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.\n\nWith TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.",
"## Features\n- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.\n- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.\n- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented. \n- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.",
"## Installation",
"### From pip",
"### From Source",
"## Using Pre-trained Models",
"## Documentation\nFor more details follow the documentation.\n\n1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip. \n2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest\n 1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.\n 2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation. \n3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.\n 1. Sentence-level Examples\n 2. Word-level Examples\n4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level\n 1. Sentence-level Models\n 2. Word-level Models\n5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest\n\n\ns\nIf you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.\n\n\n\nIf you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020."
] |
[
"TAGS\n#transformers #pytorch #xlm-roberta #feature-extraction #Quality Estimation #siamesetransquest #da #license-apache-2.0 #endpoints_compatible #region-us \n",
"# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers\nThe goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.\n\nWith TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.",
"## Features\n- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.\n- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.\n- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented. \n- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.",
"## Installation",
"### From pip",
"### From Source",
"## Using Pre-trained Models",
"## Documentation\nFor more details follow the documentation.\n\n1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip. \n2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest\n 1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.\n 2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation. \n3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.\n 1. Sentence-level Examples\n 2. Word-level Examples\n4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level\n 1. Sentence-level Models\n 2. Word-level Models\n5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest\n\n\ns\nIf you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.\n\n\n\nIf you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020."
] |
feature-extraction
|
transformers
|
# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers
The goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.
With TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in [WMT 2020](http://www.statmt.org/wmt20/quality-estimation-task.html). TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as [OpenKiwi](https://github.com/Unbabel/OpenKiwi) and [DeepQuest](https://github.com/sheffieldnlp/deepQuest).
## Features
- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.
- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.
- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented.
- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in [HuggingFace.](https://huggingface.co/TransQuest)
## Installation
### From pip
```bash
pip install transquest
```
### From Source
```bash
git clone https://github.com/TharinduDR/TransQuest.git
cd TransQuest
pip install -r requirements.txt
```
## Using Pre-trained Models
```python
import torch
from transquest.algo.sentence_level.siamesetransquest.run_model import SiameseTransQuestModel
model = SiameseTransQuestModel("TransQuest/siamesetransquest-da-en_zh-wiki")
predictions = model.predict([["Reducerea acestor conflicte este importantă pentru conservare.", "Reducing these conflicts is not important for preservation."]])
print(predictions)
```
## Documentation
For more details follow the documentation.
1. **[Installation](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/install/)** - Install TransQuest locally using pip.
2. **Architectures** - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest
1. [Sentence-level Architectures](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/architectures/sentence_level_architectures/) - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.
2. [Word-level Architecture](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/architectures/word_level_architecture/) - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation.
3. **Examples** - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.
1. [Sentence-level Examples](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/examples/sentence_level_examples/)
2. [Word-level Examples](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/examples/word_level_examples/)
4. **Pre-trained Models** - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level
1. [Sentence-level Models](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/models/sentence_level_pretrained/)
2. [Word-level Models](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/models/word_level_pretrained/)
5. **[Contact](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/contact/)** - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest
## Citations
If you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to [ACL 2021](https://2021.aclweb.org/).
```bash
@InProceedings{ranasinghe2021,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {An Exploratory Analysis of Multilingual Word Level Quality Estimation with Cross-Lingual Transformers},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics},
year = {2021}
}
```
If you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in [COLING 2020](https://coling2020.org/) and in [WMT 2020](http://www.statmt.org/wmt20/) at EMNLP 2020.
```bash
@InProceedings{transquest:2020a,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Computational Linguistics},
year = {2020}
}
```
```bash
@InProceedings{transquest:2020b,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {TransQuest at WMT2020: Sentence-Level Direct Assessment},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the Fifth Conference on Machine Translation},
year = {2020}
}
```
|
{"language": "en-zh", "license": "apache-2.0", "tags": ["Quality Estimation", "siamesetransquest", "da"]}
|
TransQuest/siamesetransquest-da-en_zh-wiki
| null |
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"xlm-roberta",
"feature-extraction",
"Quality Estimation",
"siamesetransquest",
"da",
"license:apache-2.0",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[
"en-zh"
] |
TAGS
#transformers #pytorch #xlm-roberta #feature-extraction #Quality Estimation #siamesetransquest #da #license-apache-2.0 #endpoints_compatible #region-us
|
# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers
The goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.
With TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.
## Features
- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.
- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.
- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented.
- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.
## Installation
### From pip
### From Source
## Using Pre-trained Models
## Documentation
For more details follow the documentation.
1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip.
2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest
1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.
2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation.
3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.
1. Sentence-level Examples
2. Word-level Examples
4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level
1. Sentence-level Models
2. Word-level Models
5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest
s
If you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.
If you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020.
|
[
"# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers\nThe goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.\n\nWith TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.",
"## Features\n- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.\n- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.\n- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented. \n- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.",
"## Installation",
"### From pip",
"### From Source",
"## Using Pre-trained Models",
"## Documentation\nFor more details follow the documentation.\n\n1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip. \n2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest\n 1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.\n 2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation. \n3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.\n 1. Sentence-level Examples\n 2. Word-level Examples\n4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level\n 1. Sentence-level Models\n 2. Word-level Models\n5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest\n\n\ns\nIf you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.\n\n\n\nIf you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020."
] |
[
"TAGS\n#transformers #pytorch #xlm-roberta #feature-extraction #Quality Estimation #siamesetransquest #da #license-apache-2.0 #endpoints_compatible #region-us \n",
"# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers\nThe goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.\n\nWith TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.",
"## Features\n- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.\n- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.\n- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented. \n- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.",
"## Installation",
"### From pip",
"### From Source",
"## Using Pre-trained Models",
"## Documentation\nFor more details follow the documentation.\n\n1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip. \n2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest\n 1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.\n 2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation. \n3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.\n 1. Sentence-level Examples\n 2. Word-level Examples\n4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level\n 1. Sentence-level Models\n 2. Word-level Models\n5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest\n\n\ns\nIf you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.\n\n\n\nIf you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020."
] |
feature-extraction
|
transformers
|
# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers
The goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.
With TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in [WMT 2020](http://www.statmt.org/wmt20/quality-estimation-task.html). TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as [OpenKiwi](https://github.com/Unbabel/OpenKiwi) and [DeepQuest](https://github.com/sheffieldnlp/deepQuest).
## Features
- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.
- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.
- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented.
- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in [HuggingFace.](https://huggingface.co/TransQuest)
## Installation
### From pip
```bash
pip install transquest
```
### From Source
```bash
git clone https://github.com/TharinduDR/TransQuest.git
cd TransQuest
pip install -r requirements.txt
```
## Using Pre-trained Models
```python
import torch
from transquest.algo.sentence_level.siamesetransquest.run_model import SiameseTransQuestModel
model = SiameseTransQuestModel("TransQuest/siamesetransquest-da-et_en-wiki")
predictions = model.predict([["Reducerea acestor conflicte este importantă pentru conservare.", "Reducing these conflicts is not important for preservation."]])
print(predictions)
```
## Documentation
For more details follow the documentation.
1. **[Installation](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/install/)** - Install TransQuest locally using pip.
2. **Architectures** - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest
1. [Sentence-level Architectures](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/architectures/sentence_level_architectures/) - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.
2. [Word-level Architecture](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/architectures/word_level_architecture/) - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation.
3. **Examples** - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.
1. [Sentence-level Examples](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/examples/sentence_level_examples/)
2. [Word-level Examples](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/examples/word_level_examples/)
4. **Pre-trained Models** - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level
1. [Sentence-level Models](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/models/sentence_level_pretrained/)
2. [Word-level Models](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/models/word_level_pretrained/)
5. **[Contact](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/contact/)** - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest
## Citations
If you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to [ACL 2021](https://2021.aclweb.org/).
```bash
@InProceedings{ranasinghe2021,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {An Exploratory Analysis of Multilingual Word Level Quality Estimation with Cross-Lingual Transformers},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics},
year = {2021}
}
```
If you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in [COLING 2020](https://coling2020.org/) and in [WMT 2020](http://www.statmt.org/wmt20/) at EMNLP 2020.
```bash
@InProceedings{transquest:2020a,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Computational Linguistics},
year = {2020}
}
```
```bash
@InProceedings{transquest:2020b,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {TransQuest at WMT2020: Sentence-Level Direct Assessment},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the Fifth Conference on Machine Translation},
year = {2020}
}
```
|
{"language": "et-en", "license": "apache-2.0", "tags": ["Quality Estimation", "siamesetransquest", "da"]}
|
TransQuest/siamesetransquest-da-et_en-wiki
| null |
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"xlm-roberta",
"feature-extraction",
"Quality Estimation",
"siamesetransquest",
"da",
"license:apache-2.0",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[
"et-en"
] |
TAGS
#transformers #pytorch #xlm-roberta #feature-extraction #Quality Estimation #siamesetransquest #da #license-apache-2.0 #endpoints_compatible #region-us
|
# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers
The goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.
With TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.
## Features
- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.
- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.
- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented.
- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.
## Installation
### From pip
### From Source
## Using Pre-trained Models
## Documentation
For more details follow the documentation.
1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip.
2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest
1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.
2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation.
3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.
1. Sentence-level Examples
2. Word-level Examples
4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level
1. Sentence-level Models
2. Word-level Models
5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest
s
If you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.
If you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020.
|
[
"# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers\nThe goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.\n\nWith TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.",
"## Features\n- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.\n- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.\n- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented. \n- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.",
"## Installation",
"### From pip",
"### From Source",
"## Using Pre-trained Models",
"## Documentation\nFor more details follow the documentation.\n\n1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip. \n2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest\n 1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.\n 2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation. \n3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.\n 1. Sentence-level Examples\n 2. Word-level Examples\n4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level\n 1. Sentence-level Models\n 2. Word-level Models\n5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest\n\n\ns\nIf you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.\n\n\n\nIf you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020."
] |
[
"TAGS\n#transformers #pytorch #xlm-roberta #feature-extraction #Quality Estimation #siamesetransquest #da #license-apache-2.0 #endpoints_compatible #region-us \n",
"# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers\nThe goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.\n\nWith TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.",
"## Features\n- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.\n- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.\n- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented. \n- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.",
"## Installation",
"### From pip",
"### From Source",
"## Using Pre-trained Models",
"## Documentation\nFor more details follow the documentation.\n\n1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip. \n2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest\n 1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.\n 2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation. \n3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.\n 1. Sentence-level Examples\n 2. Word-level Examples\n4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level\n 1. Sentence-level Models\n 2. Word-level Models\n5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest\n\n\ns\nIf you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.\n\n\n\nIf you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020."
] |
feature-extraction
|
transformers
|
# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers
The goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.
With TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in [WMT 2020](http://www.statmt.org/wmt20/quality-estimation-task.html). TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as [OpenKiwi](https://github.com/Unbabel/OpenKiwi) and [DeepQuest](https://github.com/sheffieldnlp/deepQuest).
## Features
- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.
- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.
- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented.
- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in [HuggingFace.](https://huggingface.co/TransQuest)
## Installation
### From pip
```bash
pip install transquest
```
### From Source
```bash
git clone https://github.com/TharinduDR/TransQuest.git
cd TransQuest
pip install -r requirements.txt
```
## Using Pre-trained Models
```python
import torch
from transquest.algo.sentence_level.siamesetransquest.run_model import SiameseTransQuestModel
model = SiameseTransQuestModel("TransQuest/siamesetransquest-da-multilingual")
predictions = model.predict([["Reducerea acestor conflicte este importantă pentru conservare.", "Reducing these conflicts is not important for preservation."]])
print(predictions)
```
## Documentation
For more details follow the documentation.
1. **[Installation](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/install/)** - Install TransQuest locally using pip.
2. **Architectures** - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest
1. [Sentence-level Architectures](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/architectures/sentence_level_architectures/) - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.
2. [Word-level Architecture](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/architectures/word_level_architecture/) - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation.
3. **Examples** - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.
1. [Sentence-level Examples](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/examples/sentence_level_examples/)
2. [Word-level Examples](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/examples/word_level_examples/)
4. **Pre-trained Models** - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level
1. [Sentence-level Models](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/models/sentence_level_pretrained/)
2. [Word-level Models](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/models/word_level_pretrained/)
5. **[Contact](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/contact/)** - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest
## Citations
If you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to [ACL 2021](https://2021.aclweb.org/).
```bash
@InProceedings{ranasinghe2021,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {An Exploratory Analysis of Multilingual Word Level Quality Estimation with Cross-Lingual Transformers},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics},
year = {2021}
}
```
If you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in [COLING 2020](https://coling2020.org/) and in [WMT 2020](http://www.statmt.org/wmt20/) at EMNLP 2020.
```bash
@InProceedings{transquest:2020a,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Computational Linguistics},
year = {2020}
}
```
```bash
@InProceedings{transquest:2020b,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {TransQuest at WMT2020: Sentence-Level Direct Assessment},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the Fifth Conference on Machine Translation},
year = {2020}
}
```
|
{"language": "multilingual-multilingual", "license": "apache-2.0", "tags": ["Quality Estimation", "siamesetransquest", "da"]}
|
TransQuest/siamesetransquest-da-multilingual
| null |
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"xlm-roberta",
"feature-extraction",
"Quality Estimation",
"siamesetransquest",
"da",
"license:apache-2.0",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[
"multilingual-multilingual"
] |
TAGS
#transformers #pytorch #xlm-roberta #feature-extraction #Quality Estimation #siamesetransquest #da #license-apache-2.0 #endpoints_compatible #region-us
|
# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers
The goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.
With TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.
## Features
- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.
- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.
- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented.
- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.
## Installation
### From pip
### From Source
## Using Pre-trained Models
## Documentation
For more details follow the documentation.
1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip.
2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest
1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.
2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation.
3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.
1. Sentence-level Examples
2. Word-level Examples
4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level
1. Sentence-level Models
2. Word-level Models
5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest
s
If you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.
If you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020.
|
[
"# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers\nThe goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.\n\nWith TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.",
"## Features\n- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.\n- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.\n- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented. \n- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.",
"## Installation",
"### From pip",
"### From Source",
"## Using Pre-trained Models",
"## Documentation\nFor more details follow the documentation.\n\n1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip. \n2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest\n 1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.\n 2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation. \n3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.\n 1. Sentence-level Examples\n 2. Word-level Examples\n4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level\n 1. Sentence-level Models\n 2. Word-level Models\n5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest\n\n\ns\nIf you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.\n\n\n\nIf you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020."
] |
[
"TAGS\n#transformers #pytorch #xlm-roberta #feature-extraction #Quality Estimation #siamesetransquest #da #license-apache-2.0 #endpoints_compatible #region-us \n",
"# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers\nThe goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.\n\nWith TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.",
"## Features\n- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.\n- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.\n- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented. \n- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.",
"## Installation",
"### From pip",
"### From Source",
"## Using Pre-trained Models",
"## Documentation\nFor more details follow the documentation.\n\n1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip. \n2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest\n 1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.\n 2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation. \n3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.\n 1. Sentence-level Examples\n 2. Word-level Examples\n4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level\n 1. Sentence-level Models\n 2. Word-level Models\n5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest\n\n\ns\nIf you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.\n\n\n\nIf you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020."
] |
feature-extraction
|
transformers
|
# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers
The goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.
With TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in [WMT 2020](http://www.statmt.org/wmt20/quality-estimation-task.html). TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as [OpenKiwi](https://github.com/Unbabel/OpenKiwi) and [DeepQuest](https://github.com/sheffieldnlp/deepQuest).
## Features
- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.
- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.
- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented.
- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in [HuggingFace.](https://huggingface.co/TransQuest)
## Installation
### From pip
```bash
pip install transquest
```
### From Source
```bash
git clone https://github.com/TharinduDR/TransQuest.git
cd TransQuest
pip install -r requirements.txt
```
## Using Pre-trained Models
```python
import torch
from transquest.algo.sentence_level.siamesetransquest.run_model import SiameseTransQuestModel
model = SiameseTransQuestModel("TransQuest/siamesetransquest-da-ne_en-wiki")
predictions = model.predict([["Reducerea acestor conflicte este importantă pentru conservare.", "Reducing these conflicts is not important for preservation."]])
print(predictions)
```
## Documentation
For more details follow the documentation.
1. **[Installation](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/install/)** - Install TransQuest locally using pip.
2. **Architectures** - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest
1. [Sentence-level Architectures](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/architectures/sentence_level_architectures/) - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.
2. [Word-level Architecture](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/architectures/word_level_architecture/) - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation.
3. **Examples** - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.
1. [Sentence-level Examples](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/examples/sentence_level_examples/)
2. [Word-level Examples](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/examples/word_level_examples/)
4. **Pre-trained Models** - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level
1. [Sentence-level Models](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/models/sentence_level_pretrained/)
2. [Word-level Models](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/models/word_level_pretrained/)
5. **[Contact](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/contact/)** - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest
## Citations
If you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to [ACL 2021](https://2021.aclweb.org/).
```bash
@InProceedings{ranasinghe2021,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {An Exploratory Analysis of Multilingual Word Level Quality Estimation with Cross-Lingual Transformers},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics},
year = {2021}
}
```
If you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in [COLING 2020](https://coling2020.org/) and in [WMT 2020](http://www.statmt.org/wmt20/) at EMNLP 2020.
```bash
@InProceedings{transquest:2020a,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Computational Linguistics},
year = {2020}
}
```
```bash
@InProceedings{transquest:2020b,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {TransQuest at WMT2020: Sentence-Level Direct Assessment},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the Fifth Conference on Machine Translation},
year = {2020}
}
```
|
{"language": "ne-en", "license": "apache-2.0", "tags": ["Quality Estimation", "siamesetransquest", "da"]}
|
TransQuest/siamesetransquest-da-ne_en-wiki
| null |
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"xlm-roberta",
"feature-extraction",
"Quality Estimation",
"siamesetransquest",
"da",
"license:apache-2.0",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[
"ne-en"
] |
TAGS
#transformers #pytorch #xlm-roberta #feature-extraction #Quality Estimation #siamesetransquest #da #license-apache-2.0 #endpoints_compatible #region-us
|
# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers
The goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.
With TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.
## Features
- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.
- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.
- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented.
- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.
## Installation
### From pip
### From Source
## Using Pre-trained Models
## Documentation
For more details follow the documentation.
1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip.
2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest
1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.
2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation.
3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.
1. Sentence-level Examples
2. Word-level Examples
4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level
1. Sentence-level Models
2. Word-level Models
5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest
s
If you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.
If you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020.
|
[
"# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers\nThe goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.\n\nWith TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.",
"## Features\n- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.\n- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.\n- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented. \n- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.",
"## Installation",
"### From pip",
"### From Source",
"## Using Pre-trained Models",
"## Documentation\nFor more details follow the documentation.\n\n1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip. \n2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest\n 1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.\n 2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation. \n3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.\n 1. Sentence-level Examples\n 2. Word-level Examples\n4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level\n 1. Sentence-level Models\n 2. Word-level Models\n5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest\n\n\ns\nIf you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.\n\n\n\nIf you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020."
] |
[
"TAGS\n#transformers #pytorch #xlm-roberta #feature-extraction #Quality Estimation #siamesetransquest #da #license-apache-2.0 #endpoints_compatible #region-us \n",
"# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers\nThe goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.\n\nWith TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.",
"## Features\n- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.\n- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.\n- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented. \n- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.",
"## Installation",
"### From pip",
"### From Source",
"## Using Pre-trained Models",
"## Documentation\nFor more details follow the documentation.\n\n1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip. \n2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest\n 1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.\n 2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation. \n3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.\n 1. Sentence-level Examples\n 2. Word-level Examples\n4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level\n 1. Sentence-level Models\n 2. Word-level Models\n5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest\n\n\ns\nIf you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.\n\n\n\nIf you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020."
] |
feature-extraction
|
transformers
|
# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers
The goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.
With TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in [WMT 2020](http://www.statmt.org/wmt20/quality-estimation-task.html). TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as [OpenKiwi](https://github.com/Unbabel/OpenKiwi) and [DeepQuest](https://github.com/sheffieldnlp/deepQuest).
## Features
- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.
- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.
- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented.
- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in [HuggingFace.](https://huggingface.co/TransQuest)
## Installation
### From pip
```bash
pip install transquest
```
### From Source
```bash
git clone https://github.com/TharinduDR/TransQuest.git
cd TransQuest
pip install -r requirements.txt
```
## Using Pre-trained Models
```python
import torch
from transquest.algo.sentence_level.siamesetransquest.run_model import SiameseTransQuestModel
model = SiameseTransQuestModel("TransQuest/siamesetransquest-da-ro_en-wiki")
predictions = model.predict([["Reducerea acestor conflicte este importantă pentru conservare.", "Reducing these conflicts is not important for preservation."]])
print(predictions)
```
## Documentation
For more details follow the documentation.
1. **[Installation](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/install/)** - Install TransQuest locally using pip.
2. **Architectures** - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest
1. [Sentence-level Architectures](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/architectures/sentence_level_architectures/) - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.
2. [Word-level Architecture](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/architectures/word_level_architecture/) - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation.
3. **Examples** - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.
1. [Sentence-level Examples](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/examples/sentence_level_examples/)
2. [Word-level Examples](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/examples/word_level_examples/)
4. **Pre-trained Models** - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level
1. [Sentence-level Models](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/models/sentence_level_pretrained/)
2. [Word-level Models](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/models/word_level_pretrained/)
5. **[Contact](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/contact/)** - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest
## Citations
If you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to [ACL 2021](https://2021.aclweb.org/).
```bash
@InProceedings{ranasinghe2021,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {An Exploratory Analysis of Multilingual Word Level Quality Estimation with Cross-Lingual Transformers},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics},
year = {2021}
}
```
If you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in [COLING 2020](https://coling2020.org/) and in [WMT 2020](http://www.statmt.org/wmt20/) at EMNLP 2020.
```bash
@InProceedings{transquest:2020a,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Computational Linguistics},
year = {2020}
}
```
```bash
@InProceedings{transquest:2020b,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {TransQuest at WMT2020: Sentence-Level Direct Assessment},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the Fifth Conference on Machine Translation},
year = {2020}
}
```
|
{"language": "ro-en", "license": "apache-2.0", "tags": ["Quality Estimation", "siamesetransquest", "da"]}
|
TransQuest/siamesetransquest-da-ro_en-wiki
| null |
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"xlm-roberta",
"feature-extraction",
"Quality Estimation",
"siamesetransquest",
"da",
"license:apache-2.0",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[
"ro-en"
] |
TAGS
#transformers #pytorch #xlm-roberta #feature-extraction #Quality Estimation #siamesetransquest #da #license-apache-2.0 #endpoints_compatible #region-us
|
# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers
The goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.
With TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.
## Features
- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.
- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.
- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented.
- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.
## Installation
### From pip
### From Source
## Using Pre-trained Models
## Documentation
For more details follow the documentation.
1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip.
2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest
1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.
2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation.
3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.
1. Sentence-level Examples
2. Word-level Examples
4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level
1. Sentence-level Models
2. Word-level Models
5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest
s
If you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.
If you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020.
|
[
"# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers\nThe goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.\n\nWith TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.",
"## Features\n- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.\n- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.\n- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented. \n- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.",
"## Installation",
"### From pip",
"### From Source",
"## Using Pre-trained Models",
"## Documentation\nFor more details follow the documentation.\n\n1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip. \n2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest\n 1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.\n 2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation. \n3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.\n 1. Sentence-level Examples\n 2. Word-level Examples\n4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level\n 1. Sentence-level Models\n 2. Word-level Models\n5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest\n\n\ns\nIf you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.\n\n\n\nIf you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020."
] |
[
"TAGS\n#transformers #pytorch #xlm-roberta #feature-extraction #Quality Estimation #siamesetransquest #da #license-apache-2.0 #endpoints_compatible #region-us \n",
"# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers\nThe goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.\n\nWith TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.",
"## Features\n- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.\n- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.\n- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented. \n- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.",
"## Installation",
"### From pip",
"### From Source",
"## Using Pre-trained Models",
"## Documentation\nFor more details follow the documentation.\n\n1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip. \n2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest\n 1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.\n 2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation. \n3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.\n 1. Sentence-level Examples\n 2. Word-level Examples\n4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level\n 1. Sentence-level Models\n 2. Word-level Models\n5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest\n\n\ns\nIf you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.\n\n\n\nIf you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020."
] |
feature-extraction
|
transformers
|
# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers
The goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.
With TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in [WMT 2020](http://www.statmt.org/wmt20/quality-estimation-task.html). TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as [OpenKiwi](https://github.com/Unbabel/OpenKiwi) and [DeepQuest](https://github.com/sheffieldnlp/deepQuest).
## Features
- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.
- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.
- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented.
- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in [HuggingFace.](https://huggingface.co/TransQuest)
## Installation
### From pip
```bash
pip install transquest
```
### From Source
```bash
git clone https://github.com/TharinduDR/TransQuest.git
cd TransQuest
pip install -r requirements.txt
```
## Using Pre-trained Models
```python
import torch
from transquest.algo.sentence_level.siamesetransquest.run_model import SiameseTransQuestModel
model = SiameseTransQuestModel("TransQuest/siamesetransquest-da-ru_en-reddit_wikiquotes")
predictions = model.predict([["Reducerea acestor conflicte este importantă pentru conservare.", "Reducing these conflicts is not important for preservation."]])
print(predictions)
```
## Documentation
For more details follow the documentation.
1. **[Installation](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/install/)** - Install TransQuest locally using pip.
2. **Architectures** - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest
1. [Sentence-level Architectures](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/architectures/sentence_level_architectures/) - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.
2. [Word-level Architecture](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/architectures/word_level_architecture/) - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation.
3. **Examples** - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.
1. [Sentence-level Examples](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/examples/sentence_level_examples/)
2. [Word-level Examples](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/examples/word_level_examples/)
4. **Pre-trained Models** - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level
1. [Sentence-level Models](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/models/sentence_level_pretrained/)
2. [Word-level Models](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/models/word_level_pretrained/)
5. **[Contact](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/contact/)** - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest
## Citations
If you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to [ACL 2021](https://2021.aclweb.org/).
```bash
@InProceedings{ranasinghe2021,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {An Exploratory Analysis of Multilingual Word Level Quality Estimation with Cross-Lingual Transformers},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics},
year = {2021}
}
```
If you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in [COLING 2020](https://coling2020.org/) and in [WMT 2020](http://www.statmt.org/wmt20/) at EMNLP 2020.
```bash
@InProceedings{transquest:2020a,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Computational Linguistics},
year = {2020}
}
```
```bash
@InProceedings{transquest:2020b,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {TransQuest at WMT2020: Sentence-Level Direct Assessment},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the Fifth Conference on Machine Translation},
year = {2020}
}
```
|
{"language": "ru-en", "license": "apache-2.0", "tags": ["Quality Estimation", "siamesetransquest", "da"]}
|
TransQuest/siamesetransquest-da-ru_en-reddit_wikiquotes
| null |
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"xlm-roberta",
"feature-extraction",
"Quality Estimation",
"siamesetransquest",
"da",
"license:apache-2.0",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[
"ru-en"
] |
TAGS
#transformers #pytorch #xlm-roberta #feature-extraction #Quality Estimation #siamesetransquest #da #license-apache-2.0 #endpoints_compatible #region-us
|
# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers
The goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.
With TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.
## Features
- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.
- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.
- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented.
- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.
## Installation
### From pip
### From Source
## Using Pre-trained Models
## Documentation
For more details follow the documentation.
1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip.
2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest
1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.
2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation.
3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.
1. Sentence-level Examples
2. Word-level Examples
4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level
1. Sentence-level Models
2. Word-level Models
5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest
s
If you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.
If you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020.
|
[
"# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers\nThe goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.\n\nWith TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.",
"## Features\n- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.\n- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.\n- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented. \n- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.",
"## Installation",
"### From pip",
"### From Source",
"## Using Pre-trained Models",
"## Documentation\nFor more details follow the documentation.\n\n1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip. \n2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest\n 1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.\n 2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation. \n3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.\n 1. Sentence-level Examples\n 2. Word-level Examples\n4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level\n 1. Sentence-level Models\n 2. Word-level Models\n5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest\n\n\ns\nIf you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.\n\n\n\nIf you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020."
] |
[
"TAGS\n#transformers #pytorch #xlm-roberta #feature-extraction #Quality Estimation #siamesetransquest #da #license-apache-2.0 #endpoints_compatible #region-us \n",
"# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers\nThe goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.\n\nWith TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.",
"## Features\n- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.\n- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.\n- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented. \n- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.",
"## Installation",
"### From pip",
"### From Source",
"## Using Pre-trained Models",
"## Documentation\nFor more details follow the documentation.\n\n1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip. \n2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest\n 1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.\n 2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation. \n3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.\n 1. Sentence-level Examples\n 2. Word-level Examples\n4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level\n 1. Sentence-level Models\n 2. Word-level Models\n5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest\n\n\ns\nIf you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.\n\n\n\nIf you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020."
] |
feature-extraction
|
transformers
|
# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers
The goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.
With TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in [WMT 2020](http://www.statmt.org/wmt20/quality-estimation-task.html). TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as [OpenKiwi](https://github.com/Unbabel/OpenKiwi) and [DeepQuest](https://github.com/sheffieldnlp/deepQuest).
## Features
- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.
- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.
- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented.
- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in [HuggingFace.](https://huggingface.co/TransQuest)
## Installation
### From pip
```bash
pip install transquest
```
### From Source
```bash
git clone https://github.com/TharinduDR/TransQuest.git
cd TransQuest
pip install -r requirements.txt
```
## Using Pre-trained Models
```python
import torch
from transquest.algo.sentence_level.siamesetransquest.run_model import SiameseTransQuestModel
model = SiameseTransQuestModel("TransQuest/siamesetransquest-da-si_en-wiki")
predictions = model.predict([["Reducerea acestor conflicte este importantă pentru conservare.", "Reducing these conflicts is not important for preservation."]])
print(predictions)
```
## Documentation
For more details follow the documentation.
1. **[Installation](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/install/)** - Install TransQuest locally using pip.
2. **Architectures** - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest
1. [Sentence-level Architectures](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/architectures/sentence_level_architectures/) - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.
2. [Word-level Architecture](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/architectures/word_level_architecture/) - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation.
3. **Examples** - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.
1. [Sentence-level Examples](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/examples/sentence_level_examples/)
2. [Word-level Examples](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/examples/word_level_examples/)
4. **Pre-trained Models** - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level
1. [Sentence-level Models](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/models/sentence_level_pretrained/)
2. [Word-level Models](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/models/word_level_pretrained/)
5. **[Contact](https://tharindudr.github.io/TransQuest/contact/)** - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest
## Citations
If you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to [ACL 2021](https://2021.aclweb.org/).
```bash
@InProceedings{ranasinghe2021,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {An Exploratory Analysis of Multilingual Word Level Quality Estimation with Cross-Lingual Transformers},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics},
year = {2021}
}
```
If you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in [COLING 2020](https://coling2020.org/) and in [WMT 2020](http://www.statmt.org/wmt20/) at EMNLP 2020.
```bash
@InProceedings{transquest:2020a,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Computational Linguistics},
year = {2020}
}
```
```bash
@InProceedings{transquest:2020b,
author = {Ranasinghe, Tharindu and Orasan, Constantin and Mitkov, Ruslan},
title = {TransQuest at WMT2020: Sentence-Level Direct Assessment},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the Fifth Conference on Machine Translation},
year = {2020}
}
```
|
{"language": "si-en", "license": "apache-2.0", "tags": ["Quality Estimation", "siamesetransquest", "da"]}
|
TransQuest/siamesetransquest-da-si_en-wiki
| null |
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"xlm-roberta",
"feature-extraction",
"Quality Estimation",
"siamesetransquest",
"da",
"license:apache-2.0",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[
"si-en"
] |
TAGS
#transformers #pytorch #xlm-roberta #feature-extraction #Quality Estimation #siamesetransquest #da #license-apache-2.0 #endpoints_compatible #region-us
|
# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers
The goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.
With TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.
## Features
- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.
- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.
- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented.
- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.
## Installation
### From pip
### From Source
## Using Pre-trained Models
## Documentation
For more details follow the documentation.
1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip.
2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest
1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.
2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation.
3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.
1. Sentence-level Examples
2. Word-level Examples
4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level
1. Sentence-level Models
2. Word-level Models
5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest
s
If you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.
If you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020.
|
[
"# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers\nThe goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.\n\nWith TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.",
"## Features\n- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.\n- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.\n- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented. \n- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.",
"## Installation",
"### From pip",
"### From Source",
"## Using Pre-trained Models",
"## Documentation\nFor more details follow the documentation.\n\n1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip. \n2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest\n 1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.\n 2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation. \n3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.\n 1. Sentence-level Examples\n 2. Word-level Examples\n4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level\n 1. Sentence-level Models\n 2. Word-level Models\n5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest\n\n\ns\nIf you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.\n\n\n\nIf you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020."
] |
[
"TAGS\n#transformers #pytorch #xlm-roberta #feature-extraction #Quality Estimation #siamesetransquest #da #license-apache-2.0 #endpoints_compatible #region-us \n",
"# TransQuest: Translation Quality Estimation with Cross-lingual Transformers\nThe goal of quality estimation (QE) is to evaluate the quality of a translation without having access to a reference translation. High-accuracy QE that can be easily deployed for a number of language pairs is the missing piece in many commercial translation workflows as they have numerous potential uses. They can be employed to select the best translation when several translation engines are available or can inform the end user about the reliability of automatically translated content. In addition, QE systems can be used to decide whether a translation can be published as it is in a given context, or whether it requires human post-editing before publishing or translation from scratch by a human. The quality estimation can be done at different levels: document level, sentence level and word level.\n\nWith TransQuest, we have opensourced our research in translation quality estimation which also won the sentence-level direct assessment quality estimation shared task in WMT 2020. TransQuest outperforms current open-source quality estimation frameworks such as OpenKiwi and DeepQuest.",
"## Features\n- Sentence-level translation quality estimation on both aspects: predicting post editing efforts and direct assessment.\n- Word-level translation quality estimation capable of predicting quality of source words, target words and target gaps.\n- Outperform current state-of-the-art quality estimation methods like DeepQuest and OpenKiwi in all the languages experimented. \n- Pre-trained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs are available in HuggingFace.",
"## Installation",
"### From pip",
"### From Source",
"## Using Pre-trained Models",
"## Documentation\nFor more details follow the documentation.\n\n1. Installation - Install TransQuest locally using pip. \n2. Architectures - Checkout the architectures implemented in TransQuest\n 1. Sentence-level Architectures - We have released two architectures; MonoTransQuest and SiameseTransQuest to perform sentence level quality estimation.\n 2. Word-level Architecture - We have released MicroTransQuest to perform word level quality estimation. \n3. Examples - We have provided several examples on how to use TransQuest in recent WMT quality estimation shared tasks.\n 1. Sentence-level Examples\n 2. Word-level Examples\n4. Pre-trained Models - We have provided pretrained quality estimation models for fifteen language pairs covering both sentence-level and word-level\n 1. Sentence-level Models\n 2. Word-level Models\n5. Contact - Contact us for any issues with TransQuest\n\n\ns\nIf you are using the word-level architecture, please consider citing this paper which is accepted to ACL 2021.\n\n\n\nIf you are using the sentence-level architectures, please consider citing these papers which were presented in COLING 2020 and in WMT 2020 at EMNLP 2020."
] |
text-generation
|
transformers
|
#Michael Scott DialoGPT model
|
{"tags": ["conversational"]}
|
TrebleJeff/DialoGPT-small-Michael
| null |
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"gpt2",
"text-generation",
"conversational",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"text-generation-inference",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[] |
TAGS
#transformers #pytorch #gpt2 #text-generation #conversational #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #text-generation-inference #region-us
|
#Michael Scott DialoGPT model
|
[] |
[
"TAGS\n#transformers #pytorch #gpt2 #text-generation #conversational #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #text-generation-inference #region-us \n"
] |
text-generation
|
transformers
|
#Deadpool DialoGPT Model
|
{"tags": ["conversational"]}
|
TrimPeachu/Deadpool
| null |
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"gpt2",
"text-generation",
"conversational",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"text-generation-inference",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[] |
TAGS
#transformers #pytorch #gpt2 #text-generation #conversational #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #text-generation-inference #region-us
|
#Deadpool DialoGPT Model
|
[] |
[
"TAGS\n#transformers #pytorch #gpt2 #text-generation #conversational #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #text-generation-inference #region-us \n"
] |
text-generation
|
transformers
|
# GPT-2 for Music
Language Models such as GPT-2 can be used for Music Generation. The idea is to represent pieces of music as texts, effectively reducing the task to Language Generation.
This model is a rather small instance of GPT-2 trained on [TristanBehrens/js-fakes-4bars](https://huggingface.co/datasets/TristanBehrens/js-fakes-4bars). The model generates 4 bars at a time of Bach-like chorales with four voices (soprano, alto, tenor, bass).
If you are contribute, if you want to say hello, if you want to know more, find me on [LinkedIn](https://www.linkedin.com/in/dr-tristan-behrens-734967a2/)
## Model description
The model is GPT-2 with 6 decoders and 8 attention-heads each. The context length is 512. The embedding dimensions are 512 as well. The vocabulary size is 119.
## Intended uses & limitations
This model is just a proof of concept. It shows that HuggingFace can be used to compose music.
### How to use
There is a notebook in the repo that you can run on Google Colab.
### Limitations and bias
Since this model has been trained on a very small corpus of music, it is overfitting heavily.
|
{"tags": ["gpt2", "text-generation", "music-modeling", "music-generation"], "widget": [{"text": "PIECE_START"}, {"text": "PIECE_START STYLE=JSFAKES GENRE=JSFAKES TRACK_START INST=48 BAR_START NOTE_ON=60"}, {"text": "PIECE_START STYLE=JSFAKES GENRE=JSFAKES TRACK_START INST=48 BAR_START NOTE_ON=58"}]}
|
TristanBehrens/js-fakes-4bars
| null |
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"gpt2",
"text-generation",
"music-modeling",
"music-generation",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"has_space",
"text-generation-inference",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[] |
TAGS
#transformers #pytorch #gpt2 #text-generation #music-modeling #music-generation #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #has_space #text-generation-inference #region-us
|
# GPT-2 for Music
Language Models such as GPT-2 can be used for Music Generation. The idea is to represent pieces of music as texts, effectively reducing the task to Language Generation.
This model is a rather small instance of GPT-2 trained on TristanBehrens/js-fakes-4bars. The model generates 4 bars at a time of Bach-like chorales with four voices (soprano, alto, tenor, bass).
If you are contribute, if you want to say hello, if you want to know more, find me on LinkedIn
## Model description
The model is GPT-2 with 6 decoders and 8 attention-heads each. The context length is 512. The embedding dimensions are 512 as well. The vocabulary size is 119.
## Intended uses & limitations
This model is just a proof of concept. It shows that HuggingFace can be used to compose music.
### How to use
There is a notebook in the repo that you can run on Google Colab.
### Limitations and bias
Since this model has been trained on a very small corpus of music, it is overfitting heavily.
|
[
"# GPT-2 for Music\n\nLanguage Models such as GPT-2 can be used for Music Generation. The idea is to represent pieces of music as texts, effectively reducing the task to Language Generation.\n\nThis model is a rather small instance of GPT-2 trained on TristanBehrens/js-fakes-4bars. The model generates 4 bars at a time of Bach-like chorales with four voices (soprano, alto, tenor, bass).\n\nIf you are contribute, if you want to say hello, if you want to know more, find me on LinkedIn",
"## Model description\n\nThe model is GPT-2 with 6 decoders and 8 attention-heads each. The context length is 512. The embedding dimensions are 512 as well. The vocabulary size is 119.",
"## Intended uses & limitations\n\nThis model is just a proof of concept. It shows that HuggingFace can be used to compose music.",
"### How to use\n\nThere is a notebook in the repo that you can run on Google Colab.",
"### Limitations and bias\n\nSince this model has been trained on a very small corpus of music, it is overfitting heavily."
] |
[
"TAGS\n#transformers #pytorch #gpt2 #text-generation #music-modeling #music-generation #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #has_space #text-generation-inference #region-us \n",
"# GPT-2 for Music\n\nLanguage Models such as GPT-2 can be used for Music Generation. The idea is to represent pieces of music as texts, effectively reducing the task to Language Generation.\n\nThis model is a rather small instance of GPT-2 trained on TristanBehrens/js-fakes-4bars. The model generates 4 bars at a time of Bach-like chorales with four voices (soprano, alto, tenor, bass).\n\nIf you are contribute, if you want to say hello, if you want to know more, find me on LinkedIn",
"## Model description\n\nThe model is GPT-2 with 6 decoders and 8 attention-heads each. The context length is 512. The embedding dimensions are 512 as well. The vocabulary size is 119.",
"## Intended uses & limitations\n\nThis model is just a proof of concept. It shows that HuggingFace can be used to compose music.",
"### How to use\n\nThere is a notebook in the repo that you can run on Google Colab.",
"### Limitations and bias\n\nSince this model has been trained on a very small corpus of music, it is overfitting heavily."
] |
text-generation
|
transformers
|
Rick chatbot made with GPT2 ai from the show Rick and Morty, discord bot available now!
https://discord.com/oauth2/authorize?client_id=894569097818431519&permissions=1074113536&scope=bot
(v1 is no longer supported with RickBot)
|
{"tags": ["conversational"]}
|
Trixzy/rickai-v1
| null |
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"gpt2",
"text-generation",
"conversational",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"text-generation-inference",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[] |
TAGS
#transformers #pytorch #gpt2 #text-generation #conversational #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #text-generation-inference #region-us
|
Rick chatbot made with GPT2 ai from the show Rick and Morty, discord bot available now!
URL
(v1 is no longer supported with RickBot)
|
[] |
[
"TAGS\n#transformers #pytorch #gpt2 #text-generation #conversational #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #text-generation-inference #region-us \n"
] |
text-generation
|
transformers
|
# Peppa Pig DialoGPT Model
|
{"tags": ["conversational"]}
|
Tropics/DialoGPT-small-peppa
| null |
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"gpt2",
"text-generation",
"conversational",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"text-generation-inference",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[] |
TAGS
#transformers #pytorch #gpt2 #text-generation #conversational #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #text-generation-inference #region-us
|
# Peppa Pig DialoGPT Model
|
[
"# Peppa Pig DialoGPT Model"
] |
[
"TAGS\n#transformers #pytorch #gpt2 #text-generation #conversational #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #text-generation-inference #region-us \n",
"# Peppa Pig DialoGPT Model"
] |
text-generation
|
transformers
|
# CPM-Generate
## Model description
CPM (Chinese Pre-trained Language Model) is a Transformer-based autoregressive language model, with 2.6 billion parameters and 100GB Chinese training data. To the best of our knowledge, CPM is the largest Chinese pre-trained language model, which could facilitate downstream Chinese NLP tasks, such as conversation, essay generation, cloze test, and language understanding. [[Project](https://cpm.baai.ac.cn)] [[Model](https://cpm.baai.ac.cn/download.html)] [[Paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2012.00413)]
## Intended uses & limitations
#### How to use
```python
from transformers import TextGenerationPipeline, AutoTokenizer, AutoModelWithLMHead
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("TsinghuaAI/CPM-Generate")
model = AutoModelWithLMHead.from_pretrained("TsinghuaAI/CPM-Generate")
text_generator = TextGenerationPipeline(model, tokenizer)
text_generator('清华大学', max_length=50, do_sample=True, top_p=0.9)
```
#### Limitations and bias
The text generated by CPM is automatically generated by a neural network model trained on a large number of texts, which does not represent the authors' or their institutes' official attitudes and preferences. The text generated by CPM is only used for technical and scientific purposes. If it infringes on your rights and interests or violates social morality, please do not propagate it, but contact the authors and the authors will deal with it promptly.
## Training data
We collect different kinds of texts in our pre-training, including encyclopedia, news, novels, and Q\&A. The details of our training data are shown as follows.
| Data Source | Encyclopedia | Webpage | Story | News | Dialog |
| ----------- | ------------ | ------- | ----- | ----- | ------ |
| **Size** | ~40GB | ~39GB | ~10GB | ~10GB | ~1GB |
## Training procedure
Based on the hyper-parameter searching on the learning rate and batch size, we set the learning rate as \\(1.5\times10^{-4}\\) and the batch size as \\(3,072\\), which makes the model training more stable. In the first version, we still adopt the dense attention and the max sequence length is \\(1,024\\). We will implement sparse attention in the future. We pre-train our model for \\(20,000\\) steps, and the first \\(5,000\\) steps are for warm-up. The optimizer is Adam. It takes two weeks to train our largest model using \\(64\\) NVIDIA V100.
## Eval results
| | n_param | n_layers | d_model | n_heads | d_head |
|------------|-------------------:|--------------------:|-------------------:|-------------------:|------------------:|
| CPM-Small | 109M | 12 | 768 | 12 | 64 |
| CPM-Medium | 334M | 24 | 1,024 | 16 | 64 |
| CPM-Large | 2.6B | 32 | 2,560 | 32 | 80 |
We evaluate CPM with different numbers of parameters (the details are shown above) on various Chinese NLP tasks in the few-shot (even zero-shot) settings. With the increase of parameters, CPM performs better on most datasets, indicating that larger models are more proficient at language generation and language understanding. We provide results of text classification, chinese idiom cloze test, and short text conversation generation as follows. Please refer to our [paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2012.00413) for more detailed results.
### Zero-shot performance on text classification tasks
| | TNEWS | IFLYTEK | OCNLI |
| ---------- | :------------: | :------------: | :------------: |
| CPM-Small | 0.626 | 0.584 | 0.378 |
| CPM-Medium | 0.618 | 0.635 | 0.379 |
| CPM-Large | **0.703** | **0.708** | **0.442** |
### Performance on Chinese Idiom Cloze (ChID) dataset
| | Supervised | Unsupervised |
|------------|:--------------:|:--------------:|
| CPM-Small | 0.657 | 0.433 |
| CPM-Medium | 0.695 | 0.524 |
| CPM-Large | **0.804** | **0.685** |
### Performance on Short Text Conversation Generation (STC) dataset
| | Average | Extrema | Greedy | Dist-1 | Dist-2 |
|----------------------------------|:--------------:|:--------------:|:--------------:|:-------------------------------:|:--------------------------------:|
| *Few-shot (Unsupervised)* | | | | | |
| CDial-GPT | 0.899 | 0.797 | 0.810 | 1,963 / **0.011** | 20,814 / 0.126 |
| CPM-Large | **0.928** | **0.805** | **0.815** | **3,229** / 0.007 | **68,008** / **0.154** |
| *Supervised* | | | | | |
| CDial-GPT | 0.933 | **0.814** | **0.826** | 2,468 / 0.008 | 35,634 / 0.127 |
| CPM-Large | **0.934** | 0.810 | 0.819 | **3,352** / **0.011** | **67,310** / **0.233** |
### BibTeX entry and citation info
```bibtex
@article{cpm-v1,
title={CPM: A Large-scale Generative Chinese Pre-trained Language Model},
author={Zhang, Zhengyan and Han, Xu, and Zhou, Hao, and Ke, Pei, and Gu, Yuxian and Ye, Deming and Qin, Yujia and Su, Yusheng and Ji, Haozhe and Guan, Jian and Qi, Fanchao and Wang, Xiaozhi and Zheng, Yanan and Zeng, Guoyang and Cao, Huanqi and Chen, Shengqi and Li, Daixuan and Sun, Zhenbo and Liu, Zhiyuan and Huang, Minlie and Han, Wentao and Tang, Jie and Li, Juanzi and Sun, Maosong},
year={2020}
}
```
|
{"language": ["zh"], "license": "mit", "tags": ["cpm"], "datasets": ["100GB Chinese corpus"]}
|
TsinghuaAI/CPM-Generate
| null |
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"tf",
"gpt2",
"text-generation",
"cpm",
"zh",
"arxiv:2012.00413",
"license:mit",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"text-generation-inference",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[
"2012.00413"
] |
[
"zh"
] |
TAGS
#transformers #pytorch #tf #gpt2 #text-generation #cpm #zh #arxiv-2012.00413 #license-mit #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #text-generation-inference #region-us
|
CPM-Generate
============
Model description
-----------------
CPM (Chinese Pre-trained Language Model) is a Transformer-based autoregressive language model, with 2.6 billion parameters and 100GB Chinese training data. To the best of our knowledge, CPM is the largest Chinese pre-trained language model, which could facilitate downstream Chinese NLP tasks, such as conversation, essay generation, cloze test, and language understanding. [Project] [Model] [Paper]
Intended uses & limitations
---------------------------
#### How to use
#### Limitations and bias
The text generated by CPM is automatically generated by a neural network model trained on a large number of texts, which does not represent the authors' or their institutes' official attitudes and preferences. The text generated by CPM is only used for technical and scientific purposes. If it infringes on your rights and interests or violates social morality, please do not propagate it, but contact the authors and the authors will deal with it promptly.
Training data
-------------
We collect different kinds of texts in our pre-training, including encyclopedia, news, novels, and Q&A. The details of our training data are shown as follows.
Training procedure
------------------
Based on the hyper-parameter searching on the learning rate and batch size, we set the learning rate as \(1.5\times10^{-4}\) and the batch size as \(3,072\), which makes the model training more stable. In the first version, we still adopt the dense attention and the max sequence length is \(1,024\). We will implement sparse attention in the future. We pre-train our model for \(20,000\) steps, and the first \(5,000\) steps are for warm-up. The optimizer is Adam. It takes two weeks to train our largest model using \(64\) NVIDIA V100.
Eval results
------------
We evaluate CPM with different numbers of parameters (the details are shown above) on various Chinese NLP tasks in the few-shot (even zero-shot) settings. With the increase of parameters, CPM performs better on most datasets, indicating that larger models are more proficient at language generation and language understanding. We provide results of text classification, chinese idiom cloze test, and short text conversation generation as follows. Please refer to our paper for more detailed results.
### Zero-shot performance on text classification tasks
### Performance on Chinese Idiom Cloze (ChID) dataset
### Performance on Short Text Conversation Generation (STC) dataset
### BibTeX entry and citation info
|
[
"#### How to use",
"#### Limitations and bias\n\n\nThe text generated by CPM is automatically generated by a neural network model trained on a large number of texts, which does not represent the authors' or their institutes' official attitudes and preferences. The text generated by CPM is only used for technical and scientific purposes. If it infringes on your rights and interests or violates social morality, please do not propagate it, but contact the authors and the authors will deal with it promptly.\n\n\nTraining data\n-------------\n\n\nWe collect different kinds of texts in our pre-training, including encyclopedia, news, novels, and Q&A. The details of our training data are shown as follows.\n\n\n\nTraining procedure\n------------------\n\n\nBased on the hyper-parameter searching on the learning rate and batch size, we set the learning rate as \\(1.5\\times10^{-4}\\) and the batch size as \\(3,072\\), which makes the model training more stable. In the first version, we still adopt the dense attention and the max sequence length is \\(1,024\\). We will implement sparse attention in the future. We pre-train our model for \\(20,000\\) steps, and the first \\(5,000\\) steps are for warm-up. The optimizer is Adam. It takes two weeks to train our largest model using \\(64\\) NVIDIA V100.\n\n\nEval results\n------------\n\n\n\nWe evaluate CPM with different numbers of parameters (the details are shown above) on various Chinese NLP tasks in the few-shot (even zero-shot) settings. With the increase of parameters, CPM performs better on most datasets, indicating that larger models are more proficient at language generation and language understanding. We provide results of text classification, chinese idiom cloze test, and short text conversation generation as follows. Please refer to our paper for more detailed results.",
"### Zero-shot performance on text classification tasks",
"### Performance on Chinese Idiom Cloze (ChID) dataset",
"### Performance on Short Text Conversation Generation (STC) dataset",
"### BibTeX entry and citation info"
] |
[
"TAGS\n#transformers #pytorch #tf #gpt2 #text-generation #cpm #zh #arxiv-2012.00413 #license-mit #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #text-generation-inference #region-us \n",
"#### How to use",
"#### Limitations and bias\n\n\nThe text generated by CPM is automatically generated by a neural network model trained on a large number of texts, which does not represent the authors' or their institutes' official attitudes and preferences. The text generated by CPM is only used for technical and scientific purposes. If it infringes on your rights and interests or violates social morality, please do not propagate it, but contact the authors and the authors will deal with it promptly.\n\n\nTraining data\n-------------\n\n\nWe collect different kinds of texts in our pre-training, including encyclopedia, news, novels, and Q&A. The details of our training data are shown as follows.\n\n\n\nTraining procedure\n------------------\n\n\nBased on the hyper-parameter searching on the learning rate and batch size, we set the learning rate as \\(1.5\\times10^{-4}\\) and the batch size as \\(3,072\\), which makes the model training more stable. In the first version, we still adopt the dense attention and the max sequence length is \\(1,024\\). We will implement sparse attention in the future. We pre-train our model for \\(20,000\\) steps, and the first \\(5,000\\) steps are for warm-up. The optimizer is Adam. It takes two weeks to train our largest model using \\(64\\) NVIDIA V100.\n\n\nEval results\n------------\n\n\n\nWe evaluate CPM with different numbers of parameters (the details are shown above) on various Chinese NLP tasks in the few-shot (even zero-shot) settings. With the increase of parameters, CPM performs better on most datasets, indicating that larger models are more proficient at language generation and language understanding. We provide results of text classification, chinese idiom cloze test, and short text conversation generation as follows. Please refer to our paper for more detailed results.",
"### Zero-shot performance on text classification tasks",
"### Performance on Chinese Idiom Cloze (ChID) dataset",
"### Performance on Short Text Conversation Generation (STC) dataset",
"### BibTeX entry and citation info"
] |
fill-mask
|
transformers
|
# ClinicalPubMedBERT
## Description
A BERT model pre-trained on PubMed abstracts, and continual pre-trained on clinical notes ([MIMIC-III](https://mimic.physionet.org/)). We try combining two domains that have fewer overlaps with general knowledge text corpora: EHRs and biomedical papers. We hope this model can serve better results on clinical-related downstream tasks such as readmissions.
This model is trained on 500000 clinical notes randomly sampled from MIMIC datasets, with 120k steps of training. We also used whole word masking to enhance the coherence of the language model. All notes are chunked into a length of 128 tokens.
Pre-trained model: https://huggingface.co/microsoft/BiomedNLP-PubMedBERT-base-uncased-abstract
|
{"language": ["en"], "license": "mit", "datasets": ["MIMIC-III"], "widget": [{"text": "Due to shortness of breath, the patient is diagnosed with [MASK], and other respiratory problems.", "example_title": "Example 1"}]}
|
Tsubasaz/clinical-pubmed-bert-base-128
| null |
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"bert",
"fill-mask",
"en",
"dataset:MIMIC-III",
"license:mit",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"has_space",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[
"en"
] |
TAGS
#transformers #pytorch #bert #fill-mask #en #dataset-MIMIC-III #license-mit #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #has_space #region-us
|
# ClinicalPubMedBERT
## Description
A BERT model pre-trained on PubMed abstracts, and continual pre-trained on clinical notes (MIMIC-III). We try combining two domains that have fewer overlaps with general knowledge text corpora: EHRs and biomedical papers. We hope this model can serve better results on clinical-related downstream tasks such as readmissions.
This model is trained on 500000 clinical notes randomly sampled from MIMIC datasets, with 120k steps of training. We also used whole word masking to enhance the coherence of the language model. All notes are chunked into a length of 128 tokens.
Pre-trained model: URL
|
[
"# ClinicalPubMedBERT",
"## Description\n\nA BERT model pre-trained on PubMed abstracts, and continual pre-trained on clinical notes (MIMIC-III). We try combining two domains that have fewer overlaps with general knowledge text corpora: EHRs and biomedical papers. We hope this model can serve better results on clinical-related downstream tasks such as readmissions. \n\nThis model is trained on 500000 clinical notes randomly sampled from MIMIC datasets, with 120k steps of training. We also used whole word masking to enhance the coherence of the language model. All notes are chunked into a length of 128 tokens.\n\nPre-trained model: URL"
] |
[
"TAGS\n#transformers #pytorch #bert #fill-mask #en #dataset-MIMIC-III #license-mit #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #has_space #region-us \n",
"# ClinicalPubMedBERT",
"## Description\n\nA BERT model pre-trained on PubMed abstracts, and continual pre-trained on clinical notes (MIMIC-III). We try combining two domains that have fewer overlaps with general knowledge text corpora: EHRs and biomedical papers. We hope this model can serve better results on clinical-related downstream tasks such as readmissions. \n\nThis model is trained on 500000 clinical notes randomly sampled from MIMIC datasets, with 120k steps of training. We also used whole word masking to enhance the coherence of the language model. All notes are chunked into a length of 128 tokens.\n\nPre-trained model: URL"
] |
fill-mask
|
transformers
|
# ClinicalPubMedBERT
## Description
A pre-trained model for clinical decision support, for more details, please see https://github.com/NtaylorOX/Public_Prompt_Mimic_III
A BERT model pre-trained on PubMed abstracts, and continual pre-trained on clinical notes ([MIMIC-III](https://mimic.physionet.org/)). We try combining two domains that have fewer overlaps with general knowledge text corpora: EHRs and biomedical papers. We hope this model can serve better results on clinical-related downstream tasks such as readmissions.
This model is trained on 500000 clinical notes randomly sampled from MIMIC datasets, with 100k steps of training. We also used whole word masking to enhance the coherence of the language model. All notes are chunked into a length of 512 tokens.
Pre-trained model: https://huggingface.co/microsoft/BiomedNLP-PubMedBERT-base-uncased-abstract
|
{"language": ["en"], "license": "mit", "datasets": ["MIMIC-III"], "widget": [{"text": "Due to shortness of breath, the patient is diagnosed with [MASK], and other respiratory problems.", "example_title": "Example 1"}, {"text": "Due to high blood sugar, and very low blood pressure, the patient is diagnosed with [MASK].", "example_title": "Example 2"}]}
|
Tsubasaz/clinical-pubmed-bert-base-512
| null |
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"bert",
"fill-mask",
"en",
"dataset:MIMIC-III",
"license:mit",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[
"en"
] |
TAGS
#transformers #pytorch #bert #fill-mask #en #dataset-MIMIC-III #license-mit #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #region-us
|
# ClinicalPubMedBERT
## Description
A pre-trained model for clinical decision support, for more details, please see URL
A BERT model pre-trained on PubMed abstracts, and continual pre-trained on clinical notes (MIMIC-III). We try combining two domains that have fewer overlaps with general knowledge text corpora: EHRs and biomedical papers. We hope this model can serve better results on clinical-related downstream tasks such as readmissions.
This model is trained on 500000 clinical notes randomly sampled from MIMIC datasets, with 100k steps of training. We also used whole word masking to enhance the coherence of the language model. All notes are chunked into a length of 512 tokens.
Pre-trained model: URL
|
[
"# ClinicalPubMedBERT",
"## Description\nA pre-trained model for clinical decision support, for more details, please see URL\n\nA BERT model pre-trained on PubMed abstracts, and continual pre-trained on clinical notes (MIMIC-III). We try combining two domains that have fewer overlaps with general knowledge text corpora: EHRs and biomedical papers. We hope this model can serve better results on clinical-related downstream tasks such as readmissions.\n\nThis model is trained on 500000 clinical notes randomly sampled from MIMIC datasets, with 100k steps of training. We also used whole word masking to enhance the coherence of the language model. All notes are chunked into a length of 512 tokens.\n\nPre-trained model: URL"
] |
[
"TAGS\n#transformers #pytorch #bert #fill-mask #en #dataset-MIMIC-III #license-mit #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #region-us \n",
"# ClinicalPubMedBERT",
"## Description\nA pre-trained model for clinical decision support, for more details, please see URL\n\nA BERT model pre-trained on PubMed abstracts, and continual pre-trained on clinical notes (MIMIC-III). We try combining two domains that have fewer overlaps with general knowledge text corpora: EHRs and biomedical papers. We hope this model can serve better results on clinical-related downstream tasks such as readmissions.\n\nThis model is trained on 500000 clinical notes randomly sampled from MIMIC datasets, with 100k steps of training. We also used whole word masking to enhance the coherence of the language model. All notes are chunked into a length of 512 tokens.\n\nPre-trained model: URL"
] |
null | null |
The older generation has a vulnerability, so they need to be monitored and taken care of. A large number of people, young and old, play really responsibly, but such a pastime can turn into a big problem. Many authoritative blogs and news portals of the gambling world like QYTO share statistics about this area and recommend only trusted casinos that cooperate with health organizations.
|
{}
|
Tsurakawi/erererere
| null |
[
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[] |
TAGS
#region-us
|
The older generation has a vulnerability, so they need to be monitored and taken care of. A large number of people, young and old, play really responsibly, but such a pastime can turn into a big problem. Many authoritative blogs and news portals of the gambling world like QYTO share statistics about this area and recommend only trusted casinos that cooperate with health organizations.
|
[] |
[
"TAGS\n#region-us \n"
] |
null | null |
# Model to Recognize Faces using eigenfaces and scikit-learn
Simple model that was trained on a preprocessed excerpt of the “Labeled Faces in the Wild”, aka [LFW](http://vis-www.cs.umass.edu/lfw/)
This demo was taken from [Scikit-learn](https://scikit-learn.org/stable/auto_examples/applications/plot_face_recognition.html)
The dataset includes 7 classes (individuals):

|
{}
|
Tuana/eigenfaces-sklearn-lfw
| null |
[
"joblib",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[] |
TAGS
#joblib #region-us
|
# Model to Recognize Faces using eigenfaces and scikit-learn
Simple model that was trained on a preprocessed excerpt of the “Labeled Faces in the Wild”, aka LFW
This demo was taken from Scikit-learn
The dataset includes 7 classes (individuals):
!Eigenfaces
|
[
"# Model to Recognize Faces using eigenfaces and scikit-learn\n\nSimple model that was trained on a preprocessed excerpt of the “Labeled Faces in the Wild”, aka LFW\nThis demo was taken from Scikit-learn\nThe dataset includes 7 classes (individuals):\n!Eigenfaces"
] |
[
"TAGS\n#joblib #region-us \n",
"# Model to Recognize Faces using eigenfaces and scikit-learn\n\nSimple model that was trained on a preprocessed excerpt of the “Labeled Faces in the Wild”, aka LFW\nThis demo was taken from Scikit-learn\nThe dataset includes 7 classes (individuals):\n!Eigenfaces"
] |
fill-mask
|
transformers
|
## Quickstart
**Release 1.0** (November 25, 2019)
We generally recommend the use of the cased model.
Paper presenting Finnish BERT: [arXiv:1912.07076](https://arxiv.org/abs/1912.07076)
## What's this?
A version of Google's [BERT](https://github.com/google-research/bert) deep transfer learning model for Finnish. The model can be fine-tuned to achieve state-of-the-art results for various Finnish natural language processing tasks.
FinBERT features a custom 50,000 wordpiece vocabulary that has much better coverage of Finnish words than e.g. the previously released [multilingual BERT](https://github.com/google-research/bert/blob/master/multilingual.md) models from Google:
| Vocabulary | Example |
|------------|---------|
| FinBERT | Suomessa vaihtuu kesän aikana sekä pääministeri että valtiovarain ##ministeri . |
| Multilingual BERT | Suomessa vai ##htuu kes ##än aikana sekä p ##ää ##minister ##i että valt ##io ##vara ##in ##minister ##i . |
FinBERT has been pre-trained for 1 million steps on over 3 billion tokens (24B characters) of Finnish text drawn from news, online discussion, and internet crawls. By contrast, Multilingual BERT was trained on Wikipedia texts, where the Finnish Wikipedia text is approximately 3% of the amount used to train FinBERT.
These features allow FinBERT to outperform not only Multilingual BERT but also all previously proposed models when fine-tuned for Finnish natural language processing tasks.
## Results
### Document classification
FinBERT outperforms multilingual BERT (M-BERT) on document classification over a range of training set sizes on the Yle news (left) and Ylilauta online discussion (right) corpora. (Baseline classification performance with [FastText](https://fasttext.cc/) included for reference.)
[[code](https://github.com/spyysalo/finbert-text-classification)][[Yle data](https://github.com/spyysalo/yle-corpus)] [[Ylilauta data](https://github.com/spyysalo/ylilauta-corpus)]
### Named Entity Recognition
Evaluation on FiNER corpus ([Ruokolainen et al 2019](https://arxiv.org/abs/1908.04212))
| Model | Accuracy |
|--------------------|----------|
| **FinBERT** | **92.40%** |
| Multilingual BERT | 90.29% |
| [FiNER-tagger](https://github.com/Traubert/FiNer-rules) (rule-based) | 86.82% |
(FiNER tagger results from [Ruokolainen et al. 2019](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1908.04212.pdf))
[[code](https://github.com/jouniluoma/keras-bert-ner)][[data](https://github.com/mpsilfve/finer-data)]
### Part of speech tagging
Evaluation on three Finnish corpora annotated with [Universal Dependencies](https://universaldependencies.org/) part-of-speech tags: the Turku Dependency Treebank (TDT), FinnTreeBank (FTB), and Parallel UD treebank (PUD)
| Model | TDT | FTB | PUD |
|-------------------|-------------|-------------|-------------|
| **FinBERT** | **98.23%** | **98.39%** | **98.08%** |
| Multilingual BERT | 96.97% | 95.87% | 97.58% |
[[code](https://github.com/spyysalo/bert-pos)][[data](http://hdl.handle.net/11234/1-2837)]
## Previous releases
### Release 0.2
**October 24, 2019** Beta version of the BERT base uncased model trained from scratch on a corpus of Finnish news, online discussions, and crawled data.
Download the model here: [bert-base-finnish-uncased.zip](http://dl.turkunlp.org/finbert/bert-base-finnish-uncased.zip)
### Release 0.1
**September 30, 2019** We release a beta version of the BERT base cased model trained from scratch on a corpus of Finnish news, online discussions, and crawled data.
Download the model here: [bert-base-finnish-cased.zip](http://dl.turkunlp.org/finbert/bert-base-finnish-cased.zip)
|
{"language": "fi"}
|
TurkuNLP/bert-base-finnish-cased-v1
| null |
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"tf",
"jax",
"bert",
"fill-mask",
"fi",
"arxiv:1912.07076",
"arxiv:1908.04212",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"has_space",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[
"1912.07076",
"1908.04212"
] |
[
"fi"
] |
TAGS
#transformers #pytorch #tf #jax #bert #fill-mask #fi #arxiv-1912.07076 #arxiv-1908.04212 #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #has_space #region-us
|
Quickstart
----------
Release 1.0 (November 25, 2019)
We generally recommend the use of the cased model.
Paper presenting Finnish BERT: arXiv:1912.07076
What's this?
------------
A version of Google's BERT deep transfer learning model for Finnish. The model can be fine-tuned to achieve state-of-the-art results for various Finnish natural language processing tasks.
FinBERT features a custom 50,000 wordpiece vocabulary that has much better coverage of Finnish words than e.g. the previously released multilingual BERT models from Google:
FinBERT has been pre-trained for 1 million steps on over 3 billion tokens (24B characters) of Finnish text drawn from news, online discussion, and internet crawls. By contrast, Multilingual BERT was trained on Wikipedia texts, where the Finnish Wikipedia text is approximately 3% of the amount used to train FinBERT.
These features allow FinBERT to outperform not only Multilingual BERT but also all previously proposed models when fine-tuned for Finnish natural language processing tasks.
Results
-------
### Document classification
!learning curves for Yle and Ylilauta document classification
FinBERT outperforms multilingual BERT (M-BERT) on document classification over a range of training set sizes on the Yle news (left) and Ylilauta online discussion (right) corpora. (Baseline classification performance with FastText included for reference.)
[code][Yle data] [Ylilauta data]
### Named Entity Recognition
Evaluation on FiNER corpus (Ruokolainen et al 2019)
(FiNER tagger results from Ruokolainen et al. 2019)
[code][data]
### Part of speech tagging
Evaluation on three Finnish corpora annotated with Universal Dependencies part-of-speech tags: the Turku Dependency Treebank (TDT), FinnTreeBank (FTB), and Parallel UD treebank (PUD)
[code][data]
Previous releases
-----------------
### Release 0.2
October 24, 2019 Beta version of the BERT base uncased model trained from scratch on a corpus of Finnish news, online discussions, and crawled data.
Download the model here: URL
### Release 0.1
September 30, 2019 We release a beta version of the BERT base cased model trained from scratch on a corpus of Finnish news, online discussions, and crawled data.
Download the model here: URL
|
[
"### Document classification\n\n\n!learning curves for Yle and Ylilauta document classification\n\n\nFinBERT outperforms multilingual BERT (M-BERT) on document classification over a range of training set sizes on the Yle news (left) and Ylilauta online discussion (right) corpora. (Baseline classification performance with FastText included for reference.)\n\n\n[code][Yle data] [Ylilauta data]",
"### Named Entity Recognition\n\n\nEvaluation on FiNER corpus (Ruokolainen et al 2019)\n\n\n\n(FiNER tagger results from Ruokolainen et al. 2019)\n\n\n[code][data]",
"### Part of speech tagging\n\n\nEvaluation on three Finnish corpora annotated with Universal Dependencies part-of-speech tags: the Turku Dependency Treebank (TDT), FinnTreeBank (FTB), and Parallel UD treebank (PUD)\n\n\n\n[code][data]\n\n\nPrevious releases\n-----------------",
"### Release 0.2\n\n\nOctober 24, 2019 Beta version of the BERT base uncased model trained from scratch on a corpus of Finnish news, online discussions, and crawled data.\n\n\nDownload the model here: URL",
"### Release 0.1\n\n\nSeptember 30, 2019 We release a beta version of the BERT base cased model trained from scratch on a corpus of Finnish news, online discussions, and crawled data.\n\n\nDownload the model here: URL"
] |
[
"TAGS\n#transformers #pytorch #tf #jax #bert #fill-mask #fi #arxiv-1912.07076 #arxiv-1908.04212 #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #has_space #region-us \n",
"### Document classification\n\n\n!learning curves for Yle and Ylilauta document classification\n\n\nFinBERT outperforms multilingual BERT (M-BERT) on document classification over a range of training set sizes on the Yle news (left) and Ylilauta online discussion (right) corpora. (Baseline classification performance with FastText included for reference.)\n\n\n[code][Yle data] [Ylilauta data]",
"### Named Entity Recognition\n\n\nEvaluation on FiNER corpus (Ruokolainen et al 2019)\n\n\n\n(FiNER tagger results from Ruokolainen et al. 2019)\n\n\n[code][data]",
"### Part of speech tagging\n\n\nEvaluation on three Finnish corpora annotated with Universal Dependencies part-of-speech tags: the Turku Dependency Treebank (TDT), FinnTreeBank (FTB), and Parallel UD treebank (PUD)\n\n\n\n[code][data]\n\n\nPrevious releases\n-----------------",
"### Release 0.2\n\n\nOctober 24, 2019 Beta version of the BERT base uncased model trained from scratch on a corpus of Finnish news, online discussions, and crawled data.\n\n\nDownload the model here: URL",
"### Release 0.1\n\n\nSeptember 30, 2019 We release a beta version of the BERT base cased model trained from scratch on a corpus of Finnish news, online discussions, and crawled data.\n\n\nDownload the model here: URL"
] |
fill-mask
|
transformers
|
## Quickstart
**Release 1.0** (November 25, 2019)
Download the models here:
* Cased Finnish BERT Base: [bert-base-finnish-cased-v1.zip](http://dl.turkunlp.org/finbert/bert-base-finnish-cased-v1.zip)
* Uncased Finnish BERT Base: [bert-base-finnish-uncased-v1.zip](http://dl.turkunlp.org/finbert/bert-base-finnish-uncased-v1.zip)
We generally recommend the use of the cased model.
Paper presenting Finnish BERT: [arXiv:1912.07076](https://arxiv.org/abs/1912.07076)
## What's this?
A version of Google's [BERT](https://github.com/google-research/bert) deep transfer learning model for Finnish. The model can be fine-tuned to achieve state-of-the-art results for various Finnish natural language processing tasks.
FinBERT features a custom 50,000 wordpiece vocabulary that has much better coverage of Finnish words than e.g. the previously released [multilingual BERT](https://github.com/google-research/bert/blob/master/multilingual.md) models from Google:
| Vocabulary | Example |
|------------|---------|
| FinBERT | Suomessa vaihtuu kesän aikana sekä pääministeri että valtiovarain ##ministeri . |
| Multilingual BERT | Suomessa vai ##htuu kes ##än aikana sekä p ##ää ##minister ##i että valt ##io ##vara ##in ##minister ##i . |
FinBERT has been pre-trained for 1 million steps on over 3 billion tokens (24B characters) of Finnish text drawn from news, online discussion, and internet crawls. By contrast, Multilingual BERT was trained on Wikipedia texts, where the Finnish Wikipedia text is approximately 3% of the amount used to train FinBERT.
These features allow FinBERT to outperform not only Multilingual BERT but also all previously proposed models when fine-tuned for Finnish natural language processing tasks.
## Results
### Document classification

FinBERT outperforms multilingual BERT (M-BERT) on document classification over a range of training set sizes on the Yle news (left) and Ylilauta online discussion (right) corpora. (Baseline classification performance with [FastText](https://fasttext.cc/) included for reference.)
[[code](https://github.com/spyysalo/finbert-text-classification)][[Yle data](https://github.com/spyysalo/yle-corpus)] [[Ylilauta data](https://github.com/spyysalo/ylilauta-corpus)]
### Named Entity Recognition
Evaluation on FiNER corpus ([Ruokolainen et al 2019](https://arxiv.org/abs/1908.04212))
| Model | Accuracy |
|--------------------|----------|
| **FinBERT** | **92.40%** |
| Multilingual BERT | 90.29% |
| [FiNER-tagger](https://github.com/Traubert/FiNer-rules) (rule-based) | 86.82% |
(FiNER tagger results from [Ruokolainen et al. 2019](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1908.04212.pdf))
[[code](https://github.com/jouniluoma/keras-bert-ner)][[data](https://github.com/mpsilfve/finer-data)]
### Part of speech tagging
Evaluation on three Finnish corpora annotated with [Universal Dependencies](https://universaldependencies.org/) part-of-speech tags: the Turku Dependency Treebank (TDT), FinnTreeBank (FTB), and Parallel UD treebank (PUD)
| Model | TDT | FTB | PUD |
|-------------------|-------------|-------------|-------------|
| **FinBERT** | **98.23%** | **98.39%** | **98.08%** |
| Multilingual BERT | 96.97% | 95.87% | 97.58% |
[[code](https://github.com/spyysalo/bert-pos)][[data](http://hdl.handle.net/11234/1-2837)]
## Use with PyTorch
If you want to use the model with the huggingface/transformers library, follow the steps in [huggingface_transformers.md](https://github.com/TurkuNLP/FinBERT/blob/master/huggingface_transformers.md)
## Previous releases
### Release 0.2
**October 24, 2019** Beta version of the BERT base uncased model trained from scratch on a corpus of Finnish news, online discussions, and crawled data.
Download the model here: [bert-base-finnish-uncased.zip](http://dl.turkunlp.org/finbert/bert-base-finnish-uncased.zip)
### Release 0.1
**September 30, 2019** We release a beta version of the BERT base cased model trained from scratch on a corpus of Finnish news, online discussions, and crawled data.
Download the model here: [bert-base-finnish-cased.zip](http://dl.turkunlp.org/finbert/bert-base-finnish-cased.zip)
|
{"language": "fi"}
|
TurkuNLP/bert-base-finnish-uncased-v1
| null |
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"tf",
"jax",
"bert",
"fill-mask",
"fi",
"arxiv:1912.07076",
"arxiv:1908.04212",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"has_space",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[
"1912.07076",
"1908.04212"
] |
[
"fi"
] |
TAGS
#transformers #pytorch #tf #jax #bert #fill-mask #fi #arxiv-1912.07076 #arxiv-1908.04212 #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #has_space #region-us
|
Quickstart
----------
Release 1.0 (November 25, 2019)
Download the models here:
* Cased Finnish BERT Base: URL
* Uncased Finnish BERT Base: URL
We generally recommend the use of the cased model.
Paper presenting Finnish BERT: arXiv:1912.07076
What's this?
------------
A version of Google's BERT deep transfer learning model for Finnish. The model can be fine-tuned to achieve state-of-the-art results for various Finnish natural language processing tasks.
FinBERT features a custom 50,000 wordpiece vocabulary that has much better coverage of Finnish words than e.g. the previously released multilingual BERT models from Google:
FinBERT has been pre-trained for 1 million steps on over 3 billion tokens (24B characters) of Finnish text drawn from news, online discussion, and internet crawls. By contrast, Multilingual BERT was trained on Wikipedia texts, where the Finnish Wikipedia text is approximately 3% of the amount used to train FinBERT.
These features allow FinBERT to outperform not only Multilingual BERT but also all previously proposed models when fine-tuned for Finnish natural language processing tasks.
Results
-------
### Document classification
!learning curves for Yle and Ylilauta document classification
FinBERT outperforms multilingual BERT (M-BERT) on document classification over a range of training set sizes on the Yle news (left) and Ylilauta online discussion (right) corpora. (Baseline classification performance with FastText included for reference.)
[code][Yle data] [Ylilauta data]
### Named Entity Recognition
Evaluation on FiNER corpus (Ruokolainen et al 2019)
(FiNER tagger results from Ruokolainen et al. 2019)
[code][data]
### Part of speech tagging
Evaluation on three Finnish corpora annotated with Universal Dependencies part-of-speech tags: the Turku Dependency Treebank (TDT), FinnTreeBank (FTB), and Parallel UD treebank (PUD)
[code][data]
Use with PyTorch
----------------
If you want to use the model with the huggingface/transformers library, follow the steps in huggingface\_transformers.md
Previous releases
-----------------
### Release 0.2
October 24, 2019 Beta version of the BERT base uncased model trained from scratch on a corpus of Finnish news, online discussions, and crawled data.
Download the model here: URL
### Release 0.1
September 30, 2019 We release a beta version of the BERT base cased model trained from scratch on a corpus of Finnish news, online discussions, and crawled data.
Download the model here: URL
|
[
"### Document classification\n\n\n!learning curves for Yle and Ylilauta document classification\n\n\nFinBERT outperforms multilingual BERT (M-BERT) on document classification over a range of training set sizes on the Yle news (left) and Ylilauta online discussion (right) corpora. (Baseline classification performance with FastText included for reference.)\n\n\n[code][Yle data] [Ylilauta data]",
"### Named Entity Recognition\n\n\nEvaluation on FiNER corpus (Ruokolainen et al 2019)\n\n\n\n(FiNER tagger results from Ruokolainen et al. 2019)\n\n\n[code][data]",
"### Part of speech tagging\n\n\nEvaluation on three Finnish corpora annotated with Universal Dependencies part-of-speech tags: the Turku Dependency Treebank (TDT), FinnTreeBank (FTB), and Parallel UD treebank (PUD)\n\n\n\n[code][data]\n\n\nUse with PyTorch\n----------------\n\n\nIf you want to use the model with the huggingface/transformers library, follow the steps in huggingface\\_transformers.md\n\n\nPrevious releases\n-----------------",
"### Release 0.2\n\n\nOctober 24, 2019 Beta version of the BERT base uncased model trained from scratch on a corpus of Finnish news, online discussions, and crawled data.\n\n\nDownload the model here: URL",
"### Release 0.1\n\n\nSeptember 30, 2019 We release a beta version of the BERT base cased model trained from scratch on a corpus of Finnish news, online discussions, and crawled data.\n\n\nDownload the model here: URL"
] |
[
"TAGS\n#transformers #pytorch #tf #jax #bert #fill-mask #fi #arxiv-1912.07076 #arxiv-1908.04212 #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #has_space #region-us \n",
"### Document classification\n\n\n!learning curves for Yle and Ylilauta document classification\n\n\nFinBERT outperforms multilingual BERT (M-BERT) on document classification over a range of training set sizes on the Yle news (left) and Ylilauta online discussion (right) corpora. (Baseline classification performance with FastText included for reference.)\n\n\n[code][Yle data] [Ylilauta data]",
"### Named Entity Recognition\n\n\nEvaluation on FiNER corpus (Ruokolainen et al 2019)\n\n\n\n(FiNER tagger results from Ruokolainen et al. 2019)\n\n\n[code][data]",
"### Part of speech tagging\n\n\nEvaluation on three Finnish corpora annotated with Universal Dependencies part-of-speech tags: the Turku Dependency Treebank (TDT), FinnTreeBank (FTB), and Parallel UD treebank (PUD)\n\n\n\n[code][data]\n\n\nUse with PyTorch\n----------------\n\n\nIf you want to use the model with the huggingface/transformers library, follow the steps in huggingface\\_transformers.md\n\n\nPrevious releases\n-----------------",
"### Release 0.2\n\n\nOctober 24, 2019 Beta version of the BERT base uncased model trained from scratch on a corpus of Finnish news, online discussions, and crawled data.\n\n\nDownload the model here: URL",
"### Release 0.1\n\n\nSeptember 30, 2019 We release a beta version of the BERT base cased model trained from scratch on a corpus of Finnish news, online discussions, and crawled data.\n\n\nDownload the model here: URL"
] |
sentence-similarity
|
sentence-transformers
|
# Cased Finnish Sentence BERT model
Finnish Sentence BERT trained from FinBERT. A demo on retrieving the most similar sentences from a dataset of 400 million sentences can be found [here](http://epsilon-it.utu.fi/sbert400m).
## Training
- Library: [sentence-transformers](https://www.sbert.net/)
- FinBERT model: TurkuNLP/bert-base-finnish-cased-v1
- Data: The data provided [here](https://turkunlp.org/paraphrase.html), including the Finnish Paraphrase Corpus and the automatically collected paraphrase candidates (500K positive and 5M negative)
- Pooling: mean pooling
- Task: Binary prediction, whether two sentences are paraphrases or not. Note: the labels 3 and 4 are considered paraphrases, and labels 1 and 2 non-paraphrases. [Details on labels](https://aclanthology.org/2021.nodalida-main.29/)
## Usage
The same as in the HuggingFace documentation of [the English Sentence Transformer](https://huggingface.co/sentence-transformers/bert-base-nli-mean-tokens). Either through `SentenceTransformer` or `HuggingFace Transformers`
### SentenceTransformer
```python
from sentence_transformers import SentenceTransformer
sentences = ["Tämä on esimerkkilause.", "Tämä on toinen lause."]
model = SentenceTransformer('TurkuNLP/sbert-cased-finnish-paraphrase')
embeddings = model.encode(sentences)
print(embeddings)
```
### HuggingFace Transformers
```python
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModel
import torch
#Mean Pooling - Take attention mask into account for correct averaging
def mean_pooling(model_output, attention_mask):
token_embeddings = model_output[0] #First element of model_output contains all token embeddings
input_mask_expanded = attention_mask.unsqueeze(-1).expand(token_embeddings.size()).float()
return torch.sum(token_embeddings * input_mask_expanded, 1) / torch.clamp(input_mask_expanded.sum(1), min=1e-9)
# Sentences we want sentence embeddings for
sentences = ["Tämä on esimerkkilause.", "Tämä on toinen lause."]
# Load model from HuggingFace Hub
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained('TurkuNLP/sbert-cased-finnish-paraphrase')
model = AutoModel.from_pretrained('TurkuNLP/sbert-cased-finnish-paraphrase')
# Tokenize sentences
encoded_input = tokenizer(sentences, padding=True, truncation=True, return_tensors='pt')
# Compute token embeddings
with torch.no_grad():
model_output = model(**encoded_input)
# Perform pooling. In this case, mean pooling.
sentence_embeddings = mean_pooling(model_output, encoded_input['attention_mask'])
print("Sentence embeddings:")
print(sentence_embeddings)
```
## Evaluation Results
A publication detailing the evaluation results is currently being drafted.
## Full Model Architecture
```
SentenceTransformer(
(0): Transformer({'max_seq_length': 128, 'do_lower_case': False}) with Transformer model: BertModel
(1): Pooling({'word_embedding_dimension': 768, 'pooling_mode_cls_token': False, 'pooling_mode_mean_tokens': True, 'pooling_mode_max_tokens': False, 'pooling_mode_mean_sqrt_len_tokens': False})
)
```
## Citing & Authors
While the publication is being drafted, please cite [this page](https://turkunlp.org/paraphrase.html).
## References
- J. Kanerva, F. Ginter, LH. Chang, I. Rastas, V. Skantsi, J. Kilpeläinen, HM. Kupari, J. Saarni, M. Sevón, and O. Tarkka. Finnish Paraphrase Corpus. In *NoDaLiDa 2021*, 2021.
- N. Reimers and I. Gurevych. Sentence-BERT: Sentence embeddings using Siamese BERT-networks. In *EMNLP-IJCNLP*, pages 3982–3992, 2019.
- A. Virtanen, J. Kanerva, R. Ilo, J. Luoma, J. Luotolahti, T. Salakoski, F. Ginter, and S. Pyysalo. Multilingual is not enough: BERT for Finnish. *arXiv preprint arXiv:1912.07076*, 2019.
|
{"language": ["fi"], "tags": ["sentence-transformers", "feature-extraction", "sentence-similarity", "transformers"], "pipeline_tag": "sentence-similarity", "widget": [{"text": "Minusta t\u00e4\u00e4ll\u00e4 on ihana asua!"}]}
|
TurkuNLP/sbert-cased-finnish-paraphrase
| null |
[
"sentence-transformers",
"pytorch",
"bert",
"feature-extraction",
"sentence-similarity",
"transformers",
"fi",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[
"fi"
] |
TAGS
#sentence-transformers #pytorch #bert #feature-extraction #sentence-similarity #transformers #fi #endpoints_compatible #region-us
|
# Cased Finnish Sentence BERT model
Finnish Sentence BERT trained from FinBERT. A demo on retrieving the most similar sentences from a dataset of 400 million sentences can be found here.
## Training
- Library: sentence-transformers
- FinBERT model: TurkuNLP/bert-base-finnish-cased-v1
- Data: The data provided here, including the Finnish Paraphrase Corpus and the automatically collected paraphrase candidates (500K positive and 5M negative)
- Pooling: mean pooling
- Task: Binary prediction, whether two sentences are paraphrases or not. Note: the labels 3 and 4 are considered paraphrases, and labels 1 and 2 non-paraphrases. Details on labels
## Usage
The same as in the HuggingFace documentation of the English Sentence Transformer. Either through 'SentenceTransformer' or 'HuggingFace Transformers'
### SentenceTransformer
### HuggingFace Transformers
## Evaluation Results
A publication detailing the evaluation results is currently being drafted.
## Full Model Architecture
## Citing & Authors
While the publication is being drafted, please cite this page.
## References
- J. Kanerva, F. Ginter, LH. Chang, I. Rastas, V. Skantsi, J. Kilpeläinen, HM. Kupari, J. Saarni, M. Sevón, and O. Tarkka. Finnish Paraphrase Corpus. In *NoDaLiDa 2021*, 2021.
- N. Reimers and I. Gurevych. Sentence-BERT: Sentence embeddings using Siamese BERT-networks. In *EMNLP-IJCNLP*, pages 3982–3992, 2019.
- A. Virtanen, J. Kanerva, R. Ilo, J. Luoma, J. Luotolahti, T. Salakoski, F. Ginter, and S. Pyysalo. Multilingual is not enough: BERT for Finnish. *arXiv preprint arXiv:1912.07076*, 2019.
|
[
"# Cased Finnish Sentence BERT model\n\nFinnish Sentence BERT trained from FinBERT. A demo on retrieving the most similar sentences from a dataset of 400 million sentences can be found here.",
"## Training\n\n- Library: sentence-transformers\n- FinBERT model: TurkuNLP/bert-base-finnish-cased-v1\n- Data: The data provided here, including the Finnish Paraphrase Corpus and the automatically collected paraphrase candidates (500K positive and 5M negative)\n- Pooling: mean pooling\n- Task: Binary prediction, whether two sentences are paraphrases or not. Note: the labels 3 and 4 are considered paraphrases, and labels 1 and 2 non-paraphrases. Details on labels",
"## Usage\n\nThe same as in the HuggingFace documentation of the English Sentence Transformer. Either through 'SentenceTransformer' or 'HuggingFace Transformers'",
"### SentenceTransformer",
"### HuggingFace Transformers",
"## Evaluation Results\n\nA publication detailing the evaluation results is currently being drafted.",
"## Full Model Architecture",
"## Citing & Authors\n\nWhile the publication is being drafted, please cite this page.",
"## References\n\n- J. Kanerva, F. Ginter, LH. Chang, I. Rastas, V. Skantsi, J. Kilpeläinen, HM. Kupari, J. Saarni, M. Sevón, and O. Tarkka. Finnish Paraphrase Corpus. In *NoDaLiDa 2021*, 2021.\n- N. Reimers and I. Gurevych. Sentence-BERT: Sentence embeddings using Siamese BERT-networks. In *EMNLP-IJCNLP*, pages 3982–3992, 2019.\n- A. Virtanen, J. Kanerva, R. Ilo, J. Luoma, J. Luotolahti, T. Salakoski, F. Ginter, and S. Pyysalo. Multilingual is not enough: BERT for Finnish. *arXiv preprint arXiv:1912.07076*, 2019."
] |
[
"TAGS\n#sentence-transformers #pytorch #bert #feature-extraction #sentence-similarity #transformers #fi #endpoints_compatible #region-us \n",
"# Cased Finnish Sentence BERT model\n\nFinnish Sentence BERT trained from FinBERT. A demo on retrieving the most similar sentences from a dataset of 400 million sentences can be found here.",
"## Training\n\n- Library: sentence-transformers\n- FinBERT model: TurkuNLP/bert-base-finnish-cased-v1\n- Data: The data provided here, including the Finnish Paraphrase Corpus and the automatically collected paraphrase candidates (500K positive and 5M negative)\n- Pooling: mean pooling\n- Task: Binary prediction, whether two sentences are paraphrases or not. Note: the labels 3 and 4 are considered paraphrases, and labels 1 and 2 non-paraphrases. Details on labels",
"## Usage\n\nThe same as in the HuggingFace documentation of the English Sentence Transformer. Either through 'SentenceTransformer' or 'HuggingFace Transformers'",
"### SentenceTransformer",
"### HuggingFace Transformers",
"## Evaluation Results\n\nA publication detailing the evaluation results is currently being drafted.",
"## Full Model Architecture",
"## Citing & Authors\n\nWhile the publication is being drafted, please cite this page.",
"## References\n\n- J. Kanerva, F. Ginter, LH. Chang, I. Rastas, V. Skantsi, J. Kilpeläinen, HM. Kupari, J. Saarni, M. Sevón, and O. Tarkka. Finnish Paraphrase Corpus. In *NoDaLiDa 2021*, 2021.\n- N. Reimers and I. Gurevych. Sentence-BERT: Sentence embeddings using Siamese BERT-networks. In *EMNLP-IJCNLP*, pages 3982–3992, 2019.\n- A. Virtanen, J. Kanerva, R. Ilo, J. Luoma, J. Luotolahti, T. Salakoski, F. Ginter, and S. Pyysalo. Multilingual is not enough: BERT for Finnish. *arXiv preprint arXiv:1912.07076*, 2019."
] |
sentence-similarity
|
sentence-transformers
|
# Uncased Finnish Sentence BERT model
Finnish Sentence BERT trained from FinBERT. A demo on retrieving the most similar sentences from a dataset of 400 million sentences *using [the cased model](https://huggingface.co/TurkuNLP/sbert-cased-finnish-paraphrase)* can be found [here](http://epsilon-it.utu.fi/sbert400m).
## Training
- Library: [sentence-transformers](https://www.sbert.net/)
- FinBERT model: TurkuNLP/bert-base-finnish-uncased-v1
- Data: The data provided [here](https://turkunlp.org/paraphrase.html), including the Finnish Paraphrase Corpus and the automatically collected paraphrase candidates (500K positive and 5M negative)
- Pooling: mean pooling
- Task: Binary prediction, whether two sentences are paraphrases or not. Note: the labels 3 and 4 are considered paraphrases, and labels 1 and 2 non-paraphrases. [Details on labels](https://aclanthology.org/2021.nodalida-main.29/)
## Usage
The same as in [HuggingFace documentation](https://huggingface.co/sentence-transformers/bert-base-nli-mean-tokens). Either through `SentenceTransformer` or `HuggingFace Transformers`
### SentenceTransformer
```python
from sentence_transformers import SentenceTransformer
sentences = ["Tämä on esimerkkilause.", "Tämä on toinen lause."]
model = SentenceTransformer('TurkuNLP/sbert-uncased-finnish-paraphrase')
embeddings = model.encode(sentences)
print(embeddings)
```
### HuggingFace Transformers
```python
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModel
import torch
# Mean Pooling - Take attention mask into account for correct averaging
def mean_pooling(model_output, attention_mask):
token_embeddings = model_output[0] #First element of model_output contains all token embeddings
input_mask_expanded = attention_mask.unsqueeze(-1).expand(token_embeddings.size()).float()
return torch.sum(token_embeddings * input_mask_expanded, 1) / torch.clamp(input_mask_expanded.sum(1), min=1e-9)
# Sentences we want sentence embeddings for
sentences = ["Tämä on esimerkkilause.", "Tämä on toinen lause."]
# Load model from HuggingFace Hub
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained('TurkuNLP/sbert-uncased-finnish-paraphrase')
model = AutoModel.from_pretrained('TurkuNLP/sbert-uncased-finnish-paraphrase')
# Tokenize sentences
encoded_input = tokenizer(sentences, padding=True, truncation=True, return_tensors='pt')
# Compute token embeddings
with torch.no_grad():
model_output = model(**encoded_input)
# Perform pooling. In this case, mean pooling.
sentence_embeddings = mean_pooling(model_output, encoded_input['attention_mask'])
print("Sentence embeddings:")
print(sentence_embeddings)
```
## Evaluation Results
A publication detailing the evaluation results is currently being drafted.
## Full Model Architecture
```
SentenceTransformer(
(0): Transformer({'max_seq_length': 128, 'do_lower_case': True}) with Transformer model: BertModel
(1): Pooling({'word_embedding_dimension': 768, 'pooling_mode_cls_token': False, 'pooling_mode_mean_tokens': True, 'pooling_mode_max_tokens': False, 'pooling_mode_mean_sqrt_len_tokens': False})
)
```
## Citing & Authors
While the publication is being drafted, please cite [this page](https://turkunlp.org/paraphrase.html).
## References
- J. Kanerva, F. Ginter, LH. Chang, I. Rastas, V. Skantsi, J. Kilpeläinen, HM. Kupari, J. Saarni, M. Sevón, and O. Tarkka. Finnish Paraphrase Corpus. In *NoDaLiDa 2021*, 2021.
- N. Reimers and I. Gurevych. Sentence-BERT: Sentence embeddings using Siamese BERT-networks. In *EMNLP-IJCNLP*, pages 3982–3992, 2019.
- A. Virtanen, J. Kanerva, R. Ilo, J. Luoma, J. Luotolahti, T. Salakoski, F. Ginter, and S. Pyysalo. Multilingual is not enough: BERT for Finnish. *arXiv preprint arXiv:1912.07076*, 2019.
|
{"language": ["fi"], "tags": ["sentence-transformers", "feature-extraction", "sentence-similarity", "transformers"], "pipeline_tag": "sentence-similarity", "widget": [{"text": "Minusta t\u00e4\u00e4ll\u00e4 on ihana asua!"}]}
|
TurkuNLP/sbert-uncased-finnish-paraphrase
| null |
[
"sentence-transformers",
"pytorch",
"bert",
"feature-extraction",
"sentence-similarity",
"transformers",
"fi",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[
"fi"
] |
TAGS
#sentence-transformers #pytorch #bert #feature-extraction #sentence-similarity #transformers #fi #endpoints_compatible #region-us
|
# Uncased Finnish Sentence BERT model
Finnish Sentence BERT trained from FinBERT. A demo on retrieving the most similar sentences from a dataset of 400 million sentences *using the cased model* can be found here.
## Training
- Library: sentence-transformers
- FinBERT model: TurkuNLP/bert-base-finnish-uncased-v1
- Data: The data provided here, including the Finnish Paraphrase Corpus and the automatically collected paraphrase candidates (500K positive and 5M negative)
- Pooling: mean pooling
- Task: Binary prediction, whether two sentences are paraphrases or not. Note: the labels 3 and 4 are considered paraphrases, and labels 1 and 2 non-paraphrases. Details on labels
## Usage
The same as in HuggingFace documentation. Either through 'SentenceTransformer' or 'HuggingFace Transformers'
### SentenceTransformer
### HuggingFace Transformers
## Evaluation Results
A publication detailing the evaluation results is currently being drafted.
## Full Model Architecture
## Citing & Authors
While the publication is being drafted, please cite this page.
## References
- J. Kanerva, F. Ginter, LH. Chang, I. Rastas, V. Skantsi, J. Kilpeläinen, HM. Kupari, J. Saarni, M. Sevón, and O. Tarkka. Finnish Paraphrase Corpus. In *NoDaLiDa 2021*, 2021.
- N. Reimers and I. Gurevych. Sentence-BERT: Sentence embeddings using Siamese BERT-networks. In *EMNLP-IJCNLP*, pages 3982–3992, 2019.
- A. Virtanen, J. Kanerva, R. Ilo, J. Luoma, J. Luotolahti, T. Salakoski, F. Ginter, and S. Pyysalo. Multilingual is not enough: BERT for Finnish. *arXiv preprint arXiv:1912.07076*, 2019.
|
[
"# Uncased Finnish Sentence BERT model\n\nFinnish Sentence BERT trained from FinBERT. A demo on retrieving the most similar sentences from a dataset of 400 million sentences *using the cased model* can be found here.",
"## Training\n\n- Library: sentence-transformers\n- FinBERT model: TurkuNLP/bert-base-finnish-uncased-v1\n- Data: The data provided here, including the Finnish Paraphrase Corpus and the automatically collected paraphrase candidates (500K positive and 5M negative)\n- Pooling: mean pooling\n- Task: Binary prediction, whether two sentences are paraphrases or not. Note: the labels 3 and 4 are considered paraphrases, and labels 1 and 2 non-paraphrases. Details on labels",
"## Usage\n\nThe same as in HuggingFace documentation. Either through 'SentenceTransformer' or 'HuggingFace Transformers'",
"### SentenceTransformer",
"### HuggingFace Transformers",
"## Evaluation Results\n\nA publication detailing the evaluation results is currently being drafted.",
"## Full Model Architecture",
"## Citing & Authors\nWhile the publication is being drafted, please cite this page.",
"## References\n\n- J. Kanerva, F. Ginter, LH. Chang, I. Rastas, V. Skantsi, J. Kilpeläinen, HM. Kupari, J. Saarni, M. Sevón, and O. Tarkka. Finnish Paraphrase Corpus. In *NoDaLiDa 2021*, 2021.\n- N. Reimers and I. Gurevych. Sentence-BERT: Sentence embeddings using Siamese BERT-networks. In *EMNLP-IJCNLP*, pages 3982–3992, 2019.\n- A. Virtanen, J. Kanerva, R. Ilo, J. Luoma, J. Luotolahti, T. Salakoski, F. Ginter, and S. Pyysalo. Multilingual is not enough: BERT for Finnish. *arXiv preprint arXiv:1912.07076*, 2019."
] |
[
"TAGS\n#sentence-transformers #pytorch #bert #feature-extraction #sentence-similarity #transformers #fi #endpoints_compatible #region-us \n",
"# Uncased Finnish Sentence BERT model\n\nFinnish Sentence BERT trained from FinBERT. A demo on retrieving the most similar sentences from a dataset of 400 million sentences *using the cased model* can be found here.",
"## Training\n\n- Library: sentence-transformers\n- FinBERT model: TurkuNLP/bert-base-finnish-uncased-v1\n- Data: The data provided here, including the Finnish Paraphrase Corpus and the automatically collected paraphrase candidates (500K positive and 5M negative)\n- Pooling: mean pooling\n- Task: Binary prediction, whether two sentences are paraphrases or not. Note: the labels 3 and 4 are considered paraphrases, and labels 1 and 2 non-paraphrases. Details on labels",
"## Usage\n\nThe same as in HuggingFace documentation. Either through 'SentenceTransformer' or 'HuggingFace Transformers'",
"### SentenceTransformer",
"### HuggingFace Transformers",
"## Evaluation Results\n\nA publication detailing the evaluation results is currently being drafted.",
"## Full Model Architecture",
"## Citing & Authors\nWhile the publication is being drafted, please cite this page.",
"## References\n\n- J. Kanerva, F. Ginter, LH. Chang, I. Rastas, V. Skantsi, J. Kilpeläinen, HM. Kupari, J. Saarni, M. Sevón, and O. Tarkka. Finnish Paraphrase Corpus. In *NoDaLiDa 2021*, 2021.\n- N. Reimers and I. Gurevych. Sentence-BERT: Sentence embeddings using Siamese BERT-networks. In *EMNLP-IJCNLP*, pages 3982–3992, 2019.\n- A. Virtanen, J. Kanerva, R. Ilo, J. Luoma, J. Luotolahti, T. Salakoski, F. Ginter, and S. Pyysalo. Multilingual is not enough: BERT for Finnish. *arXiv preprint arXiv:1912.07076*, 2019."
] |
token-classification
|
transformers
|
# MagBERT-NER: a state-of-the-art NER model for Moroccan French language (Maghreb)
## Introduction
[MagBERT-NER] is a state-of-the-art NER model for Moroccan French language (Maghreb). The MagBERT-NER model was fine-tuned for NER Task based the language model for French Camembert (based on the RoBERTa architecture).
For further information or requests, please visite our website at [typica.ai Website](https://typica.ai/) or send us an email at contactus@typica.ai
## How to use MagBERT-NER with HuggingFace
##### Load MagBERT-NER and its sub-word tokenizer :
```python
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForTokenClassification
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("TypicaAI/magbert-ner")
model = AutoModelForTokenClassification.from_pretrained("TypicaAI/magbert-ner")
##### Process text sample (from wikipedia about the current Prime Minister of Morocco) Using NER pipeline
from transformers import pipeline
nlp = pipeline('ner', model=model, tokenizer=tokenizer, grouped_entities=True)
nlp("Saad Dine El Otmani, né le 16 janvier 1956 à Inezgane, est un homme d'État marocain, chef du gouvernement du Maroc depuis le 5 avril 2017")
#[{'entity_group': 'I-PERSON',
# 'score': 0.8941445276141167,
# 'word': 'Saad Dine El Otmani'},
# {'entity_group': 'B-DATE',
# 'score': 0.5967703461647034,
# 'word': '16 janvier 1956'},
# {'entity_group': 'B-GPE', 'score': 0.7160899192094803, 'word': 'Inezgane'},
# {'entity_group': 'B-NORP', 'score': 0.7971733212471008, 'word': 'marocain'},
# {'entity_group': 'B-GPE', 'score': 0.8921478390693665, 'word': 'Maroc'},
# {'entity_group': 'B-DATE',
# 'score': 0.5760444005330404,
# 'word': '5 avril 2017'}]
```
## Authors
MagBert-NER Model was trained by Hicham Assoudi, Ph.D.
For any questions, comments you can contact me at assoudi@typica.ai
## Citation
If you use our work, please cite:
Hicham Assoudi, Ph.D., MagBERT-NER: a state-of-the-art NER model for Moroccan French language (Maghreb), (2020)
|
{"language": "fr", "widget": [{"text": "Je m'appelle Hicham et je vis a F\u00e8s"}]}
|
TypicaAI/magbert-ner
| null |
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"camembert",
"token-classification",
"fr",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[
"fr"
] |
TAGS
#transformers #pytorch #camembert #token-classification #fr #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #region-us
|
# MagBERT-NER: a state-of-the-art NER model for Moroccan French language (Maghreb)
## Introduction
[MagBERT-NER] is a state-of-the-art NER model for Moroccan French language (Maghreb). The MagBERT-NER model was fine-tuned for NER Task based the language model for French Camembert (based on the RoBERTa architecture).
For further information or requests, please visite our website at URL Website or send us an email at contactus@URL
## How to use MagBERT-NER with HuggingFace
##### Load MagBERT-NER and its sub-word tokenizer :
## Authors
MagBert-NER Model was trained by Hicham Assoudi, Ph.D.
For any questions, comments you can contact me at assoudi@URL
If you use our work, please cite:
Hicham Assoudi, Ph.D., MagBERT-NER: a state-of-the-art NER model for Moroccan French language (Maghreb), (2020)
|
[
"# MagBERT-NER: a state-of-the-art NER model for Moroccan French language (Maghreb)",
"## Introduction\n\n[MagBERT-NER] is a state-of-the-art NER model for Moroccan French language (Maghreb). The MagBERT-NER model was fine-tuned for NER Task based the language model for French Camembert (based on the RoBERTa architecture).\n\nFor further information or requests, please visite our website at URL Website or send us an email at contactus@URL",
"## How to use MagBERT-NER with HuggingFace",
"##### Load MagBERT-NER and its sub-word tokenizer :",
"## Authors \n\nMagBert-NER Model was trained by Hicham Assoudi, Ph.D. \nFor any questions, comments you can contact me at assoudi@URL\n\n\nIf you use our work, please cite:\nHicham Assoudi, Ph.D., MagBERT-NER: a state-of-the-art NER model for Moroccan French language (Maghreb), (2020)"
] |
[
"TAGS\n#transformers #pytorch #camembert #token-classification #fr #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #region-us \n",
"# MagBERT-NER: a state-of-the-art NER model for Moroccan French language (Maghreb)",
"## Introduction\n\n[MagBERT-NER] is a state-of-the-art NER model for Moroccan French language (Maghreb). The MagBERT-NER model was fine-tuned for NER Task based the language model for French Camembert (based on the RoBERTa architecture).\n\nFor further information or requests, please visite our website at URL Website or send us an email at contactus@URL",
"## How to use MagBERT-NER with HuggingFace",
"##### Load MagBERT-NER and its sub-word tokenizer :",
"## Authors \n\nMagBert-NER Model was trained by Hicham Assoudi, Ph.D. \nFor any questions, comments you can contact me at assoudi@URL\n\n\nIf you use our work, please cite:\nHicham Assoudi, Ph.D., MagBERT-NER: a state-of-the-art NER model for Moroccan French language (Maghreb), (2020)"
] |
fill-mask
|
transformers
|
<img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/UBC-NLP/marbert/main/ARBERT_MARBERT.jpg" alt="drawing" width="30%" height="30%" align="right"/>
**ARBERT** is one of three models described in our **ACl 2021 paper** **["ARBERT & MARBERT: Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Arabic"](https://mageed.arts.ubc.ca/files/2020/12/marbert_arxiv_2020.pdf)**. ARBERT is a large-scale pre-trained masked language model focused on Modern Standard Arabic (MSA). To train ARBERT, we use the same architecture as BERT-base: 12 attention layers, each has 12 attention heads and 768 hidden dimensions, a vocabulary of 100K WordPieces, making ∼163M parameters. We train ARBERT on a collection of Arabic datasets comprising **61GB of text** (**6.2B tokens**). For more information, please visit our own GitHub [repo](https://github.com/UBC-NLP/marbert).
# BibTex
If you use our models (ARBERT, MARBERT, or MARBERTv2) for your scientific publication, or if you find the resources in this repository useful, please cite our paper as follows (to be updated):
```bibtex
@inproceedings{abdul-mageed-etal-2021-arbert,
title = "{ARBERT} {\&} {MARBERT}: Deep Bidirectional Transformers for {A}rabic",
author = "Abdul-Mageed, Muhammad and
Elmadany, AbdelRahim and
Nagoudi, El Moatez Billah",
booktitle = "Proceedings of the 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 11th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (Volume 1: Long Papers)",
month = aug,
year = "2021",
address = "Online",
publisher = "Association for Computational Linguistics",
url = "https://aclanthology.org/2021.acl-long.551",
doi = "10.18653/v1/2021.acl-long.551",
pages = "7088--7105",
abstract = "Pre-trained language models (LMs) are currently integral to many natural language processing systems. Although multilingual LMs were also introduced to serve many languages, these have limitations such as being costly at inference time and the size and diversity of non-English data involved in their pre-training. We remedy these issues for a collection of diverse Arabic varieties by introducing two powerful deep bidirectional transformer-based models, ARBERT and MARBERT. To evaluate our models, we also introduce ARLUE, a new benchmark for multi-dialectal Arabic language understanding evaluation. ARLUE is built using 42 datasets targeting six different task clusters, allowing us to offer a series of standardized experiments under rich conditions. When fine-tuned on ARLUE, our models collectively achieve new state-of-the-art results across the majority of tasks (37 out of 48 classification tasks, on the 42 datasets). Our best model acquires the highest ARLUE score (77.40) across all six task clusters, outperforming all other models including XLM-R Large ( 3.4x larger size). Our models are publicly available at https://github.com/UBC-NLP/marbert and ARLUE will be released through the same repository.",
}
```
## Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge support from the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada, the Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council of Canada, Canadian Foundation for Innovation, [ComputeCanada](www.computecanada.ca) and [UBC ARC-Sockeye](https://doi.org/10.14288/SOCKEYE). We also thank the [Google TensorFlow Research Cloud (TFRC)](https://www.tensorflow.org/tfrc) program for providing us with free TPU access.
|
{"language": ["ar"], "tags": ["Arabic BERT", "MSA", "Twitter", "Masked Langauge Model"], "widget": [{"text": "\u0627\u0644\u0644\u063a\u0629 \u0627\u0644\u0639\u0631\u0628\u064a\u0629 \u0647\u064a \u0644\u063a\u0629 [MASK]."}]}
|
UBC-NLP/ARBERT
| null |
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"tf",
"jax",
"bert",
"fill-mask",
"Arabic BERT",
"MSA",
"Twitter",
"Masked Langauge Model",
"ar",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"has_space",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[
"ar"
] |
TAGS
#transformers #pytorch #tf #jax #bert #fill-mask #Arabic BERT #MSA #Twitter #Masked Langauge Model #ar #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #has_space #region-us
|
<img src="URL alt="drawing" width="30%" height="30%" align="right"/>
ARBERT is one of three models described in our ACl 2021 paper "ARBERT & MARBERT: Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Arabic". ARBERT is a large-scale pre-trained masked language model focused on Modern Standard Arabic (MSA). To train ARBERT, we use the same architecture as BERT-base: 12 attention layers, each has 12 attention heads and 768 hidden dimensions, a vocabulary of 100K WordPieces, making ∼163M parameters. We train ARBERT on a collection of Arabic datasets comprising 61GB of text (6.2B tokens). For more information, please visit our own GitHub repo.
# BibTex
If you use our models (ARBERT, MARBERT, or MARBERTv2) for your scientific publication, or if you find the resources in this repository useful, please cite our paper as follows (to be updated):
## Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge support from the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada, the Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council of Canada, Canadian Foundation for Innovation, ComputeCanada and UBC ARC-Sockeye. We also thank the Google TensorFlow Research Cloud (TFRC) program for providing us with free TPU access.
|
[
"# BibTex\n\nIf you use our models (ARBERT, MARBERT, or MARBERTv2) for your scientific publication, or if you find the resources in this repository useful, please cite our paper as follows (to be updated):",
"## Acknowledgments\nWe gratefully acknowledge support from the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada, the Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council of Canada, Canadian Foundation for Innovation, ComputeCanada and UBC ARC-Sockeye. We also thank the Google TensorFlow Research Cloud (TFRC) program for providing us with free TPU access."
] |
[
"TAGS\n#transformers #pytorch #tf #jax #bert #fill-mask #Arabic BERT #MSA #Twitter #Masked Langauge Model #ar #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #has_space #region-us \n",
"# BibTex\n\nIf you use our models (ARBERT, MARBERT, or MARBERTv2) for your scientific publication, or if you find the resources in this repository useful, please cite our paper as follows (to be updated):",
"## Acknowledgments\nWe gratefully acknowledge support from the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada, the Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council of Canada, Canadian Foundation for Innovation, ComputeCanada and UBC ARC-Sockeye. We also thank the Google TensorFlow Research Cloud (TFRC) program for providing us with free TPU access."
] |
text2text-generation
|
transformers
|
# AraT5-base-title-generation
# AraT5: Text-to-Text Transformers for Arabic Language Generation
<img src="https://huggingface.co/UBC-NLP/AraT5-base/resolve/main/AraT5_CR_new.png" alt="AraT5" width="45%" height="35%" align="right"/>
This is the repository accompanying our paper [AraT5: Text-to-Text Transformers for Arabic Language Understanding and Generation](https://aclanthology.org/2022.acl-long.47/). In this is the repository we Introduce **AraT5<sub>MSA</sub>**, **AraT5<sub>Tweet</sub>**, and **AraT5**: three powerful Arabic-specific text-to-text Transformer based models;
---
# How to use AraT5 models
Below is an example for fine-tuning **AraT5-base** for News Title Generation on the Aranews dataset
```python
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("UBC-NLP/AraT5-base-title-generation")
model = AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained("UBC-NLP/AraT5-base-title-generation")
Document = "تحت رعاية صاحب السمو الملكي الأمير سعود بن نايف بن عبدالعزيز أمير المنطقة الشرقية اختتمت غرفة الشرقية مؤخرا، الثاني من مبادرتها لتأهيل وتدريب أبناء وبنات المملكة ضمن مبادرتها المجانية للعام 2019 حيث قدمت 6 برامج تدريبية نوعية. وثمن رئيس مجلس إدارة الغرفة، عبدالحكيم العمار الخالدي، رعاية سمو أمير المنطقة الشرقية للمبادرة، مؤكدا أن دعم سموه لجميع أنشطة ."
encoding = tokenizer.encode_plus(Document,pad_to_max_length=True, return_tensors="pt")
input_ids, attention_masks = encoding["input_ids"], encoding["attention_mask"]
outputs = model.generate(
input_ids=input_ids, attention_mask=attention_masks,
max_length=256,
do_sample=True,
top_k=120,
top_p=0.95,
early_stopping=True,
num_return_sequences=5
)
for id, output in enumerate(outputs):
title = tokenizer.decode(output, skip_special_tokens=True,clean_up_tokenization_spaces=True)
print("title#"+str(id), title)
```
**The input news document**
<div style="white-space : pre-wrap !important;word-break: break-word; direction:rtl; text-align: right">
تحت رعاية صاحب السمو الملكي الأمير سعود بن نايف بن عبدالعزيز أمير المنطقة الشرقية اختتمت غرفة الشرقية مؤخرا، الثاني من مبادرتها لتأهيل وتدريب أبناء وبنات المملكة ضمن مبادرتها المجانية للعام 2019 حيث قدمت 6 برامج تدريبية نوعية. وثمن رئيس مجلس إدارة الغرفة، عبدالحكيم العمار الخالدي، رعاية سمو أمير المنطقة الشرقية للمبادرة، مؤكدا أن دعم سموه لجميع أنشطة .
<br>
</div>
**The generated titles**
```
title#0 غرفة الشرقية تختتم المرحلة الثانية من مبادرتها لتأهيل وتدريب أبناء وبنات المملكة
title#1 غرفة الشرقية تختتم الثاني من مبادرة تأهيل وتأهيل أبناء وبناتنا
title#2 سعود بن نايف يختتم ثانى مبادراتها لتأهيل وتدريب أبناء وبنات المملكة
title#3 أمير الشرقية يرعى اختتام برنامج برنامج تدريب أبناء وبنات المملكة
title#4 سعود بن نايف يرعى اختتام مبادرة تأهيل وتدريب أبناء وبنات المملكة
```
# AraT5 Models Checkpoints
AraT5 Pytorch and TensorFlow checkpoints are available on the Huggingface website for direct download and use ```exclusively for research```. ```For commercial use, please contact the authors via email @ (muhammad.mageed[at]ubc[dot]ca).```
| **Model** | **Link** |
|---------|:------------------:|
| **AraT5-base** | [https://huggingface.co/UBC-NLP/AraT5-base](https://huggingface.co/UBC-NLP/AraT5-base) |
| **AraT5-msa-base** | [https://huggingface.co/UBC-NLP/AraT5-msa-base](https://huggingface.co/UBC-NLP/AraT5-msa-base) |
| **AraT5-tweet-base** | [https://huggingface.co/UBC-NLP/AraT5-tweet-base](https://huggingface.co/UBC-NLP/AraT5-tweet-base) |
| **AraT5-msa-small** | [https://huggingface.co/UBC-NLP/AraT5-msa-small](https://huggingface.co/UBC-NLP/AraT5-msa-small) |
| **AraT5-tweet-small**| [https://huggingface.co/UBC-NLP/AraT5-tweet-small](https://huggingface.co/UBC-NLP/AraT5-tweet-small) |
# BibTex
If you use our models (Arat5-base, Arat5-msa-base, Arat5-tweet-base, Arat5-msa-small, or Arat5-tweet-small ) for your scientific publication, or if you find the resources in this repository useful, please cite our paper as follows (to be updated):
```bibtex
@inproceedings{nagoudi-etal-2022-arat5,
title = "{A}ra{T}5: Text-to-Text Transformers for {A}rabic Language Generation",
author = "Nagoudi, El Moatez Billah and
Elmadany, AbdelRahim and
Abdul-Mageed, Muhammad",
booktitle = "Proceedings of the 60th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers)",
month = may,
year = "2022",
address = "Dublin, Ireland",
publisher = "Association for Computational Linguistics",
url = "https://aclanthology.org/2022.acl-long.47",
pages = "628--647",
abstract = "Transfer learning with a unified Transformer framework (T5) that converts all language problems into a text-to-text format was recently proposed as a simple and effective transfer learning approach. Although a multilingual version of the T5 model (mT5) was also introduced, it is not clear how well it can fare on non-English tasks involving diverse data. To investigate this question, we apply mT5 on a language with a wide variety of dialects{--}Arabic. For evaluation, we introduce a novel benchmark for ARabic language GENeration (ARGEN), covering seven important tasks. For model comparison, we pre-train three powerful Arabic T5-style models and evaluate them on ARGEN. Although pre-trained with {\textasciitilde}49 less data, our new models perform significantly better than mT5 on all ARGEN tasks (in 52 out of 59 test sets) and set several new SOTAs. Our models also establish new SOTA on the recently-proposed, large Arabic language understanding evaluation benchmark ARLUE (Abdul-Mageed et al., 2021). Our new models are publicly available. We also link to ARGEN datasets through our repository: https://github.com/UBC-NLP/araT5.",
}
```
## Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge support from the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada, the Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council of Canada, Canadian Foundation for Innovation, [ComputeCanada](www.computecanada.ca) and [UBC ARC-Sockeye](https://doi.org/10.14288/SOCKEYE). We also thank the [Google TensorFlow Research Cloud (TFRC)](https://www.tensorflow.org/tfrc) program for providing us with free TPU access.
|
{"language": ["ar"], "tags": ["Arabic T5", "MSA", "Twitter", "Arabic Dialect", "Arabic Machine Translation", "Arabic Text Summarization", "Arabic News Title and Question Generation", "Arabic Paraphrasing and Transliteration", "Arabic Code-Switched Translation"]}
|
UBC-NLP/AraT5-base-title-generation
| null |
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"tf",
"t5",
"text2text-generation",
"Arabic T5",
"MSA",
"Twitter",
"Arabic Dialect",
"Arabic Machine Translation",
"Arabic Text Summarization",
"Arabic News Title and Question Generation",
"Arabic Paraphrasing and Transliteration",
"Arabic Code-Switched Translation",
"ar",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"has_space",
"text-generation-inference",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[
"ar"
] |
TAGS
#transformers #pytorch #tf #t5 #text2text-generation #Arabic T5 #MSA #Twitter #Arabic Dialect #Arabic Machine Translation #Arabic Text Summarization #Arabic News Title and Question Generation #Arabic Paraphrasing and Transliteration #Arabic Code-Switched Translation #ar #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #has_space #text-generation-inference #region-us
|
AraT5-base-title-generation
===========================
AraT5: Text-to-Text Transformers for Arabic Language Generation
===============================================================
<img src="URL alt="AraT5" width="45%" height="35%" align="right"/>
This is the repository accompanying our paper AraT5: Text-to-Text Transformers for Arabic Language Understanding and Generation. In this is the repository we Introduce AraT5MSA, AraT5Tweet, and AraT5: three powerful Arabic-specific text-to-text Transformer based models;
---
How to use AraT5 models
=======================
Below is an example for fine-tuning AraT5-base for News Title Generation on the Aranews dataset
The input news document
تحت رعاية صاحب السمو الملكي الأمير سعود بن نايف بن عبدالعزيز أمير المنطقة الشرقية اختتمت غرفة الشرقية مؤخرا، الثاني من مبادرتها لتأهيل وتدريب أبناء وبنات المملكة ضمن مبادرتها المجانية للعام 2019 حيث قدمت 6 برامج تدريبية نوعية. وثمن رئيس مجلس إدارة الغرفة، عبدالحكيم العمار الخالدي، رعاية سمو أمير المنطقة الشرقية للمبادرة، مؤكدا أن دعم سموه لجميع أنشطة .
The generated titles
AraT5 Models Checkpoints
========================
AraT5 Pytorch and TensorFlow checkpoints are available on the Huggingface website for direct download and use .
BibTex
======
If you use our models (Arat5-base, Arat5-msa-base, Arat5-tweet-base, Arat5-msa-small, or Arat5-tweet-small ) for your scientific publication, or if you find the resources in this repository useful, please cite our paper as follows (to be updated):
Acknowledgments
---------------
We gratefully acknowledge support from the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada, the Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council of Canada, Canadian Foundation for Innovation, ComputeCanada and UBC ARC-Sockeye. We also thank the Google TensorFlow Research Cloud (TFRC) program for providing us with free TPU access.
|
[] |
[
"TAGS\n#transformers #pytorch #tf #t5 #text2text-generation #Arabic T5 #MSA #Twitter #Arabic Dialect #Arabic Machine Translation #Arabic Text Summarization #Arabic News Title and Question Generation #Arabic Paraphrasing and Transliteration #Arabic Code-Switched Translation #ar #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #has_space #text-generation-inference #region-us \n"
] |
null |
transformers
|
# AraT5-base
# AraT5: Text-to-Text Transformers for Arabic Language Generation
<img src="https://huggingface.co/UBC-NLP/AraT5-base/resolve/main/AraT5_CR_new.png" alt="AraT5" width="45%" height="35%" align="right"/>
This is the repository accompanying our paper [AraT5: Text-to-Text Transformers for Arabic Language Understanding and Generation](https://aclanthology.org/2022.acl-long.47/). In this is the repository we Introduce **AraT5<sub>MSA</sub>**, **AraT5<sub>Tweet</sub>**, and **AraT5**: three powerful Arabic-specific text-to-text Transformer based models;
<span style="color:red"><b>A new version of AraT5 comes out and we recommend using the [AraT5v2-base-1024](https://huggingface.co/UBC-NLP/AraT5v2-base-1024) instead of this version.</b></span>
---
# How to use AraT5 models
Below is an example for fine-tuning **AraT5-base** for News Title Generation on the Aranews dataset
``` bash
!python run_trainier_seq2seq_huggingface.py \
--learning_rate 5e-5 \
--max_target_length 128 --max_source_length 128 \
--per_device_train_batch_size 8 --per_device_eval_batch_size 8 \
--model_name_or_path "UBC-NLP/AraT5-base" \
--output_dir "/content/AraT5_FT_title_generation" --overwrite_output_dir \
--num_train_epochs 3 \
--train_file "/content/ARGEn_title_genration_sample_train.tsv" \
--validation_file "/content/ARGEn_title_genration_sample_valid.tsv" \
--task "title_generation" --text_column "document" --summary_column "title" \
--load_best_model_at_end --metric_for_best_model "eval_bleu" --greater_is_better True --evaluation_strategy epoch --logging_strategy epoch --predict_with_generate\
--do_train --do_eval
```
For more details about the fine-tuning example, please read this notebook [](https://github.com/UBC-NLP/araT5/blob/main/examples/Fine_tuning_AraT5.ipynb)
In addition, we release the fine-tuned checkpoint of the News Title Generation (NGT) which is described in the paper. The model available at Huggingface ([UBC-NLP/AraT5-base-title-generation](https://huggingface.co/UBC-NLP/AraT5-base-title-generation)).
For more details, please visit our own [GitHub](https://github.com/UBC-NLP/araT5).
# AraT5 Models Checkpoints
AraT5 Pytorch and TensorFlow checkpoints are available on the Huggingface website for direct download and use ```exclusively for research```. ```For commercial use, please contact the authors via email @ (muhammad.mageed[at]ubc[dot]ca).```
| **Model** | **Link** |
|---------|:------------------:|
| **AraT5-base** | [https://huggingface.co/UBC-NLP/AraT5-base](https://huggingface.co/UBC-NLP/AraT5-base) |
| **AraT5-msa-base** | [https://huggingface.co/UBC-NLP/AraT5-msa-base](https://huggingface.co/UBC-NLP/AraT5-msa-base) |
| **AraT5-tweet-base** | [https://huggingface.co/UBC-NLP/AraT5-tweet-base](https://huggingface.co/UBC-NLP/AraT5-tweet-base) |
| **AraT5-msa-small** | [https://huggingface.co/UBC-NLP/AraT5-msa-small](https://huggingface.co/UBC-NLP/AraT5-msa-small) |
| **AraT5-tweet-small**| [https://huggingface.co/UBC-NLP/AraT5-tweet-small](https://huggingface.co/UBC-NLP/AraT5-tweet-small) |
# BibTex
If you use our models (Arat5-base, Arat5-msa-base, Arat5-tweet-base, Arat5-msa-small, or Arat5-tweet-small ) for your scientific publication, or if you find the resources in this repository useful, please cite our paper as follows (to be updated):
```bibtex
@inproceedings{nagoudi2022_arat5,
@inproceedings{nagoudi-etal-2022-arat5,
title = "{A}ra{T}5: Text-to-Text Transformers for {A}rabic Language Generation",
author = "Nagoudi, El Moatez Billah and
Elmadany, AbdelRahim and
Abdul-Mageed, Muhammad",
booktitle = "Proceedings of the 60th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers)",
month = may,
year = "2022",
address = "Dublin, Ireland",
publisher = "Association for Computational Linguistics",
url = "https://aclanthology.org/2022.acl-long.47",
pages = "628--647",
abstract = "Transfer learning with a unified Transformer framework (T5) that converts all language problems into a text-to-text format was recently proposed as a simple and effective transfer learning approach. Although a multilingual version of the T5 model (mT5) was also introduced, it is not clear how well it can fare on non-English tasks involving diverse data. To investigate this question, we apply mT5 on a language with a wide variety of dialects{--}Arabic. For evaluation, we introduce a novel benchmark for ARabic language GENeration (ARGEN), covering seven important tasks. For model comparison, we pre-train three powerful Arabic T5-style models and evaluate them on ARGEN. Although pre-trained with {\textasciitilde}49 less data, our new models perform significantly better than mT5 on all ARGEN tasks (in 52 out of 59 test sets) and set several new SOTAs. Our models also establish new SOTA on the recently-proposed, large Arabic language understanding evaluation benchmark ARLUE (Abdul-Mageed et al., 2021). Our new models are publicly available. We also link to ARGEN datasets through our repository: https://github.com/UBC-NLP/araT5.",
}
## Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge support from the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada, the Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council of Canada, Canadian Foundation for Innovation, [ComputeCanada](www.computecanada.ca) and [UBC ARC-Sockeye](https://doi.org/10.14288/SOCKEYE). We also thank the [Google TensorFlow Research Cloud (TFRC)](https://www.tensorflow.org/tfrc) program for providing us with free TPU access.
|
{"language": ["ar"], "tags": ["Arabic T5", "MSA", "Twitter", "Arabic Dialect", "Arabic Machine Translation", "Arabic Text Summarization", "Arabic News Title and Question Generation", "Arabic Paraphrasing and Transliteration", "Arabic Code-Switched Translation"]}
|
UBC-NLP/AraT5-base
| null |
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"tf",
"t5",
"Arabic T5",
"MSA",
"Twitter",
"Arabic Dialect",
"Arabic Machine Translation",
"Arabic Text Summarization",
"Arabic News Title and Question Generation",
"Arabic Paraphrasing and Transliteration",
"Arabic Code-Switched Translation",
"ar",
"endpoints_compatible",
"text-generation-inference",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[
"ar"
] |
TAGS
#transformers #pytorch #tf #t5 #Arabic T5 #MSA #Twitter #Arabic Dialect #Arabic Machine Translation #Arabic Text Summarization #Arabic News Title and Question Generation #Arabic Paraphrasing and Transliteration #Arabic Code-Switched Translation #ar #endpoints_compatible #text-generation-inference #region-us
|
AraT5-base
==========
AraT5: Text-to-Text Transformers for Arabic Language Generation
===============================================================
<img src="URL alt="AraT5" width="45%" height="35%" align="right"/>
This is the repository accompanying our paper AraT5: Text-to-Text Transformers for Arabic Language Understanding and Generation. In this is the repository we Introduce AraT5MSA, AraT5Tweet, and AraT5: three powerful Arabic-specific text-to-text Transformer based models;
**A new version of AraT5 comes out and we recommend using the AraT5v2-base-1024 instead of this version.**
---
How to use AraT5 models
=======================
Below is an example for fine-tuning AraT5-base for News Title Generation on the Aranews dataset
For more details about the fine-tuning example, please read this notebook  which is described in the paper. The model available at Huggingface (UBC-NLP/AraT5-base-title-generation).
For more details, please visit our own GitHub.
AraT5 Models Checkpoints
========================
AraT5 Pytorch and TensorFlow checkpoints are available on the Huggingface website for direct download and use .
BibTex
======
If you use our models (Arat5-base, Arat5-msa-base, Arat5-tweet-base, Arat5-msa-small, or Arat5-tweet-small ) for your scientific publication, or if you find the resources in this repository useful, please cite our paper as follows (to be updated):
'''bibtex
@inproceedings{nagoudi2022\_arat5,
@inproceedings{nagoudi-etal-2022-arat5,
title = "{A}ra{T}5: Text-to-Text Transformers for {A}rabic Language Generation",
author = "Nagoudi, El Moatez Billah and
Elmadany, AbdelRahim and
Abdul-Mageed, Muhammad",
booktitle = "Proceedings of the 60th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers)",
month = may,
year = "2022",
address = "Dublin, Ireland",
publisher = "Association for Computational Linguistics",
url = "URL
pages = "628--647",
abstract = "Transfer learning with a unified Transformer framework (T5) that converts all language problems into a text-to-text format was recently proposed as a simple and effective transfer learning approach. Although a multilingual version of the T5 model (mT5) was also introduced, it is not clear how well it can fare on non-English tasks involving diverse data. To investigate this question, we apply mT5 on a language with a wide variety of dialects{--}Arabic. For evaluation, we introduce a novel benchmark for ARabic language GENeration (ARGEN), covering seven important tasks. For model comparison, we pre-train three powerful Arabic T5-style models and evaluate them on ARGEN. Although pre-trained with {\textasciitilde}49 less data, our new models perform significantly better than mT5 on all ARGEN tasks (in 52 out of 59 test sets) and set several new SOTAs. Our models also establish new SOTA on the recently-proposed, large Arabic language understanding evaluation benchmark ARLUE (Abdul-Mageed et al., 2021). Our new models are publicly available. We also link to ARGEN datasets through our repository: URL
}
Acknowledgments
---------------
We gratefully acknowledge support from the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada, the Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council of Canada, Canadian Foundation for Innovation, ComputeCanada and UBC ARC-Sockeye. We also thank the Google TensorFlow Research Cloud (TFRC) program for providing us with free TPU access.
|
[] |
[
"TAGS\n#transformers #pytorch #tf #t5 #Arabic T5 #MSA #Twitter #Arabic Dialect #Arabic Machine Translation #Arabic Text Summarization #Arabic News Title and Question Generation #Arabic Paraphrasing and Transliteration #Arabic Code-Switched Translation #ar #endpoints_compatible #text-generation-inference #region-us \n"
] |
null |
transformers
|
# AraT5-msa-base
# AraT5: Text-to-Text Transformers for Arabic Language Generation
<img src="https://huggingface.co/UBC-NLP/AraT5-base/resolve/main/AraT5_CR_new.png" alt="AraT5" width="45%" height="35%" align="right"/>
This is the repository accompanying our paper [AraT5: Text-to-Text Transformers for Arabic Language Understanding and Generation](https://aclanthology.org/2022.acl-long.47/). In this is the repository we Introduce **AraT5<sub>MSA</sub>**, **AraT5<sub>Tweet</sub>**, and **AraT5**: three powerful Arabic-specific text-to-text Transformer based models;
<span style="color:red"><b>A new version of AraT5 comes out and we recommend using the [AraT5v2-base-1024](https://huggingface.co/UBC-NLP/AraT5v2-base-1024) instead of this version.</b></span>
---
# How to use AraT5 models
Below is an example for fine-tuning **AraT5-base** for News Title Generation on the Aranews dataset
``` bash
!python run_trainier_seq2seq_huggingface.py \
--learning_rate 5e-5 \
--max_target_length 128 --max_source_length 128 \
--per_device_train_batch_size 8 --per_device_eval_batch_size 8 \
--model_name_or_path "UBC-NLP/AraT5-base" \
--output_dir "/content/AraT5_FT_title_generation" --overwrite_output_dir \
--num_train_epochs 3 \
--train_file "/content/ARGEn_title_genration_sample_train.tsv" \
--validation_file "/content/ARGEn_title_genration_sample_valid.tsv" \
--task "title_generation" --text_column "document" --summary_column "title" \
--load_best_model_at_end --metric_for_best_model "eval_bleu" --greater_is_better True --evaluation_strategy epoch --logging_strategy epoch --predict_with_generate\
--do_train --do_eval
```
For more details about the fine-tuning example, please read this notebook [](https://github.com/UBC-NLP/araT5/blob/main/examples/Fine_tuning_AraT5.ipynb)
In addition, we release the fine-tuned checkpoint of the News Title Generation (NGT) which is described in the paper. The model available at Huggingface ([UBC-NLP/AraT5-base-title-generation](https://huggingface.co/UBC-NLP/AraT5-base-title-generation)).
For more details, please visit our own [GitHub](https://github.com/UBC-NLP/araT5).
# AraT5 Models Checkpoints
AraT5 Pytorch and TensorFlow checkpoints are available on the Huggingface website for direct download and use ```exclusively for research```. ```For commercial use, please contact the authors via email @ (muhammad.mageed[at]ubc[dot]ca).```
| **Model** | **Link** |
|---------|:------------------:|
| **AraT5-base** | [https://huggingface.co/UBC-NLP/AraT5-base](https://huggingface.co/UBC-NLP/AraT5-base) |
| **AraT5-msa-base** | [https://huggingface.co/UBC-NLP/AraT5-msa-base](https://huggingface.co/UBC-NLP/AraT5-msa-base) |
| **AraT5-tweet-base** | [https://huggingface.co/UBC-NLP/AraT5-tweet-base](https://huggingface.co/UBC-NLP/AraT5-tweet-base) |
| **AraT5-msa-small** | [https://huggingface.co/UBC-NLP/AraT5-msa-small](https://huggingface.co/UBC-NLP/AraT5-msa-small) |
| **AraT5-tweet-small**| [https://huggingface.co/UBC-NLP/AraT5-tweet-small](https://huggingface.co/UBC-NLP/AraT5-tweet-small) |
# BibTex
If you use our models (Arat5-base, Arat5-msa-base, Arat5-tweet-base, Arat5-msa-small, or Arat5-tweet-small ) for your scientific publication, or if you find the resources in this repository useful, please cite our paper as follows (to be updated):
```bibtex
@inproceedings{nagoudi-etal-2022-arat5,
title = "{A}ra{T}5: Text-to-Text Transformers for {A}rabic Language Generation",
author = "Nagoudi, El Moatez Billah and
Elmadany, AbdelRahim and
Abdul-Mageed, Muhammad",
booktitle = "Proceedings of the 60th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers)",
month = may,
year = "2022",
address = "Dublin, Ireland",
publisher = "Association for Computational Linguistics",
url = "https://aclanthology.org/2022.acl-long.47",
pages = "628--647",
abstract = "Transfer learning with a unified Transformer framework (T5) that converts all language problems into a text-to-text format was recently proposed as a simple and effective transfer learning approach. Although a multilingual version of the T5 model (mT5) was also introduced, it is not clear how well it can fare on non-English tasks involving diverse data. To investigate this question, we apply mT5 on a language with a wide variety of dialects{--}Arabic. For evaluation, we introduce a novel benchmark for ARabic language GENeration (ARGEN), covering seven important tasks. For model comparison, we pre-train three powerful Arabic T5-style models and evaluate them on ARGEN. Although pre-trained with {\textasciitilde}49 less data, our new models perform significantly better than mT5 on all ARGEN tasks (in 52 out of 59 test sets) and set several new SOTAs. Our models also establish new SOTA on the recently-proposed, large Arabic language understanding evaluation benchmark ARLUE (Abdul-Mageed et al., 2021). Our new models are publicly available. We also link to ARGEN datasets through our repository: https://github.com/UBC-NLP/araT5.",
}
```
## Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge support from the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada, the Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council of Canada, Canadian Foundation for Innovation, [ComputeCanada](www.computecanada.ca) and [UBC ARC-Sockeye](https://doi.org/10.14288/SOCKEYE). We also thank the [Google TensorFlow Research Cloud (TFRC)](https://www.tensorflow.org/tfrc) program for providing us with free TPU access.
|
{"language": ["ar"], "tags": ["Arabic T5", "MSA", "Twitter", "Arabic Dialect", "Arabic Machine Translation", "Arabic Text Summarization", "Arabic News Title and Question Generation", "Arabic Paraphrasing and Transliteration", "Arabic Code-Switched Translation"]}
|
UBC-NLP/AraT5-msa-base
| null |
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"tf",
"t5",
"Arabic T5",
"MSA",
"Twitter",
"Arabic Dialect",
"Arabic Machine Translation",
"Arabic Text Summarization",
"Arabic News Title and Question Generation",
"Arabic Paraphrasing and Transliteration",
"Arabic Code-Switched Translation",
"ar",
"endpoints_compatible",
"text-generation-inference",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[
"ar"
] |
TAGS
#transformers #pytorch #tf #t5 #Arabic T5 #MSA #Twitter #Arabic Dialect #Arabic Machine Translation #Arabic Text Summarization #Arabic News Title and Question Generation #Arabic Paraphrasing and Transliteration #Arabic Code-Switched Translation #ar #endpoints_compatible #text-generation-inference #region-us
|
AraT5-msa-base
==============
AraT5: Text-to-Text Transformers for Arabic Language Generation
===============================================================
<img src="URL alt="AraT5" width="45%" height="35%" align="right"/>
This is the repository accompanying our paper AraT5: Text-to-Text Transformers for Arabic Language Understanding and Generation. In this is the repository we Introduce AraT5MSA, AraT5Tweet, and AraT5: three powerful Arabic-specific text-to-text Transformer based models;
**A new version of AraT5 comes out and we recommend using the AraT5v2-base-1024 instead of this version.**
---
How to use AraT5 models
=======================
Below is an example for fine-tuning AraT5-base for News Title Generation on the Aranews dataset
For more details about the fine-tuning example, please read this notebook  which is described in the paper. The model available at Huggingface (UBC-NLP/AraT5-base-title-generation).
For more details, please visit our own GitHub.
AraT5 Models Checkpoints
========================
AraT5 Pytorch and TensorFlow checkpoints are available on the Huggingface website for direct download and use .
BibTex
======
If you use our models (Arat5-base, Arat5-msa-base, Arat5-tweet-base, Arat5-msa-small, or Arat5-tweet-small ) for your scientific publication, or if you find the resources in this repository useful, please cite our paper as follows (to be updated):
Acknowledgments
---------------
We gratefully acknowledge support from the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada, the Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council of Canada, Canadian Foundation for Innovation, ComputeCanada and UBC ARC-Sockeye. We also thank the Google TensorFlow Research Cloud (TFRC) program for providing us with free TPU access.
|
[] |
[
"TAGS\n#transformers #pytorch #tf #t5 #Arabic T5 #MSA #Twitter #Arabic Dialect #Arabic Machine Translation #Arabic Text Summarization #Arabic News Title and Question Generation #Arabic Paraphrasing and Transliteration #Arabic Code-Switched Translation #ar #endpoints_compatible #text-generation-inference #region-us \n"
] |
null |
transformers
|
# AraT5-msa-small
# AraT5: Text-to-Text Transformers for Arabic Language Generation
<img src="https://huggingface.co/UBC-NLP/AraT5-base/resolve/main/AraT5_CR_new.png" alt="AraT5" width="45%" height="35%" align="right"/>
This is the repository accompanying our paper [AraT5: Text-to-Text Transformers for Arabic Language Understanding and Generation](https://aclanthology.org/2022.acl-long.47/). In this is the repository we Introduce **AraT5<sub>MSA</sub>**, **AraT5<sub>Tweet</sub>**, and **AraT5**: three powerful Arabic-specific text-to-text Transformer based models;
<span style="color:red"><b>A new version of AraT5 comes out and we recommend using the [AraT5v2-base-1024](https://huggingface.co/UBC-NLP/AraT5v2-base-1024) instead of this version.</b></span>
---
# How to use AraT5 models
Below is an example for fine-tuning **AraT5-base** for News Title Generation on the Aranews dataset
``` bash
!python run_trainier_seq2seq_huggingface.py \
--learning_rate 5e-5 \
--max_target_length 128 --max_source_length 128 \
--per_device_train_batch_size 8 --per_device_eval_batch_size 8 \
--model_name_or_path "UBC-NLP/AraT5-base" \
--output_dir "/content/AraT5_FT_title_generation" --overwrite_output_dir \
--num_train_epochs 3 \
--train_file "/content/ARGEn_title_genration_sample_train.tsv" \
--validation_file "/content/ARGEn_title_genration_sample_valid.tsv" \
--task "title_generation" --text_column "document" --summary_column "title" \
--load_best_model_at_end --metric_for_best_model "eval_bleu" --greater_is_better True --evaluation_strategy epoch --logging_strategy epoch --predict_with_generate\
--do_train --do_eval
```
For more details about the fine-tuning example, please read this notebook [](https://github.com/UBC-NLP/araT5/blob/main/examples/Fine_tuning_AraT5.ipynb)
In addition, we release the fine-tuned checkpoint of the News Title Generation (NGT) which is described in the paper. The model available at Huggingface ([UBC-NLP/AraT5-base-title-generation](https://huggingface.co/UBC-NLP/AraT5-base-title-generation)).
For more details, please visit our own [GitHub](https://github.com/UBC-NLP/araT5).
# AraT5 Models Checkpoints
AraT5 Pytorch and TensorFlow checkpoints are available on the Huggingface website for direct download and use ```exclusively for research```. ```For commercial use, please contact the authors via email @ (muhammad.mageed[at]ubc[dot]ca).```
| **Model** | **Link** |
|---------|:------------------:|
| **AraT5-base** | [https://huggingface.co/UBC-NLP/AraT5-base](https://huggingface.co/UBC-NLP/AraT5-base) |
| **AraT5-msa-base** | [https://huggingface.co/UBC-NLP/AraT5-msa-base](https://huggingface.co/UBC-NLP/AraT5-msa-base) |
| **AraT5-tweet-base** | [https://huggingface.co/UBC-NLP/AraT5-tweet-base](https://huggingface.co/UBC-NLP/AraT5-tweet-base) |
| **AraT5-msa-small** | [https://huggingface.co/UBC-NLP/AraT5-msa-small](https://huggingface.co/UBC-NLP/AraT5-msa-small) |
| **AraT5-tweet-small**| [https://huggingface.co/UBC-NLP/AraT5-tweet-small](https://huggingface.co/UBC-NLP/AraT5-tweet-small) |
# BibTex
If you use our models (Arat5-base, Arat5-msa-base, Arat5-tweet-base, Arat5-msa-small, or Arat5-tweet-small ) for your scientific publication, or if you find the resources in this repository useful, please cite our paper as follows (to be updated):
```bibtex
@inproceedings{nagoudi-etal-2022-arat5,
title = "{A}ra{T}5: Text-to-Text Transformers for {A}rabic Language Generation",
author = "Nagoudi, El Moatez Billah and
Elmadany, AbdelRahim and
Abdul-Mageed, Muhammad",
booktitle = "Proceedings of the 60th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers)",
month = may,
year = "2022",
address = "Dublin, Ireland",
publisher = "Association for Computational Linguistics",
url = "https://aclanthology.org/2022.acl-long.47",
pages = "628--647",
abstract = "Transfer learning with a unified Transformer framework (T5) that converts all language problems into a text-to-text format was recently proposed as a simple and effective transfer learning approach. Although a multilingual version of the T5 model (mT5) was also introduced, it is not clear how well it can fare on non-English tasks involving diverse data. To investigate this question, we apply mT5 on a language with a wide variety of dialects{--}Arabic. For evaluation, we introduce a novel benchmark for ARabic language GENeration (ARGEN), covering seven important tasks. For model comparison, we pre-train three powerful Arabic T5-style models and evaluate them on ARGEN. Although pre-trained with {\textasciitilde}49 less data, our new models perform significantly better than mT5 on all ARGEN tasks (in 52 out of 59 test sets) and set several new SOTAs. Our models also establish new SOTA on the recently-proposed, large Arabic language understanding evaluation benchmark ARLUE (Abdul-Mageed et al., 2021). Our new models are publicly available. We also link to ARGEN datasets through our repository: https://github.com/UBC-NLP/araT5.",
}
```
## Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge support from the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada, the Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council of Canada, Canadian Foundation for Innovation, [ComputeCanada](www.computecanada.ca) and [UBC ARC-Sockeye](https://doi.org/10.14288/SOCKEYE). We also thank the [Google TensorFlow Research Cloud (TFRC)](https://www.tensorflow.org/tfrc) program for providing us with free TPU access.
|
{"language": ["ar"], "tags": ["Arabic T5", "MSA", "Twitter", "Arabic Dialect", "Arabic Machine Translation", "Arabic Text Summarization", "Arabic News Title and Question Generation", "Arabic Paraphrasing and Transliteration", "Arabic Code-Switched Translation"]}
|
UBC-NLP/AraT5-msa-small
| null |
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"tf",
"t5",
"Arabic T5",
"MSA",
"Twitter",
"Arabic Dialect",
"Arabic Machine Translation",
"Arabic Text Summarization",
"Arabic News Title and Question Generation",
"Arabic Paraphrasing and Transliteration",
"Arabic Code-Switched Translation",
"ar",
"endpoints_compatible",
"text-generation-inference",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[
"ar"
] |
TAGS
#transformers #pytorch #tf #t5 #Arabic T5 #MSA #Twitter #Arabic Dialect #Arabic Machine Translation #Arabic Text Summarization #Arabic News Title and Question Generation #Arabic Paraphrasing and Transliteration #Arabic Code-Switched Translation #ar #endpoints_compatible #text-generation-inference #region-us
|
AraT5-msa-small
===============
AraT5: Text-to-Text Transformers for Arabic Language Generation
===============================================================
<img src="URL alt="AraT5" width="45%" height="35%" align="right"/>
This is the repository accompanying our paper AraT5: Text-to-Text Transformers for Arabic Language Understanding and Generation. In this is the repository we Introduce AraT5MSA, AraT5Tweet, and AraT5: three powerful Arabic-specific text-to-text Transformer based models;
**A new version of AraT5 comes out and we recommend using the AraT5v2-base-1024 instead of this version.**
---
How to use AraT5 models
=======================
Below is an example for fine-tuning AraT5-base for News Title Generation on the Aranews dataset
For more details about the fine-tuning example, please read this notebook  which is described in the paper. The model available at Huggingface (UBC-NLP/AraT5-base-title-generation).
For more details, please visit our own GitHub.
AraT5 Models Checkpoints
========================
AraT5 Pytorch and TensorFlow checkpoints are available on the Huggingface website for direct download and use .
BibTex
======
If you use our models (Arat5-base, Arat5-msa-base, Arat5-tweet-base, Arat5-msa-small, or Arat5-tweet-small ) for your scientific publication, or if you find the resources in this repository useful, please cite our paper as follows (to be updated):
Acknowledgments
---------------
We gratefully acknowledge support from the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada, the Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council of Canada, Canadian Foundation for Innovation, ComputeCanada and UBC ARC-Sockeye. We also thank the Google TensorFlow Research Cloud (TFRC) program for providing us with free TPU access.
|
[] |
[
"TAGS\n#transformers #pytorch #tf #t5 #Arabic T5 #MSA #Twitter #Arabic Dialect #Arabic Machine Translation #Arabic Text Summarization #Arabic News Title and Question Generation #Arabic Paraphrasing and Transliteration #Arabic Code-Switched Translation #ar #endpoints_compatible #text-generation-inference #region-us \n"
] |
null |
transformers
|
# AraT5-base
# AraT5: Text-to-Text Transformers for Arabic Language Generation
<img src="https://huggingface.co/UBC-NLP/AraT5-base/resolve/main/AraT5_CR_new.png" alt="AraT5" width="45%" height="35%" align="right"/>
This is the repository accompanying our paper [AraT5: Text-to-Text Transformers for Arabic Language Understanding and Generation](https://aclanthology.org/2022.acl-long.47/). In this is the repository we Introduce **AraT5<sub>MSA</sub>**, **AraT5<sub>Tweet</sub>**, and **AraT5**: three powerful Arabic-specific text-to-text Transformer based models;
<span style="color:red"><b>A new version of AraT5 comes out and we recommend using the [AraT5v2-base-1024](https://huggingface.co/UBC-NLP/AraT5v2-base-1024) instead of this version.</b></span>
---
# How to use AraT5 models
Below is an example for fine-tuning **AraT5-base** for News Title Generation on the Aranews dataset
``` bash
!python run_trainier_seq2seq_huggingface.py \
--learning_rate 5e-5 \
--max_target_length 128 --max_source_length 128 \
--per_device_train_batch_size 8 --per_device_eval_batch_size 8 \
--model_name_or_path "UBC-NLP/AraT5-base" \
--output_dir "/content/AraT5_FT_title_generation" --overwrite_output_dir \
--num_train_epochs 3 \
--train_file "/content/ARGEn_title_genration_sample_train.tsv" \
--validation_file "/content/ARGEn_title_genration_sample_valid.tsv" \
--task "title_generation" --text_column "document" --summary_column "title" \
--load_best_model_at_end --metric_for_best_model "eval_bleu" --greater_is_better True --evaluation_strategy epoch --logging_strategy epoch --predict_with_generate\
--do_train --do_eval
```
For more details about the fine-tuning example, please read this notebook [](https://github.com/UBC-NLP/araT5/blob/main/examples/Fine_tuning_AraT5.ipynb)
In addition, we release the fine-tuned checkpoint of the News Title Generation (NGT) which is described in the paper. The model available at Huggingface ([UBC-NLP/AraT5-base-title-generation](https://huggingface.co/UBC-NLP/AraT5-base-title-generation)).
For more details, please visit our own [GitHub](https://github.com/UBC-NLP/araT5).
# AraT5 Models Checkpoints
AraT5 Pytorch and TensorFlow checkpoints are available on the Huggingface website for direct download and use ```exclusively for research```. ```For commercial use, please contact the authors via email @ (muhammad.mageed[at]ubc[dot]ca).```
| **Model** | **Link** |
|---------|:------------------:|
| **AraT5-base** | [https://huggingface.co/UBC-NLP/AraT5-base](https://huggingface.co/UBC-NLP/AraT5-base) |
| **AraT5-msa-base** | [https://huggingface.co/UBC-NLP/AraT5-msa-base](https://huggingface.co/UBC-NLP/AraT5-msa-base) |
| **AraT5-tweet-base** | [https://huggingface.co/UBC-NLP/AraT5-tweet-base](https://huggingface.co/UBC-NLP/AraT5-tweet-base) |
| **AraT5-msa-small** | [https://huggingface.co/UBC-NLP/AraT5-msa-small](https://huggingface.co/UBC-NLP/AraT5-msa-small) |
| **AraT5-tweet-small**| [https://huggingface.co/UBC-NLP/AraT5-tweet-small](https://huggingface.co/UBC-NLP/AraT5-tweet-small) |
# BibTex
If you use our models (Arat5-base, Arat5-msa-base, Arat5-tweet-base, Arat5-msa-small, or Arat5-tweet-small ) for your scientific publication, or if you find the resources in this repository useful, please cite our paper as follows (to be updated):
```bibtex
@inproceedings{nagoudi-etal-2022-arat5,
title = "{A}ra{T}5: Text-to-Text Transformers for {A}rabic Language Generation",
author = "Nagoudi, El Moatez Billah and
Elmadany, AbdelRahim and
Abdul-Mageed, Muhammad",
booktitle = "Proceedings of the 60th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers)",
month = may,
year = "2022",
address = "Dublin, Ireland",
publisher = "Association for Computational Linguistics",
url = "https://aclanthology.org/2022.acl-long.47",
pages = "628--647",
abstract = "Transfer learning with a unified Transformer framework (T5) that converts all language problems into a text-to-text format was recently proposed as a simple and effective transfer learning approach. Although a multilingual version of the T5 model (mT5) was also introduced, it is not clear how well it can fare on non-English tasks involving diverse data. To investigate this question, we apply mT5 on a language with a wide variety of dialects{--}Arabic. For evaluation, we introduce a novel benchmark for ARabic language GENeration (ARGEN), covering seven important tasks. For model comparison, we pre-train three powerful Arabic T5-style models and evaluate them on ARGEN. Although pre-trained with {\textasciitilde}49 less data, our new models perform significantly better than mT5 on all ARGEN tasks (in 52 out of 59 test sets) and set several new SOTAs. Our models also establish new SOTA on the recently-proposed, large Arabic language understanding evaluation benchmark ARLUE (Abdul-Mageed et al., 2021). Our new models are publicly available. We also link to ARGEN datasets through our repository: https://github.com/UBC-NLP/araT5.",
}
```
## Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge support from the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada, the Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council of Canada, Canadian Foundation for Innovation, [ComputeCanada](www.computecanada.ca) and [UBC ARC-Sockeye](https://doi.org/10.14288/SOCKEYE). We also thank the [Google TensorFlow Research Cloud (TFRC)](https://www.tensorflow.org/tfrc) program for providing us with free TPU access.
|
{"language": ["ar"], "tags": ["Arabic T5", "MSA", "Twitter", "Arabic Dialect", "Arabic Machine Translation", "Arabic Text Summarization", "Arabic News Title and Question Generation", "Arabic Paraphrasing and Transliteration", "Arabic Code-Switched Translation"]}
|
UBC-NLP/AraT5-tweet-base
| null |
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"tf",
"t5",
"Arabic T5",
"MSA",
"Twitter",
"Arabic Dialect",
"Arabic Machine Translation",
"Arabic Text Summarization",
"Arabic News Title and Question Generation",
"Arabic Paraphrasing and Transliteration",
"Arabic Code-Switched Translation",
"ar",
"endpoints_compatible",
"text-generation-inference",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[
"ar"
] |
TAGS
#transformers #pytorch #tf #t5 #Arabic T5 #MSA #Twitter #Arabic Dialect #Arabic Machine Translation #Arabic Text Summarization #Arabic News Title and Question Generation #Arabic Paraphrasing and Transliteration #Arabic Code-Switched Translation #ar #endpoints_compatible #text-generation-inference #region-us
|
AraT5-base
==========
AraT5: Text-to-Text Transformers for Arabic Language Generation
===============================================================
<img src="URL alt="AraT5" width="45%" height="35%" align="right"/>
This is the repository accompanying our paper AraT5: Text-to-Text Transformers for Arabic Language Understanding and Generation. In this is the repository we Introduce AraT5MSA, AraT5Tweet, and AraT5: three powerful Arabic-specific text-to-text Transformer based models;
**A new version of AraT5 comes out and we recommend using the AraT5v2-base-1024 instead of this version.**
---
How to use AraT5 models
=======================
Below is an example for fine-tuning AraT5-base for News Title Generation on the Aranews dataset
For more details about the fine-tuning example, please read this notebook  which is described in the paper. The model available at Huggingface (UBC-NLP/AraT5-base-title-generation).
For more details, please visit our own GitHub.
AraT5 Models Checkpoints
========================
AraT5 Pytorch and TensorFlow checkpoints are available on the Huggingface website for direct download and use .
BibTex
======
If you use our models (Arat5-base, Arat5-msa-base, Arat5-tweet-base, Arat5-msa-small, or Arat5-tweet-small ) for your scientific publication, or if you find the resources in this repository useful, please cite our paper as follows (to be updated):
Acknowledgments
---------------
We gratefully acknowledge support from the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada, the Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council of Canada, Canadian Foundation for Innovation, ComputeCanada and UBC ARC-Sockeye. We also thank the Google TensorFlow Research Cloud (TFRC) program for providing us with free TPU access.
|
[] |
[
"TAGS\n#transformers #pytorch #tf #t5 #Arabic T5 #MSA #Twitter #Arabic Dialect #Arabic Machine Translation #Arabic Text Summarization #Arabic News Title and Question Generation #Arabic Paraphrasing and Transliteration #Arabic Code-Switched Translation #ar #endpoints_compatible #text-generation-inference #region-us \n"
] |
null |
transformers
|
# AraT5-tweet-small
# AraT5: Text-to-Text Transformers for Arabic Language Generation
<img src="https://huggingface.co/UBC-NLP/AraT5-base/resolve/main/AraT5_CR_new.png" alt="AraT5" width="45%" height="35%" align="right"/>
This is the repository accompanying our paper [AraT5: Text-to-Text Transformers for Arabic Language Understanding and Generation](https://aclanthology.org/2022.acl-long.47/). In this is the repository we Introduce **AraT5<sub>MSA</sub>**, **AraT5<sub>Tweet</sub>**, and **AraT5**: three powerful Arabic-specific text-to-text Transformer based models;
<span style="color:red"><b>A new version of AraT5 comes out and we recommend using the [AraT5v2-base-1024](https://huggingface.co/UBC-NLP/AraT5v2-base-1024) instead of this version.</b></span>
---
# How to use AraT5 models
Below is an example for fine-tuning **AraT5-base** for News Title Generation on the Aranews dataset
``` bash
!python run_trainier_seq2seq_huggingface.py \
--learning_rate 5e-5 \
--max_target_length 128 --max_source_length 128 \
--per_device_train_batch_size 8 --per_device_eval_batch_size 8 \
--model_name_or_path "UBC-NLP/AraT5-base" \
--output_dir "/content/AraT5_FT_title_generation" --overwrite_output_dir \
--num_train_epochs 3 \
--train_file "/content/ARGEn_title_genration_sample_train.tsv" \
--validation_file "/content/ARGEn_title_genration_sample_valid.tsv" \
--task "title_generation" --text_column "document" --summary_column "title" \
--load_best_model_at_end --metric_for_best_model "eval_bleu" --greater_is_better True --evaluation_strategy epoch --logging_strategy epoch --predict_with_generate\
--do_train --do_eval
```
For more details about the fine-tuning example, please read this notebook [](https://github.com/UBC-NLP/araT5/blob/main/examples/Fine_tuning_AraT5.ipynb)
In addition, we release the fine-tuned checkpoint of the News Title Generation (NGT) which is described in the paper. The model available at Huggingface ([UBC-NLP/AraT5-base-title-generation](https://huggingface.co/UBC-NLP/AraT5-base-title-generation)).
For more details, please visit our own [GitHub](https://github.com/UBC-NLP/araT5).
# AraT5 Models Checkpoints
AraT5 Pytorch and TensorFlow checkpoints are available on the Huggingface website for direct download and use ```exclusively for research```. ```For commercial use, please contact the authors via email @ (muhammad.mageed[at]ubc[dot]ca).```
| **Model** | **Link** |
|---------|:------------------:|
| **AraT5-base** | [https://huggingface.co/UBC-NLP/AraT5-base](https://huggingface.co/UBC-NLP/AraT5-base) |
| **AraT5-msa-base** | [https://huggingface.co/UBC-NLP/AraT5-msa-base](https://huggingface.co/UBC-NLP/AraT5-msa-base) |
| **AraT5-tweet-base** | [https://huggingface.co/UBC-NLP/AraT5-tweet-base](https://huggingface.co/UBC-NLP/AraT5-tweet-base) |
| **AraT5-msa-small** | [https://huggingface.co/UBC-NLP/AraT5-msa-small](https://huggingface.co/UBC-NLP/AraT5-msa-small) |
| **AraT5-tweet-small**| [https://huggingface.co/UBC-NLP/AraT5-tweet-small](https://huggingface.co/UBC-NLP/AraT5-tweet-small) |
# BibTex
If you use our models (Arat5-base, Arat5-msa-base, Arat5-tweet-base, Arat5-msa-small, or Arat5-tweet-small ) for your scientific publication, or if you find the resources in this repository useful, please cite our paper as follows (to be updated):
```bibtex
@inproceedings{nagoudi-etal-2022-arat5,
title = "{A}ra{T}5: Text-to-Text Transformers for {A}rabic Language Generation",
author = "Nagoudi, El Moatez Billah and
Elmadany, AbdelRahim and
Abdul-Mageed, Muhammad",
booktitle = "Proceedings of the 60th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers)",
month = may,
year = "2022",
address = "Dublin, Ireland",
publisher = "Association for Computational Linguistics",
url = "https://aclanthology.org/2022.acl-long.47",
pages = "628--647",
abstract = "Transfer learning with a unified Transformer framework (T5) that converts all language problems into a text-to-text format was recently proposed as a simple and effective transfer learning approach. Although a multilingual version of the T5 model (mT5) was also introduced, it is not clear how well it can fare on non-English tasks involving diverse data. To investigate this question, we apply mT5 on a language with a wide variety of dialects{--}Arabic. For evaluation, we introduce a novel benchmark for ARabic language GENeration (ARGEN), covering seven important tasks. For model comparison, we pre-train three powerful Arabic T5-style models and evaluate them on ARGEN. Although pre-trained with {\textasciitilde}49 less data, our new models perform significantly better than mT5 on all ARGEN tasks (in 52 out of 59 test sets) and set several new SOTAs. Our models also establish new SOTA on the recently-proposed, large Arabic language understanding evaluation benchmark ARLUE (Abdul-Mageed et al., 2021). Our new models are publicly available. We also link to ARGEN datasets through our repository: https://github.com/UBC-NLP/araT5.",
}
```
## Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge support from the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada, the Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council of Canada, Canadian Foundation for Innovation, [ComputeCanada](www.computecanada.ca) and [UBC ARC-Sockeye](https://doi.org/10.14288/SOCKEYE). We also thank the [Google TensorFlow Research Cloud (TFRC)](https://www.tensorflow.org/tfrc) program for providing us with free TPU access.
|
{"language": ["ar"], "tags": ["Arabic T5", "MSA", "Twitter", "Arabic Dialect", "Arabic Machine Translation", "Arabic Text Summarization", "Arabic News Title and Question Generation", "Arabic Paraphrasing and Transliteration", "Arabic Code-Switched Translation"]}
|
UBC-NLP/AraT5-tweet-small
| null |
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"tf",
"t5",
"Arabic T5",
"MSA",
"Twitter",
"Arabic Dialect",
"Arabic Machine Translation",
"Arabic Text Summarization",
"Arabic News Title and Question Generation",
"Arabic Paraphrasing and Transliteration",
"Arabic Code-Switched Translation",
"ar",
"endpoints_compatible",
"text-generation-inference",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[
"ar"
] |
TAGS
#transformers #pytorch #tf #t5 #Arabic T5 #MSA #Twitter #Arabic Dialect #Arabic Machine Translation #Arabic Text Summarization #Arabic News Title and Question Generation #Arabic Paraphrasing and Transliteration #Arabic Code-Switched Translation #ar #endpoints_compatible #text-generation-inference #region-us
|
AraT5-tweet-small
=================
AraT5: Text-to-Text Transformers for Arabic Language Generation
===============================================================
<img src="URL alt="AraT5" width="45%" height="35%" align="right"/>
This is the repository accompanying our paper AraT5: Text-to-Text Transformers for Arabic Language Understanding and Generation. In this is the repository we Introduce AraT5MSA, AraT5Tweet, and AraT5: three powerful Arabic-specific text-to-text Transformer based models;
**A new version of AraT5 comes out and we recommend using the AraT5v2-base-1024 instead of this version.**
---
How to use AraT5 models
=======================
Below is an example for fine-tuning AraT5-base for News Title Generation on the Aranews dataset
For more details about the fine-tuning example, please read this notebook  which is described in the paper. The model available at Huggingface (UBC-NLP/AraT5-base-title-generation).
For more details, please visit our own GitHub.
AraT5 Models Checkpoints
========================
AraT5 Pytorch and TensorFlow checkpoints are available on the Huggingface website for direct download and use .
BibTex
======
If you use our models (Arat5-base, Arat5-msa-base, Arat5-tweet-base, Arat5-msa-small, or Arat5-tweet-small ) for your scientific publication, or if you find the resources in this repository useful, please cite our paper as follows (to be updated):
Acknowledgments
---------------
We gratefully acknowledge support from the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada, the Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council of Canada, Canadian Foundation for Innovation, ComputeCanada and UBC ARC-Sockeye. We also thank the Google TensorFlow Research Cloud (TFRC) program for providing us with free TPU access.
|
[] |
[
"TAGS\n#transformers #pytorch #tf #t5 #Arabic T5 #MSA #Twitter #Arabic Dialect #Arabic Machine Translation #Arabic Text Summarization #Arabic News Title and Question Generation #Arabic Paraphrasing and Transliteration #Arabic Code-Switched Translation #ar #endpoints_compatible #text-generation-inference #region-us \n"
] |
null |
transformers
|
# IndT5: A Text-to-Text Transformer for 10 Indigenous Languages
<img src="https://huggingface.co/UBC-NLP/IndT5/raw/main/IND_langs_large7.png" alt="drawing" width="45%" height="45%" align="right"/>
In this work, we introduce IndT5, the first Transformer language model for Indigenous languages. To train IndT5, we build IndCorpu, a new corpus for 10 Indigenous languages and Spanish.
# IndT5
We train an Indigenous language model adopting the unified and flexible
text-to-text transfer Transformer (T5) approach. T5 treats every
text-based language task as a “text-to-text" problem, taking text format
as input and producing new text format as output. T5 is essentially an
encoder-decoder Transformer, with the encoder and decoder similar in
configuration and size to a BERT<sub>Base</sub> but with some
architectural modifications. Modifications include applying a
normalization layer before a sub-block and adding a pre-norm (i.e.,
initial input to the sub-block output).
# IndCourpus
We build IndCorpus, a collection of 10 Indigeous languages and Spanish comprising 1.17GB of text, from both Wikipedia and the Bible.
### Data size and number of sentences in monolingual dataset (collected from Wikipedia and Bible)
| **Target Language** | **Wiki Size (MB)** | **Wiki #Sentences** | **Bible Size (MB)** | **Bible #Sentences**|
|-------------------|------------------|-------------------|------------------------|-|
|Hñähñu | - | - | 1.4 | 7.5K |
|Wixarika | - | - | 1.3 | 7.5K|
|Nahuatl | 5.8 | 61.1K | 1.5 | 7.5K|
|Guarani | 3.7 | 28.2K | 1.3 | 7.5K |
|Bribri | - | - | 1.5 | 7.5K |
|Rarámuri | - | - | 1.9 | 7.5K |
|Quechua | 5.9 | 97.3K | 4.9 | 31.1K |
|Aymara | 1.7 | 32.9K | 5 | 30.7K|
|Shipibo-Konibo | - | - | 1 | 7.9K |
|Asháninka | - | - | 1.4 | 7.8K |
|Spanish | 1.13K | 5M | - | - |
|Total | 1.15K | 5.22M | 19.8 | 125.3K|
# Github
More details about our model can be found here: https://github.com/UBC-NLP/IndT5
# BibTex
```bibtex
@inproceedings{nagoudi-etal-2021-indt5,
title = "{I}nd{T}5: A Text-to-Text Transformer for 10 Indigenous Languages",
author = "Nagoudi, El Moatez Billah and Chen, Wei-Rui and Abdul-Mageed, Muhammad and Cavusoglu, Hasan",
booktitle = "Proceedings of the First Workshop on Natural Language Processing for Indigenous Languages of the Americas",
month = jun,
year = "2021",
address = "Online",
publisher = "Association for Computational Linguistics",
url = "https://aclanthology.org/2021.americasnlp-1.30",
doi = "10.18653/v1/2021.americasnlp-1.30",
pages = "265--271"
}
```
|
{}
|
UBC-NLP/IndT5
| null |
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"t5",
"endpoints_compatible",
"text-generation-inference",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[] |
TAGS
#transformers #pytorch #t5 #endpoints_compatible #text-generation-inference #region-us
|
IndT5: A Text-to-Text Transformer for 10 Indigenous Languages
=============================================================
<img src="URL alt="drawing" width="45%" height="45%" align="right"/>
In this work, we introduce IndT5, the first Transformer language model for Indigenous languages. To train IndT5, we build IndCorpu, a new corpus for 10 Indigenous languages and Spanish.
IndT5
=====
We train an Indigenous language model adopting the unified and flexible
text-to-text transfer Transformer (T5) approach. T5 treats every
text-based language task as a “text-to-text" problem, taking text format
as input and producing new text format as output. T5 is essentially an
encoder-decoder Transformer, with the encoder and decoder similar in
configuration and size to a BERTBase but with some
architectural modifications. Modifications include applying a
normalization layer before a sub-block and adding a pre-norm (i.e.,
initial input to the sub-block output).
IndCourpus
==========
We build IndCorpus, a collection of 10 Indigeous languages and Spanish comprising 1.17GB of text, from both Wikipedia and the Bible.
### Data size and number of sentences in monolingual dataset (collected from Wikipedia and Bible)
Github
======
More details about our model can be found here: URL
BibTex
======
|
[
"### Data size and number of sentences in monolingual dataset (collected from Wikipedia and Bible)\n\n\n\nGithub\n======\n\n\nMore details about our model can be found here: URL\n\n\nBibTex\n======"
] |
[
"TAGS\n#transformers #pytorch #t5 #endpoints_compatible #text-generation-inference #region-us \n",
"### Data size and number of sentences in monolingual dataset (collected from Wikipedia and Bible)\n\n\n\nGithub\n======\n\n\nMore details about our model can be found here: URL\n\n\nBibTex\n======"
] |
fill-mask
|
transformers
|
<img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/UBC-NLP/marbert/main/ARBERT_MARBERT.jpg" alt="drawing" width="200" height="200" align="right"/>
**MARBERT** is one of three models described in our **ACL 2021 paper** **["ARBERT & MARBERT: Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Arabic"](https://aclanthology.org/2021.acl-long.551.pdf)**. MARBERT is a large-scale pre-trained masked language model focused on both Dialectal Arabic (DA) and MSA. Arabic has multiple varieties. To train MARBERT, we randomly sample 1B Arabic tweets from a large in-house dataset of about 6B tweets. We only include tweets with at least 3 Arabic words, based on character string matching, regardless whether the tweet has non-Arabic string or not. That is, we do not remove non-Arabic so long as the tweet meets the 3 Arabic word criterion. The dataset makes up **128GB of text** (**15.6B tokens**). We use the same network architecture as ARBERT (BERT-base), but without the next sentence prediction (NSP) objective since tweets are short. See our [repo](https://github.com/UBC-NLP/LMBERT) for modifying BERT code to remove NSP. For more information about MARBERT, please visit our own GitHub [repo](https://github.com/UBC-NLP/marbert).
# BibTex
If you use our models (ARBERT, MARBERT, or MARBERTv2) for your scientific publication, or if you find the resources in this repository useful, please cite our paper as follows (to be updated):
```bibtex
@inproceedings{abdul-mageed-etal-2021-arbert,
title = "{ARBERT} {\&} {MARBERT}: Deep Bidirectional Transformers for {A}rabic",
author = "Abdul-Mageed, Muhammad and
Elmadany, AbdelRahim and
Nagoudi, El Moatez Billah",
booktitle = "Proceedings of the 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 11th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (Volume 1: Long Papers)",
month = aug,
year = "2021",
address = "Online",
publisher = "Association for Computational Linguistics",
url = "https://aclanthology.org/2021.acl-long.551",
doi = "10.18653/v1/2021.acl-long.551",
pages = "7088--7105",
abstract = "Pre-trained language models (LMs) are currently integral to many natural language processing systems. Although multilingual LMs were also introduced to serve many languages, these have limitations such as being costly at inference time and the size and diversity of non-English data involved in their pre-training. We remedy these issues for a collection of diverse Arabic varieties by introducing two powerful deep bidirectional transformer-based models, ARBERT and MARBERT. To evaluate our models, we also introduce ARLUE, a new benchmark for multi-dialectal Arabic language understanding evaluation. ARLUE is built using 42 datasets targeting six different task clusters, allowing us to offer a series of standardized experiments under rich conditions. When fine-tuned on ARLUE, our models collectively achieve new state-of-the-art results across the majority of tasks (37 out of 48 classification tasks, on the 42 datasets). Our best model acquires the highest ARLUE score (77.40) across all six task clusters, outperforming all other models including XLM-R Large ( 3.4x larger size). Our models are publicly available at https://github.com/UBC-NLP/marbert and ARLUE will be released through the same repository.",
}
```
## Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge support from the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada, the Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council of Canada, Canadian Foundation for Innovation, [ComputeCanada](www.computecanada.ca) and [UBC ARC-Sockeye](https://doi.org/10.14288/SOCKEYE). We also thank the [Google TensorFlow Research Cloud (TFRC)](https://www.tensorflow.org/tfrc) program for providing us with free TPU access.
|
{"language": ["ar"], "tags": ["Arabic BERT", "MSA", "Twitter", "Masked Langauge Model"], "widget": [{"text": "\u0627\u0644\u0644\u063a\u0629 \u0627\u0644\u0639\u0631\u0628\u064a\u0629 \u0647\u064a \u0644\u063a\u0629 [MASK]."}]}
|
UBC-NLP/MARBERT
| null |
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"tf",
"jax",
"bert",
"fill-mask",
"Arabic BERT",
"MSA",
"Twitter",
"Masked Langauge Model",
"ar",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"has_space",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[
"ar"
] |
TAGS
#transformers #pytorch #tf #jax #bert #fill-mask #Arabic BERT #MSA #Twitter #Masked Langauge Model #ar #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #has_space #region-us
|
<img src="URL alt="drawing" width="200" height="200" align="right"/>
MARBERT is one of three models described in our ACL 2021 paper "ARBERT & MARBERT: Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Arabic". MARBERT is a large-scale pre-trained masked language model focused on both Dialectal Arabic (DA) and MSA. Arabic has multiple varieties. To train MARBERT, we randomly sample 1B Arabic tweets from a large in-house dataset of about 6B tweets. We only include tweets with at least 3 Arabic words, based on character string matching, regardless whether the tweet has non-Arabic string or not. That is, we do not remove non-Arabic so long as the tweet meets the 3 Arabic word criterion. The dataset makes up 128GB of text (15.6B tokens). We use the same network architecture as ARBERT (BERT-base), but without the next sentence prediction (NSP) objective since tweets are short. See our repo for modifying BERT code to remove NSP. For more information about MARBERT, please visit our own GitHub repo.
# BibTex
If you use our models (ARBERT, MARBERT, or MARBERTv2) for your scientific publication, or if you find the resources in this repository useful, please cite our paper as follows (to be updated):
## Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge support from the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada, the Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council of Canada, Canadian Foundation for Innovation, ComputeCanada and UBC ARC-Sockeye. We also thank the Google TensorFlow Research Cloud (TFRC) program for providing us with free TPU access.
|
[
"# BibTex\n\nIf you use our models (ARBERT, MARBERT, or MARBERTv2) for your scientific publication, or if you find the resources in this repository useful, please cite our paper as follows (to be updated):",
"## Acknowledgments\nWe gratefully acknowledge support from the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada, the Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council of Canada, Canadian Foundation for Innovation, ComputeCanada and UBC ARC-Sockeye. We also thank the Google TensorFlow Research Cloud (TFRC) program for providing us with free TPU access."
] |
[
"TAGS\n#transformers #pytorch #tf #jax #bert #fill-mask #Arabic BERT #MSA #Twitter #Masked Langauge Model #ar #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #has_space #region-us \n",
"# BibTex\n\nIf you use our models (ARBERT, MARBERT, or MARBERTv2) for your scientific publication, or if you find the resources in this repository useful, please cite our paper as follows (to be updated):",
"## Acknowledgments\nWe gratefully acknowledge support from the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada, the Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council of Canada, Canadian Foundation for Innovation, ComputeCanada and UBC ARC-Sockeye. We also thank the Google TensorFlow Research Cloud (TFRC) program for providing us with free TPU access."
] |
fill-mask
|
transformers
|
<img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/UBC-NLP/marbert/main/ARBERT_MARBERT.jpg" alt="drawing" width="30%" height="30%" align="right"/>
**MARBERTv2** is one of three models described in our **ACL 2021 paper** **["ARBERT & MARBERT: Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Arabic"](https://aclanthology.org/2021.acl-long.551.pdf)**.
We find that results with ARBERT and MARBERT on QA are not competitive, a clear discrepancy from what we have observed thus far on other tasksWe hypothesize this is because the two models are pre-trained with a sequence length of only 128, which does not allow them to sufficiently capture both a question and its likely answer within the same sequence window during the pre-training.
To rectify this, we further pre-train the stronger model, MARBERT, on the same MSA data as ARBERT in addition to AraNews dataset but with a bigger sequence length of 512 tokens for 40 epochs. We call this
further pre-trained model **MARBERTv2**, noting it has **29B tokens**. MARBERTv2 acquires best performance on all but one test set, where XLM-RLarge marginally outperforms us (only in F1).
For more information, please visit our own GitHub [repo](https://github.com/UBC-NLP/marbert).
# BibTex
If you use our models (ARBERT, MARBERT, or MARBERTv2) for your scientific publication, or if you find the resources in this repository useful, please cite our paper as follows (to be updated):
```bibtex
@inproceedings{abdul-mageed-etal-2021-arbert,
title = "{ARBERT} {\&} {MARBERT}: Deep Bidirectional Transformers for {A}rabic",
author = "Abdul-Mageed, Muhammad and
Elmadany, AbdelRahim and
Nagoudi, El Moatez Billah",
booktitle = "Proceedings of the 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 11th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (Volume 1: Long Papers)",
month = aug,
year = "2021",
address = "Online",
publisher = "Association for Computational Linguistics",
url = "https://aclanthology.org/2021.acl-long.551",
doi = "10.18653/v1/2021.acl-long.551",
pages = "7088--7105",
abstract = "Pre-trained language models (LMs) are currently integral to many natural language processing systems. Although multilingual LMs were also introduced to serve many languages, these have limitations such as being costly at inference time and the size and diversity of non-English data involved in their pre-training. We remedy these issues for a collection of diverse Arabic varieties by introducing two powerful deep bidirectional transformer-based models, ARBERT and MARBERT. To evaluate our models, we also introduce ARLUE, a new benchmark for multi-dialectal Arabic language understanding evaluation. ARLUE is built using 42 datasets targeting six different task clusters, allowing us to offer a series of standardized experiments under rich conditions. When fine-tuned on ARLUE, our models collectively achieve new state-of-the-art results across the majority of tasks (37 out of 48 classification tasks, on the 42 datasets). Our best model acquires the highest ARLUE score (77.40) across all six task clusters, outperforming all other models including XLM-R Large ( 3.4x larger size). Our models are publicly available at https://github.com/UBC-NLP/marbert and ARLUE will be released through the same repository.",
}
```
## Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge support from the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada, the Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council of Canada, Canadian Foundation for Innovation, [ComputeCanada](www.computecanada.ca) and [UBC ARC-Sockeye](https://doi.org/10.14288/SOCKEYE). We also thank the [Google TensorFlow Research Cloud (TFRC)](https://www.tensorflow.org/tfrc) program for providing us with free TPU access.
|
{"language": ["ar"], "tags": ["Arabic BERT", "MSA", "Twitter", "Masked Langauge Model"], "widget": [{"text": "\u0627\u0644\u0644\u063a\u0629 \u0627\u0644\u0639\u0631\u0628\u064a\u0629 \u0647\u064a \u0644\u063a\u0629 [MASK]."}]}
|
UBC-NLP/MARBERTv2
| null |
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"tf",
"bert",
"fill-mask",
"Arabic BERT",
"MSA",
"Twitter",
"Masked Langauge Model",
"ar",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[
"ar"
] |
TAGS
#transformers #pytorch #tf #bert #fill-mask #Arabic BERT #MSA #Twitter #Masked Langauge Model #ar #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #region-us
|
<img src="URL alt="drawing" width="30%" height="30%" align="right"/>
MARBERTv2 is one of three models described in our ACL 2021 paper "ARBERT & MARBERT: Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Arabic".
We find that results with ARBERT and MARBERT on QA are not competitive, a clear discrepancy from what we have observed thus far on other tasksWe hypothesize this is because the two models are pre-trained with a sequence length of only 128, which does not allow them to sufficiently capture both a question and its likely answer within the same sequence window during the pre-training.
To rectify this, we further pre-train the stronger model, MARBERT, on the same MSA data as ARBERT in addition to AraNews dataset but with a bigger sequence length of 512 tokens for 40 epochs. We call this
further pre-trained model MARBERTv2, noting it has 29B tokens. MARBERTv2 acquires best performance on all but one test set, where XLM-RLarge marginally outperforms us (only in F1).
For more information, please visit our own GitHub repo.
# BibTex
If you use our models (ARBERT, MARBERT, or MARBERTv2) for your scientific publication, or if you find the resources in this repository useful, please cite our paper as follows (to be updated):
## Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge support from the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada, the Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council of Canada, Canadian Foundation for Innovation, ComputeCanada and UBC ARC-Sockeye. We also thank the Google TensorFlow Research Cloud (TFRC) program for providing us with free TPU access.
|
[
"# BibTex\r\n\r\nIf you use our models (ARBERT, MARBERT, or MARBERTv2) for your scientific publication, or if you find the resources in this repository useful, please cite our paper as follows (to be updated):",
"## Acknowledgments\r\nWe gratefully acknowledge support from the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada, the Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council of Canada, Canadian Foundation for Innovation, ComputeCanada and UBC ARC-Sockeye. We also thank the Google TensorFlow Research Cloud (TFRC) program for providing us with free TPU access."
] |
[
"TAGS\n#transformers #pytorch #tf #bert #fill-mask #Arabic BERT #MSA #Twitter #Masked Langauge Model #ar #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #region-us \n",
"# BibTex\r\n\r\nIf you use our models (ARBERT, MARBERT, or MARBERTv2) for your scientific publication, or if you find the resources in this repository useful, please cite our paper as follows (to be updated):",
"## Acknowledgments\r\nWe gratefully acknowledge support from the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada, the Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council of Canada, Canadian Foundation for Innovation, ComputeCanada and UBC ARC-Sockeye. We also thank the Google TensorFlow Research Cloud (TFRC) program for providing us with free TPU access."
] |
token-classification
|
spacy
|
| Feature | Description |
| --- | --- |
| **Name** | `en_scibert_ScienceIE` |
| **Version** | `0.0.0` |
| **spaCy** | `>=3.1.1,<3.2.0` |
| **Default Pipeline** | `transformer`, `ner` |
| **Components** | `transformer`, `ner` |
| **Vectors** | 0 keys, 0 unique vectors (0 dimensions) |
| **Sources** | n/a |
| **License** | n/a |
| **Author** | UBIAI (https://ubiai.tools) |
### Label Scheme
<details>
<summary>View label scheme (3 labels for 1 components)</summary>
| Component | Labels |
| --- | --- |
| **`ner`** | `MATERIAL`, `PROCESS`, `TASK` |
</details>
### Accuracy
| Type | Score |
| --- | --- |
| `ENTS_F` | 99.07 |
| `ENTS_P` | 98.91 |
| `ENTS_R` | 99.24 |
| `TRANSFORMER_LOSS` | 370249.46 |
| `NER_LOSS` | 216581.66 |
|
{"language": ["en"], "tags": ["spacy", "token-classification"]}
|
UBIAI/en_scibert_ScienceIE
| null |
[
"spacy",
"token-classification",
"en",
"model-index",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[
"en"
] |
TAGS
#spacy #token-classification #en #model-index #region-us
|
### Label Scheme
View label scheme (3 labels for 1 components)
### Accuracy
|
[
"### Label Scheme\n\n\n\nView label scheme (3 labels for 1 components)",
"### Accuracy"
] |
[
"TAGS\n#spacy #token-classification #en #model-index #region-us \n",
"### Label Scheme\n\n\n\nView label scheme (3 labels for 1 components)",
"### Accuracy"
] |
text-generation
|
transformers
|
# Harry Potter DialoGPT Model
|
{"tags": ["conversational"]}
|
UKJ5/DialoGPT-small-harrypotter
| null |
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"gpt2",
"text-generation",
"conversational",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"text-generation-inference",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[] |
TAGS
#transformers #pytorch #gpt2 #text-generation #conversational #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #text-generation-inference #region-us
|
# Harry Potter DialoGPT Model
|
[
"# Harry Potter DialoGPT Model"
] |
[
"TAGS\n#transformers #pytorch #gpt2 #text-generation #conversational #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #text-generation-inference #region-us \n",
"# Harry Potter DialoGPT Model"
] |
null |
transformers
|
# CZERT
This repository keeps Czert-A model for the paper [Czert – Czech BERT-like Model for Language Representation
](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.13031)
For more information, see the paper
## Available Models
You can download **MLM & NSP only** pretrained models
~~[CZERT-A-v1](https://air.kiv.zcu.cz/public/CZERT-A-czert-albert-base-uncased.zip)
[CZERT-B-v1](https://air.kiv.zcu.cz/public/CZERT-B-czert-bert-base-cased.zip)~~
After some additional experiments, we found out that the tokenizers config was exported wrongly. In Czert-B-v1, the tokenizer parameter "do_lower_case" was wrongly set to true. In Czert-A-v1 the parameter "strip_accents" was incorrectly set to true.
Both mistakes are repaired in v2.
[CZERT-A-v2](https://air.kiv.zcu.cz/public/CZERT-A-v2-czert-albert-base-uncased.zip)
[CZERT-B-v2](https://air.kiv.zcu.cz/public/CZERT-B-v2-czert-bert-base-cased.zip)
or choose from one of **Finetuned Models**
| | Models |
| - | - |
| Sentiment Classification<br> (Facebook or CSFD) | [CZERT-A-sentiment-FB](https://air.kiv.zcu.cz/public/CZERT-A_fb.zip) <br> [CZERT-B-sentiment-FB](https://air.kiv.zcu.cz/public/CZERT-B_fb.zip) <br> [CZERT-A-sentiment-CSFD](https://air.kiv.zcu.cz/public/CZERT-A_csfd.zip) <br> [CZERT-B-sentiment-CSFD](https://air.kiv.zcu.cz/public/CZERT-B_csfd.zip) | Semantic Text Similarity <br> (Czech News Agency) | [CZERT-A-sts-CNA](https://air.kiv.zcu.cz/public/CZERT-A-sts-CNA.zip) <br> [CZERT-B-sts-CNA](https://air.kiv.zcu.cz/public/CZERT-B-sts-CNA.zip)
| Named Entity Recognition | [CZERT-A-ner-CNEC](https://air.kiv.zcu.cz/public/CZERT-A-ner-CNEC-cased.zip) <br> [CZERT-B-ner-CNEC](https://air.kiv.zcu.cz/public/CZERT-B-ner-CNEC-cased.zip) <br>[PAV-ner-CNEC](https://air.kiv.zcu.cz/public/PAV-ner-CNEC-cased.zip) <br> [CZERT-A-ner-BSNLP](https://air.kiv.zcu.cz/public/CZERT-A-ner-BSNLP-cased.zip)<br>[CZERT-B-ner-BSNLP](https://air.kiv.zcu.cz/public/CZERT-B-ner-BSNLP-cased.zip) <br>[PAV-ner-BSNLP](https://air.kiv.zcu.cz/public/PAV-ner-BSNLP-cased.zip) |
| Morphological Tagging<br> | [CZERT-A-morphtag-126k](https://air.kiv.zcu.cz/public/CZERT-A-morphtag-126k-cased.zip)<br>[CZERT-B-morphtag-126k](https://air.kiv.zcu.cz/public/CZERT-B-morphtag-126k-cased.zip) |
| Semantic Role Labelling |[CZERT-A-srl](https://air.kiv.zcu.cz/public/CZERT-A-srl-cased.zip)<br> [CZERT-B-srl](https://air.kiv.zcu.cz/public/CZERT-B-srl-cased.zip) |
## How to Use CZERT?
### Sentence Level Tasks
We evaluate our model on two sentence level tasks:
* Sentiment Classification,
* Semantic Text Similarity.
<!-- tokenizer = BertTokenizerFast.from_pretrained(CZERT_MODEL_PATH, strip_accents=False)
\tmodel = TFAlbertForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained(CZERT_MODEL_PATH, num_labels=1)
or
self.tokenizer = BertTokenizerFast.from_pretrained(CZERT_MODEL_PATH, strip_accents=False)
self.model_encoder = AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained(CZERT_MODEL_PATH, from_tf=True)
-->
\t
### Document Level Tasks
We evaluate our model on one document level task
* Multi-label Document Classification.
### Token Level Tasks
We evaluate our model on three token level tasks:
* Named Entity Recognition,
* Morphological Tagging,
* Semantic Role Labelling.
## Downstream Tasks Fine-tuning Results
### Sentiment Classification
| | mBERT | SlavicBERT | ALBERT-r | Czert-A | Czert-B |
|:----:|:------------------------:|:------------------------:|:------------------------:|:-----------------------:|:--------------------------------:|
| FB | 71.72 ± 0.91 | 73.87 ± 0.50 | 59.50 ± 0.47 | 72.47 ± 0.72 | **76.55** ± **0.14** |
| CSFD | 82.80 ± 0.14 | 82.51 ± 0.14 | 75.40 ± 0.18 | 79.58 ± 0.46 | **84.79** ± **0.26** |
Average F1 results for the Sentiment Classification task. For more information, see [the paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.13031).
### Semantic Text Similarity
| | **mBERT** | **Pavlov** | **Albert-random** | **Czert-A** | **Czert-B** |
|:-------------|:--------------:|:--------------:|:-----------------:|:--------------:|:----------------------:|
| STA-CNA | 83.335 ± 0.063 | 83.593 ± 0.050 | 43.184 ± 0.125 | 82.942 ± 0.106 | **84.345** ± **0.028** |
| STS-SVOB-img | 79.367 ± 0.486 | 79.900 ± 0.810 | 15.739 ± 2.992 | 79.444 ± 0.338 | **83.744** ± **0.395** |
| STS-SVOB-hl | 78.833 ± 0.296 | 76.996 ± 0.305 | 33.949 ± 1.807 | 75.089 ± 0.806 | **79.827 ± 0.469** |
Comparison of Pearson correlation achieved using pre-trained CZERT-A, CZERT-B, mBERT, Pavlov and randomly initialised Albert on semantic text similarity. For more information see [the paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.13031).
### Multi-label Document Classification
| | mBERT | SlavicBERT | ALBERT-r | Czert-A | Czert-B |
|:-----:|:------------:|:------------:|:------------:|:------------:|:-------------------:|
| AUROC | 97.62 ± 0.08 | 97.80 ± 0.06 | 94.35 ± 0.13 | 97.49 ± 0.07 | **98.00** ± **0.04** |
| F1 | 83.04 ± 0.16 | 84.08 ± 0.14 | 72.44 ± 0.22 | 82.27 ± 0.17 | **85.06** ± **0.11** |
Comparison of F1 and AUROC score achieved using pre-trained CZERT-A, CZERT-B, mBERT, Pavlov and randomly initialised Albert on multi-label document classification. For more information see [the paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.13031).
### Morphological Tagging
| | mBERT | Pavlov | Albert-random | Czert-A | Czert-B |
|:-----------------------|:---------------|:---------------|:---------------|:---------------|:---------------|
| Universal Dependencies | 99.176 ± 0.006 | 99.211 ± 0.008 | 96.590 ± 0.096 | 98.713 ± 0.008 | **99.300 ± 0.009** |
Comparison of F1 score achieved using pre-trained CZERT-A, CZERT-B, mBERT, Pavlov and randomly initialised Albert on morphological tagging task. For more information see [the paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.13031).
### Semantic Role Labelling
<div id="tab:SRL">
| | mBERT | Pavlov | Albert-random | Czert-A | Czert-B | dep-based | gold-dep |
|:------:|:----------:|:----------:|:-------------:|:----------:|:----------:|:---------:|:--------:|
| span | 78.547 ± 0.110 | 79.333 ± 0.080 | 51.365 ± 0.423 | 72.254 ± 0.172 | **81.861 ± 0.102** | \\- | \\- |
| syntax | 90.226 ± 0.224 | 90.492 ± 0.040 | 80.747 ± 0.131 | 80.319 ± 0.054 | **91.462 ± 0.062** | 85.19 | 89.52 |
SRL results – dep columns are evaluate with labelled F1 from CoNLL 2009 evaluation script, other columns are evaluated with span F1 score same as it was used for NER evaluation. For more information see [the paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.13031).
</div>
### Named Entity Recognition
| | mBERT | Pavlov | Albert-random | Czert-A | Czert-B |
|:-----------|:---------------|:---------------|:---------------|:---------------|:---------------|
| CNEC | **86.225 ± 0.208** | **86.565 ± 0.198** | 34.635 ± 0.343 | 72.945 ± 0.227 | 86.274 ± 0.116 |
| BSNLP 2019 | 84.006 ± 1.248 | **86.699 ± 0.370** | 19.773 ± 0.938 | 48.859 ± 0.605 | **86.729 ± 0.344** |
Comparison of f1 score achieved using pre-trained CZERT-A, CZERT-B, mBERT, Pavlov and randomly initialised Albert on named entity recognition task. For more information see [the paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.13031).
## Licence
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License. http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/
## How should I cite CZERT?
For now, please cite [the Arxiv paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.13031):
```
@article{sido2021czert,
title={Czert -- Czech BERT-like Model for Language Representation},
author={Jakub Sido and Ondřej Pražák and Pavel Přibáň and Jan Pašek and Michal Seják and Miloslav Konopík},
year={2021},
eprint={2103.13031},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CL},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2103.13031},
}
```
|
{"tags": ["cs"]}
|
UWB-AIR/Czert-A-base-uncased
| null |
[
"transformers",
"tf",
"albert",
"cs",
"arxiv:2103.13031",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[
"2103.13031"
] |
[] |
TAGS
#transformers #tf #albert #cs #arxiv-2103.13031 #endpoints_compatible #region-us
|
CZERT
=====
This repository keeps Czert-A model for the paper Czert – Czech BERT-like Model for Language Representation
For more information, see the paper
Available Models
----------------
You can download MLM & NSP only pretrained models
~~CZERT-A-v1
CZERT-B-v1~~
After some additional experiments, we found out that the tokenizers config was exported wrongly. In Czert-B-v1, the tokenizer parameter "do\_lower\_case" was wrongly set to true. In Czert-A-v1 the parameter "strip\_accents" was incorrectly set to true.
Both mistakes are repaired in v2.
CZERT-A-v2
CZERT-B-v2
or choose from one of Finetuned Models
How to Use CZERT?
-----------------
### Sentence Level Tasks
We evaluate our model on two sentence level tasks:
* Sentiment Classification,
* Semantic Text Similarity.
\t
### Document Level Tasks
We evaluate our model on one document level task
* Multi-label Document Classification.
### Token Level Tasks
We evaluate our model on three token level tasks:
* Named Entity Recognition,
* Morphological Tagging,
* Semantic Role Labelling.
Downstream Tasks Fine-tuning Results
------------------------------------
### Sentiment Classification
Average F1 results for the Sentiment Classification task. For more information, see the paper.
### Semantic Text Similarity
Comparison of Pearson correlation achieved using pre-trained CZERT-A, CZERT-B, mBERT, Pavlov and randomly initialised Albert on semantic text similarity. For more information see the paper.
### Multi-label Document Classification
Comparison of F1 and AUROC score achieved using pre-trained CZERT-A, CZERT-B, mBERT, Pavlov and randomly initialised Albert on multi-label document classification. For more information see the paper.
### Morphological Tagging
Comparison of F1 score achieved using pre-trained CZERT-A, CZERT-B, mBERT, Pavlov and randomly initialised Albert on morphological tagging task. For more information see the paper.
### Semantic Role Labelling
SRL results – dep columns are evaluate with labelled F1 from CoNLL 2009 evaluation script, other columns are evaluated with span F1 score same as it was used for NER evaluation. For more information see the paper.
### Named Entity Recognition
Comparison of f1 score achieved using pre-trained CZERT-A, CZERT-B, mBERT, Pavlov and randomly initialised Albert on named entity recognition task. For more information see the paper.
Licence
-------
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License. URL
How should I cite CZERT?
------------------------
For now, please cite the Arxiv paper:
|
[
"### Sentence Level Tasks\n\n\nWe evaluate our model on two sentence level tasks:\n\n\n* Sentiment Classification,\n* Semantic Text Similarity.\n\n\n\\t",
"### Document Level Tasks\n\n\nWe evaluate our model on one document level task\n\n\n* Multi-label Document Classification.",
"### Token Level Tasks\n\n\nWe evaluate our model on three token level tasks:\n\n\n* Named Entity Recognition,\n* Morphological Tagging,\n* Semantic Role Labelling.\n\n\nDownstream Tasks Fine-tuning Results\n------------------------------------",
"### Sentiment Classification\n\n\n\nAverage F1 results for the Sentiment Classification task. For more information, see the paper.",
"### Semantic Text Similarity\n\n\n\nComparison of Pearson correlation achieved using pre-trained CZERT-A, CZERT-B, mBERT, Pavlov and randomly initialised Albert on semantic text similarity. For more information see the paper.",
"### Multi-label Document Classification\n\n\n\nComparison of F1 and AUROC score achieved using pre-trained CZERT-A, CZERT-B, mBERT, Pavlov and randomly initialised Albert on multi-label document classification. For more information see the paper.",
"### Morphological Tagging\n\n\n\nComparison of F1 score achieved using pre-trained CZERT-A, CZERT-B, mBERT, Pavlov and randomly initialised Albert on morphological tagging task. For more information see the paper.",
"### Semantic Role Labelling\n\n\n\n\nSRL results – dep columns are evaluate with labelled F1 from CoNLL 2009 evaluation script, other columns are evaluated with span F1 score same as it was used for NER evaluation. For more information see the paper.",
"### Named Entity Recognition\n\n\n\nComparison of f1 score achieved using pre-trained CZERT-A, CZERT-B, mBERT, Pavlov and randomly initialised Albert on named entity recognition task. For more information see the paper.\n\n\nLicence\n-------\n\n\nThis work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License. URL\n\n\nHow should I cite CZERT?\n------------------------\n\n\nFor now, please cite the Arxiv paper:"
] |
[
"TAGS\n#transformers #tf #albert #cs #arxiv-2103.13031 #endpoints_compatible #region-us \n",
"### Sentence Level Tasks\n\n\nWe evaluate our model on two sentence level tasks:\n\n\n* Sentiment Classification,\n* Semantic Text Similarity.\n\n\n\\t",
"### Document Level Tasks\n\n\nWe evaluate our model on one document level task\n\n\n* Multi-label Document Classification.",
"### Token Level Tasks\n\n\nWe evaluate our model on three token level tasks:\n\n\n* Named Entity Recognition,\n* Morphological Tagging,\n* Semantic Role Labelling.\n\n\nDownstream Tasks Fine-tuning Results\n------------------------------------",
"### Sentiment Classification\n\n\n\nAverage F1 results for the Sentiment Classification task. For more information, see the paper.",
"### Semantic Text Similarity\n\n\n\nComparison of Pearson correlation achieved using pre-trained CZERT-A, CZERT-B, mBERT, Pavlov and randomly initialised Albert on semantic text similarity. For more information see the paper.",
"### Multi-label Document Classification\n\n\n\nComparison of F1 and AUROC score achieved using pre-trained CZERT-A, CZERT-B, mBERT, Pavlov and randomly initialised Albert on multi-label document classification. For more information see the paper.",
"### Morphological Tagging\n\n\n\nComparison of F1 score achieved using pre-trained CZERT-A, CZERT-B, mBERT, Pavlov and randomly initialised Albert on morphological tagging task. For more information see the paper.",
"### Semantic Role Labelling\n\n\n\n\nSRL results – dep columns are evaluate with labelled F1 from CoNLL 2009 evaluation script, other columns are evaluated with span F1 score same as it was used for NER evaluation. For more information see the paper.",
"### Named Entity Recognition\n\n\n\nComparison of f1 score achieved using pre-trained CZERT-A, CZERT-B, mBERT, Pavlov and randomly initialised Albert on named entity recognition task. For more information see the paper.\n\n\nLicence\n-------\n\n\nThis work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License. URL\n\n\nHow should I cite CZERT?\n------------------------\n\n\nFor now, please cite the Arxiv paper:"
] |
fill-mask
|
transformers
|
# CZERT
This repository keeps trained Czert-B-base-cased-long-zero-shot model for the paper [Czert – Czech BERT-like Model for Language Representation
](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.13031)
For more information, see the paper
This is long version of Czert-B-base-cased created without any finetunning on long documents. Positional embedings were created by simply repeating the positional embeddings of the original Czert-B model. For tokenization, please use BertTokenizer. Cannot be used with AutoTokenizer.
## Available Models
You can download **MLM & NSP only** pretrained models
~~[CZERT-A-v1](https://air.kiv.zcu.cz/public/CZERT-A-czert-albert-base-uncased.zip)
[CZERT-B-v1](https://air.kiv.zcu.cz/public/CZERT-B-czert-bert-base-cased.zip)~~
After some additional experiments, we found out that the tokenizers config was exported wrongly. In Czert-B-v1, the tokenizer parameter "do_lower_case" was wrongly set to true. In Czert-A-v1 the parameter "strip_accents" was incorrectly set to true.
Both mistakes are repaired in v2.
[CZERT-A-v2](https://air.kiv.zcu.cz/public/CZERT-A-v2-czert-albert-base-uncased.zip)
[CZERT-B-v2](https://air.kiv.zcu.cz/public/CZERT-B-v2-czert-bert-base-cased.zip)
or choose from one of **Finetuned Models**
| | Models |
| - | - |
| Sentiment Classification<br> (Facebook or CSFD) | [CZERT-A-sentiment-FB](https://air.kiv.zcu.cz/public/CZERT-A_fb.zip) <br> [CZERT-B-sentiment-FB](https://air.kiv.zcu.cz/public/CZERT-B_fb.zip) <br> [CZERT-A-sentiment-CSFD](https://air.kiv.zcu.cz/public/CZERT-A_csfd.zip) <br> [CZERT-B-sentiment-CSFD](https://air.kiv.zcu.cz/public/CZERT-B_csfd.zip) | Semantic Text Similarity <br> (Czech News Agency) | [CZERT-A-sts-CNA](https://air.kiv.zcu.cz/public/CZERT-A-sts-CNA.zip) <br> [CZERT-B-sts-CNA](https://air.kiv.zcu.cz/public/CZERT-B-sts-CNA.zip)
| Named Entity Recognition | [CZERT-A-ner-CNEC](https://air.kiv.zcu.cz/public/CZERT-A-ner-CNEC-cased.zip) <br> [CZERT-B-ner-CNEC](https://air.kiv.zcu.cz/public/CZERT-B-ner-CNEC-cased.zip) <br>[PAV-ner-CNEC](https://air.kiv.zcu.cz/public/PAV-ner-CNEC-cased.zip) <br> [CZERT-A-ner-BSNLP](https://air.kiv.zcu.cz/public/CZERT-A-ner-BSNLP-cased.zip)<br>[CZERT-B-ner-BSNLP](https://air.kiv.zcu.cz/public/CZERT-B-ner-BSNLP-cased.zip) <br>[PAV-ner-BSNLP](https://air.kiv.zcu.cz/public/PAV-ner-BSNLP-cased.zip) |
| Morphological Tagging<br> | [CZERT-A-morphtag-126k](https://air.kiv.zcu.cz/public/CZERT-A-morphtag-126k-cased.zip)<br>[CZERT-B-morphtag-126k](https://air.kiv.zcu.cz/public/CZERT-B-morphtag-126k-cased.zip) |
| Semantic Role Labelling |[CZERT-A-srl](https://air.kiv.zcu.cz/public/CZERT-A-srl-cased.zip)<br> [CZERT-B-srl](https://air.kiv.zcu.cz/public/CZERT-B-srl-cased.zip) |
## How to Use CZERT?
### Sentence Level Tasks
We evaluate our model on two sentence level tasks:
* Sentiment Classification,
* Semantic Text Similarity.
<!-- tokenizer = BertTokenizerFast.from_pretrained(CZERT_MODEL_PATH, strip_accents=False)
model = TFAlbertForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained(CZERT_MODEL_PATH, num_labels=1)
or
self.tokenizer = BertTokenizerFast.from_pretrained(CZERT_MODEL_PATH, strip_accents=False)
self.model_encoder = AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained(CZERT_MODEL_PATH, from_tf=True)
-->
### Document Level Tasks
We evaluate our model on one document level task
* Multi-label Document Classification.
### Token Level Tasks
We evaluate our model on three token level tasks:
* Named Entity Recognition,
* Morphological Tagging,
* Semantic Role Labelling.
## Downstream Tasks Fine-tuning Results
### Sentiment Classification
| | mBERT | SlavicBERT | ALBERT-r | Czert-A | Czert-B |
|:----:|:------------------------:|:------------------------:|:------------------------:|:-----------------------:|:--------------------------------:|
| FB | 71.72 ± 0.91 | 73.87 ± 0.50 | 59.50 ± 0.47 | 72.47 ± 0.72 | **76.55** ± **0.14** |
| CSFD | 82.80 ± 0.14 | 82.51 ± 0.14 | 75.40 ± 0.18 | 79.58 ± 0.46 | **84.79** ± **0.26** |
Average F1 results for the Sentiment Classification task. For more information, see [the paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.13031).
### Semantic Text Similarity
| | **mBERT** | **Pavlov** | **Albert-random** | **Czert-A** | **Czert-B** |
|:-------------|:--------------:|:--------------:|:-----------------:|:--------------:|:----------------------:|
| STA-CNA | 83.335 ± 0.063 | 83.593 ± 0.050 | 43.184 ± 0.125 | 82.942 ± 0.106 | **84.345** ± **0.028** |
| STS-SVOB-img | 79.367 ± 0.486 | 79.900 ± 0.810 | 15.739 ± 2.992 | 79.444 ± 0.338 | **83.744** ± **0.395** |
| STS-SVOB-hl | 78.833 ± 0.296 | 76.996 ± 0.305 | 33.949 ± 1.807 | 75.089 ± 0.806 | **79.827 ± 0.469** |
Comparison of Pearson correlation achieved using pre-trained CZERT-A, CZERT-B, mBERT, Pavlov and randomly initialised Albert on semantic text similarity. For more information see [the paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.13031).
### Multi-label Document Classification
| | mBERT | SlavicBERT | ALBERT-r | Czert-A | Czert-B |
|:-----:|:------------:|:------------:|:------------:|:------------:|:-------------------:|
| AUROC | 97.62 ± 0.08 | 97.80 ± 0.06 | 94.35 ± 0.13 | 97.49 ± 0.07 | **98.00** ± **0.04** |
| F1 | 83.04 ± 0.16 | 84.08 ± 0.14 | 72.44 ± 0.22 | 82.27 ± 0.17 | **85.06** ± **0.11** |
Comparison of F1 and AUROC score achieved using pre-trained CZERT-A, CZERT-B, mBERT, Pavlov and randomly initialised Albert on multi-label document classification. For more information see [the paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.13031).
### Morphological Tagging
| | mBERT | Pavlov | Albert-random | Czert-A | Czert-B |
|:-----------------------|:---------------|:---------------|:---------------|:---------------|:---------------|
| Universal Dependencies | 99.176 ± 0.006 | 99.211 ± 0.008 | 96.590 ± 0.096 | 98.713 ± 0.008 | **99.300 ± 0.009** |
Comparison of F1 score achieved using pre-trained CZERT-A, CZERT-B, mBERT, Pavlov and randomly initialised Albert on morphological tagging task. For more information see [the paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.13031).
### Semantic Role Labelling
<div id="tab:SRL">
| | mBERT | Pavlov | Albert-random | Czert-A | Czert-B | dep-based | gold-dep |
|:------:|:----------:|:----------:|:-------------:|:----------:|:----------:|:---------:|:--------:|
| span | 78.547 ± 0.110 | 79.333 ± 0.080 | 51.365 ± 0.423 | 72.254 ± 0.172 | **81.861 ± 0.102** | \- | \- |
| syntax | 90.226 ± 0.224 | 90.492 ± 0.040 | 80.747 ± 0.131 | 80.319 ± 0.054 | **91.462 ± 0.062** | 85.19 | 89.52 |
SRL results – dep columns are evaluate with labelled F1 from CoNLL 2009 evaluation script, other columns are evaluated with span F1 score same as it was used for NER evaluation. For more information see [the paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.13031).
</div>
### Named Entity Recognition
| | mBERT | Pavlov | Albert-random | Czert-A | Czert-B |
|:-----------|:---------------|:---------------|:---------------|:---------------|:---------------|
| CNEC | **86.225 ± 0.208** | **86.565 ± 0.198** | 34.635 ± 0.343 | 72.945 ± 0.227 | 86.274 ± 0.116 |
| BSNLP 2019 | 84.006 ± 1.248 | **86.699 ± 0.370** | 19.773 ± 0.938 | 48.859 ± 0.605 | **86.729 ± 0.344** |
Comparison of f1 score achieved using pre-trained CZERT-A, CZERT-B, mBERT, Pavlov and randomly initialised Albert on named entity recognition task. For more information see [the paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.13031).
## Licence
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License. http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/
## How should I cite CZERT?
For now, please cite [the Arxiv paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.13031):
```
@article{sido2021czert,
title={Czert -- Czech BERT-like Model for Language Representation},
author={Jakub Sido and Ondřej Pražák and Pavel Přibáň and Jan Pašek and Michal Seják and Miloslav Konopík},
year={2021},
eprint={2103.13031},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CL},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2103.13031},
}
```
|
{"tags": ["cs", "fill-mask"]}
|
UWB-AIR/Czert-B-base-cased-long-zero-shot
| null |
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"longformer",
"feature-extraction",
"cs",
"fill-mask",
"arxiv:2103.13031",
"endpoints_compatible",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[
"2103.13031"
] |
[] |
TAGS
#transformers #pytorch #longformer #feature-extraction #cs #fill-mask #arxiv-2103.13031 #endpoints_compatible #region-us
|
CZERT
=====
This repository keeps trained Czert-B-base-cased-long-zero-shot model for the paper Czert – Czech BERT-like Model for Language Representation
For more information, see the paper
This is long version of Czert-B-base-cased created without any finetunning on long documents. Positional embedings were created by simply repeating the positional embeddings of the original Czert-B model. For tokenization, please use BertTokenizer. Cannot be used with AutoTokenizer.
Available Models
----------------
You can download MLM & NSP only pretrained models
~~CZERT-A-v1
CZERT-B-v1~~
After some additional experiments, we found out that the tokenizers config was exported wrongly. In Czert-B-v1, the tokenizer parameter "do\_lower\_case" was wrongly set to true. In Czert-A-v1 the parameter "strip\_accents" was incorrectly set to true.
Both mistakes are repaired in v2.
CZERT-A-v2
CZERT-B-v2
or choose from one of Finetuned Models
How to Use CZERT?
-----------------
### Sentence Level Tasks
We evaluate our model on two sentence level tasks:
* Sentiment Classification,
* Semantic Text Similarity.
### Document Level Tasks
We evaluate our model on one document level task
* Multi-label Document Classification.
### Token Level Tasks
We evaluate our model on three token level tasks:
* Named Entity Recognition,
* Morphological Tagging,
* Semantic Role Labelling.
Downstream Tasks Fine-tuning Results
------------------------------------
### Sentiment Classification
Average F1 results for the Sentiment Classification task. For more information, see the paper.
### Semantic Text Similarity
Comparison of Pearson correlation achieved using pre-trained CZERT-A, CZERT-B, mBERT, Pavlov and randomly initialised Albert on semantic text similarity. For more information see the paper.
### Multi-label Document Classification
Comparison of F1 and AUROC score achieved using pre-trained CZERT-A, CZERT-B, mBERT, Pavlov and randomly initialised Albert on multi-label document classification. For more information see the paper.
### Morphological Tagging
Comparison of F1 score achieved using pre-trained CZERT-A, CZERT-B, mBERT, Pavlov and randomly initialised Albert on morphological tagging task. For more information see the paper.
### Semantic Role Labelling
SRL results – dep columns are evaluate with labelled F1 from CoNLL 2009 evaluation script, other columns are evaluated with span F1 score same as it was used for NER evaluation. For more information see the paper.
### Named Entity Recognition
Comparison of f1 score achieved using pre-trained CZERT-A, CZERT-B, mBERT, Pavlov and randomly initialised Albert on named entity recognition task. For more information see the paper.
Licence
-------
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License. URL
How should I cite CZERT?
------------------------
For now, please cite the Arxiv paper:
|
[
"### Sentence Level Tasks\n\n\nWe evaluate our model on two sentence level tasks:\n\n\n* Sentiment Classification,\n* Semantic Text Similarity.",
"### Document Level Tasks\n\n\nWe evaluate our model on one document level task\n\n\n* Multi-label Document Classification.",
"### Token Level Tasks\n\n\nWe evaluate our model on three token level tasks:\n\n\n* Named Entity Recognition,\n* Morphological Tagging,\n* Semantic Role Labelling.\n\n\nDownstream Tasks Fine-tuning Results\n------------------------------------",
"### Sentiment Classification\n\n\n\nAverage F1 results for the Sentiment Classification task. For more information, see the paper.",
"### Semantic Text Similarity\n\n\n\nComparison of Pearson correlation achieved using pre-trained CZERT-A, CZERT-B, mBERT, Pavlov and randomly initialised Albert on semantic text similarity. For more information see the paper.",
"### Multi-label Document Classification\n\n\n\nComparison of F1 and AUROC score achieved using pre-trained CZERT-A, CZERT-B, mBERT, Pavlov and randomly initialised Albert on multi-label document classification. For more information see the paper.",
"### Morphological Tagging\n\n\n\nComparison of F1 score achieved using pre-trained CZERT-A, CZERT-B, mBERT, Pavlov and randomly initialised Albert on morphological tagging task. For more information see the paper.",
"### Semantic Role Labelling\n\n\n\n\nSRL results – dep columns are evaluate with labelled F1 from CoNLL 2009 evaluation script, other columns are evaluated with span F1 score same as it was used for NER evaluation. For more information see the paper.",
"### Named Entity Recognition\n\n\n\nComparison of f1 score achieved using pre-trained CZERT-A, CZERT-B, mBERT, Pavlov and randomly initialised Albert on named entity recognition task. For more information see the paper.\n\n\nLicence\n-------\n\n\nThis work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License. URL\n\n\nHow should I cite CZERT?\n------------------------\n\n\nFor now, please cite the Arxiv paper:"
] |
[
"TAGS\n#transformers #pytorch #longformer #feature-extraction #cs #fill-mask #arxiv-2103.13031 #endpoints_compatible #region-us \n",
"### Sentence Level Tasks\n\n\nWe evaluate our model on two sentence level tasks:\n\n\n* Sentiment Classification,\n* Semantic Text Similarity.",
"### Document Level Tasks\n\n\nWe evaluate our model on one document level task\n\n\n* Multi-label Document Classification.",
"### Token Level Tasks\n\n\nWe evaluate our model on three token level tasks:\n\n\n* Named Entity Recognition,\n* Morphological Tagging,\n* Semantic Role Labelling.\n\n\nDownstream Tasks Fine-tuning Results\n------------------------------------",
"### Sentiment Classification\n\n\n\nAverage F1 results for the Sentiment Classification task. For more information, see the paper.",
"### Semantic Text Similarity\n\n\n\nComparison of Pearson correlation achieved using pre-trained CZERT-A, CZERT-B, mBERT, Pavlov and randomly initialised Albert on semantic text similarity. For more information see the paper.",
"### Multi-label Document Classification\n\n\n\nComparison of F1 and AUROC score achieved using pre-trained CZERT-A, CZERT-B, mBERT, Pavlov and randomly initialised Albert on multi-label document classification. For more information see the paper.",
"### Morphological Tagging\n\n\n\nComparison of F1 score achieved using pre-trained CZERT-A, CZERT-B, mBERT, Pavlov and randomly initialised Albert on morphological tagging task. For more information see the paper.",
"### Semantic Role Labelling\n\n\n\n\nSRL results – dep columns are evaluate with labelled F1 from CoNLL 2009 evaluation script, other columns are evaluated with span F1 score same as it was used for NER evaluation. For more information see the paper.",
"### Named Entity Recognition\n\n\n\nComparison of f1 score achieved using pre-trained CZERT-A, CZERT-B, mBERT, Pavlov and randomly initialised Albert on named entity recognition task. For more information see the paper.\n\n\nLicence\n-------\n\n\nThis work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License. URL\n\n\nHow should I cite CZERT?\n------------------------\n\n\nFor now, please cite the Arxiv paper:"
] |
fill-mask
|
transformers
|
# CZERT
This repository keeps trained Czert-B model for the paper [Czert – Czech BERT-like Model for Language Representation
](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.13031)
For more information, see the paper
## Available Models
You can download **MLM & NSP only** pretrained models
~~[CZERT-A-v1](https://air.kiv.zcu.cz/public/CZERT-A-czert-albert-base-uncased.zip)
[CZERT-B-v1](https://air.kiv.zcu.cz/public/CZERT-B-czert-bert-base-cased.zip)~~
After some additional experiments, we found out that the tokenizers config was exported wrongly. In Czert-B-v1, the tokenizer parameter "do_lower_case" was wrongly set to true. In Czert-A-v1 the parameter "strip_accents" was incorrectly set to true.
Both mistakes are repaired in v2.
[CZERT-A-v2](https://air.kiv.zcu.cz/public/CZERT-A-v2-czert-albert-base-uncased.zip)
[CZERT-B-v2](https://air.kiv.zcu.cz/public/CZERT-B-v2-czert-bert-base-cased.zip)
or choose from one of **Finetuned Models**
| | Models |
| - | - |
| Sentiment Classification<br> (Facebook or CSFD) | [CZERT-A-sentiment-FB](https://air.kiv.zcu.cz/public/CZERT-A_fb.zip) <br> [CZERT-B-sentiment-FB](https://air.kiv.zcu.cz/public/CZERT-B_fb.zip) <br> [CZERT-A-sentiment-CSFD](https://air.kiv.zcu.cz/public/CZERT-A_csfd.zip) <br> [CZERT-B-sentiment-CSFD](https://air.kiv.zcu.cz/public/CZERT-B_csfd.zip) | Semantic Text Similarity <br> (Czech News Agency) | [CZERT-A-sts-CNA](https://air.kiv.zcu.cz/public/CZERT-A-sts-CNA.zip) <br> [CZERT-B-sts-CNA](https://air.kiv.zcu.cz/public/CZERT-B-sts-CNA.zip)
| Named Entity Recognition | [CZERT-A-ner-CNEC](https://air.kiv.zcu.cz/public/CZERT-A-ner-CNEC-cased.zip) <br> [CZERT-B-ner-CNEC](https://air.kiv.zcu.cz/public/CZERT-B-ner-CNEC-cased.zip) <br>[PAV-ner-CNEC](https://air.kiv.zcu.cz/public/PAV-ner-CNEC-cased.zip) <br> [CZERT-A-ner-BSNLP](https://air.kiv.zcu.cz/public/CZERT-A-ner-BSNLP-cased.zip)<br>[CZERT-B-ner-BSNLP](https://air.kiv.zcu.cz/public/CZERT-B-ner-BSNLP-cased.zip) <br>[PAV-ner-BSNLP](https://air.kiv.zcu.cz/public/PAV-ner-BSNLP-cased.zip) |
| Morphological Tagging<br> | [CZERT-A-morphtag-126k](https://air.kiv.zcu.cz/public/CZERT-A-morphtag-126k-cased.zip)<br>[CZERT-B-morphtag-126k](https://air.kiv.zcu.cz/public/CZERT-B-morphtag-126k-cased.zip) |
| Semantic Role Labelling |[CZERT-A-srl](https://air.kiv.zcu.cz/public/CZERT-A-srl-cased.zip)<br> [CZERT-B-srl](https://air.kiv.zcu.cz/public/CZERT-B-srl-cased.zip) |
## How to Use CZERT?
### Sentence Level Tasks
We evaluate our model on two sentence level tasks:
* Sentiment Classification,
* Semantic Text Similarity.
<!-- tokenizer = BertTokenizerFast.from_pretrained(CZERT_MODEL_PATH, strip_accents=False)
\\tmodel = TFAlbertForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained(CZERT_MODEL_PATH, num_labels=1)
or
self.tokenizer = BertTokenizerFast.from_pretrained(CZERT_MODEL_PATH, strip_accents=False)
self.model_encoder = AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained(CZERT_MODEL_PATH, from_tf=True)
-->
\\t
### Document Level Tasks
We evaluate our model on one document level task
* Multi-label Document Classification.
### Token Level Tasks
We evaluate our model on three token level tasks:
* Named Entity Recognition,
* Morphological Tagging,
* Semantic Role Labelling.
## Downstream Tasks Fine-tuning Results
### Sentiment Classification
| | mBERT | SlavicBERT | ALBERT-r | Czert-A | Czert-B |
|:----:|:------------------------:|:------------------------:|:------------------------:|:-----------------------:|:--------------------------------:|
| FB | 71.72 ± 0.91 | 73.87 ± 0.50 | 59.50 ± 0.47 | 72.47 ± 0.72 | **76.55** ± **0.14** |
| CSFD | 82.80 ± 0.14 | 82.51 ± 0.14 | 75.40 ± 0.18 | 79.58 ± 0.46 | **84.79** ± **0.26** |
Average F1 results for the Sentiment Classification task. For more information, see [the paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.13031).
### Semantic Text Similarity
| | **mBERT** | **Pavlov** | **Albert-random** | **Czert-A** | **Czert-B** |
|:-------------|:--------------:|:--------------:|:-----------------:|:--------------:|:----------------------:|
| STA-CNA | 83.335 ± 0.063 | 83.593 ± 0.050 | 43.184 ± 0.125 | 82.942 ± 0.106 | **84.345** ± **0.028** |
| STS-SVOB-img | 79.367 ± 0.486 | 79.900 ± 0.810 | 15.739 ± 2.992 | 79.444 ± 0.338 | **83.744** ± **0.395** |
| STS-SVOB-hl | 78.833 ± 0.296 | 76.996 ± 0.305 | 33.949 ± 1.807 | 75.089 ± 0.806 | **79.827 ± 0.469** |
Comparison of Pearson correlation achieved using pre-trained CZERT-A, CZERT-B, mBERT, Pavlov and randomly initialised Albert on semantic text similarity. For more information see [the paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.13031).
### Multi-label Document Classification
| | mBERT | SlavicBERT | ALBERT-r | Czert-A | Czert-B |
|:-----:|:------------:|:------------:|:------------:|:------------:|:-------------------:|
| AUROC | 97.62 ± 0.08 | 97.80 ± 0.06 | 94.35 ± 0.13 | 97.49 ± 0.07 | **98.00** ± **0.04** |
| F1 | 83.04 ± 0.16 | 84.08 ± 0.14 | 72.44 ± 0.22 | 82.27 ± 0.17 | **85.06** ± **0.11** |
Comparison of F1 and AUROC score achieved using pre-trained CZERT-A, CZERT-B, mBERT, Pavlov and randomly initialised Albert on multi-label document classification. For more information see [the paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.13031).
### Morphological Tagging
| | mBERT | Pavlov | Albert-random | Czert-A | Czert-B |
|:-----------------------|:---------------|:---------------|:---------------|:---------------|:---------------|
| Universal Dependencies | 99.176 ± 0.006 | 99.211 ± 0.008 | 96.590 ± 0.096 | 98.713 ± 0.008 | **99.300 ± 0.009** |
Comparison of F1 score achieved using pre-trained CZERT-A, CZERT-B, mBERT, Pavlov and randomly initialised Albert on morphological tagging task. For more information see [the paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.13031).
### Semantic Role Labelling
<div id="tab:SRL">
| | mBERT | Pavlov | Albert-random | Czert-A | Czert-B | dep-based | gold-dep |
|:------:|:----------:|:----------:|:-------------:|:----------:|:----------:|:---------:|:--------:|
| span | 78.547 ± 0.110 | 79.333 ± 0.080 | 51.365 ± 0.423 | 72.254 ± 0.172 | **81.861 ± 0.102** | \\\\- | \\\\- |
| syntax | 90.226 ± 0.224 | 90.492 ± 0.040 | 80.747 ± 0.131 | 80.319 ± 0.054 | **91.462 ± 0.062** | 85.19 | 89.52 |
SRL results – dep columns are evaluate with labelled F1 from CoNLL 2009 evaluation script, other columns are evaluated with span F1 score same as it was used for NER evaluation. For more information see [the paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.13031).
</div>
### Named Entity Recognition
| | mBERT | Pavlov | Albert-random | Czert-A | Czert-B |
|:-----------|:---------------|:---------------|:---------------|:---------------|:---------------|
| CNEC | **86.225 ± 0.208** | **86.565 ± 0.198** | 34.635 ± 0.343 | 72.945 ± 0.227 | 86.274 ± 0.116 |
| BSNLP 2019 | 84.006 ± 1.248 | **86.699 ± 0.370** | 19.773 ± 0.938 | 48.859 ± 0.605 | **86.729 ± 0.344** |
Comparison of f1 score achieved using pre-trained CZERT-A, CZERT-B, mBERT, Pavlov and randomly initialised Albert on named entity recognition task. For more information see [the paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.13031).
## Licence
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License. http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/
## How should I cite CZERT?
For now, please cite [the Arxiv paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.13031):
```
@article{sido2021czert,
title={Czert -- Czech BERT-like Model for Language Representation},
author={Jakub Sido and Ondřej Pražák and Pavel Přibáň and Jan Pašek and Michal Seják and Miloslav Konopík},
year={2021},
eprint={2103.13031},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CL},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2103.13031},
}
```
|
{"tags": ["cs", "fill-mask"]}
|
UWB-AIR/Czert-B-base-cased
| null |
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"tf",
"bert",
"pretraining",
"cs",
"fill-mask",
"arxiv:2103.13031",
"endpoints_compatible",
"has_space",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[
"2103.13031"
] |
[] |
TAGS
#transformers #pytorch #tf #bert #pretraining #cs #fill-mask #arxiv-2103.13031 #endpoints_compatible #has_space #region-us
|
CZERT
=====
This repository keeps trained Czert-B model for the paper Czert – Czech BERT-like Model for Language Representation
For more information, see the paper
Available Models
----------------
You can download MLM & NSP only pretrained models
~~CZERT-A-v1
CZERT-B-v1~~
After some additional experiments, we found out that the tokenizers config was exported wrongly. In Czert-B-v1, the tokenizer parameter "do\_lower\_case" was wrongly set to true. In Czert-A-v1 the parameter "strip\_accents" was incorrectly set to true.
Both mistakes are repaired in v2.
CZERT-A-v2
CZERT-B-v2
or choose from one of Finetuned Models
How to Use CZERT?
-----------------
### Sentence Level Tasks
We evaluate our model on two sentence level tasks:
* Sentiment Classification,
* Semantic Text Similarity.
\t
### Document Level Tasks
We evaluate our model on one document level task
* Multi-label Document Classification.
### Token Level Tasks
We evaluate our model on three token level tasks:
* Named Entity Recognition,
* Morphological Tagging,
* Semantic Role Labelling.
Downstream Tasks Fine-tuning Results
------------------------------------
### Sentiment Classification
Average F1 results for the Sentiment Classification task. For more information, see the paper.
### Semantic Text Similarity
Comparison of Pearson correlation achieved using pre-trained CZERT-A, CZERT-B, mBERT, Pavlov and randomly initialised Albert on semantic text similarity. For more information see the paper.
### Multi-label Document Classification
Comparison of F1 and AUROC score achieved using pre-trained CZERT-A, CZERT-B, mBERT, Pavlov and randomly initialised Albert on multi-label document classification. For more information see the paper.
### Morphological Tagging
Comparison of F1 score achieved using pre-trained CZERT-A, CZERT-B, mBERT, Pavlov and randomly initialised Albert on morphological tagging task. For more information see the paper.
### Semantic Role Labelling
SRL results – dep columns are evaluate with labelled F1 from CoNLL 2009 evaluation script, other columns are evaluated with span F1 score same as it was used for NER evaluation. For more information see the paper.
### Named Entity Recognition
Comparison of f1 score achieved using pre-trained CZERT-A, CZERT-B, mBERT, Pavlov and randomly initialised Albert on named entity recognition task. For more information see the paper.
Licence
-------
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License. URL
How should I cite CZERT?
------------------------
For now, please cite the Arxiv paper:
|
[
"### Sentence Level Tasks\n\n\nWe evaluate our model on two sentence level tasks:\n\n\n* Sentiment Classification,\n* Semantic Text Similarity.\n\n\n\\t",
"### Document Level Tasks\n\n\nWe evaluate our model on one document level task\n\n\n* Multi-label Document Classification.",
"### Token Level Tasks\n\n\nWe evaluate our model on three token level tasks:\n\n\n* Named Entity Recognition,\n* Morphological Tagging,\n* Semantic Role Labelling.\n\n\nDownstream Tasks Fine-tuning Results\n------------------------------------",
"### Sentiment Classification\n\n\n\nAverage F1 results for the Sentiment Classification task. For more information, see the paper.",
"### Semantic Text Similarity\n\n\n\nComparison of Pearson correlation achieved using pre-trained CZERT-A, CZERT-B, mBERT, Pavlov and randomly initialised Albert on semantic text similarity. For more information see the paper.",
"### Multi-label Document Classification\n\n\n\nComparison of F1 and AUROC score achieved using pre-trained CZERT-A, CZERT-B, mBERT, Pavlov and randomly initialised Albert on multi-label document classification. For more information see the paper.",
"### Morphological Tagging\n\n\n\nComparison of F1 score achieved using pre-trained CZERT-A, CZERT-B, mBERT, Pavlov and randomly initialised Albert on morphological tagging task. For more information see the paper.",
"### Semantic Role Labelling\n\n\n\n\nSRL results – dep columns are evaluate with labelled F1 from CoNLL 2009 evaluation script, other columns are evaluated with span F1 score same as it was used for NER evaluation. For more information see the paper.",
"### Named Entity Recognition\n\n\n\nComparison of f1 score achieved using pre-trained CZERT-A, CZERT-B, mBERT, Pavlov and randomly initialised Albert on named entity recognition task. For more information see the paper.\n\n\nLicence\n-------\n\n\nThis work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License. URL\n\n\nHow should I cite CZERT?\n------------------------\n\n\nFor now, please cite the Arxiv paper:"
] |
[
"TAGS\n#transformers #pytorch #tf #bert #pretraining #cs #fill-mask #arxiv-2103.13031 #endpoints_compatible #has_space #region-us \n",
"### Sentence Level Tasks\n\n\nWe evaluate our model on two sentence level tasks:\n\n\n* Sentiment Classification,\n* Semantic Text Similarity.\n\n\n\\t",
"### Document Level Tasks\n\n\nWe evaluate our model on one document level task\n\n\n* Multi-label Document Classification.",
"### Token Level Tasks\n\n\nWe evaluate our model on three token level tasks:\n\n\n* Named Entity Recognition,\n* Morphological Tagging,\n* Semantic Role Labelling.\n\n\nDownstream Tasks Fine-tuning Results\n------------------------------------",
"### Sentiment Classification\n\n\n\nAverage F1 results for the Sentiment Classification task. For more information, see the paper.",
"### Semantic Text Similarity\n\n\n\nComparison of Pearson correlation achieved using pre-trained CZERT-A, CZERT-B, mBERT, Pavlov and randomly initialised Albert on semantic text similarity. For more information see the paper.",
"### Multi-label Document Classification\n\n\n\nComparison of F1 and AUROC score achieved using pre-trained CZERT-A, CZERT-B, mBERT, Pavlov and randomly initialised Albert on multi-label document classification. For more information see the paper.",
"### Morphological Tagging\n\n\n\nComparison of F1 score achieved using pre-trained CZERT-A, CZERT-B, mBERT, Pavlov and randomly initialised Albert on morphological tagging task. For more information see the paper.",
"### Semantic Role Labelling\n\n\n\n\nSRL results – dep columns are evaluate with labelled F1 from CoNLL 2009 evaluation script, other columns are evaluated with span F1 score same as it was used for NER evaluation. For more information see the paper.",
"### Named Entity Recognition\n\n\n\nComparison of f1 score achieved using pre-trained CZERT-A, CZERT-B, mBERT, Pavlov and randomly initialised Albert on named entity recognition task. For more information see the paper.\n\n\nLicence\n-------\n\n\nThis work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License. URL\n\n\nHow should I cite CZERT?\n------------------------\n\n\nFor now, please cite the Arxiv paper:"
] |
text-generation
|
transformers
|
<!-- This model card has been generated automatically according to the information the Trainer had access to. You
should probably proofread and complete it, then remove this comment. -->
# avengers2
This model is a fine-tuned version of [distilgpt2](https://huggingface.co/distilgpt2) on the None dataset.
It achieves the following results on the evaluation set:
- Loss: 4.0131
## Model description
More information needed
## Intended uses & limitations
More information needed
## Training and evaluation data
More information needed
## Training procedure
### Training hyperparameters
The following hyperparameters were used during training:
- learning_rate: 2e-05
- train_batch_size: 8
- eval_batch_size: 8
- seed: 42
- optimizer: Adam with betas=(0.9,0.999) and epsilon=1e-08
- lr_scheduler_type: linear
- num_epochs: 3.0
### Training results
| Training Loss | Epoch | Step | Validation Loss |
|:-------------:|:-----:|:----:|:---------------:|
| No log | 1.0 | 56 | 3.9588 |
| No log | 2.0 | 112 | 3.9996 |
| No log | 3.0 | 168 | 4.0131 |
### Framework versions
- Transformers 4.10.0
- Pytorch 1.9.0
- Datasets 1.2.1
- Tokenizers 0.10.1
|
{"license": "apache-2.0", "tags": ["generated_from_trainer"], "datasets": []}
|
Ulto/avengers2
| null |
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"tensorboard",
"gpt2",
"text-generation",
"generated_from_trainer",
"license:apache-2.0",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"text-generation-inference",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[] |
TAGS
#transformers #pytorch #tensorboard #gpt2 #text-generation #generated_from_trainer #license-apache-2.0 #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #text-generation-inference #region-us
|
avengers2
=========
This model is a fine-tuned version of distilgpt2 on the None dataset.
It achieves the following results on the evaluation set:
* Loss: 4.0131
Model description
-----------------
More information needed
Intended uses & limitations
---------------------------
More information needed
Training and evaluation data
----------------------------
More information needed
Training procedure
------------------
### Training hyperparameters
The following hyperparameters were used during training:
* learning\_rate: 2e-05
* train\_batch\_size: 8
* eval\_batch\_size: 8
* seed: 42
* optimizer: Adam with betas=(0.9,0.999) and epsilon=1e-08
* lr\_scheduler\_type: linear
* num\_epochs: 3.0
### Training results
### Framework versions
* Transformers 4.10.0
* Pytorch 1.9.0
* Datasets 1.2.1
* Tokenizers 0.10.1
|
[
"### Training hyperparameters\n\n\nThe following hyperparameters were used during training:\n\n\n* learning\\_rate: 2e-05\n* train\\_batch\\_size: 8\n* eval\\_batch\\_size: 8\n* seed: 42\n* optimizer: Adam with betas=(0.9,0.999) and epsilon=1e-08\n* lr\\_scheduler\\_type: linear\n* num\\_epochs: 3.0",
"### Training results",
"### Framework versions\n\n\n* Transformers 4.10.0\n* Pytorch 1.9.0\n* Datasets 1.2.1\n* Tokenizers 0.10.1"
] |
[
"TAGS\n#transformers #pytorch #tensorboard #gpt2 #text-generation #generated_from_trainer #license-apache-2.0 #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #text-generation-inference #region-us \n",
"### Training hyperparameters\n\n\nThe following hyperparameters were used during training:\n\n\n* learning\\_rate: 2e-05\n* train\\_batch\\_size: 8\n* eval\\_batch\\_size: 8\n* seed: 42\n* optimizer: Adam with betas=(0.9,0.999) and epsilon=1e-08\n* lr\\_scheduler\\_type: linear\n* num\\_epochs: 3.0",
"### Training results",
"### Framework versions\n\n\n* Transformers 4.10.0\n* Pytorch 1.9.0\n* Datasets 1.2.1\n* Tokenizers 0.10.1"
] |
text-generation
|
transformers
|
<!-- This model card has been generated automatically according to the information the Trainer had access to. You
should probably proofread and complete it, then remove this comment. -->
# pythonCoPilot
This model is a fine-tuned version of [](https://huggingface.co/) on the None dataset.
## Model description
More information needed
## Intended uses & limitations
More information needed
## Training and evaluation data
More information needed
## Training procedure
### Training hyperparameters
The following hyperparameters were used during training:
- learning_rate: 2e-05
- train_batch_size: 8
- eval_batch_size: 8
- seed: 42
- optimizer: Adam with betas=(0.9,0.999) and epsilon=1e-08
- lr_scheduler_type: linear
- num_epochs: 3.0
### Training results
### Framework versions
- Transformers 4.12.5
- Pytorch 1.10.0+cu111
- Datasets 1.15.1
- Tokenizers 0.10.3
|
{"tags": ["generated_from_trainer"], "model-index": [{"name": "pythonCoPilot", "results": []}]}
|
Ulto/pythonCoPilot
| null |
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"tensorboard",
"gpt2",
"text-generation",
"generated_from_trainer",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"text-generation-inference",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[] |
TAGS
#transformers #pytorch #tensorboard #gpt2 #text-generation #generated_from_trainer #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #text-generation-inference #region-us
|
# pythonCoPilot
This model is a fine-tuned version of [](URL on the None dataset.
## Model description
More information needed
## Intended uses & limitations
More information needed
## Training and evaluation data
More information needed
## Training procedure
### Training hyperparameters
The following hyperparameters were used during training:
- learning_rate: 2e-05
- train_batch_size: 8
- eval_batch_size: 8
- seed: 42
- optimizer: Adam with betas=(0.9,0.999) and epsilon=1e-08
- lr_scheduler_type: linear
- num_epochs: 3.0
### Training results
### Framework versions
- Transformers 4.12.5
- Pytorch 1.10.0+cu111
- Datasets 1.15.1
- Tokenizers 0.10.3
|
[
"# pythonCoPilot\n\nThis model is a fine-tuned version of [](URL on the None dataset.",
"## Model description\n\nMore information needed",
"## Intended uses & limitations\n\nMore information needed",
"## Training and evaluation data\n\nMore information needed",
"## Training procedure",
"### Training hyperparameters\n\nThe following hyperparameters were used during training:\n- learning_rate: 2e-05\n- train_batch_size: 8\n- eval_batch_size: 8\n- seed: 42\n- optimizer: Adam with betas=(0.9,0.999) and epsilon=1e-08\n- lr_scheduler_type: linear\n- num_epochs: 3.0",
"### Training results",
"### Framework versions\n\n- Transformers 4.12.5\n- Pytorch 1.10.0+cu111\n- Datasets 1.15.1\n- Tokenizers 0.10.3"
] |
[
"TAGS\n#transformers #pytorch #tensorboard #gpt2 #text-generation #generated_from_trainer #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #text-generation-inference #region-us \n",
"# pythonCoPilot\n\nThis model is a fine-tuned version of [](URL on the None dataset.",
"## Model description\n\nMore information needed",
"## Intended uses & limitations\n\nMore information needed",
"## Training and evaluation data\n\nMore information needed",
"## Training procedure",
"### Training hyperparameters\n\nThe following hyperparameters were used during training:\n- learning_rate: 2e-05\n- train_batch_size: 8\n- eval_batch_size: 8\n- seed: 42\n- optimizer: Adam with betas=(0.9,0.999) and epsilon=1e-08\n- lr_scheduler_type: linear\n- num_epochs: 3.0",
"### Training results",
"### Framework versions\n\n- Transformers 4.12.5\n- Pytorch 1.10.0+cu111\n- Datasets 1.15.1\n- Tokenizers 0.10.3"
] |
text-generation
|
transformers
|
<!-- This model card has been generated automatically according to the information the Trainer had access to. You
should probably proofread and complete it, then remove this comment. -->
# pythonCoPilot2
This model is a fine-tuned version of [](https://huggingface.co/) on an unknown dataset.
It achieves the following results on the evaluation set:
- Loss: 4.0479
## Model description
More information needed
## Intended uses & limitations
More information needed
## Training and evaluation data
More information needed
## Training procedure
### Training hyperparameters
The following hyperparameters were used during training:
- learning_rate: 2e-05
- train_batch_size: 8
- eval_batch_size: 8
- seed: 42
- optimizer: Adam with betas=(0.9,0.999) and epsilon=1e-08
- lr_scheduler_type: linear
- num_epochs: 3.0
### Training results
| Training Loss | Epoch | Step | Validation Loss |
|:-------------:|:-----:|:----:|:---------------:|
| No log | 1.0 | 427 | 4.3782 |
| 4.6698 | 2.0 | 854 | 4.0718 |
| 3.3953 | 3.0 | 1281 | 4.0479 |
### Framework versions
- Transformers 4.12.5
- Pytorch 1.10.0+cu111
- Datasets 1.15.1
- Tokenizers 0.10.3
|
{"tags": ["generated_from_trainer"], "model-index": [{"name": "pythonCoPilot2", "results": []}]}
|
Ulto/pythonCoPilot2
| null |
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"tensorboard",
"gpt2",
"text-generation",
"generated_from_trainer",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"text-generation-inference",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[] |
TAGS
#transformers #pytorch #tensorboard #gpt2 #text-generation #generated_from_trainer #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #text-generation-inference #region-us
|
pythonCoPilot2
==============
This model is a fine-tuned version of [](URL on an unknown dataset.
It achieves the following results on the evaluation set:
* Loss: 4.0479
Model description
-----------------
More information needed
Intended uses & limitations
---------------------------
More information needed
Training and evaluation data
----------------------------
More information needed
Training procedure
------------------
### Training hyperparameters
The following hyperparameters were used during training:
* learning\_rate: 2e-05
* train\_batch\_size: 8
* eval\_batch\_size: 8
* seed: 42
* optimizer: Adam with betas=(0.9,0.999) and epsilon=1e-08
* lr\_scheduler\_type: linear
* num\_epochs: 3.0
### Training results
### Framework versions
* Transformers 4.12.5
* Pytorch 1.10.0+cu111
* Datasets 1.15.1
* Tokenizers 0.10.3
|
[
"### Training hyperparameters\n\n\nThe following hyperparameters were used during training:\n\n\n* learning\\_rate: 2e-05\n* train\\_batch\\_size: 8\n* eval\\_batch\\_size: 8\n* seed: 42\n* optimizer: Adam with betas=(0.9,0.999) and epsilon=1e-08\n* lr\\_scheduler\\_type: linear\n* num\\_epochs: 3.0",
"### Training results",
"### Framework versions\n\n\n* Transformers 4.12.5\n* Pytorch 1.10.0+cu111\n* Datasets 1.15.1\n* Tokenizers 0.10.3"
] |
[
"TAGS\n#transformers #pytorch #tensorboard #gpt2 #text-generation #generated_from_trainer #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #text-generation-inference #region-us \n",
"### Training hyperparameters\n\n\nThe following hyperparameters were used during training:\n\n\n* learning\\_rate: 2e-05\n* train\\_batch\\_size: 8\n* eval\\_batch\\_size: 8\n* seed: 42\n* optimizer: Adam with betas=(0.9,0.999) and epsilon=1e-08\n* lr\\_scheduler\\_type: linear\n* num\\_epochs: 3.0",
"### Training results",
"### Framework versions\n\n\n* Transformers 4.12.5\n* Pytorch 1.10.0+cu111\n* Datasets 1.15.1\n* Tokenizers 0.10.3"
] |
text-generation
|
transformers
|
<!-- This model card has been generated automatically according to the information the Trainer had access to. You
should probably proofread and complete it, then remove this comment. -->
# pythonCoPilot3
This model is a fine-tuned version of [](https://huggingface.co/) on the None dataset.
## Model description
More information needed
## Intended uses & limitations
More information needed
## Training and evaluation data
More information needed
## Training procedure
### Training hyperparameters
The following hyperparameters were used during training:
- learning_rate: 2e-05
- train_batch_size: 8
- eval_batch_size: 8
- seed: 42
- optimizer: Adam with betas=(0.9,0.999) and epsilon=1e-08
- lr_scheduler_type: linear
- num_epochs: 10
### Training results
### Framework versions
- Transformers 4.12.5
- Pytorch 1.10.0+cu111
- Datasets 1.15.1
- Tokenizers 0.10.3
|
{"tags": ["generated_from_trainer"], "model-index": [{"name": "pythonCoPilot3", "results": []}]}
|
Ulto/pythonCoPilot3
| null |
[
"transformers",
"pytorch",
"tensorboard",
"gpt2",
"text-generation",
"generated_from_trainer",
"autotrain_compatible",
"endpoints_compatible",
"text-generation-inference",
"region:us"
] | null |
2022-03-02T23:29:05+00:00
|
[] |
[] |
TAGS
#transformers #pytorch #tensorboard #gpt2 #text-generation #generated_from_trainer #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #text-generation-inference #region-us
|
# pythonCoPilot3
This model is a fine-tuned version of [](URL on the None dataset.
## Model description
More information needed
## Intended uses & limitations
More information needed
## Training and evaluation data
More information needed
## Training procedure
### Training hyperparameters
The following hyperparameters were used during training:
- learning_rate: 2e-05
- train_batch_size: 8
- eval_batch_size: 8
- seed: 42
- optimizer: Adam with betas=(0.9,0.999) and epsilon=1e-08
- lr_scheduler_type: linear
- num_epochs: 10
### Training results
### Framework versions
- Transformers 4.12.5
- Pytorch 1.10.0+cu111
- Datasets 1.15.1
- Tokenizers 0.10.3
|
[
"# pythonCoPilot3\n\nThis model is a fine-tuned version of [](URL on the None dataset.",
"## Model description\n\nMore information needed",
"## Intended uses & limitations\n\nMore information needed",
"## Training and evaluation data\n\nMore information needed",
"## Training procedure",
"### Training hyperparameters\n\nThe following hyperparameters were used during training:\n- learning_rate: 2e-05\n- train_batch_size: 8\n- eval_batch_size: 8\n- seed: 42\n- optimizer: Adam with betas=(0.9,0.999) and epsilon=1e-08\n- lr_scheduler_type: linear\n- num_epochs: 10",
"### Training results",
"### Framework versions\n\n- Transformers 4.12.5\n- Pytorch 1.10.0+cu111\n- Datasets 1.15.1\n- Tokenizers 0.10.3"
] |
[
"TAGS\n#transformers #pytorch #tensorboard #gpt2 #text-generation #generated_from_trainer #autotrain_compatible #endpoints_compatible #text-generation-inference #region-us \n",
"# pythonCoPilot3\n\nThis model is a fine-tuned version of [](URL on the None dataset.",
"## Model description\n\nMore information needed",
"## Intended uses & limitations\n\nMore information needed",
"## Training and evaluation data\n\nMore information needed",
"## Training procedure",
"### Training hyperparameters\n\nThe following hyperparameters were used during training:\n- learning_rate: 2e-05\n- train_batch_size: 8\n- eval_batch_size: 8\n- seed: 42\n- optimizer: Adam with betas=(0.9,0.999) and epsilon=1e-08\n- lr_scheduler_type: linear\n- num_epochs: 10",
"### Training results",
"### Framework versions\n\n- Transformers 4.12.5\n- Pytorch 1.10.0+cu111\n- Datasets 1.15.1\n- Tokenizers 0.10.3"
] |
Subsets and Splits
No community queries yet
The top public SQL queries from the community will appear here once available.