Serial Number
int64 1
6k
| Issue Number
int64 75.6k
112k
| Title
stringlengths 3
357
| Labels
stringlengths 3
241
⌀ | Body
stringlengths 9
74.5k
⌀ | Comments
int64 0
867
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
5,201 | 81,722 |
Inconsistent naming convention for end of enum in DispatchKey
|
triaged, module: dispatch
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
Here is a clear contradiction:
```
EndOfBackendKeys = PrivateUse3Bit,
```
but
```
EndOfFunctionalityKeys, // End of functionality keys.
```
This means for iterating through backend keys you should <= the ending, but for functionality keys you should < the ending. It is inconsistent.
----
Let's take a step back. There are a few problems with our naming conventions here.
1. It's not clear if end is inclusive or exclusive
2. It's not clear if start is inclusive or exclusive
3. It's not clear if length includes the zero-valued invalid key
We should establish clear definitions for each of these (possibly renaming if the existing names are ambiguous) and then apply this uniformly.
My preference is that:
1. End is exclusive
2. Start is inclusive
3. Length includes zero-valued key
cc @bdhirsh
### Versions
master
| 0 |
5,202 | 81,717 |
PyTorch Embedding Op with max_norm is not working as expected
|
module: cuda, triaged, module: norms and normalization, module: embedding, bug
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
The behavior of renorm inside the `max_norm` will renorm the weight to the norm same as `max_norm` when it is specified.
However, under GPU and if the input is multi-dimensional (like dim = 3). Its behavior is not expected and also weight will be renormed to the wrong norm (like less than `max_norm`)
To repo this here is code snippet:
```
import torch
input_size = [36, 15, 48]
embedding_size = 28
embedding_dim = 5
embedding = torch.nn.Embedding(embedding_size, embedding_dim, max_norm=2.0, norm_type=2.0).cuda()
weight_norm = torch.linalg.norm(embedding.weight, dim=-1).clone()
original_weight_norm = weight_norm.clone()
print("weight_norm", original_weight_norm)
weight_norm[weight_norm > 2.0] = 2.0
print("expected weight_norm", weight_norm)
for i in range(4):
input = torch.randint(0, embedding_size, tuple(input_size)).cuda()
torch.nn.functional.embedding(input, embedding.weight, max_norm=2.0, norm_type=2.0)
actual_weight_norm = torch.linalg.norm(embedding.weight, dim=-1)
print("actual weight ", actual_weight_norm)
delta = actual_weight_norm - weight_norm
threshold = 0.01
print(torch.allclose(weight_norm, actual_weight_norm), "norm more than threshold ", threshold, delta[torch.abs(delta) > threshold])
```
One example output is like:
```
weight_norm tensor([2.0776, 2.0551, 2.6955, 1.9832, 1.6644, 1.8127, 2.5646, 2.5205, 1.6097,
3.0849, 1.6583, 1.6348, 2.7448, 1.6877, 1.7610, 1.9241, 0.8003, 0.7706,
2.2592, 2.0385, 2.6742, 1.5317, 2.1481, 0.9371, 1.6462, 1.7186, 1.2157,
2.8872], device='cuda:0', grad_fn=<CloneBackward0>)
expected weight_norm tensor([2.0000, 2.0000, 2.0000, 1.9832, 1.6644, 1.8127, 2.0000, 2.0000, 1.6097,
2.0000, 1.6583, 1.6348, 2.0000, 1.6877, 1.7610, 1.9241, 0.8003, 0.7706,
2.0000, 2.0000, 2.0000, 1.5317, 2.0000, 0.9371, 1.6462, 1.7186, 1.2157,
2.0000], device='cuda:0', grad_fn=<IndexPutBackward0>)
actual weight tensor([2.0000, 2.0000, 2.0000, 1.9832, 1.6644, 1.8127, 2.0000, 1.5870, 1.6097,
1.2966, 1.6583, 1.6348, 2.0000, 1.6877, 1.7610, 1.9241, 0.8003, 0.7706,
1.7705, 2.0000, 1.8975, 1.5317, 2.0000, 0.9371, 1.6462, 1.7186, 1.2157,
1.8775], device='cuda:0', grad_fn=<LinalgVectorNormBackward0>)
False norm more than threshold 0.01 tensor([-0.4130, -0.7034, -0.2295, -0.1025, -0.1225], device='cuda:0',
grad_fn=<IndexBackward0>)
```
Sometimes, you need to run it more than once to repo but it is usually within 2-3 runs.
### Versions
Run on the latest night build and Linux and cuda 11.0
cc @ngimel
| 2 |
5,203 | 81,703 |
Dispatcher debug/logging mode
|
triaged, module: dispatch
|
### 🚀 The feature, motivation and pitch
I recently ran into a situation where I was trying to understand why the dispatcher dispatched the way it had, and it (re)occurred to me that having a way of turning on chatty dispatcher mode would be pretty useful. What I'd like to see is a log something like (maybe done more compactly):
```
call aten::add
argument 1 keys: [Dense], [CPUBit]
argument 2 keys: [Python, PythonSnapshotTLS], [MetaBit]
merged keys: [Python, PythonSnapshotTLS, ...], [CPUBit, MetaBit]
include, exclude set: [], [Autograd]
dispatching to: DenseCPU
```
for every operator going through the dispatcher.
Probably this should be done using the profiler. cc @robieta
### Alternatives
_No response_
### Additional context
_No response_
| 4 |
5,204 | 81,692 |
Failed to static link latest cuDNN while compiling
|
module: build, module: cudnn, triaged
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
I tried to compile 1.12 with `TORCH_CUDA_ARCH_LIST="6.0;6.1;7.0;7.5;7.5+PTX" CUDNN_LIBRARY_PATH=/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/ CUDNN_INCLUDE_DIR=/usr/include/ USE_CUDNN=1 USE_STATIC_CUDNN=1 USE_STATIC_NCCL=1 CAFFE2_STATIC_LINK_CUDA=1 python setup.py bdist_wheel`.
It cannot find the cuDNN installed on my system:
<img width="587" alt="截屏2022-07-19 下午7 58 23" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/73142299/179744748-92517f55-a1ee-49cb-bdf8-49d94c41fd7b.png">
I located the problem in file `cmake/Modules_CUDA_fix/FindCUDNN.cmake`
```
option(CUDNN_STATIC "Look for static CUDNN" OFF)
if (CUDNN_STATIC)
set(CUDNN_LIBNAME "libcudnn_static.a")
else()
set(CUDNN_LIBNAME "cudnn")
endif()
set(CUDNN_LIBRARY $ENV{CUDNN_LIBRARY} CACHE PATH "Path to the cudnn library file (e.g., libcudnn.so)")
if (CUDNN_LIBRARY MATCHES ".*cudnn_static.a" AND NOT CUDNN_STATIC)
message(WARNING "CUDNN_LIBRARY points to a static library (${CUDNN_LIBRARY}) but CUDNN_STATIC is OFF.")
endif()
find_library(CUDNN_LIBRARY_PATH ${CUDNN_LIBNAME}
PATHS ${CUDNN_LIBRARY}
PATH_SUFFIXES lib lib64 cuda/lib cuda/lib64 lib/x64)
```
This code would look for `libcudnn_static.a` if `USE_STATIC_CUDNN` was set.
However, as follow:
<img width="1422" alt="截屏2022-07-19 下午8 02 37" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/73142299/179745670-1d27d21a-eca7-402d-b94e-c2c0701b3757.png">
Newer version of cuDNN does not have the `libcudnn_static.a`.
### Versions
Collecting environment information...
PyTorch version: N/A
Is debug build: N/A
CUDA used to build PyTorch: N/A
ROCM used to build PyTorch: N/A
OS: Ubuntu 18.04.6 LTS (x86_64)
GCC version: (Ubuntu 7.5.0-3ubuntu1~18.04) 7.5.0
Clang version: Could not collect
CMake version: version 3.22.1
Libc version: glibc-2.17
Python version: 3.7.13 (default, Mar 29 2022, 02:18:16) [GCC 7.5.0] (64-bit runtime)
Python platform: Linux-4.19.91-011.ali4000.alios7.x86_64-x86_64-with-debian-buster-sid
Is CUDA available: N/A
CUDA runtime version: 10.2.89
GPU models and configuration: Could not collect
Nvidia driver version: Could not collect
cuDNN version: Probably one of the following:
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_adv_infer.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_adv_train.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_cnn_infer.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_cnn_train.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_ops_infer.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_ops_train.so.8.4.1
HIP runtime version: N/A
MIOpen runtime version: N/A
Is XNNPACK available: N/A
Versions of relevant libraries:
[pip3] numpy==1.21.5
[pip3] torch==1.12.0
[conda] mkl 2022.0.1 h06a4308_117 defaults
[conda] mkl-include 2022.0.1 h06a4308_117 defaults
[conda] numpy 1.21.5 py37hf838250_3 defaults
[conda] numpy-base 1.21.5 py37h1e6e340_3 defaults
[conda] torch 1.12.0 pypi_0 pypi
cc @malfet @seemethere @csarofeen @ptrblck @xwang233
| 5 |
5,205 | 81,684 |
Message exchange failure when perform alltoallv (cpus)
|
high priority, triage review, oncall: distributed, module: c10d
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
When performing an alltoallv message exchange on cpus results in the following error:
--------------------------------------------------------------------
terminate called after throwing an instance of 'gloo::EnforceNotMet'
what(): [enforce fail at ../third_party/gloo/gloo/transport/tcp/pair.cc:490] op.preamble.length <= op.nbytes. 881392472 vs 881392448
---------------------------------------------------------------------
This error is reproducible and a standalone python script is included in this Issue report submission.
This is a very simple script which uses 10 machines/10-processes to reproduce this above mentioned error.
I used 10 machine cluster to reproduce this error repeatedly... however I guess the same may happen on a single machine using 10 processes.
This script performs the following tasks
1. create the processgroup with 10 ranks
2. exchanges no of int64's which will be exchanged, this no. is used on the receiving side to allocate buffers.
3. once the buffers are allocated alltoallv (which is included in the standalone script) is performed to exchange int64's.
4. The error happens when performing alltoallv using cpus.
Some observations about this error:
1. This error happens when sending large messages. The same piece of logic works when smaller messages were sent.
2. Of the 10 processes/rank some of these ranks fail with the above error message. However, the no. of ranks failing is unpredictable... suggesting there is somekind of buffer overwrite or buffer corruption.
3. This standalone script is created by mimic'ing some of the functionality in the application I am working on at the moment.
4. The hardcoded no. of int64's is one such instance when this error is deterministically reproducible.
Please use the following standalone script
```python
import numpy as np
import argparse
import torch
import os
import time
from datetime import timedelta
import torch.distributed as dist
from timeit import default_timer as timer
from datetime import timedelta
def alltoall_cpu(rank, world_size, output_tensor_list, input_tensor_list):
input_tensor_list = [tensor.to(torch.device('cpu')) for tensor in input_tensor_list]
for i in range(world_size):
dist.scatter(output_tensor_list[i], input_tensor_list if i == rank else [], src=i)
def alltoallv_cpu(rank, world_size, output_tensor_list, input_tensor_list):
senders = []
for i in range(world_size):
if i == rank:
output_tensor_list[i] = input_tensor_list[i].to(torch.device('cpu'))
else:
sender = dist.isend(input_tensor_list[i].to(torch.device('cpu')), dst=i, tag=i)
senders.append(sender)
for i in range(world_size):
if i != rank:
dist.recv(output_tensor_list[i], src=i, tag=i)
torch.distributed.barrier()
def splitdata_exec(rank, world_size):
int64_counts = np.array([
[0, 110105856, 110093280, 110116272, 110097840, 110111128, 110174059, 110087008, 110125040, 110087400],#0
[110174059, 0, 110158903, 110160317, 110149564, 110170899, 110166538, 110139263, 110163283, 110154040],#1
[110251793, 110254110, 0, 110243087, 110249640, 110270594, 110248594, 110249172, 110277587, 110242484],#2
[110191018, 110171210, 110170046, 0, 110167632, 110165475, 110174676, 110158908, 110171609, 110158631],#3
[110197278, 110198689, 110193780, 110198301, 0, 110208663, 110184046, 110194628, 110200308, 110168337],#4
[110256343, 110244546, 110248884, 110255858, 110236621, 0, 110247954, 110246921, 110247543, 110243309],#5
[110113348, 109915976, 109891208, 109908240, 109916552, 109917544, 0, 109893592, 109930888, 109895912],#6
[110024052, 109995591, 110003242, 110013125, 110002038, 110013278, 110003047, 0, 110015547, 109981915],#7
[109936439, 109948208, 109937391, 109936696, 109930888, 109941325, 109940259, 109917662, 0, 109917002],#8
[110050394, 110029327, 110036926, 110043437, 110021664, 110051453, 110036305, 110039768, 110054324, 0],#9
])
start = timer()
sizes = int64_counts[rank]
print('[Rank: ', rank, '] outgoing int64 counts: ', sizes)
# buffer sizes send/recv
send_counts = list(torch.Tensor(sizes).type(dtype=torch.int64).chunk(world_size))
recv_counts = list(torch.zeros([world_size], dtype=torch.int64).chunk(world_size))
alltoall_cpu(rank, world_size, recv_counts, send_counts)
#allocate buffers
recv_nodes = []
for i in recv_counts:
recv_nodes.append(torch.zeros(i.tolist(), dtype=torch.int64))
#form the outgoing message
send_nodes = []
for i in range(world_size):
# sending
d = np.ones(shape=(sizes[i]), dtype=np.int64)*rank
send_nodes.append(torch.from_numpy(d))
alltoallv_cpu(rank, world_size, recv_nodes, send_nodes)
end = timer()
for i in range(world_size):
data = recv_nodes[i].numpy()
assert np.all(data == np.ones(data.shape, dtype=np.int64)*i)
print('[Rank: ', rank, '] Done with the test...')
def multi_dev_proc_init(params):
rank = int(os.environ["RANK"])
dist.init_process_group("gloo", rank=rank, world_size=params.world_size, timeout=timedelta(seconds=5*60))
splitdata_exec(rank, params.world_size)
if __name__ == "__main__":
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='Construct graph partitions')
parser.add_argument('--world-size', help='no. of processes to spawn', default=1, type=int, required=True)
params = parser.parse_args()
multi_dev_proc_init(params)
```
### Versions
The output of the python collect_env.py is as follows
```
Collecting environment information...
PyTorch version: 1.8.0a0+ae5c2fe
Is debug build: False
CUDA used to build PyTorch: 11.0
ROCM used to build PyTorch: N/A
OS: Amazon Linux 2 (x86_64)
GCC version: (GCC) 7.3.1 20180712 (Red Hat 7.3.1-9)
Clang version: 7.0.1 (Amazon Linux 2 7.0.1-1.amzn2.0.2)
CMake version: version 3.18.2
Libc version: glibc-2.2.5
Python version: 3.7.9 (default, Aug 27 2020, 21:59:41) [GCC 7.3.1 20180712 (Red Hat 7.3.1-9)] (64-bit runtime)
Python platform: Linux-4.14.200-155.322.amzn2.x86_64-x86_64-with-glibc2.2.5
Is CUDA available: True
CUDA runtime version: 11.0.221
GPU models and configuration:
GPU 0: NVIDIA A10G
GPU 1: NVIDIA A10G
GPU 2: NVIDIA A10G
GPU 3: NVIDIA A10G
GPU 4: NVIDIA A10G
GPU 5: NVIDIA A10G
GPU 6: NVIDIA A10G
GPU 7: NVIDIA A10G
Nvidia driver version: 510.47.03
cuDNN version: Probably one of the following:
/usr/local/cuda-10.1/targets/x86_64-linux/lib/libcudnn.so.7.6.5
/usr/local/cuda-10.2/targets/x86_64-linux/lib/libcudnn.so.7.6.5
/usr/local/cuda-11.0/targets/x86_64-linux/lib/libcudnn.so.8.0.4
/usr/local/cuda-11.0/targets/x86_64-linux/lib/libcudnn_adv_infer.so.8.0.4
/usr/local/cuda-11.0/targets/x86_64-linux/lib/libcudnn_adv_train.so.8.0.4
/usr/local/cuda-11.0/targets/x86_64-linux/lib/libcudnn_cnn_infer.so.8.0.4
/usr/local/cuda-11.0/targets/x86_64-linux/lib/libcudnn_cnn_train.so.8.0.4
/usr/local/cuda-11.0/targets/x86_64-linux/lib/libcudnn_ops_infer.so.8.0.4
/usr/local/cuda-11.0/targets/x86_64-linux/lib/libcudnn_ops_train.so.8.0.4
HIP runtime version: N/A
MIOpen runtime version: N/A
Is XNNPACK available: True
Versions of relevant libraries:
[pip3] numpy==1.19.3
[pip3] pytorch-ignite==0.4.8
[pip3] torch==1.8.0a0
[pip3] torchaudio==0.8.2
[pip3] torchvision==0.9.2+cu111
[conda] Could not collect
```
cc @ezyang @gchanan @zou3519 @pietern @mrshenli @pritamdamania87 @zhaojuanmao @satgera @rohan-varma @gqchen @aazzolini @osalpekar @jiayisuse @SciPioneer @H-Huang @kwen2501
| 2 |
5,206 | 81,682 |
Python operator registration API for subclasses
|
feature, triaged, module: dispatch, module: __torch_dispatch__
|
### 🚀 The feature, motivation and pitch
We have python op registration by @anjali411 but this is only allowed for dispatch keys. A nice extension would be to allow tensor subclasses to be passed in lieu of dispatch key and get the same behavior. This would be an alternative to defining `__torch_dispatch__` but would have better performance in the passthrough case as we could bypass calling into Python in that case.
### Alternatives
_No response_
### Additional context
_No response_
cc @Chillee @ezyang @zou3519 @albanD @samdow
| 0 |
5,207 | 81,681 |
FakeTensor consolidated strategy for in_kernel_invocation and dispatch keys
|
triaged, module: fakeTensor
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
@eellison has done a lot of good work fixing segfaults related to meta tensors incorrectly reporting themselves as cpu tensors (due to fake tensor) and then causing in c++ code that is subsequently expecting the tensor in question to actually be a cpu tensor and have real data. This issue is an attempt to explicate the underlying conceptual strategy for how to decide whether or not to treat a fake tensor as a cpu tensor or not.
The fundamental problem is we have two opposing requirements:
* We wish fake tensors to mimic CPU/CUDA tensors as much as possible, so that a fake tensor behaves much the same way as their real brethren. This applies to both to device tests (e.g., looking at device, or is_cpu) as well as to dispatch key dispatch (relevant for any functionality keys, esp autocast)
* We don't want any code that directly accesses pointer data to operate on fake tensors, as there isn't any data and you will segfault.
Here is a simple heuristic for how to distinguish:
* In Python, direct data access never happens, we advertise as CPU/CUDA
* In C++, where direct data access can happen, we advertise as Meta
But this is inaccurate on a number of fronts:
* When we autocast, we want to get the CPU/CUDA autocast logic on meta tensors, otherwise the dtype is not accurate. But we don't set CPU/CUDA dispatch key on fake tensor, so we don't get the corresponding autocast logic. Repro:
```
import torch
from torch._subclasses.fake_tensor import FakeTensorMode
def f():
x = torch.randn(2, 3, requires_grad=True)
y = torch.randn(3, 4)
with torch.autocast('cpu'):
r = x @ y
return r
with FakeTensorMode():
r = f()
print(r)
# prints FakeTensor(cpu, torch.Size([2, 4]), torch.float32)
# should be bfloat32
```
* When we query for device on a FakeTensor, this unconditionally dispatches to `torch.ops.aten.device`, no matter if subclass dispatch is disabled. This means that without some other logic, we will report the wrong device type in C++. This is why `in_kernel_invocation_manager` exists in the fake tensor implementation today
It would be good to have a clearer delineation of the boundary here. This is also intimately related to https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/81471 where FunctionalWrapperTensors don't have full implementation and also must avoid hitting Dense kernels.
It seems to me that the right way to do this is to focus on "direct data access". Our primary problem is avoiding direct access to data pointers. This happens only at a very specific part of the dispatch key order (Dense and similar). So we just need to make sure these keys are not runnable, either by removing the Dense from the functionality dispatch key set, or by adding another dispatch key in front of all of these keys to "block" execution of those keys (this is how Python key and wrapper subclass works).
PS What's the difference between wrapper subclass and fake tensor? At this point, it seems primarily because fake tensor "is a" meta tensor, which makes it marginally more efficient (one dynamic allocation rather than two) and means in C++ we can go straight to meta tensor implementation in the back... it's kind of weak, sorry @eellison for making you suffer with is-a haha.
cc @bdhirsh @Chillee
### Versions
master
| 3 |
5,208 | 81,680 |
Provide an option to disable CUDA_GCC_VERSIONS
|
module: build, triaged
|
### 🚀 The feature, motivation and pitch
I really understand the motivations of recent additions to CUDA_GCC_VERSIONS that were done in
* https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/commit/86deecd7be248016d413e9ad6f5527a70c88b454
* https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/63230
I do think they are a step in the right direction toward improving the situation (xref https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/55267)
I'm wondering if you could add an option, as an environment variable, for us to ignore it. The motivation is that I believe that it is possible to patch up the GCC 10 compiler with a small patch to help nvidia compatibility.
https://github.com/conda-forge/ctng-compilers-feedstock/blob/main/recipe/meta.yaml#L22=
### Alternatives
I can patch things out.... However, I would rather have the override done by other packagers that assert they know what they are doing.
You can also patch things out with a sed command
```
sed -i '/ (MINIMUM_GCC_VERSION,/d' ${SP_DIR}/torch/utils/cpp_extension.py
```
### Additional context
The other motivation is that soon enough, the GCC 11 compilers should be compatible with nvidia.
I also believe that 10.4 is compatible with the nvcc
cc @malfet @seemethere
| 5 |
5,209 | 81,678 |
Export quantized shufflenet_v2_x0_5 to ONNX
|
module: onnx, triaged, onnx-triaged
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
Fail to export quantized shufflenet_v2_x0_5 to ONNX using the following code:
```python
import io
import numpy as np
import torch
import torch.utils.model_zoo as model_zoo
import torch.onnx
import torchvision.models.quantization as models
torch_model = models.shufflenet_v2_x0_5(pretrained=True, quantize=True)
torch_model.eval()
batch_size = 1
input_float = torch.zeros(1, 3, 224, 224)
input_tensor = input_float
torch_out = torch.jit.trace(torch_model, input_tensor)
# Export the model
torch.onnx.export(torch_model, # model being run
input_tensor, # model input (or a tuple for multiple inputs)
"shufflenet_v2_x0_5_qdq.onnx", # where to save the model (can be a file or file-like object)
export_params=True, # store the trained parameter weights inside the model file
opset_version=16, # the ONNX version to export the model to
do_constant_folding=True, # whether to execute constant folding for optimization
input_names = ['input'], # the model's input names
output_names = ['output'], # the model's output names
dynamic_axes={'input' : {0 : 'batch_size'}, # variable length axes
'output' : {0 : 'batch_size'}})
```
Stacktrace:
```text
/home/skyline/miniconda3/envs/torch-nightly-py39/lib/python3.9/site-packages/torchvision/models/_utils.py:208: UserWarning: The parameter 'pretrained' is deprecated since 0.13 and will be removed in 0.15, please use 'weights' instead.
warnings.warn(
/home/skyline/miniconda3/envs/torch-nightly-py39/lib/python3.9/site-packages/torchvision/models/_utils.py:223: UserWarning: Arguments other than a weight enum or `None` for 'weights' are deprecated since 0.13 and will be removed in 0.15. The current behavior is equivalent to passing `weights=ShuffleNet_V2_X0_5_QuantizedWeights.IMAGENET1K_FBGEMM_V1`. You can also use `weights=ShuffleNet_V2_X0_5_QuantizedWeights.DEFAULT` to get the most up-to-date weights.
warnings.warn(msg)
/home/skyline/miniconda3/envs/torch-nightly-py39/lib/python3.9/site-packages/torch/onnx/_patch_torch.py:67: UserWarning: The shape inference of prim::TupleConstruct type is missing, so it may result in wrong shape inference for the exported graph. Please consider adding it in symbolic function. (Triggered internally at /opt/conda/conda-bld/pytorch_1658041842671/work/torch/csrc/jit/passes/onnx/shape_type_inference.cpp:1874.)
torch._C._jit_pass_onnx_node_shape_type_inference(
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "/home/skyline/Projects/python-playground/ml/ModelConversion/torch_quantizied_model_to_onnx.py", line 20, in <module>
torch.onnx.export(torch_model, # model being run
File "/home/skyline/miniconda3/envs/torch-nightly-py39/lib/python3.9/site-packages/torch/onnx/utils.py", line 479, in export
_export(
File "/home/skyline/miniconda3/envs/torch-nightly-py39/lib/python3.9/site-packages/torch/onnx/utils.py", line 1411, in _export
graph, params_dict, torch_out = _model_to_graph(
File "/home/skyline/miniconda3/envs/torch-nightly-py39/lib/python3.9/site-packages/torch/onnx/utils.py", line 1054, in _model_to_graph
graph = _optimize_graph(
File "/home/skyline/miniconda3/envs/torch-nightly-py39/lib/python3.9/site-packages/torch/onnx/utils.py", line 624, in _optimize_graph
graph = _C._jit_pass_onnx(graph, operator_export_type)
File "/home/skyline/miniconda3/envs/torch-nightly-py39/lib/python3.9/site-packages/torch/onnx/utils.py", line 1744, in _run_symbolic_function
return symbolic_fn(g, *inputs, **attrs)
File "/home/skyline/miniconda3/envs/torch-nightly-py39/lib/python3.9/site-packages/torch/onnx/symbolic_opset13.py", line 716, in conv2d_relu
input, input_scale, _, _ = symbolic_helper.dequantize_helper(g, q_input)
File "/home/skyline/miniconda3/envs/torch-nightly-py39/lib/python3.9/site-packages/torch/onnx/symbolic_helper.py", line 1235, in dequantize_helper
unpacked_qtensors = _unpack_tuple(qtensor)
File "/home/skyline/miniconda3/envs/torch-nightly-py39/lib/python3.9/site-packages/torch/onnx/symbolic_helper.py", line 167, in _unpack_tuple
raise RuntimeError(
RuntimeError: ONNX symbolic expected node type `prim::TupleConstruct`, got `%423 : Tensor(*, *, *, *) = onnx::Slice(%x.8, %419, %422, %411), scope: __module.stage2/__module.stage2.1 # /home/skyline/miniconda3/envs/torch-nightly-py39/lib/python3.9/site-packages/torchvision/models/quantization/shufflenetv2.py:42:0
`
```
### Versions
PyTorch version: 1.13.0.dev20220717
Is debug build: False
CUDA used to build PyTorch: None
ROCM used to build PyTorch: N/A
OS: Ubuntu 22.04 LTS (x86_64)
GCC version: (Ubuntu 11.2.0-19ubuntu1) 11.2.0
Clang version: 14.0.6
CMake version: version 3.22.1
Libc version: glibc-2.35
Python version: 3.9.12 (main, Jun 1 2022, 11:38:51) [GCC 7.5.0] (64-bit runtime)
Python platform: Linux-5.10.102.1-microsoft-standard-WSL2-x86_64-with-glibc2.35
Is CUDA available: False
CUDA runtime version: No CUDA
GPU models and configuration: No CUDA
Nvidia driver version: No CUDA
cuDNN version: No CUDA
HIP runtime version: N/A
MIOpen runtime version: N/A
Is XNNPACK available: True
Versions of relevant libraries:
[pip3] numpy==1.23.1
[pip3] torch==1.13.0.dev20220717
[pip3] torchaudio==0.13.0.dev20220717
[pip3] torchvision==0.14.0.dev20220717
[conda] blas 1.0 mkl
[conda] cpuonly 2.0 0 pytorch-nightly
[conda] cudatoolkit 10.2.89 hfd86e86_1
[conda] mkl 2021.4.0 h06a4308_640
[conda] mkl-service 2.4.0 py39h7f8727e_0
[conda] mkl_fft 1.3.1 py39hd3c417c_0
[conda] mkl_random 1.2.2 py39h51133e4_0
[conda] numpy 1.23.1 pypi_0 pypi
[conda] numpy-base 1.22.3 py39hf524024_0
[conda] pytorch 1.13.0.dev20220717 py3.9_cpu_0 pytorch-nightly
[conda] pytorch-mutex 1.0 cpu pytorch-nightly
[conda] torchaudio 0.13.0.dev20220717 py39_cpu pytorch-nightly
[conda] torchvision 0.14.0.dev20220717 py39_cpu pytorch-nightly
| 4 |
5,210 | 81,669 |
Register refs for CompositeImplicitAutograd ops as decompositions
|
triaged, module: primTorch
|
There are some ops that explicitly don't have decompositions registered because they are CompositeImplicitAutograd
https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/blob/bf36d8b987b2ef2fd9cb26bae3acc29c03b05072/test/test_ops.py#L1538-L1567
However, it is still possible to observe them in inference mode (or possibly if CompositeImplicitAutograd is overridden by a different kernel)
```python
from torch.testing._internal.logging_tensor import capture_logs_with_logging_tensor_mode
with capture_logs_with_logging_tensor_mode() as logs:
with torch.inference_mode():
a = torch.ones(2, 2)
a.reshape(-1)
print('\n'.join(logs))
# $0 = torch._ops.aten.ones.default([2, 2], dtype=torch.float32, device=device(type='cpu'), pin_memory=False)
# $1 = torch._ops.aten.reshape.default($0, [-1])
```
When registering these ops as decompositions, to appease the test that detects that we have indeed registered it in the table, we may need to specify what op it decomposes into:
https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/blob/443b13fa232c52bddf20726a6da040d8957a3c49/torch/testing/_internal/common_methods_invocations.py#L744-L745
cc @ezyang @mruberry @ngimel
| 6 |
5,211 | 81,667 |
[Tracker] AO migration of quantization from `torch.nn` to `torch.ao.nn`
|
oncall: quantization, low priority, triaged
|
## Motivation
There are several locations under the `torch.nn` that are related to the quantization. In order to reduce the cluttering and "takeover" by the quantization, the nn modules that are relevant are being migrated to `torch.ao`.
## Timeline
### Upcoming deadlines
- [x] 08/2022: Migration of the code from `torch.nn` to `torch.ao.nn`. At this point both location could be used, while the old location would have `from torch.ao... import ...`
- [x] 08/2022: Importing from the `torch.nn` would show a deprecation warning
- [ ] PyTorch 1.14 ~~1.13~~: Documentation updated from old locations to AO locations
- [ ] PyTorch 1.14 ~~1.13~~: Tutorials updated from old locations to AO locations
- [ ] PyTorch 1.14 ~~1.13~~: The deprecation warning is shown
- [ ] PyTorch 1.14+: The deprecation error is shown
- [ ] PyTorch 1.14+: The `torch.nn` location is cleaned up and not usable anymore.
### TODOs
- [ ] All docstrings within `torch.ao` are up to date (classes and functions)
- Note: If not cleaned up, these will generate a lot of duplicates under the `generated`
- Example: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/blob/015b05af18b78ca9c77c997bc277eec66b5b1542/torch/ao/nn/quantized/dynamic/modules/conv.py#L22
- [ ] The documentation in the `docs` is only referring to the `torch.ao` for quantization related stuff
- Note: There are a lot of `:noindex:` in the documentation that need to be cleaned up
- Note: There are a lot of `.. py::module::` in the documentation that need to be cleaned up
- Example: https://github.dev/pytorch/pytorch/blob/015b05af18b78ca9c77c997bc277eec66b5b1542/docs/source/quantization-support.rst#L410
- [ ] Tutorials that are using the `torch.ao`
- [ ] https://pytorch.org/tutorials/intermediate/realtime_rpi.html
- [ ] https://pytorch.org/tutorials/advanced/dynamic_quantization_tutorial.html
- [ ] https://pytorch.org/tutorials/intermediate/dynamic_quantization_bert_tutorial.html
- [ ] https://pytorch.org/tutorials/intermediate/quantized_transfer_learning_tutorial.html
- [ ] https://pytorch.org/tutorials/advanced/static_quantization_tutorial.html
- [ ] Blog posts
- Note: THis is one of the blog posts: https://pytorch.org/blog/introduction-to-quantization-on-pytorch/
### Complete
- [x] `torch.nn.quantized` → `torch.ao.nn.quantized`
- [x] [`torch.nn.quantized.functional` → `torch.ao.nn.quantized.functional`](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/78712)
- [x] [`torch.nn.quantized.modules` → `torch.ao.nn.quantized.modules`](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/78713)
- [x] [`torch.nn.quantized.dynamic` → `torch.ao.nn.quantized.dynamic`](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/78714)
- [x] [`torch.nn.quantized._reference` → `torch.ao.nn.quantized._reference`](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/78715)
- [x] [`torch.nn.quantizable` → `torch.ao.nn.quantizable`](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/78717)
- [x] [`torch.nn.qat` → `torch.ao.nn.qat`](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/78716)
- [x] `torch.nn.qat.modules` → `torch.ao.nn.qat.modules`
- [x] `torch.nn.qat.dynamic` → `torch.ao.nn.qat.dynamic`
- [x] `torch.nn.intrinsic` → `torch.ao.nn.intrinsic`
- [x] [`torch.nn.intrinsic.modules` → `torch.ao.nn.intrinsic.modules`](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/84842)
- [x] [`torch.nn.intrinsic.qat` → `torch.ao.nn.intrinsic.qat`](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/86171)
- [x] [`torch.nn.intrinsic.quantized` → `torch.ao.nn.intrinsic.quantized`](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/86172)
- [x] `torch.nn.intrinsic.quantized.modules` → `torch.ao.nn.intrinsic.quantized.modules`
- [x] `torch.nn.intrinsic.quantized.dynamic` → `torch.ao.nn.intrinsic.quantized.dynamic`
## Blockers
1. Preserving the blame history
1. Currently, we are pushing for the internal blame history preservation, as the sync between internal and external history post-migration proves to be non-trivial
cc @jerryzh168 @jianyuh @raghuramank100 @jamesr66a @vkuzo @jgong5 @Xia-Weiwen @leslie-fang-intel @anjali411 @albanD
| 2 |
5,212 | 81,654 |
[packaging] Conda install missing python local version label (+cu123 or +cpu)
|
oncall: releng, triaged
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
I'm installing pytorch through Conda then using poetry in my projects.
The issue is that when I use the recommended installation method for pytorch (`conda install -y -c pytorch pytorch==1.11.0 cudatoolkit=11.3`), I end up with:
`conda list`: `pytorch 1.11.0 py3.7_cuda11.3_cudnn8.2.0_0 pytorch`.
`pip list`: `torch 1.11.0`.
My issue is that conda installed torch `1.11.0+cu113` but did not include the local version label (`+cu113`), so then when I use pip or poetry, it thinks it needs to replace torch `1.11.0` by `1.11.0+cu113`.
I use this dirty hack to fix the package version of torch:
```bash
mv /[...]/conda/lib/python3.7/site-packages/torch-1.11.0-py3.7.egg-info/ /[...]/conda/lib/python3.7/site-packages/torch-1.11.0+cu113-py3.7.egg-info/
sed -i -E 's/(Version: [^+]+)\n/\1+cu113\n/' /opt/conda/lib/python3.7/site-packages/torch-1.11.0+cu113-py3.7.egg-info/PKG-INFO
```
### Versions
PyTorch version: 1.11.0
Is debug build: False
CUDA used to build PyTorch: 11.3
ROCM used to build PyTorch: N/A
OS: Ubuntu 20.04.3 LTS (x86_64)
GCC version: Could not collect
Clang version: Could not collect
CMake version: Could not collect
Libc version: glibc-2.17
Python version: 3.7.13 (default, Mar 29 2022, 02:18:16) [GCC 7.5.0] (64-bit runtime)
| 0 |
5,213 | 81,651 |
optimize_for_mobile has an issue with constant operations at the end of a loop
|
oncall: mobile
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
I've been working on a model that I want to optimize for mobile, but when optimizing the model for mobile, I ran into an issue with an operation at the end of a loop. I'll use the code example below to show the issue:
```
import torch
from torch import nn
from torch.utils.mobile_optimizer import optimize_for_mobile
class testModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(testModel, self).__init__()
# Input is 5, output is 5
self.m = nn.ModuleList([nn.Linear(5, 5) for i in range(5)])
# Forward takes noise as input and returns 5 outputs
# from the network
def forward(self, X):
# the output is initially all ones
Y = torch.ones((5))
# array to hold the outputs
out = []
# Iterate 5 times to get 5 outputs
for i in range(0, 5):
# Send the inputs through the blocks
for b in self.m:
Y = b(Y)
# Save the ith output
out.append(Y[i])
# Add a constant to the ith value of Y. This
# is what breaks the optimized model
Y[i] *= 2
return torch.stack(out)
def main():
# Create a new network
model = testModel()
# Trash input
X = torch.zeros((5))
# Get the network output
Y = model(X)
# Create torch script form of the model
ts_model = torch.jit.trace(model, X)
ts_model_mobile = optimize_for_mobile(ts_model)
# Get the output from the torch script models
Y_ts_model = ts_model(X)
Y_ts_model_mobile = ts_model_mobile(X)
print(ts_model_mobile.code)
# What are the outputs from the model?
print("Original: ", Y)
print("Optimized: ", Y_ts_model)
print("Mobile Optimized: ", Y_ts_model_mobile)
# The output of the model should be the same as the
# output from the optimized models
assert torch.all(Y.eq(Y_ts_model)), "Torch script different from original model"
assert torch.all(Y.eq(Y_ts_model_mobile)), "Mobile torch script different from original model"
if __name__=='__main__':
main()
```
If you run the code, you would expect the output of the torch script model to be the same as the output of the original model, but the outputs of the models are slightly off. The original traced module works perfectly fine, but the mobile script runs into an issue where the output is slightly off for all values in the output vector (excluding the first). Taking a look at the mobile torch script code, I think I see what the issue is:
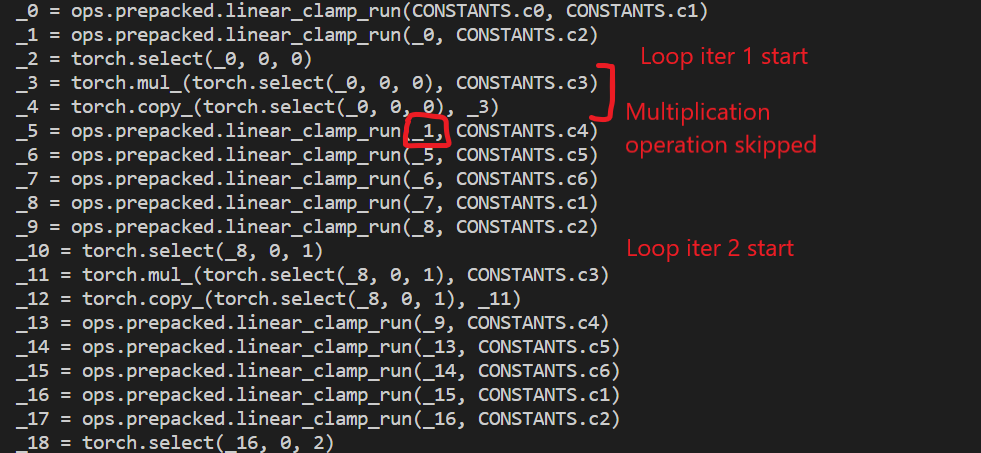
At the beginning of each loop, it applies the constant multiplication operation. The first operation is applied at _3 and _4. This operation should be applied after the loop instead of at the beginning.
Another issue (which I think is the main problem) is after the multiplication operation is performed on the Y tensor (at _3 and _4), the value is never used. As seen in _5, the _1 tensor is used which is the tensor before the constant operation is applied. Instead, the forward method at _5 should probably be using _4.
### Versions
torch: 1.12.0
| 2 |
5,214 | 81,650 |
RFC: auto-generated plain Tensor argument only sparse primitives
|
module: sparse, triaged
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
When we say `at::add(sparse_x, sparse_y)`, this is an operator that takes in two sparse tensors and produces a sparse tensor. This requires a backend compiler to have a model of what it means to be a sparse tensor. Sometimes, this is inconvenient for a backend; the backend would rather have the input all be in terms of dense inputs.
We can help by generating sparse prims that are expressed entirely in terms of dense tensors. So for example, the sparse variant of at::add above would be `sparse_prims::add(self_sparse_dim: int, self_dense_dim: int, self_size: int[], self_indices: Tensor, self_values: Tensor, other_sparse_dim: int, other_dense_dim: int, other_size: int[], other_indices: Tensor, other_values: Tensor) -> (int, int, int[], Tensor, Tensor)`. Essentially, each of the substantive fields in the sparse tensor (sparse dim, dense dim, size, indices and values) has been inlined into the function argument. The new function signature is Tensors only and doesn't have any explicit sparse tensors.
Some notes:
* In many situations, a sparse operation isn't supported in full generality. For example, the add signature above suggests that it is ok to mix different amounts of sparse/dense dims in addition. In actuality, they have to be the same (so the second pair of sparse dense dims could be deleted.) This simplification cannot be done mechanically, you have to know about the preconditions for the function. But we could imagine further decomposing these prims by hand into simpler versions, eliminating the need for backends to do this error checking.
* You need separate sparse prim for multiple dispatch; e.g. dense-sparse addition needs yet another prim. sparse-dense addition should decompose into dense-sparse and thus not require another prim.
* AOTDispatch would be responsible for unpacking and repacking the dense tensors into sparse tensors.
* This trick applies to all TensorImpl subclasses which ultimately backend to dense tensors
We could also *not* do this and force passes and compilers to know how to deal with sparse tensors directly.
cc @nikitaved @pearu @cpuhrsch @amjames, please tag anyone else relevant
cc @bdhirsh
### Versions
master
| 2 |
5,215 | 81,649 |
Idiom for PrimTorch refs for Tensor methods
|
triaged, module: primTorch
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
Right now if you want to write a ref for a Tensor method, there's no precedent for how to do this. Some of these right now are getting dumped directly in torch._refs which is wrong (since torch._refs.foo should only exist if torch.foo exists, but some methods do not exist as functions) and getting remapped with `torch_to_refs_map`
The goal would be to create some sort of synthetic class or module for tensor methods, and then automatically map tensor methods to that class, so that TorchRefsMode works out of the box with a new tensor without having to route through a special case mapping.
### Versions
master
cc @ezyang @mruberry @ngimel
| 0 |
5,216 | 81,648 |
`sparse_coo.to_dense()` produces different results between CPU and CUDA backends for boolean non-coalesced inputs.
|
module: sparse, triaged
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
As per title. To reproduce, run the following:
```python
In [1]: import torch
In [2]: idx = torch.tensor([[1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2], [2, 2, 1, 3, 3, 3]], dtype=torch.long)
In [3]: val = torch.tensor([True, False, True, False, False, True])
In [4]: s = torch.sparse_coo_tensor(idx, val, size=(10, 10))
In [5]: torch.all(s.to('cuda').to_dense() == s.to_dense().to('cuda'))
Out[5]: tensor(False, device='cuda:0')
```
The CPU result seems correct, so I assume a parallelization issue.
### Versions
Current master.
cc @nikitaved @pearu @cpuhrsch @amjames
| 4 |
5,217 | 81,635 |
Windows Debug binaries crash on forward: assert fail on IListRefIterator destructor
|
oncall: jit
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
libtorch 1.12 CUDA 11.6 on windows
I load a saved jit model, run it with the Release binary and it works.
If instead I compile and link with Debug binaries, at the 'forward' call i got an assert fail.
Line 405 of IListRef.h
In the trace i read a lot of box-unbox and a call to 'materialize'.
I believe the crash happens at the end of the forward, bceause some time has passed and the ram has been filled by some Gbs.
### Versions
[pip3] numpy==1.23.1
[pip3] torch==1.12.0+cu116
[pip3] torchaudio==0.12.0+cu116
[pip3] torchvision==0.13.0+cu116
[conda] Could not collect
| 1 |
5,218 | 81,626 |
DISABLED test_profiler (test_jit.TestJit)
|
oncall: jit, module: flaky-tests, skipped
|
Platforms: linux
This test was disabled because it is failing in CI. See [recent examples](https://hud.pytorch.org/flakytest?name=test_profiler&suite=test_jit.TestJit&file=test_jit.py) and the most recent trunk [workflow logs](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/runs/7381856543).
Over the past 3 hours, it has been determined flaky in 1 workflow(s) with 1 red and 1 green.
| 6 |
5,219 | 81,625 |
[bug] the output shape from torch::mean and torch::var is different in libtorch
|
module: cpp, triaged
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
~~~
#include <torch/torch.h>
#include <ATen/ATen.h>
torch::Tensor x = torch::randn({3,4,5});
at::IntArrayRef dim{{0,2}};
std::cout << x.mean(dim, 1).sizes() << std::endl;
/*
[1, 4, 1]
*/
std::cout << x.var(dim, 1).sizes() << std::endl;
/*
[4]
*/
~~~
the shape of output from mean and var is not compatible.
### Versions
libtorch: 1.11.0+cu113
cc @jbschlosser
| 0 |
5,220 | 81,622 |
[Distributed] test_dynamic_rpc_existing_rank_can_communicate_with_new_rank_cuda fails in caching allocator
|
oncall: distributed
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
Code to reproduce the issue:
```python
python distributed/rpc/test_tensorpipe_agent.py -v -k test_dynamic_rpc_existing_rank_can_communicate_with_new_rank_cuda
```
Output:
```python
INFO:torch.distributed.nn.jit.instantiator:Created a temporary directory at /tmp/tmpce6ewbo1
INFO:torch.distributed.nn.jit.instantiator:Writing /tmp/tmpce6ewbo1/_remote_module_non_scriptable.py
test_dynamic_rpc_existing_rank_can_communicate_with_new_rank_cuda (__main__.TensorPipeTensorPipeAgentRpcTest) ... INFO:numba.cuda.cudadrv.driver:init
INFO:torch.testing._internal.common_distributed:Started process 0 with pid 64064
INFO:torch.testing._internal.common_distributed:Started process 1 with pid 64065
INFO:torch.testing._internal.common_distributed:Started process 2 with pid 64066
INFO:torch.testing._internal.common_distributed:Started process 3 with pid 64067
INFO:torch.distributed.nn.jit.instantiator:Created a temporary directory at /tmp/tmpj5jtkv1l
INFO:torch.distributed.nn.jit.instantiator:Writing /tmp/tmpj5jtkv1l/_remote_module_non_scriptable.py
INFO:torch.distributed.nn.jit.instantiator:Created a temporary directory at /tmp/tmp3xq_65qx
INFO:torch.distributed.nn.jit.instantiator:Writing /tmp/tmp3xq_65qx/_remote_module_non_scriptable.py
INFO:torch.distributed.nn.jit.instantiator:Created a temporary directory at /tmp/tmp0oc80wck
INFO:torch.distributed.nn.jit.instantiator:Writing /tmp/tmp0oc80wck/_remote_module_non_scriptable.py
INFO:torch.distributed.nn.jit.instantiator:Created a temporary directory at /tmp/tmpp47jqr8l
INFO:torch.distributed.nn.jit.instantiator:Writing /tmp/tmpp47jqr8l/_remote_module_non_scriptable.py
INFO:torch.testing._internal.common_distributed:Starting event listener thread for rank 1
INFO:torch.testing._internal.common_distributed:Starting event listener thread for rank 0
INFO:torch.testing._internal.common_distributed:Starting event listener thread for rank 2
INFO:torch.testing._internal.common_distributed:Starting event listener thread for rank 3
INFO:torch.distributed.distributed_c10d:Added key: store_based_barrier_key:1 to store for rank: 0
INFO:torch.distributed.distributed_c10d:Added key: store_based_barrier_key:1 to store for rank: 1
INFO:torch.distributed.distributed_c10d:Added key: store_based_barrier_key:1 to store for rank: 3
INFO:torch.distributed.distributed_c10d:Rank 3: Completed store-based barrier for key:store_based_barrier_key:1 with 4 nodes.
INFO:torch.distributed.distributed_c10d:Added key: store_based_barrier_key:1 to store for rank: 2
INFO:torch.distributed.distributed_c10d:Rank 1: Completed store-based barrier for key:store_based_barrier_key:1 with 4 nodes.
INFO:torch.distributed.distributed_c10d:Rank 2: Completed store-based barrier for key:store_based_barrier_key:1 with 4 nodes.
INFO:torch.distributed.distributed_c10d:Rank 0: Completed store-based barrier for key:store_based_barrier_key:1 with 4 nodes.
terminate called after throwing an instance of 'c10::Error'
what(): 0 <= device && static_cast<size_t>(device) < device_allocator.size() INTERNAL ASSERT FAILED at "/workspace/src/pytorch/c10/cuda/CUDACachingAllocator.cpp":1602, please report a bug to PyTorch. Allocator not initialized for device 1: did you call init?
Exception raised from malloc at /workspace/src/pytorch/c10/cuda/CUDACachingAllocator.cpp:1602 (most recent call first):
frame #0: c10::Error::Error(c10::SourceLocation, std::__cxx11::basic_string<char, std::char_traits<char>, std::allocator<char> >) + 0x6c (0x7f63d94b96cc in /workspace/src/pytorch/torch/lib/libc10.so)
frame #1: c10::detail::torchCheckFail(char const*, char const*, unsigned int, std::__cxx11::basic_string<char, std::char_traits<char>, std::allocator<char> > const&) + 0xfa (0x7f63d948f12c in /workspace/src/pytorch/torch/lib/libc10.so)
frame #2: c10::detail::torchInternalAssertFail(char const*, char const*, unsigned int, char const*, std::__cxx11::basic_string<char, std::char_traits<char>, std::allocator<char> > const&) + 0x53 (0x7f63d94b73e3 in /workspace/src/pytorch/torch/lib/libc10.so)
...
```
Unsure, if the test is executed in an unsupported way or why CI isn't seeing this issue.
### Versions
Current master build at [fe7262329c](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/commit/fe7262329c6ae702df185bdbeac702e0d2edc123) on a node with 8x A100.
cc @pietern @mrshenli @pritamdamania87 @zhaojuanmao @satgera @rohan-varma @gqchen @aazzolini @osalpekar @jiayisuse @SciPioneer @H-Huang @kwen2501
| 1 |
5,221 | 81,620 |
PyTorch 1.12 cu113 Illegal Memory Access or Internal Error instead of Out of Memory cases
|
module: cudnn, module: cuda, triaged
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
I'm currently doing benchmark runs on latest timm release with PyTorch 1.12 cu113 (conda) to update timing spreadsheets. I've run into a number of cases where out of memory situations are not being picked up correctly (for illegal memory access, unrecoverable within same process). @ptrblck has mentioned these should be reported. Previous 1.11 cu113 runs were completely clean for contiguous and had only a few channels_last cases.
The illegal memory access are consistent every run (if using same starting batch size), verified across more than one machine.
`CUDA error: an illegal memory access was encountered`:
* vgg11
* vgg13
* vgg16
* vgg19
* nf_regnet_b5
The CUDNN_STATUS_INTERNAL_ERROR model failures below are not as consistent, I have reproduced most of them, but sometimes fail with correct OOM error on a different machine or across same machine restart.
`cuDNN error: CUDNN_STATUS_INTERNAL_ERROR`
* resnetv2_50x3_bitm
* resnetv2_101x3_bitm
* resnetv2_152x2_bit_teacher_384
* resnetv2_152x2_bitm
All failures were recorded on RTX 3090, running `timm` benchmark script (in root of, https://github.com/rwightman/pytorch-image-models) as per example below (with a starting batch size of 1024). Starting w/ a lower batch size for all failure cases will succeed.
ex: `python benchmark.py --amp --model nf_regnet_b5 --bench inference -b 1024`
### Versions
```
Collecting environment information...
PyTorch version: 1.12.0
Is debug build: False
CUDA used to build PyTorch: 11.3
ROCM used to build PyTorch: N/A
OS: Ubuntu 20.04.3 LTS (x86_64)
GCC version: (Ubuntu 9.3.0-17ubuntu1~20.04) 9.3.0
Clang version: Could not collect
CMake version: Could not collect
Libc version: glibc-2.31
Python version: 3.10.4 (main, Mar 31 2022, 08:41:55) [GCC 7.5.0] (64-bit runtime)
Python platform: Linux-5.4.0-99-generic-x86_64-with-glibc2.31
Is CUDA available: True
CUDA runtime version: 11.4.152
GPU models and configuration:
GPU 0: NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3090
GPU 1: NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3090
GPU 2: NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3090
Nvidia driver version: 470.103.01
cuDNN version: Could not collect
HIP runtime version: N/A
MIOpen runtime version: N/A
Is XNNPACK available: True
Versions of relevant libraries:
[pip3] numpy==1.22.3
[pip3] torch==1.12.0
[pip3] torchvision==0.13.0
[conda] blas 1.0 mkl
[conda] cudatoolkit 11.3.1 h2bc3f7f_2
[conda] ffmpeg 4.3 hf484d3e_0 pytorch
[conda] mkl 2021.4.0 h06a4308_640
[conda] mkl-service 2.4.0 py310h7f8727e_0
[conda] mkl_fft 1.3.1 py310hd6ae3a3_0
[conda] mkl_random 1.2.2 py310h00e6091_0
[conda] numpy 1.22.3 py310hfa59a62_0
[conda] numpy-base 1.22.3 py310h9585f30_0
[conda] pytorch 1.12.0 py3.10_cuda11.3_cudnn8.3.2_0 pytorch
[conda] pytorch-mutex 1.0 cuda pytorch
[conda] torchvision 0.13.0 py310_cu113 pytorch
```
cc @csarofeen @ptrblck @xwang233 @ngimel
| 6 |
5,222 | 81,608 |
FakeTensorMode cannot handle non-fake tensor, but non-fake tensors can arise from non-interposable Tensor construction calls
|
triaged, oncall: pt2
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
Currently, FakeTensorMode does not support non-Fake inputs in operations, except in a few special cases. These special cases typically have to do with cases where we produce tensors deep in the bowels of ATen via a non-dispatchable function, so FakeTensorMode doesn't get to interpose on the construction and we end up with a freshly generated non-fake tensor floating around.
The particular case I noticed this occurring was `at::scalar_to_tensor`, which internally bypasses the dispatcher (actually, I'm pretty sure the guards are unnecessary):
```
template <typename scalar_t>
inline void fill_inplace(Tensor& self, const Scalar& value_scalar) {
auto value = value_scalar.to<scalar_t>();
scalar_t* dptr = static_cast<scalar_t*>(self.data_ptr());
*dptr = value;
}
}
namespace detail {
Tensor& scalar_fill(Tensor& self, const Scalar& value) {
AT_DISPATCH_ALL_TYPES_AND_COMPLEX_AND4(
kComplexHalf, kHalf, kBool, kBFloat16, self.scalar_type(), "fill_out", [&]() {
fill_inplace<scalar_t>(self, value);
});
return self;
}
Tensor scalar_tensor_static(const Scalar& s, c10::optional<ScalarType> dtype_opt, c10::optional<Device> device_opt) {
at::tracer::impl::NoTracerDispatchMode tracer_guard;
at::AutoDispatchBelowAutograd mode;
Tensor result = at::detail::empty_cpu(
{}, dtype_opt, c10::nullopt, device_opt, c10::nullopt, c10::nullopt);
scalar_fill(result, s);
return result;
}
```
This makes it similar to `torch.tensor` in Python: a tensor constant materializes out of nowhere, and so if we want a mode to be able to interpose on it, we have to then call the result with `at::lift_fresh`.
Now, I'm a little leery about actually inserting the dispatcher call here, because we explicitly removed the dispatch call for speed (from @ailzhang in #29915). And in fact, we only have to worry about a bare `scalar_to_tensor` call for composite ops. In https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/81609 ~~I remove `scalar_to_tensor` from autograd formulas which are interpreted as composites and was the source of the bug I was tracking down. All other usages are OK.~~ I ended up *only* calling `lift_fresh` in the derivative formulas, and not in `scalar_to_tensor` generally. Testing this feels like a beefier form of composite compliance https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/blob/master/aten/src/ATen/native/README.md#composite-compliance (cc @ezyang @zou3519 ).
The crux of the matter is this: if we don't allow FakeTensorMode to handle non-fake tensor, we must audit all composite functions for calls to non-dispatching functions that construct Tensors, and make them not call that or call lift. This includes auditing for uses of `scalar_to_tensor` in composites beyond the derivative formulas (which I have finished auditing). However, we have another option: we can make FakeTensorMode handle non-fake tensors, by implicitly adding the equivalent of a `lift_fresh` call whenever it sees an unknown tensor. However, this makes it easier for an end user of fake tensor to foot-gun themselves by passing in a non-fake tensor from the ambient context, and then attempting to mutate its metadata (which is not going to ge propagated to the original). So maybe auditing is better, esp if we can come up with a better composite compliance test.
BTW, another way tensors can be created is from saved variable. Hypothetically, a wrapped number tensor could be saved as a variable and we don't currently propagate this property.
```
diff --git a/torch/csrc/autograd/saved_variable.cpp b/torch/csrc/autograd/saved_variable.cpp
index c6ca8eda13..bfc3bd6277 100644
--- a/torch/csrc/autograd/saved_variable.cpp
+++ b/torch/csrc/autograd/saved_variable.cpp
@@ -51,6 +51,7 @@ SavedVariable::SavedVariable(
is_leaf_ = variable.is_leaf();
is_output_ = is_output;
is_inplace_on_view_ = is_inplace_on_view;
+ is_wrapped_number_ = variable.unsafeGetTensorImpl()->is_wrapped_number();
if (is_inplace_on_view) {
TORCH_INTERNAL_ASSERT(!is_leaf_ && is_output);
@@ -223,6 +224,10 @@ Variable SavedVariable::unpack(std::shared_ptr<Node> saved_for) const {
var._set_fw_grad(new_fw_grad, /* level */ 0, /* is_inplace_op */ false);
}
+ if (is_wrapped_number_) {
+ var.unsafeGetTensorImpl()->set_wrapped_number(true);
+ }
+
return var;
}
diff --git a/torch/csrc/autograd/saved_variable.h b/torch/csrc/autograd/saved_variable.h
index 9136ff1a62..23f18f5b72 100644
--- a/torch/csrc/autograd/saved_variable.h
+++ b/torch/csrc/autograd/saved_variable.h
@@ -93,6 +93,7 @@ class TORCH_API SavedVariable {
bool saved_original_ = false;
bool is_leaf_ = false;
bool is_output_ = false;
+ bool is_wrapped_number_ = false;
// Hooks are a pair of functions pack_hook/unpack_hook that provides
// fine-grained control over how the SavedVariable should save its data.
```
However, I could not find any case where this actually made a difference. cc @albanD
cc @ezyang @bdhirsh @Chillee @eellison
### Versions
master
| 2 |
5,223 | 81,568 |
Improve interaction of PyTorch downstream libraries and torchdeploy
|
triaged, module: deploy
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
torchdeploy's Python library model is that each interpreter loads and manages downstream libraries (including those with compiled extension modules) separately, since the extension modules in general need to link against libpython (which is duplicated per interpreter). However, this causes a problem if the downstream libraries do custom operator registration, which hits a shared global state among all interpreters.
### Versions
master
cc @wconstab
| 1 |
5,224 | 81,565 |
__getitem__ is returned as an OverloadPacket instead of an OpOverload in __torch_dispatch__
|
triaged, module: __torch_dispatch__, bug
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
As per the title. Caught this while testing tags in a TorchDispatchMode.
### Versions
master
cc @Chillee @ezyang @zou3519 @albanD @samdow
| 5 |
5,225 | 81,559 |
[Profiler] Defer thread assignment for python startup events.
|
triaged, oncall: profiler
|
### 🚀 The feature, motivation and pitch
When the python function tracer starts, there are generally frames which are already live in the cPython interpreter. In order to produce a comprehensible trace we treat them as though they just started: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/blob/master/torch/csrc/autograd/profiler_python.cpp#L538 However, this will cause a problem when we support multiple python threads because all of these initial events will use the system TID of the thread which started the tracer. In order to treat them properly, we should lazily assign them system TIDs. This can be accomplished by keeping track of which events were start events (just tracking the number of start events is sufficient to reconstruct this information later) and then use the TID of the first call in the actual tracing block to assign the proper TID during post processing.
To take a concrete example:
```
# Initial stacks
Python thread 0: [foo()][bar()][baz()]
Python thread 1: [f0()][f1()]
```
Let's say we start the tracer from system thread 3. The five frames which were active when the tracer started will all be stored in the event buffer for thread 3 and in the current machinery that is the inferred TID. Suppose we see a call on Python thread 0 during profiling which occurs on system thread 2. We can use that information to change the system TID of the `foo`, `bar`, and `baz` frames to system TID 2 during post processing and produce a more accurate trace. (And will separate the stacks on the chrome trace.)
### Alternatives
_No response_
### Additional context
_No response_
cc @ilia-cher @robieta @chaekit @gdankel @bitfort @ngimel @nbcsm @guotuofeng @guyang3532 @gaoteng-git
| 0 |
5,226 | 81,554 |
float' object is not callable when using scheduler.step() with MultiplicativeLR
|
module: optimizer, triaged, actionable
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
## 🐛 Bug
I have initialized an optimizer and a scheduler like this:
```
def configure_optimizers(self):
opt = torch.optim.Adam(self.model.parameters(), lr=cfg.learning_rate)
sch = torch.optim.lr_scheduler.MultiplicativeLR(opt, lr_lambda = 0.95) #decrease of 5% every epoch
return [opt], [sch]`
```
Since I just want to updte the scheduler after each epoch, I did not modify this updating method in the training phase, but this is the error I get after the first epoch:
> self.update_lr_schedulers("epoch", update_plateau_schedulers=False)
> File "/home/lsa/anaconda3/envs/randla_36/lib/python3.6/site-packages/pytorch_lightning/loops/epoch/training_epoch_loop.py", line 448, in update_lr_schedulers
> opt_indices=[opt_idx for opt_idx, _ in active_optimizers],
> File "/home/lsa/anaconda3/envs/randla_36/lib/python3.6/site-packages/pytorch_lightning/loops/epoch/training_epoch_loop.py", line 509, in _update_learning_rates
> lr_scheduler["scheduler"].step()
> File "/home/lsa/anaconda3/envs/randla_36/lib/python3.6/site-packages/torch/optim/lr_scheduler.py", line 152, in step
> values = self.get_lr()
> File "/home/lsa/anaconda3/envs/randla_36/lib/python3.6/site-packages/torch/optim/lr_scheduler.py", line 329, in get_lr
> for lmbda, group in zip(self.lr_lambdas, self.optimizer.param_groups)]
> File "/home/lsa/anaconda3/envs/randla_36/lib/python3.6/site-packages/torch/optim/lr_scheduler.py", line 329, in <listcomp>
> for lmbda, group in zip(self.lr_lambdas, self.optimizer.param_groups)]
> TypeError: 'float' object is not callable
### Expected behavior
This error should not be there, in fact, using another scheduler ( in particular this
` sch = torch.optim.lr_scheduler.CosineAnnealingLR(opt, T_max=10)` ) I do not get the error and the training proceedes smoothly.
### To Reproduce
```
import torch
from torchvision.models import resnet18
net = resnet18()
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(net.parameters(), lr=0.01)
scheduler = torch.optim.lr_scheduler.MultiplicativeLR(optimizer, 0.95) # BUG SCHEDULER
#scheduler = torch.optim.lr_scheduler.StepLR(optimizer, 3, gamma=0.1) # WORKING ONE
for i in range(10):
print(i, scheduler.get_lr())
scheduler.step()
```
### Environment
* CUDA:
- GPU:
- NVIDIA RTX A6000
- available: True
- version: 11.3
* Packages:
- numpy: 1.19.2
- pyTorch_debug: False
- pyTorch_version: 1.10.2
- pytorch-lightning: 1.5.0
- tqdm: 4.64.0
* System:
- OS: Linux
- architecture:
- 64bit
-
- processor: x86_64
- python: 3.6.13
- version: #44~20.04.1-Ubuntu SMP Fri Jun 24 13:27:29 UTC 2022
cc @vincentqb @jbschlosser @albanD
| 2 |
5,227 | 81,552 |
Support Swift Package Manager (SPM) for iOS
|
oncall: mobile
|
### 🚀 The feature, motivation and pitch
Currently, Pytorch needs to be added to an iOS project via Cocoapods. However, many newer projects have migrated to Swift Package Manager. It would be fantastic if one could add Pytorch mobile via SPM, too.
### Alternatives
Alternatively, I'd also be happy to vendor pytorch into my codebase. We threw out Cocoapods a while ago and don't really want to reintroduce it if possible.
### Additional context
_No response_
| 3 |
5,228 | 81,545 |
Precision error from torch.distributed.send() to recv()
|
oncall: distributed
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
There is probably a precision error when using `torch.distributed.send()` and `torch.distributed.recv()` pairs.
`torch.distributed.recv()` can receive a tensor correctly only when that tensor is sent of type `torch.float32`. The other float types `torch.float16` and `torch.float64` leads to wrong tensor values in receiver side.
## Reproduce
(on a dual GPU platform)
```python
import torch
import torch.multiprocessing as mp
import torch.distributed as dist
import time
def main_worker(rank, world_size, args):
dist.init_process_group(
backend="nccl",
init_method="tcp://127.0.0.1:9001",
world_size=world_size,
rank=rank,
)
print("process begin", rank)
for datatype in [None,torch.float,torch.float16,torch.float32,torch.float64]:
if rank == 0:
print(f"Current datatype: {datatype}.")
t = torch.rand([4,4],dtype=datatype).to(torch.device('cuda',rank))
print(f"Generate tensor{t}")
dist.send(t,1)
elif rank == 1:
r = torch.rand([4,4]).to(torch.device('cuda',rank))
dist.recv(r,0)
print("recv",r)
print()
time.sleep(1)
def main():
mp.spawn(main_worker, nprocs=2, args=(2, 2))
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
```
## Output:
```python
process begin 0
Current datatype: None.
process begin 1
Generate tensortensor([[0.9230, 0.2856, 0.9419, 0.2844],
[0.9732, 0.7029, 0.0026, 0.9697],
[0.2188, 0.4143, 0.5163, 0.9863],
[0.1562, 0.3484, 0.1138, 0.3271]], device='cuda:0')
recv tensor([[0.9230, 0.2856, 0.9419, 0.2844],
[0.9732, 0.7029, 0.0026, 0.9697],
[0.2188, 0.4143, 0.5163, 0.9863],
[0.1562, 0.3484, 0.1138, 0.3271]], device='cuda:1')
Current datatype: torch.float32.
Generate tensortensor([[0.6158, 0.9911, 0.0677, 0.2109],
[0.0591, 0.5609, 0.4182, 0.4432],
[0.9296, 0.2350, 0.1028, 0.7265],
[0.1949, 0.0324, 0.4484, 0.8104]], device='cuda:0')
recv tensor([[0.6158, 0.9911, 0.0677, 0.2109],
[0.0591, 0.5609, 0.4182, 0.4432],
[0.9296, 0.2350, 0.1028, 0.7265],
[0.1949, 0.0324, 0.4484, 0.8104]], device='cuda:1')
Current datatype: torch.float16.
Generate tensortensor([[0.7212, 0.8945, 0.3042, 0.3184],
[0.3804, 0.9648, 0.8076, 0.9756],
[0.3862, 0.7358, 0.6611, 0.2539],
[0.4365, 0.9434, 0.7075, 0.6084]], device='cuda:0',
dtype=torch.float16)
recv tensor([[2.5669e-03, 5.6701e-07, 5.6217e-03, 6.2936e-03],
[4.3337e-04, 1.3432e-07, 4.2790e-03, 1.0597e-04],
[0.0000e+00, 0.0000e+00, 0.0000e+00, 0.0000e+00],
[0.0000e+00, 0.0000e+00, 0.0000e+00, 0.0000e+00]], device='cuda:1')
Current datatype: torch.float32.
Generate tensortensor([[0.7289, 0.0532, 0.6294, 0.5030],
[0.1043, 0.3015, 0.2626, 0.2357],
[0.8202, 0.1919, 0.3556, 0.2653],
[0.9763, 0.3292, 0.9931, 0.8236]], device='cuda:0')
recv tensor([[0.7289, 0.0532, 0.6294, 0.5030],
[0.1043, 0.3015, 0.2626, 0.2357],
[0.8202, 0.1919, 0.3556, 0.2653],
[0.9763, 0.3292, 0.9931, 0.8236]], device='cuda:1')
Current datatype: torch.float64.
Generate tensortensor([[0.1401, 0.5205, 0.3881, 0.1536],
[0.4686, 0.3280, 0.0725, 0.7440],
[0.5029, 0.2960, 0.5149, 0.2452],
[0.2024, 0.5243, 0.8930, 0.2613]], device='cuda:0',
dtype=torch.float64)
recv tensor([[-9.8724e-14, 1.5151e+00, 1.6172e-05, 1.7551e+00],
[ 1.6390e+35, 1.6941e+00, -1.9036e+12, 1.5286e+00],
[ 6.4192e-38, 1.7343e+00, 2.3965e+07, 1.6640e+00],
[-1.7412e+19, 1.3951e+00, -6.5071e+35, 1.8110e+00]], device='cuda:1')
```
### Versions
I tested and confirmed this phenomenon on two dual-GPU PCs and two versions of `PyTorch`.
#### Configure0: PyTorch `1.12.0`+`TITAN RTX`*2
```python
Collecting environment information...
PyTorch version: 1.12.0
Is debug build: False
CUDA used to build PyTorch: 11.6
ROCM used to build PyTorch: N/A
OS: Ubuntu 20.04.4 LTS (x86_64)
GCC version: (Ubuntu 7.5.0-6ubuntu2) 7.5.0
Clang version: Could not collect
CMake version: version 3.16.3
Libc version: glibc-2.31
Python version: 3.9.12 (main, Jun 1 2022, 11:38:51) [GCC 7.5.0] (64-bit runtime)
Python platform: Linux-5.13.0-52-generic-x86_64-with-glibc2.31
Is CUDA available: True
CUDA runtime version: 11.7.64
GPU models and configuration:
GPU 0: NVIDIA TITAN RTX
GPU 1: NVIDIA TITAN RTX
Nvidia driver version: 510.73.05
cuDNN version: Could not collect
HIP runtime version: N/A
MIOpen runtime version: N/A
Is XNNPACK available: True
Versions of relevant libraries:
[pip3] info-nce-pytorch==0.1.4
[pip3] numpy==1.22.3
[pip3] torch==1.12.0
[pip3] torch-tb-profiler==0.4.0
[pip3] torchaudio==0.12.0
[pip3] torchinfo==1.6.5
[pip3] torchvision==0.13.0
[conda] blas 1.0 mkl
[conda] cudatoolkit 11.6.0 hecad31d_10 conda-forge
[conda] info-nce-pytorch 0.1.4 pypi_0 pypi
[conda] libblas 3.9.0 12_linux64_mkl conda-forge
[conda] libcblas 3.9.0 12_linux64_mkl conda-forge
[conda] mkl 2021.4.0 h06a4308_640
[conda] mkl-service 2.4.0 py39h7f8727e_0
[conda] mkl_fft 1.3.1 py39hd3c417c_0
[conda] mkl_random 1.2.2 py39h51133e4_0
[conda] numpy 1.22.3 py39he7a7128_0
[conda] numpy-base 1.22.3 py39hf524024_0
[conda] pytorch 1.12.0 py3.9_cuda11.6_cudnn8.3.2_0 pytorch
[conda] pytorch-mutex 1.0 cuda pytorch
[conda] torch-tb-profiler 0.4.0 pypi_0 pypi
[conda] torchaudio 0.12.0 py39_cu116 pytorch
[conda] torchinfo 1.6.5 pyhd8ed1ab_0 conda-forge
[conda] torchvision 0.13.0 py39_cu116 pytorch
```
#### Configure1: PyTorch `1.8.2 LTS`+`TITAN RTX`*2
```python
Collecting environment information...
PyTorch version: 1.8.2
Is debug build: False
CUDA used to build PyTorch: 11.1
ROCM used to build PyTorch: N/A
OS: Ubuntu 20.04.4 LTS (x86_64)
GCC version: (Ubuntu 7.5.0-6ubuntu2) 7.5.0
Clang version: Could not collect
CMake version: version 3.16.3
Libc version: glibc-2.31
Python version: 3.8.13 (default, Mar 28 2022, 11:38:47) [GCC 7.5.0] (64-bit runtime)
Python platform: Linux-5.13.0-52-generic-x86_64-with-glibc2.17
Is CUDA available: True
CUDA runtime version: 11.7.64
GPU models and configuration:
GPU 0: NVIDIA TITAN RTX
GPU 1: NVIDIA TITAN RTX
Nvidia driver version: 510.73.05
cuDNN version: Could not collect
HIP runtime version: N/A
MIOpen runtime version: N/A
Is XNNPACK available: True
Versions of relevant libraries:
[pip3] info-nce-pytorch==0.1.4
[pip3] numpy==1.22.3
[pip3] torch==1.8.2
[pip3] torchaudio==0.8.2
[pip3] torchinfo==1.6.5
[pip3] torchvision==0.9.2
[conda] blas 1.0 mkl
[conda] cudatoolkit 11.1.74 h6bb024c_0 nvidia
[conda] info-nce-pytorch 0.1.4 pypi_0 pypi
[conda] mkl 2021.4.0 h06a4308_640
[conda] mkl-service 2.4.0 py38h7f8727e_0
[conda] mkl_fft 1.3.1 py38hd3c417c_0
[conda] mkl_random 1.2.2 py38h51133e4_0
[conda] numpy 1.21.5 py38he7a7128_2
[conda] numpy-base 1.21.5 py38hf524024_2
[conda] pytorch 1.8.2 py3.8_cuda11.1_cudnn8.0.5_0 pytorch-lts
[conda] torchaudio 0.8.2 py38 pytorch-lts
[conda] torchinfo 1.6.5 pyhd8ed1ab_0 conda-forge
[conda] torchvision 0.9.2 py38_cu111 pytorch-lts
```
#### Configure2: PyTorch `1.12.0`+`RTX3090`*2
```python
Collecting environment information...
PyTorch version: 1.12.0
Is debug build: False
CUDA used to build PyTorch: 11.6
ROCM used to build PyTorch: N/A
OS: Ubuntu 20.04.4 LTS (x86_64)
GCC version: (Ubuntu 9.4.0-1ubuntu1~20.04.1) 9.4.0
Clang version: Could not collect
CMake version: version 3.22.0-rc2
Libc version: glibc-2.31
Python version: 3.10.4 (main, Mar 31 2022, 08:41:55) [GCC 7.5.0] (64-bit runtime)
Python platform: Linux-5.13.0-52-generic-x86_64-with-glibc2.31
Is CUDA available: True
CUDA runtime version: 11.7.64
GPU models and configuration:
GPU 0: NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3090
GPU 1: NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3090
Nvidia driver version: 510.73.05
cuDNN version: Probably one of the following:
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_adv_infer.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_adv_train.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_cnn_infer.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_cnn_train.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_ops_infer.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_ops_train.so.8.4.1
HIP runtime version: N/A
MIOpen runtime version: N/A
Is XNNPACK available: True
Versions of relevant libraries:
[pip3] info-nce-pytorch==0.1.4
[pip3] numpy==1.22.3
[pip3] torch==1.12.0
[pip3] torchaudio==0.12.0
[pip3] torchvision==0.13.0
[conda] blas 1.0 mkl
[conda] cudatoolkit 11.6.0 habf752d_9 nvidia
[conda] ffmpeg 4.3 hf484d3e_0 pytorch
[conda] info-nce-pytorch 0.1.4 pypi_0 pypi
[conda] libblas 3.9.0 12_linux64_mkl conda-forge
[conda] libcblas 3.9.0 12_linux64_mkl conda-forge
[conda] liblapack 3.9.0 12_linux64_mkl conda-forge
[conda] mkl 2021.4.0 h06a4308_640
[conda] mkl-service 2.4.0 py310ha2c4b55_0 conda-forge
[conda] mkl_fft 1.3.1 py310h2b4bcf5_1 conda-forge
[conda] mkl_random 1.2.2 py310h00e6091_0
[conda] numpy 1.22.3 py310hfa59a62_0
[conda] numpy-base 1.22.3 py310h9585f30_0
[conda] pytorch 1.12.0 py3.10_cuda11.6_cudnn8.3.2_0 pytorch
[conda] pytorch-mutex 1.0 cuda pytorch
[conda] torchaudio 0.12.0 py310_cu116 pytorch
[conda] torchvision 0.13.0 py310_cu116 pytorch
```
#### Configure3: PyTorch `1.8.2 LTS`+`RTX3090`*2
```python
Collecting environment information...
PyTorch version: 1.8.2
Is debug build: False
CUDA used to build PyTorch: 11.1
ROCM used to build PyTorch: N/A
OS: Ubuntu 20.04.4 LTS (x86_64)
GCC version: (Ubuntu 9.4.0-1ubuntu1~20.04.1) 9.4.0
Clang version: Could not collect
CMake version: version 3.22.0-rc2
Libc version: glibc-2.31
Python version: 3.8.13 (default, Mar 28 2022, 11:38:47) [GCC 7.5.0] (64-bit runtime)
Python platform: Linux-5.13.0-52-generic-x86_64-with-glibc2.17
Is CUDA available: True
CUDA runtime version: 11.7.64
GPU models and configuration:
GPU 0: NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3090
GPU 1: NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3090
Nvidia driver version: 510.73.05
cuDNN version: Probably one of the following:
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_adv_infer.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_adv_train.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_cnn_infer.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_cnn_train.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_ops_infer.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_ops_train.so.8.4.1
HIP runtime version: N/A
MIOpen runtime version: N/A
Is XNNPACK available: True
Versions of relevant libraries:
[pip3] info-nce-pytorch==0.1.4
[pip3] numpy==1.21.5
[pip3] torch==1.8.2
[pip3] torch-tb-profiler==0.3.1
[pip3] torchaudio==0.8.2
[pip3] torchinfo==1.7.0
[pip3] torchvision==0.9.2
[conda] blas 1.0 mkl
[conda] cudatoolkit 11.1.74 h6bb024c_0 nvidia
[conda] mkl 2021.4.0 h06a4308_640
[conda] mkl-service 2.4.0 py38h7f8727e_0
[conda] mkl_fft 1.3.1 py38hd3c417c_0
[conda] mkl_random 1.2.2 py38h51133e4_0
[conda] numpy 1.21.5 py38he7a7128_2
[conda] numpy-base 1.21.5 py38hf524024_2
[conda] pytorch 1.8.2 py3.8_cuda11.1_cudnn8.0.5_0 pytorch-lts
[conda] torchaudio 0.8.2 py38 pytorch-lts
[conda] torchinfo 1.7.0 pyhd8ed1ab_0 conda-forge
[conda] torchvision 0.9.2 py38_cu111 pytorch-lts
```
cc @pietern @mrshenli @pritamdamania87 @zhaojuanmao @satgera @rohan-varma @gqchen @aazzolini @osalpekar @jiayisuse @SciPioneer @H-Huang @kwen2501
| 3 |
5,229 | 81,544 |
Torch does not build with Lazy TS disabled
|
module: build, triaged
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
If I compile with `BUILD_LAZY_TS_BACKEND=0`, the linker fails with:
> Creating library lib\torch_cpu.lib and object lib\torch_cpu.exp
> shape_inference.cpp.obj : error LNK2019: unresolved external symbol "public: void __cdecl torch::lazy::TSLoweringContext::Lower(class torch::lazy::Node const *)" (?Lower@TSLoweringContext@lazy@torch@@QEAAXPEBVNode@23@@Z) referenced in function "public: struct torch::jit::Value * __cdecl torch::lazy::TSLoweringContext::GetOutputOp(struct torch::lazy::Output const &)" (?GetOutputOp@TSLoweringContext@lazy@torch@@QEAAPEAUValue@jit@3@AEBUOutput@23@@Z)
> shape_inference.cpp.obj : error LNK2001: unresolved external symbol "public: virtual class torch::lazy::hash_t __cdecl torch::lazy::TsNode::hash(void)const " (?hash@TsNode@lazy@torch@@UEBA?AVhash_t@23@XZ)
> shape_inference.cpp.obj : error LNK2001: unresolved external symbol "public: virtual class torch::lazy::hash_t __cdecl torch::lazy::TsNode::shapeHash(void)const " (?shapeHash@TsNode@lazy@torch@@UEBA?AVhash_t@23@XZ)
> shape_inference.cpp.obj : error LNK2001: unresolved external symbol "public: virtual class std::vector<struct torch::jit::Value *,class std::allocator<struct torch::jit::Value *> > __cdecl torch::lazy::TsNode::Lower(class std::shared_ptr<struct torch::jit::GraphFunction>,class torch::lazy::TSLoweringContext *)const " (?Lower@TsNode@lazy@torch@@UEBA?AV?$vector@PEAUValue@jit@torch@@V?$allocator@PEAUValue@jit@torch@@@std@@@std@@V?$shared_ptr@UGraphFunction@jit@torch@@@5@PEAVTSLoweringContext@23@@Z)
> shape_inference.cpp.obj : error LNK2001: unresolved external symbol "public: virtual class std::vector<struct torch::jit::Value *,class std::allocator<struct torch::jit::Value *> > __cdecl torch::lazy::TensorList::Lower(class std::shared_ptr<struct torch::jit::GraphFunction>,class torch::lazy::TSLoweringContext *)const " (?Lower@TensorList@lazy@torch@@UEBA?AV?$vector@PEAUValue@jit@torch@@V?$allocator@PEAUValue@jit@torch@@@std@@@std@@V?$shared_ptr@UGraphFunction@jit@torch@@@5@PEAVTSLoweringContext@23@@Z)
> shape_inference.cpp.obj : error LNK2001: unresolved external symbol "public: virtual __int64 __cdecl torch::lazy::SizeNode::getStaticValue(void)const " (?getStaticValue@SizeNode@lazy@torch@@UEBA_JXZ)
> shape_inference.cpp.obj : error LNK2001: unresolved external symbol "public: virtual bool __cdecl torch::lazy::SizeNode::isDynamic(void)const " (?isDynamic@SizeNode@lazy@torch@@UEBA_NXZ)
> shape_inference.cpp.obj : error LNK2001: unresolved external symbol "public: virtual class std::basic_string<char,struct std::char_traits<char>,class std::allocator<char> > __cdecl torch::lazy::SizeNode::ToString(void)const " (?ToString@SizeNode@lazy@torch@@UEBA?AV?$basic_string@DU?$char_traits@D@std@@V?$allocator@D@2@@std@@XZ)
> shape_inference.cpp.obj : error LNK2001: unresolved external symbol "public: virtual class std::vector<struct torch::jit::Value *,class std::allocator<struct torch::jit::Value *> > __cdecl torch::lazy::SizeNode::Lower(class std::shared_ptr<struct torch::jit::GraphFunction>,class torch::lazy::TSLoweringContext *)const " (?Lower@SizeNode@lazy@torch@@UEBA?AV?$vector@PEAUValue@jit@torch@@V?$allocator@PEAUValue@jit@torch@@@std@@@std@@V?$shared_ptr@UGraphFunction@jit@torch@@@5@PEAVTSLoweringContext@23@@Z)
> shape_inference.cpp.obj : error LNK2001: unresolved external symbol "public: virtual __int64 __cdecl torch::lazy::SizeAdd::getStaticValue(void)const " (?getStaticValue@SizeAdd@lazy@torch@@UEBA_JXZ)
> shape_inference.cpp.obj : error LNK2001: unresolved external symbol "public: virtual bool __cdecl torch::lazy::SizeAdd::isDynamic(void)const " (?isDynamic@SizeAdd@lazy@torch@@UEBA_NXZ)
> shape_inference.cpp.obj : error LNK2001: unresolved external symbol "public: virtual class std::basic_string<char,struct std::char_traits<char>,class std::allocator<char> > __cdecl torch::lazy::SizeAdd::ToString(void)const " (?ToString@SizeAdd@lazy@torch@@UEBA?AV?$basic_string@DU?$char_traits@D@std@@V?$allocator@D@2@@std@@XZ)
> shape_inference.cpp.obj : error LNK2001: unresolved external symbol "public: virtual __int64 __cdecl torch::lazy::SizeMul::getStaticValue(void)const " (?getStaticValue@SizeMul@lazy@torch@@UEBA_JXZ)
> shape_inference.cpp.obj : error LNK2001: unresolved external symbol "public: virtual bool __cdecl torch::lazy::SizeMul::isDynamic(void)const " (?isDynamic@SizeMul@lazy@torch@@UEBA_NXZ)
> shape_inference.cpp.obj : error LNK2001: unresolved external symbol "public: virtual class std::basic_string<char,struct std::char_traits<char>,class std::allocator<char> > __cdecl torch::lazy::SizeMul::ToString(void)const " (?ToString@SizeMul@lazy@torch@@UEBA?AV?$basic_string@DU?$char_traits@D@std@@V?$allocator@D@2@@std@@XZ)
> shape_inference.cpp.obj : error LNK2001: unresolved external symbol "public: virtual __int64 __cdecl torch::lazy::SizeDiv::getStaticValue(void)const " (?getStaticValue@SizeDiv@lazy@torch@@UEBA_JXZ)
> shape_inference.cpp.obj : error LNK2001: unresolved external symbol "public: virtual bool __cdecl torch::lazy::SizeDiv::isDynamic(void)const " (?isDynamic@SizeDiv@lazy@torch@@UEBA_NXZ)
> shape_inference.cpp.obj : error LNK2001: unresolved external symbol "public: virtual class std::basic_string<char,struct std::char_traits<char>,class std::allocator<char> > __cdecl torch::lazy::SizeDiv::ToString(void)const " (?ToString@SizeDiv@lazy@torch@@UEBA?AV?$basic_string@DU?$char_traits@D@std@@V?$allocator@D@2@@std@@XZ)
> bin\torch_cpu.dll : fatal error LNK1120: 18 unresolved externals
I believe this has worked in the past versions of 1.12.0-dev. It now requires enabling Lazy TS backend to compile.
### Versions
Latest master
cc @malfet @seemethere
| 0 |
5,230 | 81,543 |
Linking pytorch libraries causes sstream behavior to be overridden globally
|
module: build, triaged
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
Some details here: https://github.com/ros2/geometry2/issues/540
I ran into an issue when integrating ROS2 TF2 libraries with pytorch. Here's a simple C++ file that reproduces the bug:
main.cpp
```C++
#include <sstream>
#include <iostream>
int main(int argc, char * argv[])
{
long unsigned int num = 0xdeadbeef;
std::stringstream sstream;
sstream << "transform_listener_impl_" << std::hex << reinterpret_cast<size_t>(num);
std::cout << "transform_listener_impl_" << std::hex << reinterpret_cast<size_t>(num) << std::endl;
std::cout << std::string(sstream.str()) << std::endl;
}
```
CMakeLists.txt
```
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.8)
project(torch_bug)
# Default to C++14
if(NOT CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD)
set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 14)
endif()
if(CMAKE_COMPILER_IS_GNUCXX OR CMAKE_CXX_COMPILER_ID MATCHES "Clang")
add_compile_options(-Wall -Wextra -Wpedantic)
endif()
find_package(Torch REQUIRED)
add_executable(${PROJECT_NAME} main.cpp)
target_link_libraries(${PROJECT_NAME}
${TORCH_LIBRARIES}
)
```
Expected output:
```
transform_listener_impl_deadbeef
transform_listener_impl_deadbeef
```
Actual output:
```
transform_listener_impl_deadbeef
transform_listener_impl_de,adb,eef
```
What could cause this bug? In the case of ROS, it really hates having those commas inserted and throws a run time exception. I wonder what other situations this is problematic in.
I installed libtorch using this binary link: https://download.pytorch.org/libtorch/cu116/libtorch-cxx11-abi-shared-with-deps-1.12.0%2Bcu116.zip
### Versions
Collecting environment information...
PyTorch version: 1.10.0+cu102
Is debug build: False
CUDA used to build PyTorch: 10.2
ROCM used to build PyTorch: N/A
OS: Ubuntu 20.04.4 LTS (x86_64)
GCC version: (Ubuntu 8.4.0-3ubuntu2) 8.4.0
Clang version: Could not collect
CMake version: version 3.16.3
Libc version: glibc-2.31
Python version: 3.8.10 (default, Mar 15 2022, 12:22:08) [GCC 9.4.0] (64-bit runtime)
Python platform: Linux-5.4.0-122-generic-x86_64-with-glibc2.29
Is CUDA available: True
CUDA runtime version: 11.7.64
GPU models and configuration: GPU 0: NVIDIA GeForce GTX 1080
Nvidia driver version: 515.48.07
cuDNN version: Probably one of the following:
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_adv_infer.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_adv_train.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_cnn_infer.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_cnn_train.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_ops_infer.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_ops_train.so.8.4.1
HIP runtime version: N/A
MIOpen runtime version: N/A
Is XNNPACK available: True
Versions of relevant libraries:
[pip3] mypy==0.902
[pip3] mypy-extensions==0.4.3
[pip3] numpy==1.22.4
[pip3] torch==1.10.0
[pip3] torchaudio==0.10.0+cu113
[pip3] torchvision==0.11.1
[pip3] torchviz==0.0.2
[conda] Could not collect
cc @malfet @seemethere
| 1 |
5,231 | 81,541 |
[vulkan]compiling VulkanOpContext.cpp with some errors
|
module: build, triaged, module: vulkan
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
Compiling the newest version pytorch with backend vulkan,there is some errors with VulkanOpContext
[340/1314] Building CXX object caffe2/CMakeFiles/torch_cpu.dir/__/aten/src/ATen/native/vulkan/ops/VulkanOpContext.cpp.o
FAILED: caffe2/CMakeFiles/torch_cpu.dir/__/aten/src/ATen/native/vulkan/ops/VulkanOpContext.cpp.o
/usr/bin/c++ -DAT_PER_OPERATOR_HEADERS -DBUILD_ONEDNN_GRAPH -DCPUINFO_SUPPORTED_PLATFORM=1 -DFMT_HEADER_ONLY=1 -DFXDIV_USE_INLINE_ASSEMBLY=0 -DHAVE_MALLOC_USABLE_SIZE=1 -DHAVE_MMAP=1 -DHAVE_SHM_OPEN=1 -DHAVE_SHM_UNLINK=1 -DMINIZ_DISABLE_ZIP_READER_CRC32_CHECKS -DNNP_CONVOLUTION_ONLY=0 -DNNP_INFERENCE_ONLY=0 -DONNXIFI_ENABLE_EXT=1 -DONNX_ML=1 -DONNX_NAMESPACE=onnx_torch -DUSE_C10D_GLOO -DUSE_DISTRIBUTED -DUSE_EXTERNAL_MZCRC -DUSE_RPC -DUSE_TENSORPIPE -D_FILE_OFFSET_BITS=64 -Dtorch_cpu_EXPORTS -I/home/sim/**/20220714/pytorch/build/aten/src -I/home/sim/**/20220714/pytorch/aten/src -I/home/sim/**/20220714/pytorch/build -I/home/sim/**/20220714/pytorch -I/home/sim/**/20220714/pytorch/cmake/../third_party/benchmark/include -I/home/sim/**/20220714/pytorch/third_party/onnx -I/home/sim/**/20220714/pytorch/build/third_party/onnx -I/home/sim/**/20220714/pytorch/third_party/foxi -I/home/sim/**/20220714/pytorch/build/third_party/foxi -I/home/sim/**/20220714/pytorch/torch/csrc/api -I/home/sim/**/20220714/pytorch/torch/csrc/api/include -I/home/sim/**/20220714/pytorch/caffe2/aten/src/TH -I/home/sim/**/20220714/pytorch/build/caffe2/aten/src/TH -I/home/sim/**/20220714/pytorch/build/caffe2/aten/src -I/home/sim/**/20220714/pytorch/build/caffe2/../aten/src -I/home/sim/**/20220714/pytorch/torch/csrc -I/home/sim/**/20220714/pytorch/third_party/miniz-2.1.0 -I/home/sim/**/20220714/pytorch/third_party/kineto/libkineto/include -I/home/sim/**/20220714/pytorch/third_party/kineto/libkineto/src -I/home/sim/**/20220714/pytorch/torch/csrc/distributed -I/home/sim/**/20220714/pytorch/build/vulkan -I/home/sim/**/20220714/pytorch/aten/../third_party/catch/single_include -I/home/sim/**/20220714/pytorch/aten/src/ATen/.. -I/home/sim/**/20220714/pytorch/third_party/FXdiv/include -I/home/sim/**/20220714/pytorch/c10/.. -I/home/sim/**/20220714/pytorch/third_party/pthreadpool/include -I/home/sim/**/20220714/pytorch/third_party/cpuinfo/include -I/home/sim/**/20220714/pytorch/third_party/QNNPACK/include -I/home/sim/**/20220714/pytorch/aten/src/ATen/native/quantized/cpu/qnnpack/include -I/home/sim/**/20220714/pytorch/aten/src/ATen/native/quantized/cpu/qnnpack/src -I/home/sim/**/20220714/pytorch/third_party/cpuinfo/deps/clog/include -I/home/sim/**/20220714/pytorch/third_party/NNPACK/include -I/home/sim/**/20220714/pytorch/third_party/fbgemm/include -I/home/sim/**/20220714/pytorch/third_party/fbgemm -I/home/sim/**/20220714/pytorch/third_party/fbgemm/third_party/asmjit/src -I/home/sim/**/20220714/pytorch/third_party/ittapi/src/ittnotify -I/home/sim/**/20220714/pytorch/third_party/FP16/include -I/home/sim/**/20220714/pytorch/third_party/tensorpipe -I/home/sim/**/20220714/pytorch/build/third_party/tensorpipe -I/home/sim/**/20220714/pytorch/third_party/tensorpipe/third_party/libnop/include -I/home/sim/**/20220714/pytorch/third_party/fmt/include -I/home/sim/**/20220714/pytorch/build/third_party/ideep/mkl-dnn/third_party/oneDNN/include -I/home/sim/**/20220714/pytorch/third_party/ideep/mkl-dnn/third_party/oneDNN/src/../include -I/home/sim/**/20220714/pytorch/third_party/flatbuffers/include -isystem /home/sim/**/20220714/pytorch/build/third_party/gloo -isystem /home/sim/**/20220714/pytorch/cmake/../third_party/gloo -isystem /home/sim/**/20220714/pytorch/cmake/../third_party/googletest/googlemock/include -isystem /home/sim/**/20220714/pytorch/cmake/../third_party/googletest/googletest/include -isystem /home/sim/**/20220714/pytorch/third_party/protobuf/src -isystem /home/sim/**/20220714/pytorch/third_party/gemmlowp -isystem /home/sim/**/20220714/pytorch/third_party/neon2sse -isystem /home/sim/**/20220714/pytorch/third_party/XNNPACK/include -isystem /home/sim/**/vulkansdk-linux-x86_64-1.3.216.0/1.3.216.0/x86_64/include -isystem /home/sim/**/20220714/pytorch/third_party/ittapi/include -isystem /home/sim/**/20220714/pytorch/cmake/../third_party/eigen -isystem /home/sim/**/20220714/pytorch/third_party/ideep/mkl-dnn/third_party/oneDNN/include -isystem /home/sim/**/20220714/pytorch/third_party/ideep/include -isystem /home/sim/**/20220714/pytorch/third_party/ideep/mkl-dnn/include -isystem /home/sim/**/20220714/pytorch/build/include -Wno-deprecated -fvisibility-inlines-hidden -DUSE_PTHREADPOOL -fopenmp -DNDEBUG -DUSE_KINETO -DLIBKINETO_NOCUPTI -DUSE_FBGEMM -DUSE_QNNPACK -DUSE_PYTORCH_QNNPACK -DUSE_XNNPACK -DUSE_VULKAN -DUSE_VULKAN_API -DUSE_VULKAN_SHADERC_RUNTIME -DSYMBOLICATE_MOBILE_DEBUG_HANDLE -DEDGE_PROFILER_USE_KINETO -O2 -fPIC -Wno-narrowing -Wall -Wextra -Werror=return-type -Werror=non-virtual-dtor -Wno-missing-field-initializers -Wno-type-limits -Wno-array-bounds -Wno-unknown-pragmas -Wno-unused-parameter -Wno-unused-function -Wno-unused-result -Wno-strict-overflow -Wno-strict-aliasing -Wno-error=deprecated-declarations -Wno-stringop-overflow -Wno-psabi -Wno-error=pedantic -Wno-error=redundant-decls -Wno-error=old-style-cast -fdiagnostics-color=always -faligned-new -Wno-unused-but-set-variable -Wno-maybe-uninitialized -fno-math-errno -fno-trapping-math -Werror=format -Wno-stringop-overflow -DHAVE_AVX2_CPU_DEFINITION -O3 -DNDEBUG -DNDEBUG -fPIC -DCAFFE2_USE_GLOO -DTH_HAVE_THREAD -Wall -Wextra -Wno-unused-parameter -Wno-unused-function -Wno-unused-result -Wno-unused-local-typedefs -Wno-missing-field-initializers -Wno-write-strings -Wno-unknown-pragmas -Wno-type-limits -Wno-array-bounds -Wno-sign-compare -Wno-strict-overflow -Wno-strict-aliasing -Wno-error=deprecated-declarations -Wno-missing-braces -Wno-maybe-uninitialized -fvisibility=hidden -O2 -fopenmp -DCAFFE2_BUILD_MAIN_LIB -pthread -DASMJIT_STATIC -std=gnu++14 -MD -MT caffe2/CMakeFiles/torch_cpu.dir/__/aten/src/ATen/native/vulkan/ops/VulkanOpContext.cpp.o -MF caffe2/CMakeFiles/torch_cpu.dir/__/aten/src/ATen/native/vulkan/ops/VulkanOpContext.cpp.o.d -o caffe2/CMakeFiles/torch_cpu.dir/__/aten/src/ATen/native/vulkan/ops/VulkanOpContext.cpp.o -c /home/sim/**/20220714/pytorch/aten/src/ATen/native/vulkan/ops/VulkanOpContext.cpp
In file included from /home/sim/**/20220714/pytorch/aten/src/ATen/core/List.h:483:0,
from /home/sim/**/20220714/pytorch/aten/src/ATen/core/ivalue_inl.h:9,
from /home/sim/**/20220714/pytorch/aten/src/ATen/core/ivalue.h:1369,
from /home/sim/**/20220714/pytorch/aten/src/ATen/core/function_schema.h:8,
from /home/sim/**/20220714/pytorch/aten/src/ATen/core/function.h:3,
from /home/sim/**/20220714/pytorch/aten/src/ATen/core/builtin_function.h:3,
from /home/sim/**/20220714/pytorch/torch/custom_class.h:3,
from /home/sim/**/20220714/pytorch/aten/src/ATen/native/vulkan/ops/VulkanOpContext.h:5,
from /home/sim/**/20220714/pytorch/aten/src/ATen/native/vulkan/ops/VulkanOpContext.cpp:1:
/home/sim/**/20220714/pytorch/aten/src/ATen/core/List_inl.h: In instantiation of ‘c10::List<T>::List(std::initializer_list<_Tp>) [with T = c10::IValue]’:
/home/sim/**/20220714/pytorch/aten/src/ATen/native/vulkan/ops/VulkanOpContext.cpp:11:58: required from here
/home/sim/**/20220714/pytorch/aten/src/ATen/core/List_inl.h:42:3: error: static assertion failed: This constructor is not valid for List<IValue>. Please use c10::impl::GenericList(elementType).
static_assert(!std::is_same<T, IValue>::value, "This constructor is not valid for List<IValue>. Please use c10::impl::GenericList(elementType).");
^~~~~~~~~~~~~
/home/sim/**/20220714/pytorch/aten/src/ATen/core/List_inl.h: In instantiation of ‘c10::List<T>::List(c10::ArrayRef<T>) [with T = c10::IValue]’:
/home/sim/**/20220714/pytorch/aten/src/ATen/core/List_inl.h:41:35: required from ‘c10::List<T>::List(std::initializer_list<_Tp>) [with T = c10::IValue]’
/home/sim/**/20220714/pytorch/aten/src/ATen/native/vulkan/ops/VulkanOpContext.cpp:11:58: required from here
/home/sim/**/20220714/pytorch/aten/src/ATen/core/List_inl.h:32:3: error: static assertion failed: This constructor is not valid for List<IValue>. Please use c10::impl::GenericList(elementType).
static_assert(!std::is_same<T, IValue>::value, "This constructor is not valid for List<IValue>. Please use c10::impl::GenericList(elementType).");
### Versions
Collecting environment information...
PyTorch version: N/A
Is debug build: N/A
CUDA used to build PyTorch: N/A
ROCM used to build PyTorch: N/A
OS: Ubuntu 18.04.6 LTS (x86_64)
GCC version: (Ubuntu 7.5.0-3ubuntu1~18.04) 7.5.0
Clang version: Could not collect
CMake version: version 3.22.5
Libc version: glibc-2.27
Python version: 3.9.2 (default, Jul 4 2022, 18:25:25) [GCC 7.5.0] (64-bit runtime)
Python platform: Linux-5.4.0-122-generic-x86_64-with-glibc2.27
Is CUDA available: N/A
CUDA runtime version: 11.3.58
GPU models and configuration: GPU 0: NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3080 Ti
Nvidia driver version: 470.129.06
cuDNN version: Probably one of the following:
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_adv_infer.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_adv_train.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_cnn_infer.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_cnn_train.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_ops_infer.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_ops_train.so.8.4.1
HIP runtime version: N/A
MIOpen runtime version: N/A
Is XNNPACK available: N/A
Versions of relevant libraries:
[pip3] numpy==1.23.0
[conda] Could not collect
cc @malfet @seemethere
| 2 |
5,232 | 81,539 |
CapabilityBasedPartitioner treats non-compute ops inconsistently
|
triaged, module: fx, module: CapabilityBasedPartitioner, module: fx.passes
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
Currently, only these two ops are treated as non-compute: `non_compute_ops = {"torch.ops.aten.view", "_operator.getitem"}`. However, there are plenty of other non-compute ops, e.g. all view operations. It is also unclear why view ops need to get treated specially at all; it seems like this ought to be configurable.
cc @ezyang @SherlockNoMad
### Versions
master
| 0 |
5,233 | 81,532 |
forward program terminated from __cxa_pure_virtual
|
needs reproduction, module: crash, module: cpp, module: autograd, triaged, shadow review
|
## Issue description
C++ program terminated when model forward. The core stack:
#0 __GI_raise (sig=sig@entry=6) at ../sysdeps/unix/sysv/linux/raise.c:51
#1 0x00007f42d82df7f1 in __GI_abort () at abort.c:79
#2 0x00007f42d8b53957 in ?? () from /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libstdc++.so.6
#3 0x00007f42d8b59ae6 in ?? () from /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libstdc++.so.6
#4 0x00007f42d8b59b21 in std::terminate() () from /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libstdc++.so.6
#5 0x00007f42d8b5a8ff in __cxa_pure_virtual () from /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libstdc++.so.6
#6 0x00007f42a4cc9acb in at::TensorBase::grad_fn (this=0x7f40ce00be00) at /data/work/soft/pytorch-1.10.0/aten/src/ATen/core/Tensor.cpp:120
#7 0x00007f42a93469d3 in torch::autograd::impl::gradient_edge (self=...) at /data/work/soft/pytorch-1.10.0/torch/csrc/autograd/variable.cpp:227
#8 0x00007f42a8554933 in torch::autograd::detail::MakeNextFunctionList::operator() (this=0x7f42c1e90e50, variable=...) at /data/work/soft/pytorch-1.10.0/torch/csrc/autograd/function.h:561
#9 0x00007f42a8569479 in at::IterArgs<torch::autograd::detail::MakeNextFunctionList>::apply<at::Tensor const&> (this=0x7f42c1e90e50, arg=...) at /data/work/soft/pytorch-1.10.0/aten/src/ATen/core/Variadic.h:32
#10 0x00007f42a8560595 in torch::autograd::collect_next_edges<at::Tensor const&> () at /data/work/soft/pytorch-1.10.0/torch/csrc/autograd/function.h:616
#11 0x00007f42a88f7194 in torch::autograd::VariableType::(anonymous namespace)::t (ks=..., self=...) at /data/work/soft/pytorch-1.10.0/torch/csrc/autograd/generated/VariableType_3.cpp:8723
#12 0x00007f42a89600a5 in c10::impl::detail::WrapFunctionIntoFunctor_<c10::CompileTimeFunctionPointer<at::Tensor(c10::DispatchKeySet, const at::Tensor&), torch::autograd::VariableType::(anonymous namespace)::t>, at::Tensor, c10::guts::typelist::typelist<c10::DispatchKeySet, const at::Tensor&> >::operator() (args#1=..., args#0=..., this=0x55f08e475030) at /data/work/soft/pytorch-1.10.0/aten/src/ATen/core/boxing/impl/WrapFunctionIntoFunctor.h:13
#13 c10::impl::wrap_kernel_functor_unboxed_<c10::impl::detail::WrapFunctionIntoFunctor_<c10::CompileTimeFunctionPointer<at::Tensor(c10::DispatchKeySet, const at::Tensor&), torch::autograd::VariableType::(anonymous namespace)::t>, at::Tensor, c10::guts::typelist::typelist<c10::DispatchKeySet, const at::Tensor&> >, at::Tensor(c10::DispatchKeySet, const at::Tensor&)>::call(c10::OperatorKernel *, c10::DispatchKeySet, const at::Tensor &) (functor=0x55f08e475030,
dispatchKeySet=..., args#0=...) at /data/work/soft/pytorch-1.10.0/aten/src/ATen/core/boxing/impl/make_boxed_from_unboxed_functor.h:440
#14 0x00007f42a578408e in c10::callUnboxedKernelFunction<at::Tensor, at::Tensor const&> (
unboxed_kernel_func=0x7f42a896001b <c10::impl::wrap_kernel_functor_unboxed_<c10::impl::detail::WrapFunctionIntoFunctor_<c10::CompileTimeFunctionPointer<at::Tensor(c10::DispatchKeySet, const at::Tensor&), torch::autograd::VariableType::(anonymous namespace)::t>, at::Tensor, c10::guts::typelist::typelist<c10::DispatchKeySet, const at::Tensor&> >, at::Tensor(c10::DispatchKeySet, const at::Tensor&)>::call(c10::OperatorKernel *, c10::DispatchKeySet, const at::Tensor &)>, functor=0x55f08e475030, dispatchKeySet=...) at /data/work/soft/pytorch-1.10.0/aten/src/ATen/core/boxing/KernelFunction_impl.h:57
#15 0x00007f42a5c18fc8 in c10::KernelFunction::call<at::Tensor, at::Tensor const&> (dispatchKeySet=..., opHandle=..., this=0x55f08cfd9fd0) at /data/work/soft/pytorch-1.10.0/aten/src/ATen/core/boxing/KernelFunction_impl.h:67
#16 c10::Dispatcher::call<at::Tensor, at::Tensor const&>(c10::TypedOperatorHandle<at::Tensor (at::Tensor const&)> const&, at::Tensor const&) const (op=..., this=0x7f42b6a95c40 <c10::Dispatcher::realSingleton()::_singleton>)
at /data/work/soft/pytorch-1.10.0/aten/src/ATen/core/dispatch/Dispatcher.h:531
#17 c10::TypedOperatorHandle<at::Tensor (at::Tensor const&)>::call(at::Tensor const&) const (args#0=..., this=<optimized out>) at /data/work/soft/pytorch-1.10.0/aten/src/ATen/core/dispatch/Dispatcher.h:397
#18 at::_ops::t::call (self=...) at /data/work/soft/pytorch-1.10.0/build/aten/src/ATen/Operators_3.cpp:4256
#19 0x00007f42a4eb8a78 in at::Tensor::t (this=0x7f40ce00be00) at /data/work/soft/pytorch-1.10.0/build/aten/src/ATen/core/TensorBody.h:3270
#20 0x00007f42a4f5ba47 in at::native::linear (input=..., weight=..., bias_opt=...) at /data/work/soft/pytorch-1.10.0/aten/src/ATen/native/Linear.cpp:37
#21 0x00007f42a62b5e50 in at::(anonymous namespace)::(anonymous namespace)::wrapper__linear (input=..., weight=..., bias=...) at /data/work/soft/pytorch-1.10.0/build/aten/src/ATen/RegisterCompositeImplicitAutograd.cpp:3043
#22 0x00007f42a63c2bc0 in c10::impl::detail::WrapFunctionIntoFunctor_<c10::CompileTimeFunctionPointer<at::Tensor(const at::Tensor&, const at::Tensor&, const c10::optional<at::Tensor>&), at::(anonymous namespace)::(anonymous namespace)::wrapper__linear>, at::Tensor, c10::guts::typelist::typelist<const at::Tensor&, const at::Tensor&, const c10::optional<at::Tensor>&> >::operator() (args#2=..., args#1=..., args#0=..., this=0x55f08d9dedf0)
at /data/work/soft/pytorch-1.10.0/aten/src/ATen/core/boxing/impl/WrapFunctionIntoFunctor.h:13
#23 c10::impl::wrap_kernel_functor_unboxed_<c10::impl::detail::WrapFunctionIntoFunctor_<c10::CompileTimeFunctionPointer<at::Tensor(const at::Tensor&, const at::Tensor&, const c10::optional<at::Tensor>&), at::(anonymous namespace)::(anonymous namespace)::wrapper__linear>, at::Tensor, c10::guts::typelist::typelist<const at::Tensor&, const at::Tensor&, const c10::optional<at::Tensor>&> >, at::Tensor(const at::Tensor&, const at::Tensor&, const c10::optional<at::Tensor>&)>::call(c10::OperatorKernel *, c10::DispatchKeySet, const at::Tensor &, const at::Tensor &, const c10::optional<at::Tensor> &) (functor=0x55f08d9dedf0, args#0=..., args#1=..., args#2=...)
at /data/work/soft/pytorch-1.10.0/aten/src/ATen/core/boxing/impl/make_boxed_from_unboxed_functor.h:423
#24 0x00007f42a57a6120 in c10::callUnboxedKernelFunction<at::Tensor, at::Tensor const&, at::Tensor const&, c10::optional<at::Tensor> const&> (
unboxed_kernel_func=0x7f42a63c2aff <c10::impl::wrap_kernel_functor_unboxed_<c10::impl::detail::WrapFunctionIntoFunctor_<c10::CompileTimeFunctionPointer<at::Tensor(const at::Tensor&, const at::Tensor&, const c10::optional<at::Tensor>&), at::(anonymous namespace)::(anonymous namespace)::wrapper__linear>, at::Tensor, c10::guts::typelist::typelist<const at::Tensor&, const at::Tensor&, const c10::optional<at::Tensor>&> >, at::Tensor(const at::Tensor&, const at::Tensor&, const c10::optional<at::Tensor>&)>::call(c10::OperatorKernel *, c10::DispatchKeySet, const at::Tensor &, const at::Tensor &, const c10::optional<at::Tensor> &)>, functor=0x55f08d9dedf0, dispatchKeySet=...)
at /data/work/soft/pytorch-1.10.0/aten/src/ATen/core/boxing/KernelFunction_impl.h:57
#25 0x00007f42a5624c88 in c10::KernelFunction::call<at::Tensor, at::Tensor const&, at::Tensor const&, c10::optional<at::Tensor> const&> (dispatchKeySet=..., opHandle=..., this=0x55f08d0da620)
at /data/work/soft/pytorch-1.10.0/aten/src/ATen/core/boxing/KernelFunction_impl.h:67
#26 c10::Dispatcher::call<at::Tensor, at::Tensor const&, at::Tensor const&, c10::optional<at::Tensor> const&>(c10::TypedOperatorHandle<at::Tensor (at::Tensor const&, at::Tensor const&, c10::optional<at::Tensor> const&)> const&, at::Tensor const&, at::Tensor const&, c10::optional<at::Tensor> const&) const (op=..., this=0x7f42b6a95c40 <c10::Dispatcher::realSingleton()::_singleton>) at /data/work/soft/pytorch-1.10.0/aten/src/ATen/core/dispatch/Dispatcher.h:531
#27 c10::TypedOperatorHandle<at::Tensor (at::Tensor const&, at::Tensor const&, c10::optional<at::Tensor> const&)>::call(at::Tensor const&, at::Tensor const&, c10::optional<at::Tensor> const&) const (args#2=..., args#1=..., args#0=...,
this=<optimized out>) at /data/work/soft/pytorch-1.10.0/aten/src/ATen/core/dispatch/Dispatcher.h:397
#28 at::_ops::linear::call (input=..., weight=..., bias=...) at /data/work/soft/pytorch-1.10.0/build/aten/src/ATen/Operators_0.cpp:2715
#29 0x00007f42a4c2155d in at::linear (input=..., weight=..., bias=...) at /data/work/soft/pytorch-1.10.0/build/aten/src/ATen/Functions.h:3109
#30 0x00007f42a505347d in at::native::(anonymous namespace)::CellParams::linear_ih (this=0x7f40e2297320, input=...) at /data/work/soft/pytorch-1.10.0/aten/src/ATen/native/RNN.cpp:120
#31 0x00007f42a508702c in at::native::(anonymous namespace)::FullBidirectionalLayer<std::tuple<at::Tensor, at::Tensor>, at::native::(anonymous namespace)::CellParams>::operator() (this=0x7f42c1e91770, input=..., input_hidden={...},
params={...}) at /data/work/soft/pytorch-1.10.0/aten/src/ATen/native/RNN.cpp:921
#32 0x00007f42a5074da2 in at::native::(anonymous namespace)::apply_layer_stack<at::Tensor, std::pair<std::tuple<at::Tensor, at::Tensor>, std::tuple<at::Tensor, at::Tensor> >, std::pair<at::native::(anonymous namespace)::CellParams, at::native::(anonymous namespace)::CellParams> > (layer=..., input=..., hiddens=std::vector of length 3, capacity 3 = {...}, weights=std::vector of length 3, capacity 3 = {...}, num_layers=3, dropout_p=0, train=false)
---Type <return> to continue, or q <return> to quit---
at /data/work/soft/pytorch-1.10.0/aten/src/ATen/native/RNN.cpp:1125
## Code example
std::vector<float> input_values_;
...
torch::Tensor input_tensor = torch::from_blob(input_values_.data() + (begin_index * column_num_), {1, row_num_, column_num_}, options_).clone();
std::vector<torch::jit::IValue> inputs_;
inputs_.push_back(input_tensor);
if(inputs_.size() == 0)
{
return ret;
}
// Terminated from this line ====>
at::Tensor output = module_.forward(inputs_).toTensor();
## System Info
- PyTorch version: v1.10.0
- Python version: 3.7
- CPU forward
cc @jbschlosser @ezyang @albanD @zou3519 @gqchen @pearu @nikitaved @soulitzer @Lezcano @Varal7
| 1 |
5,234 | 81,531 |
CapabilityBasedPartitioner doesn't support horizontal (vertical?) fusion
|
triaged, module: nvfuser
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
steps to reproduce:
```
diff --git a/test/test_fx_passes.py b/test/test_fx_passes.py
index 39fe501f44..9fe5e4002e 100644
--- a/test/test_fx_passes.py
+++ b/test/test_fx_passes.py
@@ -158,6 +158,12 @@ class TestPartitionFunctions:
out = torch.stack([add_1, add_2, add_3])
return out
+ @staticmethod
+ def forward12(a):
+ add_1 = a + 1
+ add_2 = a + 2
+ return add_1, add_2
+
# A mock OperatorSupport class, where only operator.add is supported
class MockOperatorSupport(OperatorSupport):
def is_node_supported(self, submodules, node: torch.fx.Node) -> bool:
@@ -179,6 +185,7 @@ class TestFXGraphPasses(JitTestCase):
(TestPartitionFunctions.forward9, [['add_3', 'add_2', 'add_1', 'add']]),
(TestPartitionFunctions.forward10, [['add_3', 'add_2', 'add', 'add_1']]),
(TestPartitionFunctions.forward11, [['add_1'], ['add']]),
+ (TestPartitionFunctions.forward12, [['add_1', 'add_2']]),
])
def test_partitioner(self, fn, expected_partition):
traced = symbolic_trace(fn)
@@ -188,7 +195,7 @@ class TestFXGraphPasses(JitTestCase):
partitions = partitioner.propose_partitions()
partitions_name = [[node.name for node in partition.nodes] for partition in partitions]
- assert len(partitions_name) == len(expected_partition)
+ assert len(partitions_name) == len(expected_partition), partitions_name
for i in range(len(partitions_name)):
assert set(partitions_name[i]) == set(expected_partition[i])
```
I don't know if nvFuser supports horizontal fusion or not, but if the backend supports it (e.g., cuda graphs does) loss of fusion here is bad as you are doubling your memory traffic.
cc @SherlockNoMad @Chillee
### Versions
master
| 0 |
5,235 | 81,482 |
[onnx] Add support for prim::DictConstruct in pytorch-ONNX converter
|
module: onnx, triaged
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
Current handling of dict types is very limited in pytorch-ONNX converter is extremely limited.
In tracing mode, all the dict types are flattened such that only the values in the key-value pair are preserved.
In scripting mode, no such flattening occurs, and the conversion just errors out.
### Versions
Python version: 3.8.12 (default, Oct 12 2021, 13:49:34) [GCC 7.5.0] (64-bit runtime)
Python platform: Linux-5.15.0-1014-azure-x86_64-with-glibc2.17
Is CUDA available: N/A
CUDA runtime version: Could not collect
GPU models and configuration: Could not collect
Nvidia driver version: Could not collect
cuDNN version: Could not collect
HIP runtime version: N/A
MIOpen runtime version: N/A
Is XNNPACK available: N/A
Versions of relevant libraries:
[pip3] mypy==0.950
[pip3] mypy-extensions==0.4.3
[pip3] numpy==1.21.6
[pip3] torch==1.13.0a0+gitf1aeea2
[pip3] torchvision==0.13.0a0+8e5844f
[conda] mkl 2022.0.1 h06a4308_117
[conda] mkl-include 2022.0.1 h06a4308_117
[conda] numpy 1.21.6 pypi_0 pypi
[conda] torch 1.13.0a0+git6997ac7 pypi_0 pypi
[conda] torchvision 0.13.0a0+8e5844f dev_0 <develop>
| 2 |
5,236 | 81,478 |
[onnx] support more combinations of args/kwargs as model inputs for pytorch-onnx converter
|
module: onnx, triaged
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
Currently for a given model such that:
```
class Model(torch.nn.Module):
def forward(self, args, *kwargs):
....
```
The pytorch-ONNX converter only support certain combinations of model inputs such as:
```
(self, args, *kwargs)
(self, args)
```
and does not support combinations like:
```
(self, *kwargs)
(self, arg1, arg2, args, kwarg1, kwarg2, *kwargs)
... and many more
```
The fix would require somewhat of a redesign as to how the exporter deals with processing of model inputs.
### Versions
Python version: 3.8.12 (default, Oct 12 2021, 13:49:34) [GCC 7.5.0] (64-bit runtime)
Python platform: Linux-5.15.0-1014-azure-x86_64-with-glibc2.17
Is CUDA available: N/A
CUDA runtime version: Could not collect
GPU models and configuration: Could not collect
Nvidia driver version: Could not collect
cuDNN version: Could not collect
HIP runtime version: N/A
MIOpen runtime version: N/A
Is XNNPACK available: N/A
Versions of relevant libraries:
[pip3] mypy==0.950
[pip3] mypy-extensions==0.4.3
[pip3] numpy==1.21.6
[pip3] torch==1.13.0a0+gitf1aeea2
[pip3] torchvision==0.13.0a0+8e5844f
[conda] mkl 2022.0.1 h06a4308_117
[conda] mkl-include 2022.0.1 h06a4308_117
[conda] numpy 1.21.6 pypi_0 pypi
[conda] torch 1.13.0a0+git6997ac7 pypi_0 pypi
[conda] torchvision 0.13.0a0+8e5844f dev_0 <develop>
| 0 |
5,237 | 81,465 |
jit gives surprising results with lists of objects
|
oncall: jit
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
Hello, I have found something weird related to the use of jit on classes, using lists. On my IDE (Spyder) The following code can execute perfectly the first time, but will fail everytime after that. I need to kill the console and open a new one again for it to work a second time.
``` python
import torch
from typing import List
@torch.jit.script
class Mother():
def __init__(self):
pass
@torch.jit.script
def f():
l : List[Mother] = []
for i in range(3):
obj = Mother()
l.append(obj)
f()
```
On the second time, I get this message:
```
RuntimeError:
aten::append.t(t[](a!) self, t(c -> *) el) -> (t[](a!)):
Could not match type __torch__.Mother (of Python compilation unit at: 000001DE1823F0C0) to t in argument 'el': Type variable 't' previously matched to type __torch__.___torch_mangle_1.Mother (of Python compilation unit at: 000001DE1823F0C0) is matched to type __torch__.Mother (of Python compilation unit at: 000001DE1823F0C0).
:
File "untitled0.py", line 22
for i in range(3):
obj = Mother()
l.append(obj)
~~~~~~~~ <--- HERE
```
It seems that the name mangling causes a problem, but I am really not an expert on that. I guess it could cause issues in the future, although I have no idea how hard it is to fix it
### Versions
PyTorch version: 1.11.0+cpu
Is debug build: False
CUDA used to build PyTorch: None
ROCM used to build PyTorch: N/A
OS: Microsoft Windows 10 Home
GCC version: (Rev5, Built by MSYS2 project) 10.3.0
Clang version: Could not collect
CMake version: Could not collect
Libc version: N/A
Python version: 3.8.8 (default, Apr 13 2021, 15:08:03) [MSC v.1916 64 bit (AMD64)] (64-bit runtime)
Python platform: Windows-10-10.0.19041-SP0
Is CUDA available: False
CUDA runtime version: No CUDA
GPU models and configuration: No CUDA
Nvidia driver version: No CUDA
cuDNN version: No CUDA
HIP runtime version: N/A
MIOpen runtime version: N/A
Is XNNPACK available: True
Versions of relevant libraries:
[pip3] mypy-extensions==0.4.3
[pip3] numpy==1.20.1
[pip3] numpydoc==1.1.0
[pip3] torch==1.11.0
[pip3] torchvision==0.12.0
[conda] blas 1.0 mkl
[conda] mkl 2021.2.0 haa95532_296
[conda] mkl-service 2.3.0 py38h2bbff1b_1
[conda] mkl_fft 1.3.0 py38h277e83a_2
[conda] mkl_random 1.2.1 py38hf11a4ad_2
[conda] numpy 1.20.1 py38h34a8a5c_0
[conda] numpy-base 1.20.1 py38haf7ebc8_0
[conda] numpydoc 1.1.0 pyhd3eb1b0_1
[conda] torch 1.11.0 pypi_0 pypi
[conda] torchvision 0.12.0 pypi_0 pypi
| 0 |
5,238 | 81,460 |
[JIT] Request Constant Propagation to keep fake_quantize_per_tensor_affine and fake_quantize_per_channel_affine on the graph
|
oncall: jit
|
### 🚀 The feature, motivation and pitch
We are using [torch-blade](https://github.com/alibaba/BladeDISC) to accelerate torchscript with TensorRT backend. And we are going to support Quantization-aware-training model with torch-blade and compile the subgraph to TensorRT INT8 engine. During the optimization process, we will first export the QAT-model to torchscript with fake quant (`aten::fake_quantize_per_tensor_affine` and `aten::fake_quantize_per_channel_affine`). Then the torchscript will be converted to onnx graph with fake quant (onnx::QuantizeLinear and onnx::DeQuantizedLinear). TensorRT would parse the onnx model and build the int engine.
To simplify the torchscript and make more nodes optimized by trt, we would use some jit passes to optimize the torchscript with fake-quant. However, the `aten::fake_quantize_per_tensor_affine` and `aten::fake_quantize_per_channel_affine` would be folded by `torch._C._jit_pass_constant_propagation`:
Given a graph like:
```
weight -> fake_quant -> aten::convolution
```
After `torch._C._jit_pass_constant_propagation`, the graph would be:
```
weight -> aten::convolution
```
However, the TensorRT recommends that there should be a q-dq onnx node pair in the graph for the weight(see [here](https://docs.nvidia.com/deeplearning/tensorrt/developer-guide/index.html#qdq-placement-recs))
So is that possible to add `aten::fake_quantize_per_tensor_affine` and `aten::fake_quantize_per_channel_affine` to the skip_list of `torch._C._jit_pass_constant_propagation` or provide an interface to customize the skip_list
The aten::dequantize has been added to the skip_list of `torch._C._jit_pass_constant_propagation`. see #63991
### Alternatives
_No response_
### Additional context
_No response_
| 1 |
5,239 | 81,459 |
Missing corner case handling in ATen ctc_loss implementation
|
module: loss, module: error checking, triaged
|
The current ctc_loss implementation seems not to handle the case when input_length=0. In this case, the loss should be 0 if target_length=0 or -infinity otherwise, by definition.
Moreover, if max_input_length=0, the following code snippet might cause an index out-of-range bug.
https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/blob/62f1ff23fbf9e8f1281c135aadb3af87d2d69e7e/aten/src/ATen/native/LossCTC.cpp#L114-L117
| 0 |
5,240 | 81,448 |
torch.utils.checkpoint optimization opportunity
|
module: autograd, triaged, enhancement, has workaround
|
Currently checkpointing will always rerun the entirety of the forward function in backward, but sometimes that is not needed to recompute all the tensors that are needed for backward.
In the below snippet, suppose we want to avoid saving X2 for backward. With checkpointing, we'd need to checkpoint the function: `W2 @ gelu(X1)`, which would compute both gelu and matmul in backward. However, only the inputs of the last operation are saved for backward, so it is not actually necessary to compute the last matmul. The workaround for that is to use a custom function and do checkpointing manually.
```
X1 = W1 @ X
X2 = gelu(X1)
Y = W2 @ X2
```
Can we have an automated solution for this though? Some possible implementations:
1. interpose checks (e.g. using python dispatch level) to see if we've already computed all the needed saved tensors, and early stop. We should be careful though: if we use python dispatch, we actually go through a different composite compliant specific path which changes some in-place ops to out-of-place ops. I wonder if torch_function works though.
2. allow user to pass in a separate function(s) that are used to recompute the tensors. The issue with this is that what is saved is not really public API and subject to change.
Thanks @ngoyal2707 for reporting the issue
cc @ezyang @albanD @zou3519 @gqchen @pearu @nikitaved @soulitzer @Lezcano @Varal7
| 2 |
5,241 | 81,446 |
torch.randint should accept high=2**63
|
triaged, module: random, module: edge cases
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
It is not possible to use `torch.randint` to get random values in the range [0, 2^63-1].
That is, the non-negative integers that fit in an int64.
```
>>> torch.randint(2**63, (2,2))
RuntimeError: Overflow when unpacking long
```
This is of course because `2**63` doesn't itself fit into an int64.
However, the specification of `torch.randint` is "high (int): **One above** the highest integer to be drawn from the distribution." So it would make sense to support this "high" value to take advantage of the full range of int64 in the generated tensor.
### Versions
Collecting environment information...
PyTorch version: 1.11.0
Is debug build: False
CUDA used to build PyTorch: None
ROCM used to build PyTorch: N/A
OS: macOS 12.3.1 (x86_64)
GCC version: Could not collect
Clang version: 13.1.6 (clang-1316.0.21.2.3)
CMake version: version 3.21.4
Libc version: N/A
Python version: 3.9.13 (main, Jun 15 2022, 01:24:55) [Clang 13.1.6 (clang-1316.0.21.2.3)] (64-bit runtime)
Python platform: macOS-12.3.1-x86_64-i386-64bit
Is CUDA available: False
CUDA runtime version: No CUDA
GPU models and configuration: No CUDA
Nvidia driver version: No CUDA
cuDNN version: No CUDA
HIP runtime version: N/A
MIOpen runtime version: N/A
Is XNNPACK available: True
Versions of relevant libraries:
[pip3] functorch==0.1.1
[pip3] numpy==1.22.4
[pip3] torch==1.11.0
[pip3] torchmetrics==0.8.2
[pip3] torchvision==0.12.0
[conda] Could not collect
cc @pbelevich
| 0 |
5,242 | 81,428 |
torch.stft does not normalize non-rectangular windows correctly
|
triaged, module: complex, module: fft
|
## Issue description
When normalizing within torch.stft, the function divides by the $\sqrt{framelength}$ or otherwise $\sqrt{nfft}$. This would make sense for a rectangular window, or when the window is `None`.
When window is not None, or it is not a rectangular window however, it would make sense to normalize with regards to the values within the window, as can be seen in the link below, you normalize with the L2 norm of the window
https://ccrma.stanford.edu/~jos/sasp/Normalized_STFT_Basis.html
This is especially applicable when using normalizing for audio spectrograms, where the default window is a hann_window.
I believe that normalization should happen with ```output /= window.pow(2.0).sum().sqrt()``` If window is None like default, then it should fall back to its current normalization.
## System Info
- PyTorch or Caffe2: PyTorch
- How you installed PyTorch (conda, pip, source): conda
- Build command you used (if compiling from source):
- OS: macOS 12.3.1 (arm64)
- PyTorch version: 1.13.0.dev20220601
- Python version: 3.9.12
- CUDA/cuDNN version: N/A
- GPU models and configuration: N/A
- GCC version (if compiling from source): N/A
- CMake version: N/A
- Versions of any other relevant libraries: N/A
cc @ezyang @anjali411 @dylanbespalko @mruberry @Lezcano @nikitaved @peterbell10
| 1 |
5,243 | 81,426 |
[FSDP] `test_mp_embedding_reduce()` fails with `transformer_auto_wrap_policy()`
|
triaged, module: fsdp
|
`test_mp_embedding_reduce()` fails if we wrap the `TransformerWithSharedParams` with the typical `transformer_auto_wrap_policy()` with `transformer_layer_cls={TransformerEncoderLayer, TransformerDecoderLayer}`.
For now, we only wrap with a single top-level `FullyShardedDataParallel`, but we should investigate whether this failure is due to how the unit test is written or due to a gap in the mixed precision implementation.
cc @zhaojuanmao @mrshenli @rohan-varma @ezyang
| 0 |
5,244 | 81,417 |
Add a check to detect mutation of the inputs during backward
|
module: autograd, module: molly-guard, triaged, actionable
|
Modifying the grad_input during the backward pass is unexpected to the user and can produce silently incorrect gradients. However, currently you're allowed to do something like this:
```
import torch
class Func(torch.autograd.Function):
@staticmethod
def forward(ctx, x):
return x
@staticmethod
def vjp(ctx, x):
x += 1
return x
a = torch.rand(2, 4, requires_grad=True)
out = Func.apply(a)
grad_out = torch.ones_like(out)
grad_a, = torch.autograd.grad(out, (a,), grad_outputs=grad_out)
print(grad_out)
```
cc @ezyang @albanD @zou3519 @gqchen @pearu @nikitaved @soulitzer @Lezcano @Varal7
| 0 |
5,245 | 81,413 |
torch.searchsorted error message and documentation is unclear
|
module: docs, triaged, module: sorting and selection
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
## Case 1
```python
x = torch.randn(2, 3)
y = torch.randn([])
torch.searchsorted(x, y)
# RuntimeError: torch.searchsorted(): input value can be a scalar only when boundaries tensor dimension is 1, but we got boundaries tensor dim(2)
# and input value's dim(0) numel(1)
```
the args to searchsorted are `searchsorted(sorted_sequence, values)` according to the [documentation](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.searchsorted.html#torch.searchsorted); "boundaries" and "inputs" is ambiguous and we should be consistent
## Case 2
```python
x = torch.randn(2, 3)
y = torch.randn(1)
torch.searchsorted(x, y)
# RuntimeError: torch.searchsorted(): boundaries tensor should be 1 dimension or the first N-1 dimensions of boundaries tensor and input value te
# nsor must match, but we got boundaries tensor [2, 3] and input value tensor [1]
```
What is N? The documentation is a little unclear on this, but it looks like boundaries and inputs must have the same number of dimensions (or the inputs must have rank 0)
## Problem 3
https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.searchsorted.html#torch.searchsorted
From the docs, it is not clear how the input tensors "broadcast". This logic is captured in the chart with rules, but it would be nice to have some english that says that there are actually 2 cases for torch.searchsorted:
- boundaries is 1D, input is anything
- boundaries is ND, input is ND (with both Ns being the same and we require the shapes to be the same except in the last dimension)
We should enumerate the cases and describe what happens in each.
### Versions
1.12, main
cc @svekars @holly1238
| 1 |
5,246 | 81,412 |
num_worker and prefetch_factor in DataLoader do not scale
|
module: multiprocessing, module: dataloader, triaged
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
It seems like serialization and deserialization associated with python's multiprocessing limit the benefits of processing data in parallel.
In the following example, I create a custom iterable that returns a numpy array. As the size of the numpy array increases, the data fetching process becomes the bottleneck. This is expected. However, I would expect increasing `num_worker` and `prefetch_factor` would reduce this bottleneck by preparing batches in advance. But I do not see this behavior in the example below.
I test two cases where `MyIterable` returns
1. small object `np.array((10, 150))`
2. large object `np.array((1000, 150))`
The average time to process a batch in both scenarios is as follows:
```
# small np object
avg time per batch for num workers=0: 0.47068126868714444
avg time per batch for num workers=2: 0.20982365206225495
avg time per batch for num workers=4: 0.10560789656221914
avg time per batch for num workers=6: 0.07202646931250456
avg time per batch for num workers=8: 0.05311137337469063
```
```
# large np object
avg time per batch for num workers=0: 0.6090951558124971
avg time per batch for num workers=2: 0.4594530961876444
avg time per batch for num workers=4: 0.45023533212543043
avg time per batch for num workers=6: 0.3830978863124983
avg time per batch for num workers=8: 0.3811495694375253
```
For the small object, the time for each batch drops as expected when `num_workers` are increased. But for larger object, it does not change much. I attribute it to the fact the the worker process has to serialize the np object and the main process would then deserialize it. The larger the object, the more time it will take.
However, with large enough `num_worker` and `prefetch_factor`, shouldn't the queue in the dataloader be always filled such that data fetching is not the bottleneck? In this [line](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/blob/e9b3bc2eadb8ffe10c002abcd5a34a5b7d36f390/torch/utils/data/_utils/worker.py#L316) in `torch/utils/data/_utils/worker.py`, I see the batch is put in the queue by a worker in parallel. But I don't understand why queue is not filling up in advance. Am I missing something here?
Moreover, changing the `prefetch_factor` does not change anything. What is the point of `prefetch_factor`? The document says the main process pre-loads `num_worker * prefetch_factor` batches but as you can there is no effect in reducing the bottleneck.
I have added a more detailed step-by-step analysis in this [question](https://discuss.pytorch.org/t/queue-in-dataloader-does-not-behave-as-expected-when-using-num-workers/156487) for reference.
```
import time
import torch
import numpy as np
from time import sleep
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader, IterableDataset
def collate_fn(records):
# some custom collation function
return records
class MyIterable(object):
def __init__(self, n):
self.n = n
self.i = 0
def __iter__(self):
return self
def __next__(self):
if self.i < self.n:
sleep(0.003125) # simulates data fetch time
# return np.random.random((10, 150)) # small data item
return np.random.random((1000, 150)) # large data item
else:
raise StopIteration
class MyIterableDataset(IterableDataset):
def __init__(self, n):
super(MyIterableDataset).__init__()
self.n = n
def __iter__(self):
return MyIterable(self.n)
def get_performance_metrics(num_workers):
ds = MyIterableDataset(n=10000)
if num_workers == 0:
dl = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(ds, num_workers=0, batch_size=128, collate_fn=collate_fn)
else:
dl = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(ds, num_workers=num_workers, prefetch_factor=4, persistent_workers=True,
batch_size=128, collate_fn=collate_fn,
multiprocessing_context='spawn')
warmup = 5
times = []
t0 = time.perf_counter()
for i, batch in enumerate(dl):
sleep(0.05) # simulates train step
e = time.perf_counter()
if i >= warmup:
times.append(e - t0)
t0 = time.perf_counter()
if i >= 20:
break
print(f'avg time per batch for num workers={num_workers}: {sum(times) / len(times)}')
if __name__ == '__main__':
num_worker_options = [0, 2, 4, 6, 8]
for n in num_worker_options:
get_performance_metrics(n)
```
### Versions
Collecting environment information...
PyTorch version: 1.10.1
Is debug build: False
CUDA used to build PyTorch: None
ROCM used to build PyTorch: N/A
OS: macOS 11.6.1 (x86_64)
GCC version: Could not collect
Clang version: 12.0.5 (clang-1205.0.22.11)
CMake version: version 3.17.3
Libc version: N/A
Python version: 3.9.7 (default, Sep 16 2021, 08:50:36) [Clang 10.0.0 ] (64-bit runtime)
Python platform: macOS-10.16-x86_64-i386-64bit
Is CUDA available: False
CUDA runtime version: No CUDA
GPU models and configuration: No CUDA
Nvidia driver version: No CUDA
cuDNN version: No CUDA
HIP runtime version: N/A
MIOpen runtime version: N/A
Is XNNPACK available: True
Versions of relevant libraries:
[pip3] mypy-extensions==0.4.3
[pip3] numpy==1.21.2
[pip3] torch==1.10.1
[pip3] torchaudio==0.10.1
[pip3] torchvision==0.11.2
[conda] blas 1.0 mkl
[conda] ffmpeg 4.3 h0a44026_0 pytorch
[conda] mkl 2021.4.0 hecd8cb5_637
[conda] mkl-service 2.4.0 py39h9ed2024_0
[conda] mkl_fft 1.3.1 py39h4ab4a9b_0
[conda] mkl_random 1.2.2 py39hb2f4e1b_0
[conda] numpy 1.21.2 py39h4b4dc7a_0
[conda] numpy-base 1.21.2 py39he0bd621_0
[conda] pytorch 1.10.1 py3.9_0 pytorch
[conda] torchaudio 0.10.1 py39_cpu pytorch
[conda] torchvision 0.11.2 py39_cpu pytorch
cc @VitalyFedyunin @SsnL @ejguan @NivekT
| 11 |
5,247 | 81,405 |
Implement shape/size functions for nestedtensor
|
triaged, module: nestedtensor
|
### 🚀 The feature, motivation and pitch
Currently, nt.shape does not work. It just throws an error:
```
>>> import torch
>>> x = torch.nested_tensor([torch.rand(2), torch.rand(3)])
<stdin>:1: UserWarning: The PyTorch API of nested tensors is in prototype stage and will change in the near future. (Triggered internally at /Users/runner/work/pytorch/pytorch/pytorch/aten/src/ATen/NestedTensorImpl.cpp:99.)
>>> x.shape
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
RuntimeError: Internal error: NestedTensorImpl doesn't support sizes. Please file an issue on https://github.com/pytorch/nestedtensor
```
The shape function has been implemented, as seen [in this colab](https://colab.research.google.com/github/pytorch/nestedtensor/blob/master/tutorials/notebooks/basic.ipynb#scrollTo=STGxLWXXVg5Z), it just hasn't been migrated to torch.
I do not see any downside to implementing this function, as it is easy it implement (the code is already written; it just needs to be migrated), and it's much better than throwing an error.
### Alternatives
_No response_
### Additional context
My use case:
I am working with graph neural networks, which involve a variable number of agents, each of which can observe a variable number of objects in the environment. if fully functional, nestedtensor would significantly simply the problem, as it would obviate the need to store and manipulate tensors of batch indices.
cc @cpuhrsch
| 6 |
5,248 | 93,782 |
Global lambda function is not properly guarded
|
triaged, oncall: pt2, module: dynamo
|
The below code alters the lambda function `toy_sum` at the 3rd iteration, but the dynamo does not catch that modification.
**Code**
```python
import torch
import torchdynamo
toy_sum = lambda tlist: sum(tlist)
def toy_example(tlist):
ret_val = 0
for _ in range(5):
ret_val += toy_sum(tlist)
return ret_val
tlist = [torch.ones(10), torch.ones(10), torch.ones(10)]
print("with dynamo")
with torchdynamo.optimize("eager"):
for i in range(5):
if i == 2: # alter `toy_sum` after the third iteration
toy_sum = lambda tlist: tlist[0]
print(toy_example(tlist))
print("without dynamo")
toy_sum = lambda tlist: sum(tlist)
for i in range(5):
if i == 2: # alter `toy_sum` after the third iteration
toy_sum = lambda tlist: tlist[0]
print(toy_example(tlist))
```
**Result**
```
with dynamo
tensor([15., 15., 15., 15., 15., 15., 15., 15., 15., 15.])
tensor([15., 15., 15., 15., 15., 15., 15., 15., 15., 15.])
tensor([15., 15., 15., 15., 15., 15., 15., 15., 15., 15.])
tensor([15., 15., 15., 15., 15., 15., 15., 15., 15., 15.])
tensor([15., 15., 15., 15., 15., 15., 15., 15., 15., 15.])
without dynamo
tensor([15., 15., 15., 15., 15., 15., 15., 15., 15., 15.])
tensor([15., 15., 15., 15., 15., 15., 15., 15., 15., 15.])
tensor([5., 5., 5., 5., 5., 5., 5., 5., 5., 5.])
tensor([5., 5., 5., 5., 5., 5., 5., 5., 5., 5.])
tensor([5., 5., 5., 5., 5., 5., 5., 5., 5., 5.])
```
<details>
<summary>logs with torchdynamo.config.debug</summary>
```
with dynamo
skipping __init__ /Users/kinetc/opt/anaconda3/envs/dynamo/lib/python3.8/contextlib.py
skipping __enter__ /Users/kinetc/opt/anaconda3/envs/dynamo/lib/python3.8/contextlib.py
__compiled_fn_0 <eval_with_key>.1
opcode name target args kwargs
------------- -------- ------------------------ ------------------ --------
placeholder tlist_0_ tlist_0_ () {}
placeholder tlist_1_ tlist_1_ () {}
placeholder tlist_2_ tlist_2_ () {}
call_function add <built-in function add> (0, tlist_0_) {}
call_function add_1 <built-in function add> (add, tlist_1_) {}
call_function add_2 <built-in function add> (add_1, tlist_2_) {}
call_function add_3 <built-in function add> (add_2, 0) {}
call_function add_4 <built-in function add> (0, tlist_0_) {}
call_function add_5 <built-in function add> (add_4, tlist_1_) {}
call_function add_6 <built-in function add> (add_5, tlist_2_) {}
call_function iadd <built-in function iadd> (add_3, add_6) {}
call_function add_7 <built-in function add> (0, tlist_0_) {}
call_function add_8 <built-in function add> (add_7, tlist_1_) {}
call_function add_9 <built-in function add> (add_8, tlist_2_) {}
call_function iadd_1 <built-in function iadd> (iadd, add_9) {}
call_function add_10 <built-in function add> (0, tlist_0_) {}
call_function add_11 <built-in function add> (add_10, tlist_1_) {}
call_function add_12 <built-in function add> (add_11, tlist_2_) {}
call_function iadd_2 <built-in function iadd> (iadd_1, add_12) {}
call_function add_13 <built-in function add> (0, tlist_0_) {}
call_function add_14 <built-in function add> (add_13, tlist_1_) {}
call_function add_15 <built-in function add> (add_14, tlist_2_) {}
call_function iadd_3 <built-in function iadd> (iadd_2, add_15) {}
output output output ((iadd_3,),) {}
ORIGINAL BYTECODE toy_example test.py 11
12 0 LOAD_CONST 1 (0)
2 STORE_FAST 1 (ret_val)
13 4 LOAD_GLOBAL 0 (range)
6 LOAD_CONST 2 (5)
8 CALL_FUNCTION 1
10 GET_ITER
12 FOR_ITER 16 (to 30)
14 STORE_FAST 2 (_)
14 16 LOAD_FAST 1 (ret_val)
18 LOAD_GLOBAL 1 (toy_sum)
20 LOAD_FAST 0 (tlist)
22 CALL_FUNCTION 1
24 INPLACE_ADD
26 STORE_FAST 1 (ret_val)
28 JUMP_ABSOLUTE 12
15 >> 30 LOAD_FAST 1 (ret_val)
32 RETURN_VALUE
MODIFIED BYTECODE
11 0 LOAD_GLOBAL 2 (__compiled_fn_0)
2 LOAD_FAST 0 (tlist)
4 LOAD_CONST 1 (0)
6 BINARY_SUBSCR
8 LOAD_FAST 0 (tlist)
10 LOAD_CONST 3 (1)
12 BINARY_SUBSCR
14 LOAD_FAST 0 (tlist)
16 LOAD_CONST 4 (2)
18 BINARY_SUBSCR
20 CALL_FUNCTION 3
22 UNPACK_SEQUENCE 1
24 RETURN_VALUE
GUARDS:
-
local 'tlist' LIST_LENGTH"
{
'guard_types': ['LIST_LENGTH'],
'code': ['___check_type_id(tlist, 4346971272)', 'len(tlist) == 3'],
'obj_weakref': None
'guarded_class': <weakref at 0x7fc50003bae0; to 'type' at 0x103198488 (list)>
}
-
local 'tlist[0]' TENSOR_MATCH"
{
'guard_types': ['TENSOR_MATCH'],
'code': None,
'obj_weakref': <weakref at 0x7fc4f17e0310; to 'Tensor' at 0x7fc4f018f090>
'guarded_class': <weakref at 0x7fc4f088a040; to 'torch._C._TensorMeta' at 0x7fc4ea5964b0 (Tensor)>
}
-
local 'tlist[1]' TENSOR_MATCH"
{
'guard_types': ['TENSOR_MATCH'],
'code': None,
'obj_weakref': <weakref at 0x7fc4f17e0360; to 'Tensor' at 0x7fc4f0189e00>
'guarded_class': <weakref at 0x7fc4f088a040; to 'torch._C._TensorMeta' at 0x7fc4ea5964b0 (Tensor)>
}
-
local 'tlist[2]' TENSOR_MATCH"
{
'guard_types': ['TENSOR_MATCH'],
'code': None,
'obj_weakref': <weakref at 0x7fc4f17e03b0; to 'Tensor' at 0x7fc4f0251450>
'guarded_class': <weakref at 0x7fc4f088a040; to 'torch._C._TensorMeta' at 0x7fc4ea5964b0 (Tensor)>
}
-
global 'sum' BUILTIN_MATCH"
{
'guard_types': None,
'code': None,
'obj_weakref': None
'guarded_class': None
}
-
global 'range' BUILTIN_MATCH"
{
'guard_types': None,
'code': None,
'obj_weakref': None
'guarded_class': None
}
-
global 'toy_sum' FUNCTION_MATCH"
{
'guard_types': None,
'code': None,
'obj_weakref': None
'guarded_class': None
}
skipping _fn /Users/kinetc/work/torchdynamo/torchdynamo/eval_frame.py
skipping nothing /Users/kinetc/work/torchdynamo/torchdynamo/eval_frame.py
skipping __exit__ /Users/kinetc/opt/anaconda3/envs/dynamo/lib/python3.8/contextlib.py
skipping __repr__ /Users/kinetc/opt/anaconda3/envs/dynamo/lib/python3.8/site-packages/torch/_tensor.py
skipping _str /Users/kinetc/opt/anaconda3/envs/dynamo/lib/python3.8/site-packages/torch/_tensor_str.py
skipping __init__ /Users/kinetc/opt/anaconda3/envs/dynamo/lib/python3.8/site-packages/torch/autograd/grad_mode.py
skipping is_scripting /Users/kinetc/opt/anaconda3/envs/dynamo/lib/python3.8/site-packages/torch/_jit_internal.py
skipping __enter__ /Users/kinetc/opt/anaconda3/envs/dynamo/lib/python3.8/site-packages/torch/autograd/grad_mode.py
skipping __init__ /Users/kinetc/opt/anaconda3/envs/dynamo/lib/python3.8/site-packages/torch/autograd/grad_mode.py
skipping _str_intern /Users/kinetc/opt/anaconda3/envs/dynamo/lib/python3.8/site-packages/torch/_tensor_str.py
skipping unpack_dual /Users/kinetc/opt/anaconda3/envs/dynamo/lib/python3.8/site-packages/torch/autograd/forward_ad.py
skipping _tensor_str /Users/kinetc/opt/anaconda3/envs/dynamo/lib/python3.8/site-packages/torch/_tensor_str.py
skipping __init__ /Users/kinetc/opt/anaconda3/envs/dynamo/lib/python3.8/site-packages/torch/_tensor_str.py
skipping __exit__ /Users/kinetc/opt/anaconda3/envs/dynamo/lib/python3.8/site-packages/torch/autograd/grad_mode.py
skipping tensor_totype /Users/kinetc/opt/anaconda3/envs/dynamo/lib/python3.8/site-packages/torch/_tensor_str.py
skipping __iter__ /Users/kinetc/opt/anaconda3/envs/dynamo/lib/python3.8/site-packages/torch/_tensor.py
skipping __format__ /Users/kinetc/opt/anaconda3/envs/dynamo/lib/python3.8/site-packages/torch/_tensor.py
skipping _tensor_str_with_formatter /Users/kinetc/opt/anaconda3/envs/dynamo/lib/python3.8/site-packages/torch/_tensor_str.py
skipping _vector_str /Users/kinetc/opt/anaconda3/envs/dynamo/lib/python3.8/site-packages/torch/_tensor_str.py
skipping width /Users/kinetc/opt/anaconda3/envs/dynamo/lib/python3.8/site-packages/torch/_tensor_str.py
skipping <listcomp> /Users/kinetc/opt/anaconda3/envs/dynamo/lib/python3.8/site-packages/torch/_tensor_str.py
skipping _val_formatter /Users/kinetc/opt/anaconda3/envs/dynamo/lib/python3.8/site-packages/torch/_tensor_str.py
skipping format /Users/kinetc/opt/anaconda3/envs/dynamo/lib/python3.8/site-packages/torch/_tensor_str.py
skipping <listcomp> /Users/kinetc/opt/anaconda3/envs/dynamo/lib/python3.8/site-packages/torch/_tensor_str.py
skipping <listcomp> /Users/kinetc/opt/anaconda3/envs/dynamo/lib/python3.8/site-packages/torch/_tensor_str.py
skipping _add_suffixes /Users/kinetc/opt/anaconda3/envs/dynamo/lib/python3.8/site-packages/torch/_tensor_str.py
skipping __instancecheck__ /Users/kinetc/opt/anaconda3/envs/dynamo/lib/python3.8/site-packages/torch/nn/parameter.py
tensor([15., 15., 15., 15., 15., 15., 15., 15., 15., 15.])
tensor([15., 15., 15., 15., 15., 15., 15., 15., 15., 15.])
tensor([15., 15., 15., 15., 15., 15., 15., 15., 15., 15.])
tensor([15., 15., 15., 15., 15., 15., 15., 15., 15., 15.])
tensor([15., 15., 15., 15., 15., 15., 15., 15., 15., 15.])
skipping __exit__ /Users/kinetc/work/torchdynamo/torchdynamo/eval_frame.py
without dynamo
tensor([15., 15., 15., 15., 15., 15., 15., 15., 15., 15.])
tensor([15., 15., 15., 15., 15., 15., 15., 15., 15., 15.])
tensor([5., 5., 5., 5., 5., 5., 5., 5., 5., 5.])
tensor([5., 5., 5., 5., 5., 5., 5., 5., 5., 5.])
tensor([5., 5., 5., 5., 5., 5., 5., 5., 5., 5.])
```
</details>
Is there any resources that this kind of behavior (modifying lambda variable at a runtime) is not considered while tracing?
cc: @nunoplopes
cc @ezyang @soumith @msaroufim @wconstab @ngimel @bdhirsh @voznesenskym @yanboliang @penguinwu @anijain2305 @EikanWang @jgong5 @Guobing-Chen @XiaobingSuper @zhuhaozhe @blzheng @Xia-Weiwen @wenzhe-nrv @jiayisunx @desertfire
| 3 |
5,249 | 81,385 |
"Attempted to resize a view tensor to a larger size. This is not allowed in the functionalization pass" reported on non view tensor
|
triaged, module: functionalization
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
Repro test:
```
def test_resize_intermediate(self):
def f(x):
y = x.clone()
z = y.view(0)
y.resize_(20)
return y
self.assert_functionalization(f, torch.ones(0))
```
this raises
```
======================================================================
ERROR: test_resize_intermediate (__main__.TestFunctionalization)
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "test/test_functionalization.py", line 120, in test_resize_intermediate
self.assert_functionalization(f, torch.ones(0))
File "test/test_functionalization.py", line 93, in assert_functionalization
out_functional = func(input_functional)
File "test/test_functionalization.py", line 117, in f
y.resize_(20)
RuntimeError: Attempted to resize a view tensor to a larger size. This is not allowed in the functionalization pass
```
However, y is not a view.
This variant of the program does work:
```
def f(x):
y = x.clone()
y.resize_(20)
return y
```
cc @bdhirsh @ezyang this is low priority
### Versions
master
| 1 |
5,250 | 81,383 |
Investigate ncclRedOpCreatePreMulSum operator for gradient reduction
|
oncall: distributed
|
### 🚀 The feature, motivation and pitch
Per @kwen2501's comment here: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/78774#issuecomment-1148272714, we should investigate this operator and see whether it is more efficient than gradient pre/post divide in DDP / FSDP.
### Alternatives
_No response_
### Additional context
_No response_
cc @pietern @mrshenli @pritamdamania87 @zhaojuanmao @satgera @rohan-varma @gqchen @aazzolini @osalpekar @jiayisuse @SciPioneer @H-Huang @kwen2501
| 1 |
5,251 | 81,381 |
quantization: QConfigMapping should be easy to print
|
oncall: quantization, triaged
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
Currently printing out the contents of a `QConfigMapping` object does not make it easy to see the contents:
```
import torch
qconfig_mapping = torch.ao.quantization.get_default_qconfig_mapping()
print(qconfig_mapping)
> <torch.ao.quantization.qconfig_mapping.QConfigMapping object at 0x7f29785c45e0>
```
Ideally printing this object would display the contents, so users can inspect the configs they are passing in to the quantization APIs.
### Versions
master
cc @jerryzh168 @jianyuh @raghuramank100 @jamesr66a @jgong5 @Xia-Weiwen @leslie-fang-intel @vkuzo
| 0 |
5,252 | 81,361 |
Segfault with fake tensor
|
triaged, module: fakeTensor
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
This torchdynamo branch https://github.com/ezyang/torchdynamo/tree/fake-segfault triggers a segfault in mutation analysis with `python tests/test_optimizations.py -k test_has_mutation`. I'm pretty sure it's fake tensor related. I have a workaround so fixing the segfault isn't urgent, but it should be looked into.
gdb backtrace:
```
#0 0x00007fffb0d5d2b4 in c10::SafePyObject::ptr(c10::impl::PyInterpreter const*) const ()
from /raid/ezyang/pytorch-scratch2/torch/lib/libc10.so
#1 0x00007fffc714afc9 in torch::handle_torch_function_no_python_arg_parser(c10::ArrayRef<pybind11::handle>, _object*, _object*, char const*, _object*, char const*, torch::TorchFunctionName) ()
from /raid/ezyang/pytorch-scratch2/torch/lib/libtorch_python.so
#2 0x00007fffc6e0c763 in (anonymous namespace)::concrete_dispatch_fn(c10::impl::PyInterpreter const*, c10::OperatorHandle const&, std::vector<c10::IValue, std::allocator<c10::IValue> >*) ()
from /raid/ezyang/pytorch-scratch2/torch/lib/libtorch_python.so
#3 0x00007fffbd01ef6e in void c10::KernelFunction::make_boxed_function<&(anonymous namespace)::pythonFallback>(c10::OperatorKernel*, c10::OperatorHandle const&, c10::DispatchKeySet, std::vector<c10::IValue, std::allocator<c10::IValue> >*) ()
from /raid/ezyang/pytorch-scratch2/torch/lib/libtorch_cpu.so
#4 0x00007fffbd94696d in c10::impl::BoxedKernelWrapper<at::Tensor (at::Tensor const&), void>::call(void (*)(c10::OperatorKernel*, c10::OperatorHandle const&, c10::DispatchKeySet, std::vector<c10::IValue, std::allocator<c10::IValue> >*), c10::OperatorKernel*, c10::OperatorHandle const&, c10::DispatchKeySet, at::Tensor const&) ()
from /raid/ezyang/pytorch-scratch2/torch/lib/libtorch_cpu.so
#5 0x00007fffbdc49d0c in at::_ops::t::redispatch(c10::DispatchKeySet, at::Tensor const&) ()
from /raid/ezyang/pytorch-scratch2/torch/lib/libtorch_cpu.so
#6 0x00007fffbf8ee5a8 in torch::ADInplaceOrView::(anonymous namespace)::t(c10::DispatchKeySet, at::Tensor const&) ()
from /raid/ezyang/pytorch-scratch2/torch/lib/libtorch_cpu.so
#7 0x00007fffbf8ee7a8 in c10::impl::wrap_kernel_functor_unboxed_<c10::impl::detail::WrapFunctionIntoFunctor_<c10::CompileTimeFunctionPointer<at::Tensor (c10::DispatchKeySet, at::Tensor const&), &torch::ADInplaceOrView::(anonymous namespace)::t>, at::Tensor, c10::guts::typelist::typelist<c10::DispatchKeySet, at::Tensor const&> >, at::Tensor (c10::DispatchKeySet, at::Tensor const&)>::call(c10::OperatorKernel*, c10::DispatchKeySet, at::Tensor const&) ()
from /raid/ezyang/pytorch-scratch2/torch/lib/libtorch_cpu.so
#8 0x00007fffbdc49c61 in at::_ops::t::redispatch(c10::DispatchKeySet, at::Tensor const&) ()
from /raid/ezyang/pytorch-scratch2/torch/lib/libtorch_cpu.so
#9 0x00007fffbf3f1b99 in torch::autograd::VariableType::(anonymous namespace)::t(c10::DispatchKeySet, at::Tensor const&) ()
from /raid/ezyang/pytorch-scratch2/torch/lib/libtorch_cpu.so
#10 0x00007fffbf3f2108 in c10::impl::make_boxed_from_unboxed_functor<c10::impl::detail::WrapFunctionIntoFunctor_<c10::CompileTimeFunctionPointer<at::Tensor (c10::DispatchKeySet, at::Tensor const&), &torch::autograd::VariableType::(anonymous namespace)::t>, at::Tensor, c10::guts::typelist::typelist<c10::DispatchKeySet, at::Tensor const&> >, false>::call(c10::OperatorKernel*, c10::OperatorHandle const&, c10::DispatchKeySet, std::vector<c10::IValue, std::allocator<c10::IValue> >*) ()
from /raid/ezyang/pytorch-scratch2/torch/lib/libtorch_cpu.so
#11 0x00007fffbd01edfe in void c10::KernelFunction::make_boxed_function<&(anonymous namespace)::pythonTLSSnapshotFallback>(c10::OperatorKernel*, c10::OperatorHandle const&, c10::DispatchKeySet, std::vector<c10::IValue, std::allocator<c10::IValue> >*) ()
from /raid/ezyang/pytorch-scratch2/torch/lib/libtorch_cpu.so
#12 0x00007fffbd94696d in c10::impl::BoxedKernelWrapper<at::Tensor (at::Tensor const&), void>::call(void (*)(c10::OperatorKernel*, c10::OperatorHandle const&, c10::DispatchKeySet, std::vector<c10::IValue, std::allocator<c10::IValue> >*), c10::OperatorKernel*, c10::OperatorHandle const&, c10::DispatchKeySet, at::Tensor const&) ()
from /raid/ezyang/pytorch-scratch2/torch/lib/libtorch_cpu.so
#13 0x00007fffbdc8755f in at::_ops::t::call(at::Tensor const&) () from /raid/ezyang/pytorch-scratch2/torch/lib/libtorch_cpu.so
#14 0x00007fffbd25b780 in at::native::linear(at::Tensor const&, at::Tensor const&, c10::optional<at::Tensor> const&) ()
from /raid/ezyang/pytorch-scratch2/torch/lib/libtorch_cpu.so
#15 0x00007fffbe182943 in c10::impl::make_boxed_from_unboxed_functor<c10::impl::detail::WrapFunctionIntoFunctor_<c10::CompileTimeFunctionPointer<at::Tensor (at::Tensor const&, at::Tensor const&, c10::optional<at::Tensor> const&), &at::(anonymous namespace)::(anonymous namespace)::wrapper__linear>, at::Tensor, c10::guts::typelist::typelist<at::Tensor const&, at::Tensor const&, c10::optional<at::Tensor> const&> >, false>::call(c10::OperatorKernel*, c10::OperatorHandle const&, c10::DispatchKeySet, std::vector<c10::IValue, std::allocator<c10::IValue> >*) () from /raid/ezyang/pytorch-scratch2/torch/lib/libtorch_cpu.so
#16 0x00007fffbd01edfe in void c10::KernelFunction::make_boxed_function<&(anonymous namespace)::pythonTLSSnapshotFallback>(c10::OperatorKernel*, c10::OperatorHandle const&, c10::DispatchKeySet, std::vector<c10::IValue, std::allocator<c10::IValue> >*) ()
from /raid/ezyang/pytorch-scratch2/torch/lib/libtorch_cpu.so
#17 0x00007fffbd94f25f in c10::impl::BoxedKernelWrapper<at::Tensor (at::Tensor const&, at::Tensor const&, c10::optional<at::Tensor> const&), void>::call(void (*)(c10::OperatorKernel*, c10::OperatorHandle const&, c10::DispatchKeySet, std::vector<c10::IValue, std::allocator<c10::IValue> >*), c10::OperatorKernel*, c10::OperatorHandle const&, c10::DispatchKeySet, at::Tensor const&, at::Tensor const&, c10::optional<at::Tensor> const&) () from /raid/ezyang/pytorch-scratch2/torch/lib/libtorch_cpu.so
#18 0x00007fffbd8f37ae in at::_ops::linear::call(at::Tensor const&, at::Tensor const&, c10::optional<at::Tensor> const&) ()
```
### Versions
master
| 1 |
5,253 | 81,358 |
[Prims+NvFuser] Issue with aten.where.ScalarSelf
|
triaged, module: nvfuser
|
Running into **"Invoked with: <torch._C._nvfuser.FusionDefinition object at 0x7f6628a0d530>, <class 'TypeError'>, TypeError("where(): incompatible function arguments."** if I include aten.Where.ScalarSelf in the supported_op list.
Full log here:
skipping aten.embedding_dense_backward.default
skipping aten.addmm.default
skipping aten.native_layer_norm_backward.default
====== BERT_pytorch_forward_0 ======
Generating testing data...
aten2aten decomp: aten.embedding.default <function embedding at 0x7f66317bb160>
aten2aten decomp: aten.embedding.default <function embedding at 0x7f66317bb160>
aten2aten decomp: aten.std.correction <function std_decomposition at 0x7f66317bbd30>
aten2aten decomp: aten.var.correction <function var_correction at 0x7f66317bbc10>
aten2aten decomp: aten.transpose.int <function transpose_int at 0x7f66317bbf70>
aten2aten decomp: aten.transpose.int <function transpose_int at 0x7f66317bbf70>
aten2aten decomp: aten.transpose.int <function transpose_int at 0x7f66317bbf70>
aten2aten decomp: aten.transpose.int <function transpose_int at 0x7f66317bbf70>
aten2aten decomp: aten.masked_fill.Scalar <function masked_fill_Scalar at 0x7f6631823790>
aten2aten decomp: aten._softmax.default <function _softmax at 0x7f6631823c10>
aten2aten decomp: aten.transpose.int <function transpose_int at 0x7f66317bbf70>
aten2aten decomp: aten.std.correction <function std_decomposition at 0x7f66317bbd30>
aten2aten decomp: aten.var.correction <function var_correction at 0x7f66317bbc10>
aten2aten decomp: aten.std.correction <function std_decomposition at 0x7f66317bbd30>
aten2aten decomp: aten.var.correction <function var_correction at 0x7f66317bbc10>
aten2aten decomp: aten.transpose.int <function transpose_int at 0x7f66317bbf70>
aten2aten decomp: aten.transpose.int <function transpose_int at 0x7f66317bbf70>
aten2aten decomp: aten.transpose.int <function transpose_int at 0x7f66317bbf70>
aten2aten decomp: aten.transpose.int <function transpose_int at 0x7f66317bbf70>
aten2aten decomp: aten.masked_fill.Scalar <function masked_fill_Scalar at 0x7f6631823790>
aten2aten decomp: aten._softmax.default <function _softmax at 0x7f6631823c10>
aten2aten decomp: aten.transpose.int <function transpose_int at 0x7f66317bbf70>
aten2aten decomp: aten.std.correction <function std_decomposition at 0x7f66317bbd30>
aten2aten decomp: aten.var.correction <function var_correction at 0x7f66317bbc10>
aten2aten decomp: aten.std.correction <function std_decomposition at 0x7f66317bbd30>
aten2aten decomp: aten.var.correction <function var_correction at 0x7f66317bbc10>
aten2aten decomp: aten.transpose.int <function transpose_int at 0x7f66317bbf70>
aten2aten decomp: aten.transpose.int <function transpose_int at 0x7f66317bbf70>
aten2aten decomp: aten.transpose.int <function transpose_int at 0x7f66317bbf70>
aten2aten decomp: aten.transpose.int <function transpose_int at 0x7f66317bbf70>
aten2aten decomp: aten.masked_fill.Scalar <function masked_fill_Scalar at 0x7f6631823790>
aten2aten decomp: aten._softmax.default <function _softmax at 0x7f6631823c10>
aten2aten decomp: aten.transpose.int <function transpose_int at 0x7f66317bbf70>
aten2aten decomp: aten.std.correction <function std_decomposition at 0x7f66317bbd30>
aten2aten decomp: aten.var.correction <function var_correction at 0x7f66317bbc10>
aten2aten decomp: aten.std.correction <function std_decomposition at 0x7f66317bbd30>
aten2aten decomp: aten.var.correction <function var_correction at 0x7f66317bbc10>
aten2aten decomp: aten.transpose.int <function transpose_int at 0x7f66317bbf70>
aten2aten decomp: aten.transpose.int <function transpose_int at 0x7f66317bbf70>
aten2aten decomp: aten.transpose.int <function transpose_int at 0x7f66317bbf70>
aten2aten decomp: aten.transpose.int <function transpose_int at 0x7f66317bbf70>
aten2aten decomp: aten.masked_fill.Scalar <function masked_fill_Scalar at 0x7f6631823790>
aten2aten decomp: aten._softmax.default <function _softmax at 0x7f6631823c10>
aten2aten decomp: aten.transpose.int <function transpose_int at 0x7f66317bbf70>
aten2aten decomp: aten.std.correction <function std_decomposition at 0x7f66317bbd30>
aten2aten decomp: aten.var.correction <function var_correction at 0x7f66317bbc10>
aten2aten decomp: aten.std.correction <function std_decomposition at 0x7f66317bbd30>
aten2aten decomp: aten.var.correction <function var_correction at 0x7f66317bbc10>
aten2aten decomp: aten.transpose.int <function transpose_int at 0x7f66317bbf70>
aten2aten decomp: aten.transpose.int <function transpose_int at 0x7f66317bbf70>
aten2aten decomp: aten.transpose.int <function transpose_int at 0x7f66317bbf70>
aten2aten decomp: aten.transpose.int <function transpose_int at 0x7f66317bbf70>
aten2aten decomp: aten.masked_fill.Scalar <function masked_fill_Scalar at 0x7f6631823790>
aten2aten decomp: aten._softmax.default <function _softmax at 0x7f6631823c10>
aten2aten decomp: aten.transpose.int <function transpose_int at 0x7f66317bbf70>
aten2aten decomp: aten.std.correction <function std_decomposition at 0x7f66317bbd30>
aten2aten decomp: aten.var.correction <function var_correction at 0x7f66317bbc10>
aten2aten decomp: aten.std.correction <function std_decomposition at 0x7f66317bbd30>
aten2aten decomp: aten.var.correction <function var_correction at 0x7f66317bbc10>
aten2aten decomp: aten.transpose.int <function transpose_int at 0x7f66317bbf70>
aten2aten decomp: aten.transpose.int <function transpose_int at 0x7f66317bbf70>
aten2aten decomp: aten.transpose.int <function transpose_int at 0x7f66317bbf70>
aten2aten decomp: aten.transpose.int <function transpose_int at 0x7f66317bbf70>
aten2aten decomp: aten.masked_fill.Scalar <function masked_fill_Scalar at 0x7f6631823790>
aten2aten decomp: aten._softmax.default <function _softmax at 0x7f6631823c10>
aten2aten decomp: aten.transpose.int <function transpose_int at 0x7f66317bbf70>
aten2aten decomp: aten.std.correction <function std_decomposition at 0x7f66317bbd30>
aten2aten decomp: aten.var.correction <function var_correction at 0x7f66317bbc10>
aten2aten decomp: aten.std.correction <function std_decomposition at 0x7f66317bbd30>
aten2aten decomp: aten.var.correction <function var_correction at 0x7f66317bbc10>
aten2aten decomp: aten.transpose.int <function transpose_int at 0x7f66317bbf70>
aten2aten decomp: aten.transpose.int <function transpose_int at 0x7f66317bbf70>
aten2aten decomp: aten.transpose.int <function transpose_int at 0x7f66317bbf70>
aten2aten decomp: aten.transpose.int <function transpose_int at 0x7f66317bbf70>
aten2aten decomp: aten.masked_fill.Scalar <function masked_fill_Scalar at 0x7f6631823790>
aten2aten decomp: aten._softmax.default <function _softmax at 0x7f6631823c10>
aten2aten decomp: aten.transpose.int <function transpose_int at 0x7f66317bbf70>
aten2aten decomp: aten.std.correction <function std_decomposition at 0x7f66317bbd30>
aten2aten decomp: aten.var.correction <function var_correction at 0x7f66317bbc10>
aten2aten decomp: aten.std.correction <function std_decomposition at 0x7f66317bbd30>
aten2aten decomp: aten.var.correction <function var_correction at 0x7f66317bbc10>
aten2aten decomp: aten.transpose.int <function transpose_int at 0x7f66317bbf70>
aten2aten decomp: aten.transpose.int <function transpose_int at 0x7f66317bbf70>
aten2aten decomp: aten.transpose.int <function transpose_int at 0x7f66317bbf70>
aten2aten decomp: aten.transpose.int <function transpose_int at 0x7f66317bbf70>
aten2aten decomp: aten.masked_fill.Scalar <function masked_fill_Scalar at 0x7f6631823790>
aten2aten decomp: aten._softmax.default <function _softmax at 0x7f6631823c10>
aten2aten decomp: aten.transpose.int <function transpose_int at 0x7f66317bbf70>
aten2aten decomp: aten.std.correction <function std_decomposition at 0x7f66317bbd30>
aten2aten decomp: aten.var.correction <function var_correction at 0x7f66317bbc10>
aten2aten decomp: aten.std.correction <function std_decomposition at 0x7f66317bbd30>
aten2aten decomp: aten.var.correction <function var_correction at 0x7f66317bbc10>
aten2aten decomp: aten.transpose.int <function transpose_int at 0x7f66317bbf70>
aten2aten decomp: aten.transpose.int <function transpose_int at 0x7f66317bbf70>
aten2aten decomp: aten.transpose.int <function transpose_int at 0x7f66317bbf70>
aten2aten decomp: aten.transpose.int <function transpose_int at 0x7f66317bbf70>
aten2aten decomp: aten.masked_fill.Scalar <function masked_fill_Scalar at 0x7f6631823790>
aten2aten decomp: aten._softmax.default <function _softmax at 0x7f6631823c10>
aten2aten decomp: aten.transpose.int <function transpose_int at 0x7f66317bbf70>
aten2aten decomp: aten.std.correction <function std_decomposition at 0x7f66317bbd30>
aten2aten decomp: aten.var.correction <function var_correction at 0x7f66317bbc10>
aten2aten decomp: aten.std.correction <function std_decomposition at 0x7f66317bbd30>
aten2aten decomp: aten.var.correction <function var_correction at 0x7f66317bbc10>
aten2aten decomp: aten.transpose.int <function transpose_int at 0x7f66317bbf70>
aten2aten decomp: aten.transpose.int <function transpose_int at 0x7f66317bbf70>
aten2aten decomp: aten.transpose.int <function transpose_int at 0x7f66317bbf70>
aten2aten decomp: aten.transpose.int <function transpose_int at 0x7f66317bbf70>
aten2aten decomp: aten.masked_fill.Scalar <function masked_fill_Scalar at 0x7f6631823790>
aten2aten decomp: aten._softmax.default <function _softmax at 0x7f6631823c10>
aten2aten decomp: aten.transpose.int <function transpose_int at 0x7f66317bbf70>
aten2aten decomp: aten.std.correction <function std_decomposition at 0x7f66317bbd30>
aten2aten decomp: aten.var.correction <function var_correction at 0x7f66317bbc10>
aten2aten decomp: aten.std.correction <function std_decomposition at 0x7f66317bbd30>
aten2aten decomp: aten.var.correction <function var_correction at 0x7f66317bbc10>
aten2aten decomp: aten.transpose.int <function transpose_int at 0x7f66317bbf70>
aten2aten decomp: aten.transpose.int <function transpose_int at 0x7f66317bbf70>
aten2aten decomp: aten.transpose.int <function transpose_int at 0x7f66317bbf70>
aten2aten decomp: aten.transpose.int <function transpose_int at 0x7f66317bbf70>
aten2aten decomp: aten.masked_fill.Scalar <function masked_fill_Scalar at 0x7f6631823790>
aten2aten decomp: aten._softmax.default <function _softmax at 0x7f6631823c10>
aten2aten decomp: aten.transpose.int <function transpose_int at 0x7f66317bbf70>
aten2aten decomp: aten.std.correction <function std_decomposition at 0x7f66317bbd30>
aten2aten decomp: aten.var.correction <function var_correction at 0x7f66317bbc10>
aten2aten decomp: aten.std.correction <function std_decomposition at 0x7f66317bbd30>
aten2aten decomp: aten.var.correction <function var_correction at 0x7f66317bbc10>
aten2aten decomp: aten.transpose.int <function transpose_int at 0x7f66317bbf70>
aten2aten decomp: aten.transpose.int <function transpose_int at 0x7f66317bbf70>
aten2aten decomp: aten.transpose.int <function transpose_int at 0x7f66317bbf70>
aten2aten decomp: aten.transpose.int <function transpose_int at 0x7f66317bbf70>
aten2aten decomp: aten.masked_fill.Scalar <function masked_fill_Scalar at 0x7f6631823790>
aten2aten decomp: aten._softmax.default <function _softmax at 0x7f6631823c10>
aten2aten decomp: aten.transpose.int <function transpose_int at 0x7f66317bbf70>
aten2aten decomp: aten.std.correction <function std_decomposition at 0x7f66317bbd30>
aten2aten decomp: aten.var.correction <function var_correction at 0x7f66317bbc10>
Partitions proposed:
partition 2 ['add_tensor_72', 'mul_tensor_47', 'sub_tensor_59', 'add_tensor_71', 'div_tensor_71']
partition 4 ['mul_tensor_46', 'sum_dim_int_list_35', 'sub_tensor_58', 'div_tensor_70']
partition 6 ['sub_tensor_57', 'sum_dim_int_list_34', 'div_tensor_69', 'exp_default_11']
partition 7 ['div_tensor_68', 'where_scalar_self_11', 'eq_scalar_11']
partition 8 ['mul_tensor_45', 'sub_tensor_56', 'add_tensor_68', 'div_tensor_67', 'add_tensor_69']
partition 10 ['sub_tensor_55', 'div_tensor_66', 'mul_tensor_44', 'sum_dim_int_list_33']
partition 13 ['mul_tensor_43', 'sub_tensor_54', 'add_tensor_65', 'div_tensor_65', 'add_tensor_66']
partition 15 ['mul_tensor_42', 'sum_dim_int_list_32', 'sub_tensor_53', 'div_tensor_64']
partition 17 ['exp_default_10', 'div_tensor_63', 'sub_tensor_52', 'sum_dim_int_list_31']
partition 18 ['div_tensor_62', 'eq_scalar_10', 'where_scalar_self_10']
partition 19 ['add_tensor_62', 'sub_tensor_51', 'mul_tensor_41', 'add_tensor_63', 'div_tensor_61']
partition 21 ['div_tensor_60', 'sub_tensor_50', 'sum_dim_int_list_30', 'mul_tensor_40']
partition 24 ['add_tensor_59', 'div_tensor_59', 'add_tensor_60', 'mul_tensor_39', 'sub_tensor_49']
partition 26 ['sum_dim_int_list_29', 'sub_tensor_48', 'div_tensor_58', 'mul_tensor_38']
partition 28 ['exp_default_9', 'sum_dim_int_list_28', 'sub_tensor_47', 'div_tensor_57']
partition 29 ['div_tensor_56', 'where_scalar_self_9', 'eq_scalar_9']
partition 30 ['div_tensor_55', 'add_tensor_57', 'add_tensor_56', 'sub_tensor_46', 'mul_tensor_37']
partition 32 ['sum_dim_int_list_27', 'mul_tensor_36', 'div_tensor_54', 'sub_tensor_45']
partition 35 ['div_tensor_53', 'add_tensor_54', 'mul_tensor_35', 'sub_tensor_44', 'add_tensor_53']
partition 37 ['sum_dim_int_list_26', 'sub_tensor_43', 'div_tensor_52', 'mul_tensor_34']
partition 39 ['exp_default_8', 'sum_dim_int_list_25', 'sub_tensor_42', 'div_tensor_51']
partition 40 ['div_tensor_50', 'where_scalar_self_8', 'eq_scalar_8']
partition 41 ['add_tensor_51', 'div_tensor_49', 'add_tensor_50', 'sub_tensor_41', 'mul_tensor_33']
partition 43 ['mul_tensor_32', 'div_tensor_48', 'sub_tensor_40', 'sum_dim_int_list_24']
partition 46 ['add_tensor_48', 'div_tensor_47', 'add_tensor_47', 'sub_tensor_39', 'mul_tensor_31']
partition 48 ['sum_dim_int_list_23', 'mul_tensor_30', 'div_tensor_46', 'sub_tensor_38']
partition 50 ['sum_dim_int_list_22', 'exp_default_7', 'div_tensor_45', 'sub_tensor_37']
partition 51 ['where_scalar_self_7', 'div_tensor_44', 'eq_scalar_7']
partition 52 ['sub_tensor_36', 'mul_tensor_29', 'add_tensor_45', 'div_tensor_43', 'add_tensor_44']
partition 54 ['mul_tensor_28', 'div_tensor_42', 'sub_tensor_35', 'sum_dim_int_list_21']
partition 57 ['add_tensor_42', 'div_tensor_41', 'add_tensor_41', 'sub_tensor_34', 'mul_tensor_27']
partition 59 ['mul_tensor_26', 'div_tensor_40', 'sub_tensor_33', 'sum_dim_int_list_20']
partition 61 ['sum_dim_int_list_19', 'exp_default_6', 'div_tensor_39', 'sub_tensor_32']
partition 62 ['where_scalar_self_6', 'div_tensor_38', 'eq_scalar_6']
partition 63 ['add_tensor_38', 'sub_tensor_31', 'mul_tensor_25', 'add_tensor_39', 'div_tensor_37']
partition 65 ['mul_tensor_24', 'div_tensor_36', 'sub_tensor_30', 'sum_dim_int_list_18']
partition 68 ['add_tensor_35', 'sub_tensor_29', 'mul_tensor_23', 'add_tensor_36', 'div_tensor_35']
partition 70 ['mul_tensor_22', 'div_tensor_34', 'sub_tensor_28', 'sum_dim_int_list_17']
partition 72 ['sum_dim_int_list_16', 'exp_default_5', 'div_tensor_33', 'sub_tensor_27']
partition 73 ['where_scalar_self_5', 'div_tensor_32', 'eq_scalar_5']
partition 74 ['add_tensor_33', 'div_tensor_31', 'add_tensor_32', 'sub_tensor_26', 'mul_tensor_21']
partition 76 ['div_tensor_30', 'sub_tensor_25', 'sum_dim_int_list_15', 'mul_tensor_20']
partition 79 ['div_tensor_29', 'add_tensor_29', 'sub_tensor_24', 'mul_tensor_19', 'add_tensor_30']
partition 81 ['mul_tensor_18', 'div_tensor_28', 'sub_tensor_23', 'sum_dim_int_list_14']
partition 83 ['sum_dim_int_list_13', 'exp_default_4', 'div_tensor_27', 'sub_tensor_22']
partition 84 ['div_tensor_26', 'where_scalar_self_4', 'eq_scalar_4']
partition 85 ['mul_tensor_17', 'sub_tensor_21', 'add_tensor_26', 'div_tensor_25', 'add_tensor_27']
partition 87 ['sub_tensor_20', 'div_tensor_24', 'mul_tensor_16', 'sum_dim_int_list_12']
partition 90 ['mul_tensor_15', 'sub_tensor_19', 'add_tensor_23', 'div_tensor_23', 'add_tensor_24']
partition 92 ['mul_tensor_14', 'sum_dim_int_list_11', 'sub_tensor_18', 'div_tensor_22']
partition 94 ['exp_default_3', 'sum_dim_int_list_10', 'sub_tensor_17', 'div_tensor_21']
partition 95 ['div_tensor_20', 'where_scalar_self_3', 'eq_scalar_3']
partition 96 ['add_tensor_20', 'div_tensor_19', 'add_tensor_21', 'mul_tensor_13', 'sub_tensor_16']
partition 98 ['sub_tensor_15', 'div_tensor_18', 'mul_tensor_12', 'sum_dim_int_list_9']
partition 101 ['sub_tensor_14', 'mul_tensor_11', 'add_tensor_18', 'div_tensor_17', 'add_tensor_17']
partition 103 ['sum_dim_int_list_8', 'mul_tensor_10', 'div_tensor_16', 'sub_tensor_13']
partition 105 ['exp_default_2', 'div_tensor_15', 'sub_tensor_12', 'sum_dim_int_list_7']
partition 106 ['div_tensor_14', 'eq_scalar_2', 'where_scalar_self_2']
partition 107 ['add_tensor_14', 'add_tensor_15', 'sub_tensor_11', 'div_tensor_13', 'mul_tensor_9']
partition 109 ['mul_tensor_8', 'div_tensor_12', 'sub_tensor_10', 'sum_dim_int_list_6']
partition 112 ['add_tensor_11', 'sub_tensor_9', 'mul_tensor_7', 'add_tensor_12', 'div_tensor_11']
partition 114 ['mul_tensor_6', 'div_tensor_10', 'sub_tensor_8', 'sum_dim_int_list_5']
partition 116 ['sum_dim_int_list_4', 'exp_default_1', 'div_tensor_9', 'sub_tensor_7']
partition 117 ['where_scalar_self_1', 'div_tensor_8', 'eq_scalar_1']
partition 118 ['mul_tensor_5', 'sub_tensor_6', 'add_tensor_9', 'div_tensor_7', 'add_tensor_8']
partition 120 ['sub_tensor_5', 'div_tensor_6', 'mul_tensor_4', 'sum_dim_int_list_3']
partition 123 ['add_tensor_6', 'sub_tensor_4', 'div_tensor_5', 'mul_tensor_3', 'add_tensor_5']
partition 125 ['sub_tensor_3', 'div_tensor_4', 'mul_tensor_2', 'sum_dim_int_list_2']
partition 127 ['sub_tensor_2', 'div_tensor_3', 'exp_default', 'sum_dim_int_list_1']
partition 128 ['where_scalar_self', 'div_tensor_2', 'eq_scalar']
partition 129 ['div_tensor_1', 'mul_tensor_1', 'sub_tensor_1', 'add_tensor_3', 'add_tensor_2']
partition 131 ['sum_dim_int_list', 'div_tensor', 'sub_tensor', 'mul_tensor']
partition 132 ['add_tensor', 'add_tensor_1']
num_partitions: 73
Eager execution time: 95.252 ms
Aten decomp time: 112.277 ms
aten2prim decomp: aten.add.Tensor <function add at 0x7f66317a04c0>
aten2prim decomp: aten.add.Tensor <function add at 0x7f66317a04c0>
aten2prim decomp: aten.sub.Tensor <function sub at 0x7f663176a310>
aten2prim decomp: aten.mul.Tensor <function _make_elementwise_binary_reference.<locals>._ref at 0x7f66317579d0>
aten2prim decomp: aten.sum.dim_IntList <function sum at 0x7f66316fa280>
aten2prim decomp: aten.div.Tensor <function div at 0x7f6631736280>
aten2prim decomp: aten.sub.Tensor <function sub at 0x7f663176a310>
aten2prim decomp: aten.add.Tensor <function add at 0x7f66317a04c0>
aten2prim decomp: aten.mul.Tensor <function _make_elementwise_binary_reference.<locals>._ref at 0x7f66317579d0>
aten2prim decomp: aten.div.Tensor <function div at 0x7f6631736280>
aten2prim decomp: aten.add.Tensor <function add at 0x7f66317a04c0>
aten2prim decomp: aten.div.Tensor <function div at 0x7f6631736280>
aten2prim decomp: aten.eq.Scalar <function _make_elementwise_binary_reference.<locals>._ref at 0x7f66317363a0>
aten2prim decomp: aten.where.self <function where at 0x7f663176adc0>
nvFuser 1st call execution time: 2703.377 ms
**BERT_pytorch_forward_0 failed! __exit__(): incompatible function arguments. The following argument types are supported:
1. (self: torch._C._nvfuser.FusionDefinition, arg0: capsule, arg1: capsule, arg2: capsule) -> None**
Invoked with: <torch._C._nvfuser.FusionDefinition object at 0x7f6628a0d530>, <class 'TypeError'>, TypeError("where(): incompatible function arguments. The following argument types are supported:\n 1. (arg0: torch._C._nvfuser.TensorView, arg1: torch._C._nvfuser.TensorView, arg2: torch._C._nvfuser.TensorView) -> torch._C._nvfuser.TensorView\n 2. (arg0: torch._C._nvfuser.TensorView, arg1: torch._C._nvfuser.TensorView, arg2: torch._C._nvfuser.Val) -> torch._C._nvfuser.TensorView\n 3. (arg0: torch._C._nvfuser.TensorView, arg1: torch._C._nvfuser.Val, arg2: torch._C._nvfuser.TensorView) -> torch._C._nvfuser.TensorView\n 4. (arg0: torch._C._nvfuser.TensorView, arg1: torch._C._nvfuser.Val, arg2: torch._C._nvfuser.Val) -> torch._C._nvfuser.TensorView\n 5. (arg0: torch._C._nvfuser.Val, arg1: torch._C._nvfuser.TensorView, arg2: torch._C._nvfuser.TensorView) -> torch._C._nvfuser.TensorView\n 6. (arg0: torch._C._nvfuser.Val, arg1: torch._C._nvfuser.TensorView, arg2: torch._C._nvfuser.Val) -> torch._C._nvfuser.TensorView\n 7. (arg0: torch._C._nvfuser.Val, arg1: torch._C._nvfuser.Val, arg2: torch._C._nvfuser.TensorView) -> torch._C._nvfuser.TensorView\n 8. (arg0: torch._C._nvfuser.Val, arg1: torch._C._nvfuser.Val, arg2: torch._C._nvfuser.Val) -> torch._C._nvfuser.Val\n\nInvoked with: <torch._C._nvfuser.TensorView object at 0x7f6621060ef0>, tensor([[[[-.......e+09,\n -1.0000e+09, -1.0000e+09]]]], device='cuda:0'), <torch._C._nvfuser.TensorView object at 0x7f66210610f0>"), <traceback object at 0x7f66210198c0>
non_fusible_op {'aten.sqrt.default', 'aten.mean.dim', 'aten.to.dtype', 'aten.amax.default', 'aten.gt.Scalar', '<built-in function getitem>', 'aten.add.Tensor', 'aten.index_select.default', 'aten._unsafe_view.default', 'aten.gelu.default', 'aten.t.default', 'aten.repeat.default', 'aten.reshape.default', 'aten.slice.Tensor', 'aten.unsqueeze.default', 'aten.addmm.default', 'aten.clone.default', 'aten.view.default', 'aten.bmm.default', 'aten.permute.default', 'aten.expand.default'}
BERT_pytorch_forward_0 73 95.25213693268597 112.27697692811489 None None None
| 0 |
5,254 | 81,337 |
JIT trace takes forever on a simple method
|
oncall: jit
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
```python
import torch
import torch.utils.benchmark as bench
from torch import Tensor
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
input_size = [64, 16, 2048, 2048//16]
m1 = torch.randn(input_size, device=device, dtype=torch.bfloat16)
m2 = torch.randn(input_size, device=device, dtype=torch.bfloat16)
def _matmul_max_impl(m1: Tensor, m2: Tensor) -> tuple[Tensor, Tensor]:
_LOW = -64000.0
out_shape = m1.shape[:-1]
max = torch.full(out_shape, _LOW, dtype=m1.dtype, device=m1.device)
max_i = torch.full(
out_shape, 0, dtype=torch.long, device=m1.device
)
for i in range(m1.size(-1)): # dimension m
m = torch.matmul(m1, m2[:, :, i, :].unsqueeze(-1)).squeeze(-1)
increased = m > max
max = torch.where(increased, m, max)
max_i = torch.where(increased, i, max_i)
return max, max_i
def custom_matmul_max(m1: Tensor, m2: Tensor) -> tuple[Tensor, Tensor]:
return _matmul_max_impl(m1, m2)
traced_matmul_max = torch.jit.trace(custom_matmul_max, (m1, m2))
# this next call has not finished after 1h running on a single core of 5950X
# no GPU load
traced_matmul_max(m1, m2)
```
### Versions
PyTorch version: 1.12.0+cu116
Is debug build: False
CUDA used to build PyTorch: 11.6
ROCM used to build PyTorch: N/A
OS: Microsoft Windows 10 Pro
GCC version: Could not collect
Clang version: 13.0.0 (https://github.com/llvm/llvm-project.git d7b669b3a30345cfcdb2fde2af6f48aa4b94845d)
CMake version: version 3.22.22040401-MSVC_2
Libc version: N/A
Python version: 3.10.4 | packaged by conda-forge | (main, Mar 30 2022, 08:38:02) [MSC v.1916 64 bit (AMD64)] (64-bit runtime)
Python platform: Windows-10-10.0.19044-SP0
Is CUDA available: True
CUDA runtime version: 11.7.64
GPU models and configuration:
GPU 0: NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3090
GPU 1: NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3090
Nvidia driver version: 516.59
cuDNN version: Could not collect
HIP runtime version: N/A
MIOpen runtime version: N/A
Is XNNPACK available: True
Versions of relevant libraries:
[pip3] mypy-extensions==0.4.3
[pip3] numpy==1.22.3
[pip3] performer-pytorch==1.1.4
[pip3] torch==1.12.0+cu116
[pip3] torchaudio==0.12.0+cu116
[pip3] torchvision==0.13.0+cu116
[conda] numpy 1.22.3 pypi_0 pypi
[conda] performer-pytorch 1.1.4 pypi_0 pypi
[conda] torch 1.12.0+cu116 pypi_0 pypi
[conda] torchaudio 0.12.0+cu116 pypi_0 pypi
[conda] torchvision 0.13.0+cu116 pypi_0 pypi
| 3 |
5,255 | 81,333 |
Reductions on tensors larger than GPU memory
|
feature, module: cuda, triaged, needs research
|
### 🚀 The feature, motivation and pitch
I am interested in the ability to compute reductions on tensors larger than memory. For example:
```python
A = zeros(size=(100,100))
B = zeros(size=(10000000,100,100))
A.uniform_()
B.uniform_()
(A@B).min()
```
This falls under the scope of the concept of lazy computation. The output is a single integer, the input doesn't fit in GPU memory or CPU memory, but fits on disk. The data is juggled between disk, CPU and GPU based on whatever is available automatically.
Per this thread on dev-discuss, we were wondering if this is presently a capability to any extent with current backends: https://dev-discuss.pytorch.org/t/lazy-tensor-core/232/20
For example, perhaps computation on tensors larger than GPU memory for some reductions (but not this one - since the data is all random, it must be swapped to CPU RAM or disk) is currently possible on an existing backend.
cc @ngimel @wconstab
### Alternatives
_No response_
### Additional context
_No response_
| 0 |
5,256 | 81,323 |
`torch.overrides.get_testing_overrides` does not function as intended for native tensor methods/operations
|
triaged, module: __torch_function__
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
`torch.overrides.get_testing_overrides` (introduced in #33791) does not appear function as intended for native tensor methods/operations. For example, the following code can be used to discern the signature of `torch.Tensor.size`, as simply using `inspect.signature(torch.Tensor.size)` will yield an error:
```
import torch
import inspect
d = torch.overrides.get_testing_overrides()
print(inspect.signature(d[torch.Tensor.size])
```
This returns `size (self)`. As can be seen here: https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.Tensor.size.html, the expected output is `size (self, dim=None)`. Surprisingly, for `torch.Tensor.permute`, `permute (self, dim)` is returned. This is neither consistent with https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.Tensor.permute.html#torch.Tensor.permute or https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.permute.html#torch.permute.
It appears that the dictionary created and used in https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/blob/master/torch/overrides.py#L1301 is outdated and/or contains incorrect entries.
### Versions
Collecting environment information...
PyTorch version: 1.11.0
Is debug build: False
CUDA used to build PyTorch: 11.3
ROCM used to build PyTorch: N/A
OS: Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8.5 (Ootpa) (x86_64)
GCC version: (GCC) 8.5.0 20210514 (Red Hat 8.5.0-4)
Clang version: Could not collect
CMake version: version 3.19.6
Libc version: glibc-2.28
Python version: 3.9.12 (main, Apr 5 2022, 06:56:58) [GCC 7.5.0] (64-bit runtime)
Python platform: Linux-4.18.0-348.23.1.el8_5.x86_64-x86_64-with-glibc2.28
Is CUDA available: True
CUDA runtime version: 11.4.100
GPU models and configuration:
GPU 0: NVIDIA GeForce GTX 1080 Ti
GPU 1: NVIDIA GeForce GTX 1080 Ti
Nvidia driver version: 470.57.02
cuDNN version: Probably one of the following:
/usr/lib64/libcudnn.so.8.1.1
/usr/lib64/libcudnn_adv_infer.so.8.1.1
/usr/lib64/libcudnn_adv_train.so.8.1.1
/usr/lib64/libcudnn_cnn_infer.so.8.1.1
/usr/lib64/libcudnn_cnn_train.so.8.1.1
/usr/lib64/libcudnn_ops_infer.so.8.1.1
/usr/lib64/libcudnn_ops_train.so.8.1.1
HIP runtime version: N/A
MIOpen runtime version: N/A
Is XNNPACK available: True
Versions of relevant libraries:
[pip3] memtorch==1.1.6
[pip3] mypy-extensions==0.4.3
[pip3] numpy==1.21.5
[pip3] numpydoc==1.2
[pip3] torch==1.11.0
[pip3] torchaudio==0.11.0
[pip3] torchvision==0.12.0
[conda] blas 1.0 mkl
[conda] cudatoolkit 11.3.1 h2bc3f7f_2
[conda] ffmpeg 4.3 hf484d3e_0 pytorch
[conda] memtorch 1.1.6 pypi_0 pypi
[conda] mkl 2021.4.0 h06a4308_640
[conda] mkl-devel 2018.0.1 h470d631_5
[conda] mkl-include 2021.4.0 intel_640 intel
[conda] mkl-service 2.4.0 py39h7f8727e_0
[conda] mkl-static 2021.4.0 intel_640 intel
[conda] mkl_fft 1.3.1 py39hd3c417c_0
[conda] mkl_random 1.2.2 py39h51133e4_0
[conda] numpy 1.21.5 py39he7a7128_1
[conda] numpy-base 1.21.5 py39hf524024_1
[conda] numpydoc 1.2 pyhd3eb1b0_0
[conda] pytorch 1.11.0 py3.9_cuda11.3_cudnn8.2.0_0 pytorch
[conda] pytorch-mutex 1.0 cuda pytorch
[conda] torchaudio 0.11.0 py39_cu113 pytorch
[conda] torchvision 0.12.0 py39_cu113 pytorch
cc @hameerabbasi @rgommers @peterbell10 @ezyang
| 1 |
5,257 | 81,317 |
Incorrect results for mean or sum kernels on aarch64 when building with gcc-7
|
triaged, module: arm
|
## Issue description
Some aarch64 kernels produce wrong results when building with gcc-7 in native aarch64 environement.
Probably related to #47098 (presumably fixed in #47099 and then reverted in ##50389)
## Code example
The problem is reproducible by building with the following Dockerfile
```
FROM arm64v8/ubuntu:bionic
ENV DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive
RUN apt-get update && \
apt-get install -y --no-install-recommends \
gcc-7 \
g++-7 \
libstdc++-7-dev \
make \
cpp \
python3.8 \
python3.8-dev \
python3-pip \
git \
curl \
ssh \
ca-certificates && \
update-ca-certificates && \
# Clean up
apt-get autoremove -y && \
apt-get clean -y && \
rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/*
# Installing cmake from a GitHub release && \
RUN export CMAKE_VERSION="3.21.4" && \
curl -L https://github.com/Kitware/CMake/releases/download/v${CMAKE_VERSION}/cmake-${CMAKE_VERSION}-linux-aarch64.sh -o cmake-${CMAKE_VERSION}-linux-aarch64.sh && \
chmod +x cmake-${CMAKE_VERSION}-linux-aarch64.sh && \
./cmake-${CMAKE_VERSION}-linux-aarch64.sh --skip-license --prefix=/usr/local/
RUN git clone https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch.git -b v1.12.0 --recursive
WORKDIR /pytorch
RUN python3.8 -m pip install -U setuptools wheel pip && \
python3.8 -m pip install pyyaml numpy typing_extensions
RUN USE_CUDA=0 \
USE_CUDNN=0 \
USE_MKLDNN=0 \
USE_DISTRIBUTED=0 \
USE_OPENMP=1 \
USE_MAGMA=0 \
USE_NCCL=0 \
USE_FBGEMM=0 \
CC=gcc-7 \
CXX=g++-7 \
python3.8 setup.py bdist_wheel
RUN python3.8 -m pip install dist/torch-*.whl
WORKDIR /
RUN python3.8 -c 'import torch; m=torch.ones(5,12); print(torch.mean(m,axis=1), torch.sum(m, axis=1))'
RUN python3.8 -mtorch.utils.collect_env
```
produces the following results:
```
tensor([0.8333, 0.8333, 0.8333, 0.8333, 0.8333]) # expecting tensor([1., 1., 1., 1., 1.])
tensor([10., 10., 10., 10., 10.]) # expecting tensor([12., 12., 12., 12., 12.])
```
## System Info
```
PyTorch version: 1.12.0a0+git67ece03
Is debug build: False
CUDA used to build PyTorch: None
ROCM used to build PyTorch: N/A
OS: Ubuntu 18.04.6 LTS (aarch64)
GCC version: Could not collect
Clang version: Could not collect
CMake version: version 3.21.4
Libc version: glibc-2.27
Python version: 3.8.0 (default, Dec 9 2021, 17:53:27) [GCC 8.4.0] (64-bit runtime)
Python platform: Linux-5.13.0-1031-aws-aarch64-with-glibc2.27
Is CUDA available: False
CUDA runtime version: No CUDA
GPU models and configuration: No CUDA
Nvidia driver version: No CUDA
cuDNN version: No CUDA
HIP runtime version: N/A
MIOpen runtime version: N/A
Is XNNPACK available: True
Versions of relevant libraries:
[pip3] numpy==1.23.1
[pip3] torch==1.12.0a0+git67ece03
[conda] Could not collect
```
cc @malfet
| 2 |
5,258 | 81,307 |
[Prims+NvFuser] Non-fusible ops Tracker
|
triaged, module: nvfuser
|
Following is the complete list of ops that appear in the torchbench + huggingface + TIMM models, but are not included in the nvFuser fusion group.
They are not included due to one (or more) of the following reasons:
1. nvFuser backend does not support this op
2. aten2aten missing
3. aten2prim ref missing
4. nvfuser_impl missing for prims op
5. not included in NvFuserOperatorSupport dict
Tracking is moved here: https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/1kmFvpIQ42XB4okN2WYrLX7D6svkRhbJX_iCFqM231YQ/edit#gid=0
| Occurance
-- | --
aten.view.default' | 14567
aten.t.default' | 10085
aten.to.dtype' | 8595
aten.unsqueeze.default' | 6639
aten.permute.default' | 5395
aten.mm.default' | 4915
aten._unsafe_view.default' | 3585
aten.clone.default' | 2890
aten.new_zeros.default' | 2408
aten.bmm.default' | 2312
aten.reshape.default' | 1866
aten.expand.default' | 1674
aten.addmm.default' | 1423
aten.convolution.default' | 1112
aten.convolution_backward.default' | 1045
aten.slice.Tensor' | 1030
aten.native_layer_norm_backward.default' | 568
aten.mean.dim' | 436
aten.amax.default' | 362
aten.squeeze.dim' | 260
aten.cat.default' | 205
aten.narrow.default' | 192
aten.var.dim' | 114
aten.empty_like.default' | 103
aten._to_copy.default' | 75
aten.where.ScalarSelf' | 73
aten.select.int' | 70
aten.embedding_dense_backward.default' | 65
aten.zero.default' | 55
aten.fill.Scalar' | 49
aten.index_select.default' | 48
aten.select_scatter.default' | 41
aten.hardtanh.default' | 35
aten.max_pool2d_with_indices.default' | 35
aten.reflection_pad2d.default' | 31
aten.max_pool2d_with_indices_backward.default' | 28
aten.reflection_pad2d_backward.default' | 28
aten.avg_pool2d.default' | 23
aten.constant_pad_nd.default' | 21
aten.upsample_bilinear2d.vec' | 18
aten.avg_pool2d_backward.default' | 13
aten.col2im.default' | 12
aten.im2col.default' | 12
aten.index.Tensor' | 11
aten.mean.default' | 10
aten.slice_scatter.default' | 9
aten._embedding_bag.default' | 8
aten.upsample_bilinear2d_backward.vec' | 8
aten.grid_sampler_2d.default' | 6
aten.stack.default' | 6
aten._adaptive_avg_pool2d_backward.default' | 2
aten._adaptive_avg_pool2d.default' | 2
aten.any.default' | 1
aten.gather.default' | 1
aten.new_empty.default' | 1
aten.repeat.default' | 1
aten.scatter_add.default' | 1
| 12 |
5,259 | 81,297 |
Files downloaded with torch.hub should respect umask
|
triaged, module: hub
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
torch.hub code uses the `download_url_to_file` function to download and cache files. This function first downloads the data to a temporary file (using `NamedTemporaryFile`), then moves it into the cache directory. As a result, the file will always have 0600 permissions (this is hard-coded for files created using `NamedTemporaryFile`, and moving the file copies these permissions). As a result, umask is not respected and there is therefore no way to control the permissions of files created in the cache. This is a problem for multi-user systems that want to share the files in the torch.hub cache directory, as they will only be user-readable.
See here for discussion of a similar issue in a different Python project: https://github.com/zarr-developers/zarr-python/issues/325
### Versions
Collecting environment information...
PyTorch version: 1.11.0
Is debug build: False
CUDA used to build PyTorch: 11.5
ROCM used to build PyTorch: N/A
OS: Ubuntu 22.04 LTS (x86_64)
GCC version: (Ubuntu 11.2.0-19ubuntu1) 11.2.0
Clang version: Could not collect
CMake version: Could not collect
Libc version: glibc-2.35
Python version: 3.9.13 | packaged by conda-forge | (main, May 27 2022, 16:56:21) [GCC 10.3.0] (64-bit runtime)
Python platform: Linux-5.15.0-40-generic-x86_64-with-glibc2.35
Is CUDA available: True
CUDA runtime version: 11.7.64
GPU models and configuration:
GPU 0: NVIDIA GeForce GTX TITAN X
GPU 1: NVIDIA GeForce GTX TITAN X
Nvidia driver version: 515.48.07
cuDNN version: Could not collect
HIP runtime version: N/A
MIOpen runtime version: N/A
Is XNNPACK available: True
Versions of relevant libraries:
[pip3] numpy==1.22.4
[pip3] torch==1.11.0
[pip3] torchmetrics==0.9.2
[pip3] torchvision==0.12.0
[conda] blas 2.114 mkl conda-forge
[conda] blas-devel 3.9.0 14_linux64_mkl conda-forge
[conda] cudatoolkit 11.5.1 h59c8dcf_10 conda-forge
[conda] libblas 3.9.0 14_linux64_mkl conda-forge
[conda] libcblas 3.9.0 14_linux64_mkl conda-forge
[conda] liblapack 3.9.0 14_linux64_mkl conda-forge
[conda] liblapacke 3.9.0 14_linux64_mkl conda-forge
[conda] mkl 2022.0.1 h8d4b97c_803 conda-forge
[conda] mkl-devel 2022.0.1 ha770c72_804 conda-forge
[conda] mkl-include 2022.0.1 h8d4b97c_803 conda-forge
[conda] numpy 1.22.4 py39hc58783e_0 conda-forge
[conda] pytorch 1.11.0 py3.9_cuda11.5_cudnn8.3.2_0 pytorch
[conda] pytorch-mutex 1.0 cuda pytorch
[conda] torchmetrics 0.9.2 pyhd8ed1ab_0 conda-forge
[conda] torchvision 0.12.0 py39_cu115 pytorch
cc @nairbv @NicolasHug @vmoens @jdsgomes
| 4 |
5,260 | 81,287 |
Runtime error in Libtorch cpp project (Didn't find engine for operation quantized::conv2d_prepack NoQEngine)
|
oncall: quantization, triaged
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
I am working on cpp project having quantization process using qnnpack. However, I encounter the error when I execute the build result. Building with torchscript models is successful, but executing the build result gives me this error.
```
terminate called after throwing an instance of 'std::runtime_error'
what(): The following operation failed in the TorchScript interpreter.
Traceback of TorchScript, serialized code (most recent call last):
File "code/__torch__/torch/nn/quantized/modules/conv.py", line 72, in __setstate__
self.groups = (state)[8]
self.padding_mode = (state)[9]
_7 = (self).set_weight_bias((state)[10], (state)[11], )
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ <--- HERE
self.scale = (state)[12]
self.zero_point = (state)[13]
File "code/__torch__/torch/nn/quantized/modules/conv.py", line 94, in set_weight_bias
_13 = [_11, _12]
_14, _15, = dilation
_16 = ops.quantized.conv2d_prepack(w, b, _10, _13, [_14, _15], groups)
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ <--- HERE
self._packed_params = _16
else:
Traceback of TorchScript, original code (most recent call last):
File "/opt/conda/lib/python3.8/site-packages/torch/nn/quantized/modules/conv.py", line 176, in __setstate__
self.groups = state[8]
self.padding_mode = state[9]
self.set_weight_bias(state[10], state[11])
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ <--- HERE
self.scale = state[12]
self.zero_point = state[13]
File "/opt/conda/lib/python3.8/site-packages/torch/nn/quantized/modules/conv.py", line 432, in set_weight_bias
def set_weight_bias(self, w: torch.Tensor, b: Optional[torch.Tensor]) -> None:
if self.padding_mode == 'zeros':
self._packed_params = torch.ops.quantized.conv2d_prepack(
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ <--- HERE
w, b, self.stride, self.padding, self.dilation, self.groups)
else:
RuntimeError: Didn't find engine for operation quantized::conv2d_prepack NoQEngine
Aborted (core dumped)
```
When I check `torch.backends.quantized.supported_engines`, qnnpack comes out to be supported.
```
Python 3.8.10 (default, Mar 15 2022, 12:22:08)
[GCC 9.4.0] on linux
Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.
>>> import torch
>>> torch.backends.quantized.supported_engines
['qnnpack', 'none']
```
### Machine
`Linux 674db9b68c77 5.15.0-1013-aws #17-Ubuntu SMP Fri Jun 10 10:43:12 UTC 2022 aarch64 aarch64 aarch64 GNU/Linux`
What can be the causes of this error?
### Versions
```
python collect_env.py
Collecting environment information...
PyTorch version: 1.11.0
Is debug build: False
CUDA used to build PyTorch: None
ROCM used to build PyTorch: N/A
OS: Ubuntu 20.04.4 LTS (aarch64)
GCC version: (Ubuntu 10.3.0-1ubuntu1~20.04) 10.3.0
Clang version: Could not collect
CMake version: version 3.16.3
Libc version: glibc-2.31
Python version: 3.8.10 (default, Mar 15 2022, 12:22:08) [GCC 9.4.0] (64-bit runtime)
Python platform: Linux-5.15.0-1013-aws-aarch64-with-glibc2.29
Is CUDA available: False
CUDA runtime version: No CUDA
GPU models and configuration: No CUDA
Nvidia driver version: No CUDA
cuDNN version: No CUDA
HIP runtime version: N/A
MIOpen runtime version: N/A
Is XNNPACK available: True
Versions of relevant libraries:
[pip3] numpy==1.21.5
[pip3] torch==1.11.0
[pip3] torchdata==0.3.0
[pip3] torchtext==0.12.0a0+d7a34d6
[pip3] torchvision==0.12.0
[conda] Could not collect
```
### Additional context
I have built the torchscript model in `x86_64` machine and am trying to compile the model in `aarch64` machine for deployment. Does it have possibility of causing this issue?
cc @jerryzh168 @jianyuh @raghuramank100 @jamesr66a @vkuzo @jgong5 @Xia-Weiwen @leslie-fang-intel
| 3 |
5,261 | 81,259 |
Refactor linter adapters to avoid code duplication
|
module: lint, triaged, enhancement
|
### 🚀 The feature, motivation and pitch
[Linter adapters](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/tree/master/tools/linter/adapters) are used by `lintrunner` to check and format pytorch code. There are close to 20 of them at the moment, and the list could grow to include many more in the future. At the moment, adding a new linter requires copy/paste the code structure from other linters, and make the necessary modification, i.e. updating `check_file`. This approach doesn't scale and leads to code duplication. It's better to have a well-defined interface for linter adapters and use that to define new linters
### Alternatives
* Define a base class for linter adapter (require design), i.e.
```
class LinterAdapter(abc)
@abstract
def check_file(filename: str) -> Optional[LintMessage]:
pass
def execute()
# Run check_file in parallel
```
* Put as much common logic in [linter adapters](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/tree/master/tools/linter/adapters) to the base class as possible
* Refactor other existing linter adapters to use the base class
* Update [README.md](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/blob/master/tools/linter/adapters/README.md) to provide instructions and examples on how to create a new linter
### Additional context
* [lintrunner GH](https://github.com/suo/lintrunner)
* [lintrunner](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/wiki/lintrunner)
| 1 |
5,262 | 81,257 |
High GPU context memory on Torch 1.11.0 but none on Torch 1.10.0
|
needs reproduction, module: cuda, triaged
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
I am running a multi-gpu code on 2 GPUs and tested it with Torch 1.10.0 and Torch 1.11.0. While using Torch 1.10.0 I only see 2 processes (1 on each GPU), while running it on Torch 1.11.0 I can see 3 processes (2 on GPU 0, and 1 on GPU 1). The additional process on GPU 0 has same pid as GPU 1 and takes around 500 MB of space. I believe it is because of the context memory as per my search on the forums. But wanted to understand why it only occurs with Torch 1.11.0 and not with Torch 1.10.0. The details are mentioned below.
Torch 1.10.0:
Docker Image: nvcr.io/nvidia/pytorch:21.09-py3 (CUDA 11.4)
Memory usage:
| 0 N/A N/A 1123607 C /opt/conda/bin/python 4521MiB |
| 1 N/A N/A 1123611 C /opt/conda/bin/python 4501MiB |
Torch 1.11.0:
Docker Image: nvcr.io/nvidia/pytorch:21.11-py3 (CUDA 11.5)
Memory usage:
| 0 N/A N/A 1418076 C /opt/conda/bin/python 4537MiB |
| 0 N/A N/A 1418077 C /opt/conda/bin/python 543MiB |
| 1 N/A N/A 1418077 C /opt/conda/bin/python 4537MiB |
### Versions
Collecting environment information...
PyTorch version: 1.11.0a0+b6df043
Is debug build: False
CUDA used to build PyTorch: 11.5
ROCM used to build PyTorch: N/A
OS: Ubuntu 20.04.3 LTS (x86_64)
GCC version: (Ubuntu 9.3.0-17ubuntu1~20.04) 9.3.0
Clang version: Could not collect
CMake version: version 3.21.3
Libc version: glibc-2.31
Python version: 3.8.12 | packaged by conda-forge | (default, Oct 12 2021, 21:59:51) [GCC 9.4.0] (64-bit runtime)
Python platform: Linux-5.4.0-109-generic-x86_64-with-glibc2.10
Is CUDA available: True
CUDA runtime version: 11.5.50
GPU models and configuration:
GPU 0: NVIDIA GeForce GTX 1070
GPU 1: NVIDIA GeForce GTX 1070
Nvidia driver version: 510.73.05
cuDNN version: Probably one of the following:
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn.so.8.3.0
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_adv_infer.so.8.3.0
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_adv_train.so.8.3.0
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_cnn_infer.so.8.3.0
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_cnn_train.so.8.3.0
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_ops_infer.so.8.3.0
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_ops_train.so.8.3.0
HIP runtime version: N/A
MIOpen runtime version: N/A
Is XNNPACK available: True
Versions of relevant libraries:
[pip3] numpy==1.21.4
[pip3] nvidia-dlprof-pytorch-nvtx==1.7.0
[pip3] pytorch-quantization==2.1.2
[pip3] torch==1.11.0a0+b6df043
[pip3] torch-tensorrt==1.0.0a0
[pip3] torchtext==0.12.0a0
[pip3] torchvision==0.11.0a0
[conda] magma-cuda110 2.5.2 5 local
[conda] mkl 2019.5 281 conda-forge
[conda] mkl-include 2019.5 281 conda-forge
[conda] numpy 1.21.4 py38he2449b9_0 conda-forge
[conda] nvidia-dlprof-pytorch-nvtx 1.7.0 pypi_0 pypi
[conda] pytorch-quantization 2.1.2 pypi_0 pypi
[conda] torch 1.11.0a0+b6df043 pypi_0 pypi
[conda] torch-tensorrt 1.0.0a0 pypi_0 pypi
[conda] torchtext 0.12.0a0 pypi_0 pypi
[conda] torchvision 0.11.0a0 pypi_0 pypi
cc @ngimel
| 9 |
5,263 | 81,255 |
[FSDP] Avoid explicit replace of activation checkpoint prefixes
|
oncall: distributed, better-engineering, module: fsdp
|
### 🚀 The feature, motivation and pitch
FSDP has two instances where we explicitly replace the AC prefix: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/80936/files and https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/81253/files. We should figure out a better solution as this is not great for composability.
### Alternatives
_No response_
### Additional context
_No response_
cc @pietern @mrshenli @pritamdamania87 @zhaojuanmao @satgera @rohan-varma @gqchen @aazzolini @osalpekar @jiayisuse @SciPioneer @H-Huang @kwen2501 @ezyang
| 0 |
5,264 | 81,245 |
Libtorch cannot load TrochScript Module correctly, when a network contains conv2d(inchannels=64, outchannels=128, kernelsize=1) .
|
oncall: jit
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
Libtorch cannot load TrochScript Module correctly, when a network contains`` conv2d(inchannels=64, outchannels=128, kernelsize=1)`` .
### Versions
I need to convert a model in python to c++, so I use torch.jit.trace produce a 'pt' file:
pytorch == 1.12
python == 3.10
```python
import torch
class m(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self) -> None:
super().__init__()
self.conv1 = torch.nn.Conv2d(64, 128, (1, 1))
def forward(self, x):
return self.conv1(x)
a = m()
b = torch.rand((1, 64, 128, 128)).cpu().float()
x = torch.jit.trace(a, b)
x.save('model.pt')
c = torch.zeros((1, 64, 128, 128)).cpu()
print(x(c)[0,0,0,0]) # tensor(0.0301, grad_fn=<SelectBackward0>)
````
so I use libtorch==1.12 to load the pt file:
c++17
```c++
#include <iostream>
#include <torch/torch.h>
#include <torch/script.h>
using namespace torch;
using namespace std;
int main() {
auto fuck = torch::jit::load("model.pt");
auto t = torch::zeros({1, 64, 128, 128}).toType(torch::kFloat32);
std::vector<torch::jit::IValue> inputs;
inputs.push_back(t);
auto output = fuck.forward(inputs).toTensor().squeeze();
output.print();
cout<<output[0][0][0]<<endl; //-8.44151e+33
return 0;
}
```
However, when I set the in_channels=1 out_channels=128, their outputs are equal!!
```python
import torch
class m(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self) -> None:
super().__init__()
self.conv1 = torch.nn.Conv2d(1, 128, (1, 1)) # in_channel = 1
def forward(self, x):
return self.conv1(x)
a = m()
b = torch.rand((1, 1, 128, 128)).cpu().float()
x = torch.jit.trace(a, b)
x.save('model.pt')
c = torch.zeros((1, 1, 128, 128)).cpu()
print(x(c)[0,0,0,0]) # tensor(-0.3926, grad_fn=<SelectBackward0>)
```
```c++
#include <iostream>
#include <torch/torch.h>
#include <torch/script.h>
using namespace torch;
using namespace std;
int main() {
auto fuck = torch::jit::load("model.pt");
auto t = torch::zeros({1, 1, 128, 128}).toType(torch::kFloat32);
std::vector<torch::jit::IValue> inputs;
inputs.push_back(t);
auto output = fuck.forward(inputs).toTensor().squeeze();
output.print();
cout<<output[0][0][0]<<endl; //-0.392607
return 0;
}
```
I think this maybe a bug.
| 0 |
5,265 | 81,244 |
CapabilityBasedPartitioner does not work correctly with mutating operations
|
triaged, module: fx, module: CapabilityBasedPartitioner
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
Here is a diff adding a test case that triggers the error
```
diff --git a/test/test_fx_passes.py b/test/test_fx_passes.py
index 39fe501f44..b09f0e71e5 100644
--- a/test/test_fx_passes.py
+++ b/test/test_fx_passes.py
@@ -158,11 +158,23 @@ class TestPartitionFunctions:
out = torch.stack([add_1, add_2, add_3])
return out
+ @staticmethod
+ def forward12(a):
+ b = a.clone()
+ b_1 = b.fill_(2)
+ b_2 = b.fill_(3)
+ return b
+
# A mock OperatorSupport class, where only operator.add is supported
class MockOperatorSupport(OperatorSupport):
def is_node_supported(self, submodules, node: torch.fx.Node) -> bool:
return node.op == "call_function" and node.target in {operator.add}
+# A mock OperatorSupport where all ops are supported
+class MockAllOperatorSupport(OperatorSupport):
+ def is_node_supported(self, submodules, node: torch.fx.Node) -> bool:
+ return node.op == "call_function"
+
class TestFXGraphPasses(JitTestCase):
@parametrize("fn, expected_partition", [
@@ -179,16 +191,20 @@ class TestFXGraphPasses(JitTestCase):
(TestPartitionFunctions.forward9, [['add_3', 'add_2', 'add_1', 'add']]),
(TestPartitionFunctions.forward10, [['add_3', 'add_2', 'add', 'add_1']]),
(TestPartitionFunctions.forward11, [['add_1'], ['add']]),
+
+ (TestPartitionFunctions.forward12, [['b_2', 'b_1', 'b']]),
])
def test_partitioner(self, fn, expected_partition):
traced = symbolic_trace(fn)
supported_ops = MockOperatorSupport()
+ if fn is TestPartitionFunctions.forward12:
+ supported_ops = MockAllOperatorSupport()
partitioner = CapabilityBasedPartitioner(traced, supported_ops, allows_single_node_partition=True)
partitions = partitioner.propose_partitions()
partitions_name = [[node.name for node in partition.nodes] for partition in partitions]
- assert len(partitions_name) == len(expected_partition)
+ assert len(partitions_name) == len(expected_partition), f"{partitions_name}, {expected_partition}"
for i in range(len(partitions_name)):
assert set(partitions_name[i]) == set(expected_partition[i])
```
cc @ezyang @SherlockNoMad
### Versions
master
| 1 |
5,266 | 81,240 |
Functionalization and fake tensors failure in torture test
|
triaged, module: __torch_dispatch__, module: functionalization
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
```
@patch("torchdynamo.config.verify_correctness", True)
@patch("functorch._src.config.use_functionalize", True)
def test_mutated_metadata(self):
def model(x):
y = x.view(0)
x.resize_(20)
x.fill_(2)
y.fill_(3)
return x, y
with torchdynamo.optimize("aot_autograd"):
for i in range(5):
with self.subTest(i):
x = torch.empty(0, device="cuda:0")
rx, ry = model(x)
self.assertEqual(x, torch.full((20,), 2., device="cuda:0"))
self.assertEqual(rx, torch.full((20,), 2., device="cuda:0"))
self.assertEqual(ry, torch.empty(0, device="cuda:0"))
```
I don't think the device here matters. This fails with
```
File "/raid/ezyang/pytorch-scratch2/torch/fx/experimental/proxy_tensor.py", line 268, in wrapped
out = f(*tree_args)
File "/raid/ezyang/functorch/functorch/_src/eager_transforms.py", line 1420, in wrapped
func_outputs = func(*func_args, **func_kwargs)
File "/raid/ezyang/functorch/functorch/_src/aot_autograd.py", line 202, in fake_fn
return fx_g(primals, tangents)
File "/raid/ezyang/pytorch-scratch2/torch/fx/graph_module.py", line 652, in call_wrapped
return self._wrapped_call(self, *args, **kwargs)
File "/raid/ezyang/pytorch-scratch2/torch/fx/graph_module.py", line 277, in __call__
raise e
File "/raid/ezyang/pytorch-scratch2/torch/fx/graph_module.py", line 267, in __call__
return super(self.cls, obj).__call__(*args, **kwargs) # type: ignore[misc]
File "/raid/ezyang/pytorch-scratch2/torch/fx/_symbolic_trace.py", line 692, in module_call_wrapper
return self.call_module(mod, forward, args, kwargs)
File "/raid/ezyang/pytorch-scratch2/torch/fx/experimental/proxy_tensor.py", line 217, in call_module
return forward(*args, **kwargs)
File "/raid/ezyang/pytorch-scratch2/torch/fx/_symbolic_trace.py", line 685, in forward
return _orig_module_call(mod, *args, **kwargs)
File "/raid/ezyang/pytorch-scratch2/torch/nn/modules/module.py", line 1186, in _call_impl
return forward_call(*input, **kwargs)
File "<eval_with_key>.9", line 10, in forward
fill__scalar = torch.ops.aten.fill_.Scalar(primals_1, 2); primals_1 = None
File "/raid/ezyang/pytorch-scratch2/torch/_ops.py", line 49, in __call__
return self._op(*args, **kwargs or {})
File "/raid/ezyang/pytorch-scratch2/torch/utils/_python_dispatch.py", line 74, in wrapped
return f(self, *args, **kwargs)
File "/raid/ezyang/pytorch-scratch2/torch/fx/experimental/proxy_tensor.py", line 326, in __torch_dispatch__
inner_res = func_overload(*args, **kwargs)
File "/raid/ezyang/pytorch-scratch2/torch/_ops.py", line 49, in __call__
return self._op(*args, **kwargs or {})
File "/raid/ezyang/pytorch-scratch2/torch/utils/_python_dispatch.py", line 74, in wrapped
return f(self, *args, **kwargs)
File "/raid/ezyang/pytorch-scratch2/torch/_subclasses/fake_tensor.py", line 512, in __torch_dispatch__
raise Exception(
Exception: Invoking operators with non-Fake Tensor inputs in FakeTensorMode is not yet supported. Please convert all Tensors to FakeTensors first. Found in aten.fill_.Scalar(*(tensor(..., device='meta', size=(20,)), 2), **{})
```
cc @Chillee @ezyang @zou3519 @albanD @samdow @bdhirsh
### Versions
master
| 1 |
5,267 | 81,229 |
torch.fx.node.map_aggregate and torch.utils._pytree.tree_map do the same thing
|
triaged, module: fx, module: pytree
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
Should deduplicate the implementations somehow
### Versions
master
cc @ezyang @SherlockNoMad @zou3519
| 0 |
5,268 | 81,213 |
DISABLED test_trace_dependencies (test_analyze.TestAnalyze)
|
triaged, module: flaky-tests, skipped, module: deploy, oncall: package/deploy, imported
|
Platforms: linux
This test was disabled because it is failing in CI. See [recent examples](https://hud.pytorch.org/flakytest?name=test_trace_dependencies&suite=test_analyze.TestAnalyze&file=package/test_analyze.py) and the most recent trunk [workflow logs](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/runs/7275940320).
Over the past 3 hours, it has been determined flaky in 1 workflow(s) with 1 red and 1 green.
cc @wconstab @bdhirsh @ezyang
| 5 |
5,269 | 81,195 |
torch._weight_norm with specified dim returns wrong output
|
module: nn, module: error checking, triaged, module: regression, module: norms and normalization
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
# Problem
`torch._weight_norm` outputs wrong result from torch 1.12
Though `torch._weight_norm` is an undocumented API, I report this issue since the API is made public.
#### torch 1.11 and before
```python3
$ python3
Python 3.8.10 (default, Mar 15 2022, 12:22:08)
[GCC 9.4.0] on linux
Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.
>>> import torch
>>> a = torch.Tensor([[1,2],[3,4]])
>>> b = torch.Tensor([[5],[6]])
>>> torch._weight_norm(a,b,dim=1)
tensor([[1.5811, 2.2361],
[5.6921, 5.3666]])
```
#### torch 1.12
```python3
$ python3
Python 3.8.10 (default, Mar 15 2022, 12:22:08)
[GCC 9.4.0] on linux
Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.
>>> import torch
>>> a = torch.Tensor([[1,2],[3,4]])
>>> b = torch.Tensor([[5],[6]])
>>> torch._weight_norm(a,b,dim=1)
tensor([[1.5811, 2.6833],
[4.7434, 5.3666]])
```
#### manual computation
```python3
>>> def weight_norm_dim1(a, b):
... norm = a.norm(2, [0], True)
... return a * b / norm
...
>>> weight_norm_dim1(a, b)
tensor([[1.5811, 2.2361],
[5.6921, 5.3666]])
```
### Versions
```
Collecting environment information...
PyTorch version: N/A
Is debug build: N/A
CUDA used to build PyTorch: N/A
ROCM used to build PyTorch: N/A
OS: Ubuntu 20.04.4 LTS (x86_64)
GCC version: (Ubuntu 10.3.0-1ubuntu1~20.04) 10.3.0
Clang version: Could not collect
CMake version: version 3.22.2
Libc version: glibc-2.31
Python version: 3.8.10 (default, Mar 15 2022, 12:22:08) [GCC 9.4.0] (64-bit runtime)
Python platform: Linux-5.4.0-100-generic-x86_64-with-glibc2.2.5
Is CUDA available: N/A
CUDA runtime version: Could not collect
GPU models and configuration:
GPU 0: Tesla V100-SXM2-16GB
GPU 1: Tesla V100-SXM2-16GB
GPU 2: Tesla V100-SXM2-16GB
GPU 3: Tesla V100-SXM2-16GB
GPU 4: Tesla V100-SXM2-16GB
GPU 5: Tesla V100-SXM2-16GB
GPU 6: Tesla V100-SXM2-16GB
GPU 7: Tesla V100-SXM2-16GB
Nvidia driver version: 470.103.01
cuDNN version: Probably one of the following:
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn.so.8.0.5
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_adv_infer.so.8.0.5
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_adv_train.so.8.0.5
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_cnn_infer.so.8.0.5
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_cnn_train.so.8.0.5
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_ops_infer.so.8.0.5
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_ops_train.so.8.0.5
HIP runtime version: N/A
MIOpen runtime version: N/A
Is XNNPACK available: N/A
Versions of relevant libraries:
[pip3] numpy==1.18.4
[pip3] torch==1.12.0
[pip3] torchvision==0.13.0
[conda] Could not collect
```
cc @ezyang @gchanan @zou3519 @albanD @mruberry @jbschlosser @walterddr @kshitij12345 @saketh-are
| 13 |
5,270 | 81,186 |
grad not preserved during copying or pickling
|
triaged, module: python frontend
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
I would like to (cloud-)pickle some Tensors. However, their `grad` attribute is lost during pickling. The following snippet
```python
import cloudpickle
import copy
import torch
def square(x):
return x*x
x = torch.tensor([2.0], requires_grad=True)
loss = square(x)
loss.backward()
print (type(x), x, x.grad)
y = copy.copy(x)
print (type(y), y, y.grad)
y = cloudpickle.loads(cloudpickle.dumps(x))
print (type(y), y, y.grad)
```
yields the following output:
```
<class 'torch.Tensor'> tensor([2.], requires_grad=True) tensor([4.])
<class 'torch.Tensor'> tensor([2.], requires_grad=True) None
<class 'torch.Tensor'> tensor([2.], requires_grad=True) None
```
I can work around this using a custom reduction function for `torch.Tensor` like
```python
import copyreg
def reconstruct_tensor(val, requires_grad, grad, device):
t = torch.tensor(val, device=device, requires_grad=requires_grad)
if grad:
t.grad = torch.from_numpy(grad)
return t
def reduce_tensor(t):
if t.requires_grad:
return reconstruct_tensor, (t.detach().numpy(), True, t.grad.numpy(), t.device.type)
else:
return reconstruct_tensor, (t.numpy(), False, None, t.device.type)
copyreg.pickle(torch.Tensor, reduce_tensor)
# Include previous snippet here
```
which yields the expected output
```
<class 'torch.Tensor'> tensor([2.], requires_grad=True) tensor([4.])
<class 'torch.Tensor'> tensor([2.], requires_grad=True) tensor([4.])
<class 'torch.Tensor'> tensor([2.], requires_grad=True) tensor([4.])
```
This is basically what [Dask does](https://github.com/dask/distributed/blob/main/distributed/protocol/torch.py). But a better place to fix this would seem to be in [`Tensor.__reduce_ex__`](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/blob/3c2199b159b6ec57af3f7ea22d61ace9ce5cf5bc/torch/_tensor.py#L208)
### Versions
PyTorch version: 1.12.0+cpu
Is debug build: False
CUDA used to build PyTorch: None
ROCM used to build PyTorch: N/A
OS: Fedora Linux 35 (Container Image) (x86_64)
GCC version: (GCC) 11.2.1 20220127 (Red Hat 11.2.1-9)
Clang version: Could not collect
CMake version: Could not collect
Libc version: glibc-2.34
Python version: 3.8.13 (default, Mar 28 2022, 11:38:47) [GCC 7.5.0] (64-bit runtime)
Python platform: Linux-5.18.9-200.fc36.x86_64-x86_64-with-glibc2.17
Is CUDA available: False
CUDA runtime version: No CUDA
GPU models and configuration: No CUDA
Nvidia driver version: No CUDA
cuDNN version: No CUDA
HIP runtime version: N/A
MIOpen runtime version: N/A
Is XNNPACK available: True
Versions of relevant libraries:
[pip3] numpy==1.23.0
[pip3] torch==1.12.0+cpu
[pip3] torchaudio==0.12.0+cpu
[pip3] torchvision==0.13.0+cpu
[conda] numpy 1.23.0 pypi_0 pypi
[conda] torch 1.12.0+cpu pypi_0 pypi
[conda] torchaudio 0.12.0+cpu pypi_0 pypi
[conda] torchvision 0.13.0+cpu pypi_0 pypi
| 2 |
5,271 | 81,185 |
[Mac M1] `torch.mm` sometimes produces incorrect results
|
high priority, module: cpu, triaged, module: correctness (silent), module: arm, module: m1
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
Observed unexpected nan outputs from the `torch.nn.functional.conv1d` function on M1 Mac
```python
# bug_demo.py
import torch
n_trials = 100
for ii in range(n_trials):
a = torch.randn(1024, device='mps')
b = torch.randn(499, device='mps')
c = torch.nn.functional.conv1d(a.view(1, 1, -1), b.view(1, 1, -1))
if torch.isnan(torch.sum(c)):
print(f'mps: trial {ii}, nan elements {torch.isnan(c.squeeze()).nonzero().view(-1).cpu().numpy()}')
for ii in range(n_trials):
a = torch.randn(1024, device='cpu')
b = torch.randn(499, device='cpu')
c = torch.nn.functional.conv1d(a.view(1, 1, -1), b.view(1, 1, -1))
if torch.isnan(torch.sum(c)):
print(f'cpu: trial {ii}, elements {torch.isnan(c.squeeze()).nonzero().view(-1).numpy()}')
```
Which results in:
```
$ python bug_demo.py
cpu: trial 1, nan elements [512 513 514 515 516 517 518 519 520 521 522 523]
cpu: trial 3, nan elements [514 515 520 521 524 525]
cpu: trial 6, nan elements [514 515 520 521 524 525]
cpu: trial 7, nan elements [520 521]
cpu: trial 21, nan elements [520 521]
cpu: trial 22, nan elements [514 515 518 519 520 521 522 523 524 525]
cpu: trial 23, nan elements [514 515 520 521 524 525]
cpu: trial 26, nan elements [514 515 518 519 520 521 522 523 524 525]
# ... 15 more trials
$ python bug_demo.py
$ python bug_demo.py
cpu: trial 4, nan elements [512 513 521 522 523]
cpu: trial 53, nan elements [512 513 521 522 523]
cpu: trial 67, nan elements [512 513 521 522 523]
cpu: trial 89, nan elements [512 513 521 522 523]
$ python bug_demo.py
mps: trial 36, nan elements [ 0 1 2 3 4 5 ... 525] # Notice: MPS. All elements are nan
cpu: trial 1, nan elements [514 515 518 519 520 521 522 523 524 525]
# ... 12 more trials, all with the same nan elements
```
**Few observations:**
* The bug was observed both on CPU and MPS devices
* The bug occurs much more frequently on CPU than on MPS
* For CPU it was observed almost on every run
* For MPS it was observed once every 30/40 runs
* The bug occurs much more frequently when running first on MPS and then on CPU
* Most of the nan values were observed at the +- end of the output vector when running on CPU. In this example, the output has 526 elements; unexpected nan values were observed most frequently on elements 520 and 521. On MPS device, on the other hand, when it happened, *usually* the whole output vector was all nan
* The bug was observed even for deterministic inputs (e.g., `arange(0, L, ..., dtype=torch.float32)` instead of `randn(...)`), although less frequently
* On my very non-exhaustive set of trials, the problem didn't reproduce so frequently for shorter `a` and `b` vectors. I managed to observe the problem on MPS for `a` with 512 elements and `b` with 299, but couldn't reproduce at all for shorter `b` (doesn't mean that it can't happen, though)
One last thing: the execution time on the MPS was > x100 than the run time on CPU. For `n_trials = 1000`, it's `11.359s` vs `0.102s` (on M1 Max).
### Versions
Observed on the stable and the nightly builds.
Nightly build:
```
Collecting environment information...
PyTorch version: 1.13.0.dev20220710
Is debug build: False
CUDA used to build PyTorch: None
ROCM used to build PyTorch: N/A
OS: macOS 12.4 (arm64)
GCC version: Could not collect
Clang version: 13.1.6 (clang-1316.0.21.2.5)
CMake version: version 3.23.2
Libc version: N/A
Python version: 3.9.12 (main, Apr 5 2022, 01:52:34) [Clang 12.0.0 ] (64-bit runtime)
Python platform: macOS-12.4-arm64-arm-64bit
Is CUDA available: False
CUDA runtime version: No CUDA
GPU models and configuration: No CUDA
Nvidia driver version: No CUDA
cuDNN version: No CUDA
HIP runtime version: N/A
MIOpen runtime version: N/A
Is XNNPACK available: True
Versions of relevant libraries:
[pip3] numpy==1.22.3
[pip3] torch==1.13.0.dev20220710
[pip3] torchvision==0.14.0.dev20220710
[conda] numpy 1.22.3 py39h25ab29e_0
[conda] numpy-base 1.22.3 py39h974a1f5_0
[conda] pytorch 1.13.0.dev20220710 py3.9_0 pytorch-nightly
[conda] torchvision 0.14.0.dev20220710 py39_cpu pytorch-nightly
```
Stable build:
```
...
Versions of relevant libraries:
[pip3] numpy==1.22.3
[pip3] torch==1.12.0
[pip3] torchvision==0.13.0
[conda] numpy 1.22.3 py39h25ab29e_0
[conda] numpy-base 1.22.3 py39h974a1f5_0
[conda] pytorch 1.12.0 py3.9_0 pytorch
[conda] torchvision 0.13.0 py39_cpu pytorch
```
cc @ezyang @gchanan @zou3519 @VitalyFedyunin @malfet @kulinseth @albanD
| 26 |
5,272 | 81,172 |
build libtorch with the same mkl as Matlab
|
oncall: binaries, triaged, module: mkl
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
after doing a matrix multiplication in mex function, matlab crushes because of different mkl using Matlab and libtorch.
How can I use the same MKL that matlab uses, or somehow make it compatible.
this is the trace that I get.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Segmentation violation detected at 2022-07-09 20:17:30 +0200
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Configuration:
Crash Decoding : Disabled - No sandbox or build area path
Crash Mode : continue (default)
Default Encoding : UTF-8
Deployed : false
Desktop Environment : ubuntu:GNOME
GNU C Library : 2.27 stable
Graphics Driver : Uninitialized hardware
Graphics card 1 : 0x10de ( 0x10de ) 0x1e90 Version 495.29.5.0 (0-0-0)
Graphics card 2 : 0x8086 ( 0x8086 ) 0x3e9b Version 0.0.0.0 (0-0-0)
Java Version : Java 1.8.0_202-b08 with Oracle Corporation Java HotSpot(TM) 64-Bit Server VM mixed mode
MATLAB Architecture : glnxa64
MATLAB Entitlement ID : 8786298
MATLAB Root : /usr/local/MATLAB/R2022a
MATLAB Version : 9.12.0.1975300 (R2022a) Update 3
OpenGL : hardware
Operating System : Ubuntu 18.04.6 LTS
Process ID : 7612
Processor ID : x86 Family 6 Model 158 Stepping 10, GenuineIntel
Session Key : d4230444-ddaf-42e5-a573-924e2acf3f37
Window System : The X.Org Foundation (12008000), display :1
Fault Count: 6
Abnormal termination:
Segmentation violation
Current Thread: 'MCR 0 interpret' id 139819670337280
Register State (from fault):
RAX = 0000000000000018 RBX = 0000000000000001
RCX = 0000002400000050 RDX = 00007f27b8066c60
RSP = 00007f2a4dc7ef58 RBP = 0000000000000000
RSI = 0000000000000a80 RDI = 00000000000000c0
R8 = 00007fb7b8066d40 R9 = 00007f27b8200700
R10 = 00007f27b8066c00 R11 = 0000006c000000f0
R12 = 0000000000003e80 R13 = 00000000000000c0
R14 = 0000000000000000 R15 = 0000000000000a80
RIP = 00007f27b6123da4 EFL = 0000000000010206
CS = 0033 FS = 0000 GS = 0000
Stack Trace (from fault):
[ 0] 0x00007f27b6123da4 /usr/local/MATLAB/R2022a/bin/glnxa64/mkl.so+63008164 mkl_blas_avx2_sgemm_scopy_down24_ea+00000164
Abnormal termination:
Segmentation violation
Current Thread: 'MCR 0 interpret' id 139812355454720
Register State (from fault):
RAX = 0000000000000018 RBX = 0000000000000001
RCX = 0000002400000050 RDX = 00007f27b806ea60
RSP = 00007f2899c81f58 RBP = 0000000000001f80
RSI = 0000000000000a80 RDI = 00000000000000c0
R8 = 00007fb7b806eb40 R9 = 00007f27b87e8700
R10 = 00007f27b806ea00 R11 = 0000006c000000f0
R12 = 0000000000003e80 R13 = 00000000000000c0
R14 = 0000000000000000 R15 = 0000000000000a80
RIP = 00007f27b6123da4 EFL = 0000000000010206
CS = 0033 FS = 0000 GS = 0000
Stack Trace (from fault):
[ 0] 0x00007f27b6123da4 /usr/local/MATLAB/R2022a/bin/glnxa64/mkl.so+63008164 mkl_blas_avx2_sgemm_scopy_down24_ea+00000164
Abnormal termination:
Segmentation violation
Current Thread: 'MCR 0 interpret' id 139812372449024
Register State (from fault):
RAX = 0000000000000018 RBX = 0000000000000001
RCX = 0000002400000050 RDX = 00007f27b8073e60
RSP = 00007f289acb6ed8 RBP = 0000000000003480
RSI = 0000000000000a00 RDI = 00000000000000c0
R8 = 00007fb7b8073f40 R9 = 00007f27b8bd8700
R10 = 00007f27b8073e00 R11 = 0000006c000000f0
R12 = 0000000000003e80 R13 = 00000000000000c0
R14 = 0000000000000000 R15 = 0000000000000a00
RIP = 00007f27b6123da4 EFL = 0000000000010206
CS = 0033 FS = 0000 GS = 0000
Stack Trace (from fault):
[ 0] 0x00007f27b6123da4 /usr/local/MATLAB/R2022a/bin/glnxa64/mkl.so+63008164 mkl_blas_avx2_sgemm_scopy_down24_ea+00000164
Abnormal termination:
Segmentation violation
Current Thread: 'MCR 0 interpret' id 139812354402048
Register State (from fault):
RAX = 0000000000000018 RBX = 0000000000000001
RCX = 0000002400000050 RDX = 00007f27b8071460
RSP = 00007f2899b80f58 RBP = 0000000000002a00
RSI = 0000000000000a80 RDI = 00000000000000c0
R8 = 00007fb7b8071540 R9 = 00007f27b89e0700
R10 = 00007f27b8071400 R11 = 0000006c000000f0
R12 = 0000000000003e80 R13 = 00000000000000c0
R14 = 0000000000000000 R15 = 0000000000000a80
RIP = 00007f27b6123da4 EFL = 0000000000010206
CS = 0033 FS = 0000 GS = 0000
Stack Trace (from fault):
[ 0] 0x00007f27b6123da4 /usr/local/MATLAB/R2022a/bin/glnxa64/mkl.so+63008164 mkl_blas_avx2_sgemm_scopy_down24_ea+00000164
Abnormal termination:
Segmentation violation
Current Thread: 'MCR 0 interpret' id 139812863497984
Register State (from fault):
RAX = 0000000000000018 RBX = 0000000000000001
RCX = 0000002400000050 RDX = 00007f27b806c060
RSP = 00007f28b8103fd8 RBP = 0000000000001500
RSI = 0000000000000a80 RDI = 00000000000000c0
R8 = 00007fb7b806c140 R9 = 00007f27b85f0700
R10 = 00007f27b806c000 R11 = 0000006c000000f0
R12 = 0000000000003e80 R13 = 00000000000000c0
R14 = 0000000000000000 R15 = 0000000000000a80
RIP = 00007f27b6123da4 EFL = 0000000000010206
CS = 0033 FS = 0000 GS = 0000
Stack Trace (from fault):
[ 0] 0x00007f27b6123da4 /usr/local/MATLAB/R2022a/bin/glnxa64/mkl.so+63008164 mkl_blas_avx2_sgemm_scopy_down24_ea+00000164
Abnormal termination:
Segmentation violation
Current Thread: 'MCR 0 interpret' id 139811983693568
Register State (from fault):
RAX = 0000000000000018 RBX = 0000000000000001
RCX = 0000002400000050 RDX = 00007f27b8069660
RSP = 00007f28839f7fd8 RBP = 0000000000000a80
RSI = 0000000000000a80 RDI = 00000000000000c0
R8 = 00007fb7b8069740 R9 = 00007f27b83f8700
R10 = 00007f27b8069600 R11 = 0000006c000000f0
R12 = 0000000000003e80 R13 = 00000000000000c0
R14 = 0000000000000000 R15 = 0000000000000a80
RIP = 00007f27b6123da4 EFL = 0000000000010206
CS = 0033 FS = 0000 GS = 0000
Stack Trace (from fault):
[ 0] 0x00007f27b6123da4 /usr/local/MATLAB/R2022a/bin/glnxa64/mkl.so+63008164 mkl_blas_avx2_sgemm_scopy_down24_ea+00000164
### Versions
I'm using this version
https://download.pytorch.org/libtorch/cu116/libtorch-cxx11-abi-shared-with-deps-1.12.0%2Bcu116.zip
cc @ezyang @seemethere @malfet
| 0 |
5,273 | 81,167 |
move bazel files out of pytorch repo root
|
triaged, module: bazel
|
https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/commit/03847808a0f98faf91790802a9f5be49de82360b added a bunch of bazel files to pytorch repo root. Can we move these somewhere out of the way? As is, they make the "front page" of the repo really long and make it so you have to scroll to get to the readme
| 3 |
5,274 | 81,162 |
SparseAdam performance issue during optimizer step
|
module: performance, module: sparse, module: optimizer, triaged
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
I read the code and found that Sparse Adam optimizer add sparse to dense tensor and called coalesce method on Sparse Tensor during step, and that operation on CPU is extremely slow. I run Node2Vec model on pubmed dataset, using Sparse Tensor with Sparse Adam optimizer is slower than using dense tensor with Adam optimizer.
And I noticed that during tensor add and coalesce operation, only one CPU was used. Do we have some method to accelerate these processes with multiple CPU cores usage?
### Versions
```
Collecting environment information...
PyTorch version: 1.12.0
Is debug build: False
CUDA used to build PyTorch: None
ROCM used to build PyTorch: N/A
OS: Ubuntu 20.04 LTS (x86_64)
GCC version: (Ubuntu 9.4.0-1ubuntu1~20.04.1) 9.4.0
Clang version: Could not collect
CMake version: Could not collect
Libc version: glibc-2.31
Python version: 3.9.12 (main, Apr 5 2022, 06:56:58) [GCC 7.5.0] (64-bit runtime)
Python platform: Linux-5.15.35-1-pve-x86_64-with-glibc2.31
Is CUDA available: False
CUDA runtime version: No CUDA
GPU models and configuration: No CUDA
Nvidia driver version: No CUDA
cuDNN version: No CUDA
HIP runtime version: N/A
MIOpen runtime version: N/A
Is XNNPACK available: True
Versions of relevant libraries:
[pip3] intel-extension-for-pytorch==1.12.0
[pip3] mypy-extensions==0.4.3
[pip3] numpy==1.21.5
[pip3] numpydoc==1.2
[pip3] torch==1.12.0
[pip3] torchaudio==0.12.0
[pip3] torchvision==0.13.0
[conda] blas 1.0 mkl
[conda] cpuonly 2.0 0 pytorch
[conda] ffmpeg 4.3 hf484d3e_0 pytorch
[conda] intel-extension-for-pytorch 1.12.0 pypi_0 pypi
[conda] mkl 2021.4.0 h06a4308_640
[conda] mkl-service 2.4.0 py39h7f8727e_0
[conda] mkl_fft 1.3.1 py39hd3c417c_0
[conda] mkl_random 1.2.2 py39h51133e4_0
[conda] numpy 1.21.5 py39he7a7128_1
[conda] numpy-base 1.21.5 py39hf524024_1
[conda] numpydoc 1.2 pyhd3eb1b0_0
[conda] pytorch 1.12.0 py3.9_cpu_0 pytorch
[conda] pytorch-mutex 1.0 cpu pytorch
[conda] torchaudio 0.12.0 py39_cpu pytorch
[conda] torchvision 0.13.0 py39_cpu pytorch
```
cc @VitalyFedyunin @ngimel @nikitaved @pearu @cpuhrsch @amjames @bhosmer @vincentqb @jbschlosser @albanD
| 0 |
5,275 | 81,140 |
libprotobuf version compatibility
|
triaged, module: build warnings
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
Just wanna test out **classifier.py**, but failed with the following **ERROR** message
```console
[libprotobuf FATAL google/protobuf/stubs/common.cc:83] This program was compiled against version 3.9.2 of the Protocol Buffer runtime library, which is not compatible with the installed version (3.19.4). Contact the program author for an update. If you compiled the program yourself, make sure that your headers are from the same version of Protocol Buffers as your link-time library. (Version verification failed in "bazel-out/k8-opt/bin/tensorflow/core/framework/tensor_shape.pb.cc".)
```
### Versions
```console
➜ ~ python collect_env.py
Collecting environment information...
PyTorch version: 1.13.0a0+git4b6ba34
Is debug build: False
CUDA used to build PyTorch: 11.7
ROCM used to build PyTorch: N/A
OS: Ubuntu 22.04 LTS (x86_64)
GCC version: (Ubuntu 11.2.0-19ubuntu1) 11.2.0
Clang version: 15.0.0-++20220707031229+438ffdb821bb-1~exp1~20220707151338.282
CMake version: version 3.22.1
Libc version: glibc-2.35
Python version: 3.10.4 (main, Apr 2 2022, 09:04:19) [GCC 11.2.0] (64-bit runtime)
Python platform: Linux-5.15.0-40-generic-x86_64-with-glibc2.35
Is CUDA available: True
CUDA runtime version: 11.7.64
GPU models and configuration: GPU 0: NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3080 Ti Laptop GPU
Nvidia driver version: 515.48.07
cuDNN version: Probably one of the following:
/usr/local/cuda-11.7/targets/x86_64-linux/lib/libcudnn.so.8.4.1
/usr/local/cuda-11.7/targets/x86_64-linux/lib/libcudnn_adv_infer.so.8.4.1
/usr/local/cuda-11.7/targets/x86_64-linux/lib/libcudnn_adv_train.so.8.4.1
/usr/local/cuda-11.7/targets/x86_64-linux/lib/libcudnn_cnn_infer.so.8.4.1
/usr/local/cuda-11.7/targets/x86_64-linux/lib/libcudnn_cnn_train.so.8.4.1
/usr/local/cuda-11.7/targets/x86_64-linux/lib/libcudnn_ops_infer.so.8.4.1
/usr/local/cuda-11.7/targets/x86_64-linux/lib/libcudnn_ops_train.so.8.4.1
HIP runtime version: N/A
MIOpen runtime version: N/A
Is XNNPACK available: True
Versions of relevant libraries:
[pip3] mypy-extensions==0.4.3
[pip3] numpy==1.23.0
[pip3] torch==1.13.0a0+git4b6ba34
[pip3] torch-model-archiver==0.6.0
[pip3] torchserve==0.6.0
[pip3] torchvision==0.14.0a0+fb7f9a1
[conda] Could not collect
```
| 7 |
5,276 | 81,127 |
Docker updates cause subsequent builds to fail
|
high priority, module: ci, triaged
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
Most recent example:
https://hud.pytorch.org/pytorch/pytorch/commit/8a5d9843ff5d5dd865fc922853a15b3e7e459fdb (underlying workflows [trunk](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/actions/runs/2637230403/attempts/1) and [pull](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/actions/runs/2637230400) )
And subsequent commits after this one started to fail as well until I've manually re-run docker image build in https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/actions/runs/2637584738
We are having those regressions periodically, despite numerous claims that race conditions have been fixed
### Versions
CI
cc @ezyang @gchanan @zou3519 @seemethere @malfet @pytorch/pytorch-dev-infra
| 2 |
5,277 | 81,115 |
torch.package can not be used to serialize `resnet18` from TorchVision-0.12
|
high priority, module: vision, module: regression, oncall: package/deploy, imported
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
Running `ModelTest.test_model` will fail if PyTorch-1.12 + TorchVision are installed with the following error:
```
torch.package.package_exporter.PackagingError:
* Module had no __file__ defined.
sys
_io
_imp
py.io
six.moves.urllib.parse
* Module is a C extension module. torch.package supports Python modules only.
numpy.core._multiarray_umath
_ctypes
numpy.linalg.lapack_lite
numpy.linalg._umath_linalg
psutil._psutil_osx
psutil._psutil_posix
numpy.random.mtrand
numpy.random._philox
numpy.random._pcg64
numpy.random._sfc64
numpy.random._generator
numpy.random._mt19937
numpy.random._common
numpy.random._bounded_integers
numpy.random.bit_generator
numpy.fft._pocketfft_internal
scipy._lib._ccallback_c
_cffi_backend
PIL._imaging
PIL._imagingft
```
This failures have started with commit https://github.com/pytorch/vision/commit/183a722169421c83638e68ee2d8fc5bd3415c4b4
that introduced unused by generated model, but still serialized dependency on `sys` buildin module, see
```
% python3 test_package.py -v -k test_resnet
test_resnet (test_model.ModelTest) ... ERROR
======================================================================
ERROR: test_resnet (test_model.ModelTest)
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "/Users/nshulga/git/pytorch/pytorch/test/package/test_model.py", line 45, in test_resnet
e.save_pickle("model", "model.pkl", resnet)
File "/Users/nshulga/git/pytorch/pytorch/torch/package/package_exporter.py", line 951, in __exit__
self.close()
File "/Users/nshulga/git/pytorch/pytorch/torch/package/package_exporter.py", line 1055, in close
self._execute_dependency_graph()
File "/Users/nshulga/git/pytorch/pytorch/torch/package/package_exporter.py", line 992, in _execute_dependency_graph
self._validate_dependency_graph()
File "/Users/nshulga/git/pytorch/pytorch/torch/package/package_exporter.py", line 974, in _validate_dependency_graph
raise PackagingError(self.dependency_graph)
torch.package.package_exporter.PackagingError:
* Module had no __file__ defined.
sys
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Ran 1 test in 0.919s
FAILED (errors=1)
```
### Versions
Nightly, 1.12/0.12
cc @ezyang @gchanan @zou3519 @fmassa @vfdev-5 @pmeier
| 1 |
5,278 | 81,110 |
CI: Run cpu tests in parallel processes?
|
module: ci, triaged
|
AFAICT CI is running on multi-core workers, but only launching a single process to run the tests. Since most individual test cases have low thread utilization, this means under-utilizing the available hardware.
For example, using [`pytest-xdist`](https://pypi.org/project/pytest-xdist/) I see a 4x speedup from running 8 parallel processes on a 32-core machine
```
$ time OMP_NUM_THREADS=32 pytest test_ops.py -k cpu
real 24m13.282s
user 369m12.584s
sys 11m12.221s
$ time OMP_NUM_THREADS=4 pytest test_ops.py -k cpu -n 8
real 5m22.487s
user 61m53.781s
sys 2m21.365s
```
There is some risk of additional flakiness. For example, two tests allocating large tensors might fail if run at the same time. This could be mitigated though, by marking problematic tests as not suitable for running in parallel.
cc @seemethere @malfet @pytorch/pytorch-dev-infra
| 3 |
5,279 | 81,104 |
Resize/reshape of sparse compressed tensors - design
|
module: sparse, triaged
|
## Issue description
Currently, resizing sparse compressed tensors works correctly only in the CSR layout and non-hybrid case. Other cases are silently broken and the resize operation produces invalid tensors.
The issue is relevant for designing the reshape operation on sparse compressed tensors as well.
## Code example
```python
>>> import torch
>>> s = torch.tensor([[1, 2], [3, 4]]).to_sparse_csc()
>>> torch._validate_sparse_csc_tensor_args(s.ccol_indices(), s.row_indices(), s.values(), s.shape)
>>> s.resize_(2, 4)
tensor(ccol_indices=tensor([0, 2, 4]),
row_indices=tensor([0, 1, 0, 1]),
values=tensor([1, 3, 2, 4]), size=(2, 4), nnz=4,
layout=torch.sparse_csc)
>>> torch._validate_sparse_csc_tensor_args(s.ccol_indices(), s.row_indices(), s.values(), s.shape)
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
RuntimeError: ccol_indices.shape[-1] must be equal to the number of columns + 1 (=5), but got 3
```
- PyTorch version: master
## Design
The size of a compressed sparse tensor has the following general form
```python
batchsize + (ncompressed_indices * blocksize[0], nplain_indices * blocksize[1]) + densesize
```
(see https://pearu.github.io/bsr_tensor_invariants.html#shape-and-strides-invariants-1) where for CSR/CSC tensors `blocksize[0] == blocksize[1] == 1` by definition.
For the attributes of a compressed sparse tensor we have the following relations:
```python
compressed_indices.shape == batchsize + (ncompressed_indices + 1,)
plain_indices.shape == batchsize + (nnz,)
values.shape == batchsize + (nnz,) + blocksize + densesize
0 <= compressed_indices[..., i] - compressed_indices[..., i-1] <= nplain_indices
plain_indices.max() < nplain_indices
```
where for CSR/CSC tensors `blocksize == ()` by definition and `...` corresponds to batch dimensions.
### Resizing batch and dense dimensions
Resizing batch and dense dimensions is straightforward:
```python
compressed_indices.resize_(new_batchsize + ...)
plain_indices.resize_(new_batchsize + ...)
values.resize_(new_batchsize + ...)
size = new_batchsize + ...
```
and
```python
values.resize_(... + new_densesize)
size = ... + new_densesize
```
respectively. `...` correspond to sparse and dense dimensions, and batch or sparse dimensions, respectively.
### Ambiguity in resizing sparse dimensions and a solution
Resizing compressed and plain dimensions requires re-computing both compressed and plain dimensions. In the case of blocked formats, the resize is ambiguous in general as the system of equations:
```python
ncompressed_indices * blocksize[0] == new_compressed_size
nplain_indices * blocksize[1] == new_plain_size
```
may not have a solution at all (that would lead to an exception) or have multiple solutions. In case of multiple solutions, conservation of `blocksize` is preferred, that is,
```python
new_ncompressed_indices = new_compressed_size / blocksize[0]
new_nplain_indices = new_plain_size / blocksize[1]
```
if new sizes are greater or equal than the corresponding blocksizes, otherwise, new blocksizes will be re-computed by maximizing these.
### Ambiguity in changing dimensionality and a solution
While the total dimensionality is allowed to change in the resize operation, in general, specifying a new dimensionality (when `len(new_shape) != len(tensor.shape)`) is ambiguous without specifying whether the newly specified dimensions correspond to batch, sparse, or dense dimensions.
To resolve these ambiguities, we distinguish non-hybrid and hybrid shapes.
A non-hybrid shape (`new_shape`) is defined by
```python
2 <= len(new_shape) <= len(tensor.shape) - tensor.dense_dim()
```
that is, the last two items in `new_shape` correspond to sparse dimensions and possibly non-zero dense dimensions will be dropped.
`len(new_shape) < 2` is disallowed by sparse compressed tensor definition and would lead to an exception.
A hybrid shape is defined by
```python
len(tensor.shape) - tensor.dense_dim() < len(new_shape)
```
that is, batched and sparse dimensionalities are preserved in the shape change (but the corresponding dimensions are allowed to change).
Limitations: one cannot introduce new batch dimensions with this approach, only changing the existing batch dimensions is possible.
### Validity of the resize result
When resizing involves changing sparse dimensions (compressed or plain), the corresponding indices attributes may need to be updated as well as the indices' compression result depends on the sparse dimensions.
### Questions
Does this make sense?
cc @nikitaved @pearu @cpuhrsch @amjames
| 4 |
5,280 | 81,102 |
[discussion] Consolidation of audio-visual I/O in a new package
|
module: build, triaged, module: vision, module: third_party
|
### 🚀 The feature, motivation and pitch
Both torchvision (VideoReader) and torchaudio (StreamReader) have implemented different wrappers for ffmpeg for reading both video (and audio) with their own api / decisions / problems on building from source and linking: https://github.com/pytorch/vision/issues/5720#issuecomment-1171715173. And also torchdata has its own entity named StreamReader dealing with something else completely: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/blob/cac16e2ee293964033dffa6616f78b68603cd565/torch/utils/data/datapipes/iter/streamreader.py#L8-L9 (for StreamReader is a quite generic name), so audio's naming is also not very good IMO
I propose to consolidate this complex code in a separate package (`torchio`? `torchavio`?) and confine these issues to this package only. It would simplify building / testing of torchvision/torchaudio
It may make sense to move to this package image/audio reading/writing functionality too (although less urged because building of those seems simpler).
@ezyang @soumith @albanD
### Alternatives
_No response_
### Additional context
_No response_
cc @malfet @seemethere @fmassa @vfdev-5 @pmeier
| 25 |
5,281 | 81,100 |
[jit] Failed to load a saved scripted function
|
oncall: jit
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
The following code is failing:
```python
import torch # '1.13.0.dev20220707'
from typing import Union, List
def func(padding: Union[int, List[int]]) -> None:
if isinstance(padding, list) and len(padding) not in [1, 2, 4]:
raise ValueError(f"Padding must be an int or a 1, 2, or 4 element tuple, not a {len(padding)} element tuple")
s = torch.jit.script(func)
s.save("test")
ss = torch.jit.load("test")
```
Output:
```
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
RuntimeError Traceback (most recent call last)
/var/folders/8r/t4lgs4t95xjgyj6g63kz10mm0000gn/T/ipykernel_47279/2244443921.py in <module>
----> 1 ss = torch.jit.load("test")
~/opt/miniconda3/envs/test/lib/python3.8/site-packages/torch/jit/_serialization.py in load(f, map_location, _extra_files)
160 cu = torch._C.CompilationUnit()
161 if isinstance(f, str) or isinstance(f, pathlib.Path):
--> 162 cpp_module = torch._C.import_ir_module(cu, str(f), map_location, _extra_files)
163 else:
164 cpp_module = torch._C.import_ir_module_from_buffer(
RuntimeError:
Type mismatch: padding0 is set to type List[int] in the true branch and type int in the false branch:
File "code/__torch__.py", line 9
_0 = "Padding must be an int or a 1, 2, or 4 element tuple, not a {} element tuple"
_1 = isinstance(padding, list)
if _1:
~~~~~~
padding1 = unchecked_cast(List[int], padding)
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
_3 = torch.len(padding1)
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
_4 = torch.__not__(torch.__contains__([1, 2, 4], _3))
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
_2, padding0 = _4, padding1
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
else:
~~~~~
_2, padding0 = False, unchecked_cast(int, padding)
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ <--- HERE
if _2:
padding2 = unchecked_cast(List[int], padding0)
and was used here:
File "code/__torch__.py", line 17
_2, padding0 = False, unchecked_cast(int, padding)
if _2:
padding2 = unchecked_cast(List[int], padding0)
~~~~~~~~ <--- HERE
_5 = torch.format(_0, torch.len(padding2))
ops.prim.RaiseException(_5, "builtins.ValueError")
```
Looks like the issue is related to the call `len(padding)` in the value error message.
1) if we split if condition into two then everything works:
```diff
def func(padding: Union[int, List[int]]) -> None:
- if isinstance(padding, list) and len(padding) not in [1, 2, 4]:
+ if isinstance(padding, list):
+ if len(padding) not in [1, 2, 4]:
raise ValueError(f"Padding must be an int or a 1, 2, or 4 element tuple, not a {len(padding)} element tuple")
```
2) If removed `len(padding)` from message error then everything works.
```diff
def func(padding: Union[int, List[int]]) -> None:
if isinstance(padding, list) and len(padding) not in [1, 2, 4]:
- raise ValueError(f"Padding must be an int or a 1, 2, or 4 element tuple, not a {len(padding)} element tuple")
+ raise ValueError(f"Padding must be an int or a 1, 2, or 4 element tuple")
```
### Versions
1.13.0.dev20220707
| 0 |
5,282 | 81,085 |
RuntimeError: required keyword attribute 'value' is undefined
|
high priority, triage review, oncall: jit
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
Hi,
While loading loading a `.pt` file, I'm getting following error:
```
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
File "/home/sort/miniconda3/envs/openmmlab/lib/python3.8/site-packages/torch/jit/_serialization.py", line 162, in load
cpp_module = torch._C.import_ir_module(cu, str(f), map_location, _extra_files)
RuntimeError: required keyword attribute 'value' is undefined
```
Code:
```
import torch
loaded = torch.jit.load('end2end.pt')
```
### Versions
Collecting environment information...
PyTorch version: 1.12.0
Is debug build: False
CUDA used to build PyTorch: 11.3
ROCM used to build PyTorch: N/A
OS: Ubuntu 20.04.4 LTS (x86_64)
GCC version: (Ubuntu 9.4.0-1ubuntu1~20.04.1) 9.4.0
Clang version: Could not collect
CMake version: version 3.16.3
Libc version: glibc-2.31
Python version: 3.8.13 (default, Mar 28 2022, 11:38:47) [GCC 7.5.0] (64-bit runtime)
Python platform: Linux-5.13.0-52-generic-x86_64-with-glibc2.17
Is CUDA available: True
CUDA runtime version: Could not collect
GPU models and configuration:
GPU 0: NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3080 Ti
GPU 1: NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3090
Nvidia driver version: 470.103.01
cuDNN version: Probably one of the following:
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn.so.8.2.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_adv_infer.so.8.2.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_adv_train.so.8.2.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_cnn_infer.so.8.2.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_cnn_train.so.8.2.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_ops_infer.so.8.2.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_ops_train.so.8.2.1
HIP runtime version: N/A
MIOpen runtime version: N/A
Is XNNPACK available: True
Versions of relevant libraries:
[pip3] numpy==1.23.0
[pip3] torch==1.12.0
[pip3] torchvision==0.13.0
[conda] blas 1.0 mkl
[conda] cudatoolkit 11.3.1 h2bc3f7f_2
[conda] ffmpeg 4.3 hf484d3e_0 pytorch
[conda] libblas 3.9.0 12_linux64_mkl conda-forge
[conda] libcblas 3.9.0 12_linux64_mkl conda-forge
[conda] liblapack 3.9.0 12_linux64_mkl conda-forge
[conda] liblapacke 3.9.0 12_linux64_mkl conda-forge
[conda] mkl 2021.4.0 h06a4308_640
[conda] mkl-service 2.4.0 py38h7f8727e_0
[conda] mkl_fft 1.3.1 py38hd3c417c_0
[conda] mkl_random 1.2.2 py38h51133e4_0
[conda] numpy 1.23.0 pypi_0 pypi
[conda] numpy-base 1.22.3 py38hf524024_0
[conda] pytorch 1.12.0 py3.8_cuda11.3_cudnn8.3.2_0 pytorch
[conda] pytorch-mutex 1.0 cuda pytorch
[conda] torchvision 0.13.0 py38_cu113 pytorch
cc @ezyang @gchanan @zou3519
| 19 |
5,283 | 81,084 |
[ONNX] Exporting the operator `::svd` to ONNX opset version 13 is not supported.
|
module: onnx, triaged, OSS contribution wanted, onnx-triaged
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
Exporting the operator ::svd to ONNX opset version 13 is not supported.
```
File "C:\Users\kimju\anaconda3\envs\HybrIK\lib\site-packages\torch\onnx\__init__.py", line 350, in export
return utils.export(
File "C:\Users\kimju\anaconda3\envs\HybrIK\lib\site-packages\torch\onnx\utils.py", line 163, in export
_export(
File "C:\Users\kimju\anaconda3\envs\HybrIK\lib\site-packages\torch\onnx\utils.py", line 1074, in _export
graph, params_dict, torch_out = _model_to_graph(
File "C:\Users\kimju\anaconda3\envs\HybrIK\lib\site-packages\torch\onnx\utils.py", line 731, in _model_to_graph
graph = _optimize_graph(
File "C:\Users\kimju\anaconda3\envs\HybrIK\lib\site-packages\torch\onnx\utils.py", line 308, in _optimize_graph
graph = _C._jit_pass_onnx(graph, operator_export_type)
File "C:\Users\kimju\anaconda3\envs\HybrIK\lib\site-packages\torch\onnx\__init__.py", line 416, in _run_symbolic_function
return utils._run_symbolic_function(*args, **kwargs)
File "C:\Users\kimju\anaconda3\envs\HybrIK\lib\site-packages\torch\onnx\utils.py", line 1421, in _run_symbolic_function
raise symbolic_registry.UnsupportedOperatorError(
torch.onnx.symbolic_registry.UnsupportedOperatorError: Exporting the operator ::svd to ONNX opset version 13 is not supported. Please feel free to request support or submit a pull request on PyTorch GitHub.
```
### Versions
pytorch 1.12.0
| 7 |
5,284 | 81,075 |
[ONNX] Support opset 17 operators
|
module: onnx, good first issue, triaged, OSS contribution wanted, onnx-triaged
|
Tracking issue on the onnx opset 17 support. Contributions welcome.
- [x] Add version 17 as a known version #83287
- [ ] fft
- [ ] ifft
- [ ] fft_fft
- [ ] fft_ifft
- [ ] fft_rfft
- [ ] fft_irfft
- [ ] fft_hfft
- [ ] fft_ihfft
- [ ] fft_fft2
- [ ] fft_ifft2
- [ ] fft_rfft2
- [ ] fft_irfft2
- [ ] fft_hfft2
- [ ] fft_ihfft2
- [ ] fft_fftn
- [ ] fft_ifftn
- [ ] fft_rfftn
- [ ] fft_irfftn
- [ ] fft_hfftn
- [ ] fft_ihfftn
- [ ] fft_fftfreq
- [ ] fft_rfftfreq
- [ ] fft_fftshift
- [ ] fft_ifftshift
- [x] stft #83944
- [ ] istft
- [ ] bartlett_window
- [ ] blackman_window
- [ ] hamming_window
- [ ] hann_window
- [ ] kaiser_window
- [x] LayerNormalization #84293
Closes #80834
| 23 |
5,285 | 81,065 |
[Releng] Improve the tutorials release process
|
module: build, module: ci, triaged
|
### 📚 The doc issue
Copying from [tutorials](https://github.com/pytorch/tutorials/issues/1964) by @b0noI' request.
We need a better way to test tutorials against the RC than we have now. Today we wait until the release to merge the tutorials which is a confusing way of doing it. We don't have a clear way to know against which dependencies the tutorial was tested against.
### Suggest a potential alternative/fix
We should be able to merge to a branch that runs against RCs and publish under pytorch.org/some-link so that we can preview and make sure the tutorials build correctly before the release.
It would also help to have some kind of printenv output that would tell exactly against which binaries for all pytorch components and related dependancies we have build the tutorials.
cc @malfet @seemethere @pytorch/pytorch-dev-infra
| 0 |
5,286 | 81,046 |
three typing inconsistencies on Tensor methods
|
module: typing, triaged
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
* `Tensor.aslist` is typed to return `def tolist(self) -> List: ...` but returns a scalar if Tensor is 0-dim
* `Tensor.unbind` is typed to return `def unbind(self, ...) -> List[Tensor]: ...` but returns a tuple in 1.12
* `Tensor.chunk` is typed to return `def chunk(self, ...) -> List[Tensor]: ...` but returns a tuple in 1.12
* There's probably more like these, including the torch namespace, but these were the breakers I found in my build after upgrading
* Use case for fixing: It breaks mypyc compilation (unless hacked via getattr).
### Versions
Collecting environment information...
PyTorch version: 1.12.0+cu116
Is debug build: False
CUDA used to build PyTorch: 11.6
ROCM used to build PyTorch: N/A
OS: Manjaro Linux (x86_64)
GCC version: (GCC) 12.1.0
Clang version: 13.0.1
CMake version: version 3.23.2
Libc version: glibc-2.35
Python version: 3.10.5 (main, Jun 6 2022, 18:49:26) [GCC 12.1.0] (64-bit runtime)
Python platform: Linux-5.15.50-1-MANJARO-x86_64-with-glibc2.35
Is CUDA available: True
CUDA runtime version: 11.7.64
GPU models and configuration: GPU 0: NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3080
Nvidia driver version: 515.57
cuDNN version: Probably one of the following:
/usr/lib/libcudnn.so.8.4.0
/usr/lib/libcudnn_adv_infer.so.8.4.0
/usr/lib/libcudnn_adv_train.so.8.4.0
/usr/lib/libcudnn_cnn_infer.so.8.4.0
/usr/lib/libcudnn_cnn_train.so.8.4.0
/usr/lib/libcudnn_ops_infer.so.8.4.0
/usr/lib/libcudnn_ops_train.so.8.4.0
HIP runtime version: N/A
MIOpen runtime version: N/A
Is XNNPACK available: True
Versions of relevant libraries:
[pip3] mypy==0.950
[pip3] mypy-extensions==0.4.3
[pip3] numpy==1.22.3
[pip3] torch==1.12.0+cu116
[pip3] torch-lr-finder==0.2.1
[conda] Could not collect
cc @ezyang @malfet @rgommers @xuzhao9 @gramster
| 4 |
5,287 | 80,986 |
[Prims+NVFuser] nvFuser running into "Tensors of type SparseTensorImpl do not have strides"
|
triaged, module: nvfuser
|
After enabling aten2aten decomps:
===== dlrm_backward_0 ======
Generating testing data...
aten2aten decomp: aten.detach.default <function nop_decomposition at 0x7f1c8b87d430>
aten2aten decomp: aten.detach.default <function nop_decomposition at 0x7f1c8b87d430>
aten2aten decomp: aten.detach.default <function nop_decomposition at 0x7f1c8b87d430>
aten2aten decomp: aten.detach.default <function nop_decomposition at 0x7f1c8b87d430>
aten2aten decomp: aten.detach.default <function nop_decomposition at 0x7f1c8b87d430>
aten2aten decomp: aten.detach.default <function nop_decomposition at 0x7f1c8b87d430>
aten2aten decomp: aten.detach.default <function nop_decomposition at 0x7f1c8b87d430>
aten2aten decomp: aten.detach.default <function nop_decomposition at 0x7f1c8b87d430>
aten2aten decomp: aten.detach.default <function nop_decomposition at 0x7f1c8b87d430>
aten2aten decomp: aten.detach.default <function nop_decomposition at 0x7f1c8b87d430>
aten2aten decomp: aten.detach.default <function nop_decomposition at 0x7f1c8b87d430>
aten2aten decomp: aten.detach.default <function nop_decomposition at 0x7f1c8b87d430>
aten2aten decomp: aten.detach.default <function nop_decomposition at 0x7f1c8b87d430>
aten2aten decomp: aten.detach.default <function nop_decomposition at 0x7f1c8b87d430>
aten2aten decomp: aten.threshold_backward.default <function threshold_backward at 0x7f1c8b8dd310>
aten2aten decomp: aten.detach.default <function nop_decomposition at 0x7f1c8b87d430>
aten2aten decomp: aten.detach.default <function nop_decomposition at 0x7f1c8b87d430>
aten2aten decomp: aten.threshold_backward.default <function threshold_backward at 0x7f1c8b8dd310>
aten2aten decomp: aten.detach.default <function nop_decomposition at 0x7f1c8b87d430>
aten2aten decomp: aten.detach.default <function nop_decomposition at 0x7f1c8b87d430>
aten2aten decomp: aten.threshold_backward.default <function threshold_backward at 0x7f1c8b8dd310>
aten2aten decomp: aten.detach.default <function nop_decomposition at 0x7f1c8b87d430>
aten2aten decomp: aten.detach.default <function nop_decomposition at 0x7f1c8b87d430>
aten2aten decomp: aten.threshold_backward.default <function threshold_backward at 0x7f1c8b8dd310>
aten2aten decomp: aten.slice_backward.default <function slice_backward at 0x7f1c8b8e78b0>
aten2aten decomp: aten.transpose.int <function transpose_int at 0x7f1c8b87d5e0>
aten2aten decomp: aten.transpose.int <function transpose_int at 0x7f1c8b87d5e0>
aten2aten decomp: aten.transpose.int <function transpose_int at 0x7f1c8b87d5e0>
**dlrm_backward_0 failed! Tensors of type SparseTensorImpl do not have strides**
| 3 |
5,288 | 80,985 |
Nested tensor: Support Noncontiguous Buffer
|
triaged, topic: not user facing, release notes: nested tensor
|
Current implementation of nested tensor assume the buffer memory to be contiguous. However, some operations can break that assumption:
* reshape
* transpose
* slice
To deal with discontinuity, metadata strides and offsets are introduced in [#79831](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/79831) and [#80981](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/80981).
Let's update existing nested tensor functionalities that assumed continuity to embrace the discontinuity and make use of the new metadata. For example, the way to access unbinded tensors from discontinuous buffer is `buffer.as_strided(size, stride, offset)`
| 1 |
5,289 | 80,982 |
[Prims+NVFuser] aten.to.dtype refs impl causing segfault
|
triaged, module: nvfuser
|
model: pytorch_struct_forward_0
Condition: enable aten2aten decomps
Partitions proposed:
partition 0 ['to_dtype_45', 'exp_default_2', 'sum_dim_int_list_2', 'log_default_2', 'sub_tensor_5', 'sub_tensor_4']
partition 2 ['relu_default_7', 'to_dtype_43', 'add_tensor_12', 'mul_tensor_19', 'to_dtype_40', 'mul_tensor_18', 'add_tensor_13']
partition 4 ['to_dtype_39', 'relu_default_6', 'to_dtype_36', 'add_tensor_11', 'mul_tensor_16', 'to_dtype_41', 'mul_tensor_17']
partition 6 ['add_tensor_10', 'to_dtype_35', 'relu_default_5', 'to_dtype_37', 'mul_tensor_15', 'to_dtype_32', 'mul_tensor_14', 'add_tensor_9']
partition 8 ['to_dtype_33', 'mul_tensor_13', 'add_tensor_8', 'to_dtype_31', 'to_dtype_28', 'relu_default_4', 'mul_tensor_12']
partition 10 ['to_dtype_27', 'add_tensor_7', 'mul_tensor_11', 'mul_tensor_10', 'to_dtype_29', 'to_dtype_24']
partition 13 ['log_default_1', 'sum_dim_int_list_1', 'exp_default_1', 'sub_tensor_2', 'to_dtype_23', 'sub_tensor_3']
partition 15 ['sub_tensor_1', 'log_default', 'sum_dim_int_list', 'exp_default', 'sub_tensor', 'to_dtype_21']
partition 17 ['to_dtype_16', 'add_tensor_6', 'relu_default_3', 'to_dtype_19', 'add_tensor_5', 'mul_tensor_9', 'mul_tensor_8']
partition 19 ['mul_tensor_6', 'to_dtype_17', 'mul_tensor_7', 'add_tensor_4', 'to_dtype_12', 'to_dtype_15', 'relu_default_2']
partition 21 ['mul_tensor_5', 'to_dtype_13', 'to_dtype_8', 'add_tensor_2', 'to_dtype_11', 'relu_default_1', 'add_tensor_3', 'mul_tensor_4']
partition 23 ['mul_tensor_2', 'to_dtype_9', 'mul_tensor_3', 'add_tensor_1', 'to_dtype_7', 'to_dtype_4', 'relu_default']
partition 25 ['mul_tensor', 'mul_tensor_1', 'to_dtype', 'add_tensor', 'to_dtype_3', 'to_dtype_5']
**srun: error: a100-st-p4d24xlarge-6: task 0: Segmentation fault (core dumped)**
Workaround:
Remove "torch.ops.aten.to.dtype" from operator_support list.
My guess:
Following ref implementation has some issue.
def aten_to_dtype(self, dtype: torch.dtype, **kwargs):
if len(kwargs) > 0 or not dtype:
raise RuntimeError("No support for other to.dtype() formats other than to.dtype(self, dtype)")
return torch._prims.convert_element_type(self, dtype)
| 6 |
5,290 | 80,973 |
[ONNX] Tool to find mismatch in exported ONNX model
|
module: onnx, triaged, onnx-triaged, onnx-needs-info
|
### 🚀 The feature, motivation and pitch
Output mismatch between exported ONNX and PyTorch models has been a hard to debug problem. Developers and data scientists usually encounter this problem in the following scenarios.
* A new kind of model exports successfully to ONNX, but outputs don’t match.
* An ONNX model that works correctly on a given set of inputs (usually the ones it was originally exported with), but outputs don’t match for other set of inputs.
* An ONNX model that matched results previously, but due to package version changes the results start to differ.
So far there hasn’t been any effective/automatic tools to help with investigation. Developers had to manually compare results between subgraph of ONNX and PyTorch.
Usually, the root cause of mismatch problem is not hard to fix, after it was discovered. It could be any one of the following scenarios:
* The operator use case is new and not exported correctly.
* Dynamic value (sometimes could be configuration or hyperparameter) exported as constant.
* Dynamic graph (controlflow) exported as static graph.
* Discrepancies between PyTorch and ONNX operator spec/implementation.
## Proposal
Proposing a new API under `torch.onnx` module to try export the model and automatically find the first operator/node that produces mismatch results.
## Goals
* To find the first operator/node in ONNX model, and corresponding line in PyTorch that starts the mismatch.
* The first version may support only tracing based export.
## Non-Goals
* This tool does not fix the mismatch.
* This tool requires successful export as pre-condition: it does not fix and cannot work under export failures.
### Alternatives
_No response_
### Additional context
_No response_
| 4 |
5,291 | 80,966 |
[Prims+NVFuser] Aten2Aten decomp hurting performance
|
triaged, module: nvfuser, module: primTorch
|
Following aten2aten decomps are not latter fused by nvFuser, thus hurting the performance.
- [ ] aten.native_layer_norm_backward.default
| Module Name | Eager Time (ms) | WithAtenDecomp Time (ms) | nvFuser Time (ms)
-- | -- | -- | -- | --
with | hf_T5_backward_0 | 159.1049759 | 3191.585663 | 3186.037783
without | hf_T5_backward_0 | 183.5727645 | 170.5960212 | 165.7386031
with | hf_T5_backward_8 | 237.4839457 | 3832.827996 | 3867.255308
without | hf_T5_backward_8 | 256.4443965 | 256.3290102 | 249.5397562
- [ ] aten.embedding_dense_backward.default
| Module Name | Eager Time (ms) | AtenDecomp Time | nvFuser Time (ms)
-- | -- | -- | -- | --
with | hf_DistilBert_backward_0 | 13.35794386 | 1523.864605 | 31.73270822
without | hf_DistilBert_backward_0 | 13.90568446 | 13.46321963 | 13.67696188
cc @ezyang @mruberry @ngimel
| 7 |
5,292 | 80,954 |
ExpandedWeights sometimes fail silently and doesn't compute .grad_sample attribute
|
module: nn, triaged
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
Normally `call_for_per_sample_grads` detects inputs where it can't compute per sample gradients and throws user-friendly exception with the explanation.
However, in some scenarios (see below) it just skips certain parameters and doesn't do anything with them. As such, after the backward pass some parameters would have only `.grad_sample` attribute, and some - only `.grad` attribute. All this happens silently to the user and the user would only notice the issue when they try to access `.grad_sample` attribute.
I haven't done a detailed investigation as to when this occurs, but it might have something to do with recurrent nets. Below is the example using opacus custom-written RNN implementation.
```python
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from torch.nn.utils._per_sample_grad import call_for_per_sample_grads
from opacus.layers import DPRNN
N=1
T=1
D=4
H=8
num_layers=1
bias=False
batch_first=True
bidirectional=False
using_packed_sequences=False
packed_sequences_sorted=False
rnn = DPRNN(
D,
H,
num_layers=num_layers,
batch_first=batch_first,
bias=bias,
bidirectional=bidirectional,
)
x = torch.randn([N, T, D])
# out, _ = rnn(x)
out, _ = call_for_per_sample_grads(rnn, x.shape[0], x)
out.sum().backward()
rnn.l0.ih.weight.grad_sample
```
Error
```
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
AttributeError Traceback (most recent call last)
/var/folders/_r/hzffvgfd23sc3w0gr577_qmc0000gn/T/ipykernel_71302/2553106598.py in <module>
26 out.sum().backward()
27
---> 28 rnn.l0.ih.weight.grad_sample
AttributeError: 'Parameter' object has no attribute 'grad_sample'
```
### Versions
PyTorch version: 1.12.0
Is debug build: False
CUDA used to build PyTorch: None
ROCM used to build PyTorch: N/A
OS: macOS 12.4 (x86_64)
GCC version: Could not collect
Clang version: 12.0.5 (clang-1205.0.22.9)
CMake version: Could not collect
Libc version: N/A
Python version: 3.7.5 (default, Oct 22 2019, 10:35:10) [Clang 10.0.1 (clang-1001.0.46.4)] (64-bit runtime)
Python platform: Darwin-21.5.0-x86_64-i386-64bit
Is CUDA available: False
CUDA runtime version: No CUDA
GPU models and configuration: No CUDA
Nvidia driver version: No CUDA
cuDNN version: No CUDA
HIP runtime version: N/A
MIOpen runtime version: N/A
Is XNNPACK available: True
Versions of relevant libraries:
[pip3] mypy==0.910
[pip3] mypy-extensions==0.4.3
[pip3] numpy==1.21.4
[pip3] pytorch-lightning==1.5.3
[pip3] torch==1.12.0
[pip3] torchaudio==0.12.0
[pip3] torchmetrics==0.6.0
[pip3] torchvision==0.13.0
[conda] Could not collect
cc @albanD @mruberry @jbschlosser @walterddr @kshitij12345 @saketh-are
| 2 |
5,293 | 80,951 |
ExpandedWeights can't handle modules with tied weights
|
module: nn, triaged
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
`call_for_per_sample_grads` throws a (seemingly irrelevant) error when processing a module with tied parameters (i.e. one parameter tensor is shared between two layers)
See this [forum thread](https://discuss.pytorch.org/t/how-to-share-weights-between-two-layers/55541) for an example where such a technique can be useful
Code:
```python
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from torch.nn.utils._per_sample_grad import call_for_per_sample_grads
class SampleTiedWeights(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.emb = nn.Embedding(100, 8)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(8, 100)
w = torch.empty(100, 8)
nn.init.uniform_(w, -100, 100)
p = nn.Parameter(w)
self.emb.weight = p
self.fc2.weight = p
def forward(self, x):
x = x.unsqueeze(1)
x = self.emb(x)
x = self.fc2(x)
x = x.squeeze(1)
return x
m = SampleTiedWeights()
x = torch.randint(low=0, high=100, size=(512,))
out = call_for_per_sample_grads(m, x.shape[0], x)
out.sum().backward()
```
Error:
```
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
RuntimeError Traceback (most recent call last)
/var/folders/_r/hzffvgfd23sc3w0gr577_qmc0000gn/T/ipykernel_71302/2108605639.py in <module>
2 x = torch.randint(low=0, high=100, size=(512,))
3 out = call_for_per_sample_grads(m, x.shape[0], x)
----> 4 out.sum().backward()
~/Documents/opacus/venv/lib/python3.7/site-packages/torch/_tensor.py in backward(self, gradient, retain_graph, create_graph, inputs)
394 create_graph=create_graph,
395 inputs=inputs)
--> 396 torch.autograd.backward(self, gradient, retain_graph, create_graph, inputs=inputs)
397
398 def register_hook(self, hook):
~/Documents/opacus/venv/lib/python3.7/site-packages/torch/autograd/__init__.py in backward(tensors, grad_tensors, retain_graph, create_graph, grad_variables, inputs)
173 Variable._execution_engine.run_backward( # Calls into the C++ engine to run the backward pass
174 tensors, grad_tensors_, retain_graph, create_graph, inputs,
--> 175 allow_unreachable=True, accumulate_grad=True) # Calls into the C++ engine to run the backward pass
176
177 def grad(
~/Documents/opacus/venv/lib/python3.7/site-packages/torch/autograd/function.py in apply(self, *args)
251 "of them.")
252 user_fn = vjp_fn if vjp_fn is not Function.vjp else backward_fn
--> 253 return user_fn(self, *args)
254
255 def apply_jvp(self, *args):
~/Documents/opacus/venv/lib/python3.7/site-packages/torch/nn/utils/_expanded_weights/linear_expanded_weights.py in backward(ctx, grad_output)
29
30 if input.requires_grad:
---> 31 results.append(grad_output.matmul(unpack_expanded_weight_or_tensor(weight)))
32 else:
33 results.append(None)
~/Documents/opacus/venv/lib/python3.7/site-packages/torch/nn/utils/_expanded_weights/expanded_weights_utils.py in unpack_expanded_weight_or_tensor(maybe_expanded_weight, func)
73 return func(maybe_expanded_weight)
74 elif isinstance(maybe_expanded_weight, torch.Tensor):
---> 75 raise RuntimeError("ExpandedWeights currently does not support a mixture of ExpandedWeight parameters "
76 "and normal Parameters. Please file and issue with pytorch/pytorch")
77
RuntimeError: ExpandedWeights currently does not support a mixture of ExpandedWeight parameters and normal Parameters. Please file and issue with pytorch/pytorch
```
### Versions
PyTorch version: 1.12.0
Is debug build: False
CUDA used to build PyTorch: None
ROCM used to build PyTorch: N/A
OS: macOS 12.4 (x86_64)
GCC version: Could not collect
Clang version: 12.0.5 (clang-1205.0.22.9)
CMake version: Could not collect
Libc version: N/A
Python version: 3.7.5 (default, Oct 22 2019, 10:35:10) [Clang 10.0.1 (clang-1001.0.46.4)] (64-bit runtime)
Python platform: Darwin-21.5.0-x86_64-i386-64bit
Is CUDA available: False
CUDA runtime version: No CUDA
GPU models and configuration: No CUDA
Nvidia driver version: No CUDA
cuDNN version: No CUDA
HIP runtime version: N/A
MIOpen runtime version: N/A
Is XNNPACK available: True
Versions of relevant libraries:
[pip3] mypy==0.910
[pip3] mypy-extensions==0.4.3
[pip3] numpy==1.21.4
[pip3] pytorch-lightning==1.5.3
[pip3] torch==1.12.0
[pip3] torchaudio==0.12.0
[pip3] torchmetrics==0.6.0
[pip3] torchvision==0.13.0
[conda] Could not collect
cc @albanD @mruberry @jbschlosser @walterddr @kshitij12345 @saketh-are
| 2 |
5,294 | 80,946 |
torch.nn.functional.linear fails for multi-dimensional bias from torch 1.12
|
module: nn, triaged, module: regression
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
~As [docs](https://pytorch.org/docs/1.12/generated/torch.nn.functional.linear.html?highlight=linear#torch.nn.functional.linear) explains, `torch.nn.functional.linear` supports inputs of~
```
input: (*, in_features)
weight: (out_features, in_features)
bias: (*, out_features)
```
(UPD 9 July 2022: This is a never-documented behaviour https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/80946#issuecomment-1178272323)
, but torch 1.12 seems to raise error for multi-dimensional inputs.
```python
>>> import torch.nn.functional as F
>>> import torch
>>> F.linear(torch.randn(2,3,5),torch.randn(7,5),torch.randn(2,3,7))
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
RuntimeError: expand(torch.FloatTensor{[2, 3, 7]}, size=[6, 7]): the number of sizes provided (2) must be greater or equal to the number of dimensions in the tensor (3)
```
With torch 1.11,
```python
>>> import torch.nn.functional as F
>>> import torch
>>> F.linear(torch.randn(2,3,5),torch.randn(7,5),torch.randn(2,3,7))
tensor([[[ 1.5270e+00, -1.6008e+00, 1.0397e+00, -1.7440e-01, -1.2764e+00,
1.1950e-01, -1.8383e+00],
[-3.3737e+00, 1.9518e+00, 8.4368e-01, -5.5560e+00, 6.5014e-01,
-8.5247e-01, -3.3299e+00],
[ 5.3961e-01, 1.1424e+00, 9.3576e-01, 3.1827e-01, -6.9256e-01,
1.6097e+00, 7.8738e-01]],
[[-6.2245e-01, -2.4926e+00, -1.8944e+00, -1.0425e+00, 2.6903e+00,
-5.9798e+00, -4.5269e-03],
[-6.0497e-01, -2.6881e+00, -1.4605e+00, -1.7330e+00, 1.9412e-01,
-3.6541e+00, -1.1137e+00],
[ 2.1674e+00, -5.5175e+00, -4.5325e+00, 5.0340e+00, 5.5341e-01,
-4.4188e+00, 5.1751e-01]]])
```
### Versions
```
Collecting environment information...
PyTorch version: N/A
Is debug build: N/A
CUDA used to build PyTorch: N/A
ROCM used to build PyTorch: N/A
OS: Ubuntu 20.04.4 LTS (x86_64)
GCC version: (Ubuntu 10.3.0-1ubuntu1~20.04) 10.3.0
Clang version: Could not collect
CMake version: version 3.22.2
Libc version: glibc-2.31
Python version: 3.8.10 (default, Mar 15 2022, 12:22:08) [GCC 9.4.0] (64-bit runtime)
Python platform: Linux-5.4.0-100-generic-x86_64-with-glibc2.2.5
Is CUDA available: N/A
CUDA runtime version: Could not collect
GPU models and configuration:
GPU 0: Tesla V100-SXM2-16GB
GPU 1: Tesla V100-SXM2-16GB
GPU 2: Tesla V100-SXM2-16GB
GPU 3: Tesla V100-SXM2-16GB
GPU 4: Tesla V100-SXM2-16GB
GPU 5: Tesla V100-SXM2-16GB
GPU 6: Tesla V100-SXM2-16GB
GPU 7: Tesla V100-SXM2-16GB
Nvidia driver version: 470.103.01
cuDNN version: Probably one of the following:
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn.so.8.0.5
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_adv_infer.so.8.0.5
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_adv_train.so.8.0.5
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_cnn_infer.so.8.0.5
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_cnn_train.so.8.0.5
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_ops_infer.so.8.0.5
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_ops_train.so.8.0.5
HIP runtime version: N/A
MIOpen runtime version: N/A
Is XNNPACK available: N/A
Versions of relevant libraries:
[pip3] numpy==1.18.4
[pip3] torch==1.12.0
[pip3] torchvision==0.13.0
[conda] Could not collect
```
cc @ezyang @gchanan @zou3519 @albanD @mruberry @jbschlosser @walterddr @kshitij12345 @saketh-are
| 6 |
5,295 | 80,942 |
[LTC] OOM on mnist example
|
triaged, module: lazy
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
OOM on the example mnist.py while enabling CUDA device, the error logs is as the following. I just use `torch.cuda.memory_stats` to print the allocated CUDA memory, and we can see the memory is increasing:
``` text
Train Epoch: 1 [0/60000 (0%)] Loss: 2.305605
allocated_bytes.all.current: 33812992
Train Epoch: 1 [640/60000 (1%)] Loss: 1.253851
allocated_bytes.all.current: 180380160
....
Train Epoch: 2 [0/60000 (0%)] Loss: 0.034653
allocated_bytes.all.current: 13733059072
Train Epoch: 2 [640/60000 (1%)] Loss: 0.074930
allocated_bytes.all.current: 13879101952
Train Epoch: 2 [1280/60000 (2%)] Loss: 0.003717
allocated_bytes.all.current: 14025144832
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "test_mnist.py", line 86, in <module>
train(log_interval, model, device, train_loader, optimizer, epoch)
File "test_mnist.py", line 49, in train
torch._lazy.mark_step()
File "/workspace/BladeDISC/venv-py38/lib/python3.8/site-packages/torch/_lazy/__init__.py", line 12, in mark_step
torch._C._lazy._mark_step(device, [], wait=wait)
RuntimeError: The following operation failed in the TorchScript interpreter.
Traceback of TorchScript (most recent call last):
RuntimeError: CUDA out of memory. Tried to allocate 20.00 MiB (GPU 0; 14.76 GiB total capacity; 13.18 GiB already allocated; 9.75 MiB free; 13.66 GiB reserved in total by PyTorch) If reserved memory is >> allocated memory try setting max_split_size_mb to avoid fragmentation. See documentation for Memory Management and PYTORCH_CUDA_ALLOC_CONF
```
## Reproduce Steps
``` bash
git clone git@github.com:pytorch/pytorch.git
LTC_TS_CUDA=1 python pytorch/torch/csrc/lazy/test_mnist.py
```
### Versions
Collecting environment information...
PyTorch version: 1.12.0+cu113
Is debug build: False
CUDA used to build PyTorch: 11.3
ROCM used to build PyTorch: N/A
OS: Ubuntu 20.04.4 LTS (x86_64)
GCC version: (Ubuntu 9.4.0-1ubuntu1~20.04.1) 9.4.0
Clang version: Could not collect
CMake version: version 3.20.0
Libc version: glibc-2.31
Python version: 3.8.10 (default, Mar 15 2022, 12:22:08) [GCC 9.4.0] (64-bit runtime)
Python platform: Linux-4.15.0-162-generic-x86_64-with-glibc2.29
Is CUDA available: True
CUDA runtime version: 11.3.109
GPU models and configuration:
GPU 0: Tesla T4
GPU 1: Tesla T4
Nvidia driver version: 460.91.03
cuDNN version: Probably one of the following:
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn.so.8.2.0
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_adv_infer.so.8.2.0
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_adv_train.so.8.2.0
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_cnn_infer.so.8.2.0
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_cnn_train.so.8.2.0
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_ops_infer.so.8.2.0
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_ops_train.so.8.2.0
/usr/local/cuda-11.3/targets/x86_64-linux/lib/libcudnn.so.8
/usr/local/cuda-11.3/targets/x86_64-linux/lib/libcudnn_adv_infer.so.8
/usr/local/cuda-11.3/targets/x86_64-linux/lib/libcudnn_adv_train.so.8
/usr/local/cuda-11.3/targets/x86_64-linux/lib/libcudnn_cnn_infer.so.8
/usr/local/cuda-11.3/targets/x86_64-linux/lib/libcudnn_cnn_train.so.8
/usr/local/cuda-11.3/targets/x86_64-linux/lib/libcudnn_ops_infer.so.8
/usr/local/cuda-11.3/targets/x86_64-linux/lib/libcudnn_ops_train.so.8
HIP runtime version: N/A
MIOpen runtime version: N/A
Is XNNPACK available: True
Versions of relevant libraries:
[pip3] numpy==1.23.0
[pip3] torch==1.12.0+cu113
[conda] Could not collect
cc @wconstab
| 19 |
5,296 | 80,940 |
Wrong example of sliced computation in doc page Numerical Accuracy
|
module: docs, triaged, module: numerical-reproducibility
|
### 📚 The doc issue
This issue is related to the page [Numerical Accuracy](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/notes/numerical_accuracy.html#batched-computations-or-slice-computations)
(Accessed July 6 2022)
(The source of the page in the repository is [here](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/blob/master/docs/source/notes/numerical_accuracy.rst#batched-computations-or-slice-computations). But I'm not sure which commit).
Quote from the page:
> let `A` be a 2-dimentional tensor. `A.sum(-1)[0]` is not guaranteed to be bitwise equal to `A[:,0].sum()`.
Viewing `A` as a matrix, notice that `A.sum(-1)[0]` is the sum of the first row, whereas `A[:,0].sum()` is the sum of the first column. These are trivially different, and this difference is not related to numerical accuracy.
See for example:
```python
import torch
A = torch.ones(4,5)
x = A.sum(-1)[0] # equals 5
y = A[:,0].sum() # equals 4
```
I suspect that the intention in this example was either to use `A.sum(0)[0]` for the first calculation or `A[0].sum()` for the second.
### Suggest a potential alternative/fix
I believe that this sentence:
> `A.sum(-1)[0]` is not guaranteed to be bitwise equal to `A[:,0].sum()`.
should be replaced with one of the following:
> `A.sum(0)[0]` is not guaranteed to be bitwise equal to `A[:,0].sum()`.
> `A.sum(-1)[0]` is not guaranteed to be bitwise equal to `A[0].sum()`.
(which one? depends on the numerical accuracy issue here...)
cc @svekars @holly1238
| 2 |
5,297 | 80,939 |
[jit] script backward wrong gradient
|
oncall: jit
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
Consider the following simple pnorm implementation
```py
def pnorm(x: torch.Tensor, p: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
return x.abs().pow(p).sum().pow(1 / p)
script_pnorm = torch.jit.script(pnorm)
```
When `x` contains any entry of *zero*, gradient of `p` will become `NaN` for script version, but works normally (not `NaN`) for eager version.
See this gist for full example.
https://gist.github.com/SsnL/07f58873766a2e8456741b1281e04c24
### Versions
```
PyTorch version: 1.11.0+cu113
Is debug build: False
CUDA used to build PyTorch: 11.3
ROCM used to build PyTorch: N/A
OS: Ubuntu 18.04.5 LTS (x86_64)
GCC version: (Ubuntu 7.5.0-3ubuntu1~18.04) 7.5.0
Clang version: 6.0.0-1ubuntu2 (tags/RELEASE_600/final)
CMake version: version 3.22.5
Libc version: glibc-2.26
Python version: 3.7.13 (default, Apr 24 2022, 01:04:09) [GCC 7.5.0] (64-bit runtime)
Python platform: Linux-5.4.188+-x86_64-with-Ubuntu-18.04-bionic
Is CUDA available: False
CUDA runtime version: 11.1.105
GPU models and configuration: Could not collect
Nvidia driver version: Could not collect
cuDNN version: Probably one of the following:
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn.so.7.6.5
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn.so.8.0.5
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_adv_infer.so.8.0.5
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_adv_train.so.8.0.5
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_cnn_infer.so.8.0.5
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_cnn_train.so.8.0.5
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_ops_infer.so.8.0.5
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_ops_train.so.8.0.5
HIP runtime version: N/A
MIOpen runtime version: N/A
Is XNNPACK available: True
Versions of relevant libraries:
[pip3] numpy==1.21.6
[pip3] torch==1.11.0+cu113
[pip3] torchaudio==0.11.0+cu113
[pip3] torchsummary==1.5.1
[pip3] torchtext==0.12.0
[pip3] torchvision==0.12.0+cu113
[conda] Could not collect
```
| 0 |
5,298 | 80,932 |
Position embedding aware global circular convolution
|
feature, module: nn, triaged
|
### 🚀 The feature, motivation and pitch
Recently, we propose a new basic operation position embedding aware global circular convolution (GCC). Differing from previous convolution operations, the proposed GCC has global receptive field. Experimental results show that GCC uniformly
improves performance of various typical models.
This work has been accpted by ECCV 2022, we hope the proposed GCC can be used by other researchers. Someone may refer to https://arxiv.org/abs/2203.03952 to find more details.
### Alternatives
We will prepare a CUDA optimized version GCC following tutorial in https://pytorch.org/tutorials/advanced/cpp_extension.html.
We also want to propose a pull request to merge our code into Pytorch. Will such a pull request be accpted ? If it is acceptable, is there anyone can provide us a demo of proposing this kind of pull request to Pytorch?
### Additional context
_No response_
cc @albanD @mruberry @jbschlosser @walterddr @kshitij12345 @saketh-are
| 1 |
5,299 | 80,929 |
Interpolation artifacts when using nn.interpolate, trilinear mode for 3D label images
|
module: nn, triaged, module: interpolation
|
### 📚 The doc issue
It seems a functional bug. I have use nn.interpolate trilinear to umsample a 2 classes(and background) 3D image. The function tend to interpolate a "1" between label 2 and the background using trilinear. I could be solved by transfer the label image into one-hot format and than resample. Or i can also use nearest mode of nn.interpolate, its ok with label image.
It seems trilinear is not a suitable method for label image. If i use trilinear to upsample the training images, and use nearest to upsample the labels. If there could be some errors between images and labels because of the different upsample method?
### Suggest a potential alternative/fix
_No response_
cc @albanD @mruberry @jbschlosser @walterddr @kshitij12345 @saketh-are
| 5 |
5,300 | 80,921 |
[primTorch] `|` operator does not work with FakeTensor in _refs
|
feature, triaged, module: meta tensors, module: primTorch
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
Change this line:
https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/blob/9ca561cbd4ab2bee3279b998e3ea4d1f302ced7e/torch/_refs/__init__.py#L1187
to
```python
a | b
```
And you will see some failures in `nan_to_num`. Example failure:
```
======================================================================
ERROR: test_python_ref_meta__refs_nan_to_num_cpu_int16 (__main__.TestCommonCPU)
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "/home/gaoxiang/.local/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/testing/_internal/common_device_type.py", line 377, in instantiated_test
result = test(self, **param_kwargs)
File "/home/gaoxiang/.local/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/testing/_internal/common_device_type.py", line 813, in test_wrapper
return test(*args, **kwargs)
File "/home/gaoxiang/.local/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/testing/_internal/common_device_type.py", line 1006, in only_fn
return fn(self, *args, **kwargs)
File "/home/gaoxiang/pytorch-prims/test/test_ops.py", line 380, in test_python_ref_meta
meta_result = op(meta_sample.input, *meta_sample.args, **meta_sample.kwargs)
File "/home/gaoxiang/.local/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/testing/_internal/common_methods_invocations.py", line 952, in __call__
return self.op(*args, **kwargs)
File "/home/gaoxiang/.local/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/_prims/wrappers.py", line 195, in _fn
result = fn(*args, **kwargs)
File "/home/gaoxiang/.local/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/_prims/wrappers.py", line 114, in _fn
result = fn(**bound.arguments)
File "/home/gaoxiang/.local/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/_refs/__init__.py", line 609, in nan_to_num
is_neginf = bitwise_and(isinf(a), is_neg)
File "/home/gaoxiang/.local/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/_prims/wrappers.py", line 195, in _fn
result = fn(*args, **kwargs)
File "/home/gaoxiang/.local/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/_prims/wrappers.py", line 265, in _fn
return fn(*args, **kwargs)
File "/home/gaoxiang/.local/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/_prims/wrappers.py", line 114, in _fn
result = fn(**bound.arguments)
File "/home/gaoxiang/.local/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/_refs/__init__.py", line 348, in _ref
return prim(a)
File "/home/gaoxiang/.local/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/_refs/__init__.py", line 506, in isinf
return logical_not(logical_or(isnan(a), isfinite(a)))
File "/home/gaoxiang/.local/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/_prims/wrappers.py", line 195, in _fn
result = fn(*args, **kwargs)
File "/home/gaoxiang/.local/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/_prims/wrappers.py", line 114, in _fn
result = fn(**bound.arguments)
File "/home/gaoxiang/.local/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/_refs/__init__.py", line 754, in _ref
return prim(a, b)
File "/home/gaoxiang/.local/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/_refs/__init__.py", line 1187, in _logical_or
return a | b
File "/home/gaoxiang/.local/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/utils/_python_dispatch.py", line 74, in wrapped
return f(self, *args, **kwargs)
File "/home/gaoxiang/.local/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/_subclasses/fake_tensor.py", line 482, in __torch_dispatch__
raise Exception(
Exception: Invoking operators with non-Fake Tensor inputs in FakeTensorMode is not yet supported. Please convert all Tensors to FakeTensors first. Found in aten.bitwise_or.Tensor
```
### Versions
```
Collecting environment information...
PyTorch version: 1.13.0a0+gitd8d8a48
Is debug build: True
CUDA used to build PyTorch: 11.7
ROCM used to build PyTorch: N/A
OS: Arch Linux (x86_64)
GCC version: (GCC) 12.1.0
Clang version: 14.0.6
CMake version: version 3.23.2
Libc version: glibc-2.35
Python version: 3.10.5 (main, Jun 6 2022, 18:49:26) [GCC 12.1.0] (64-bit runtime)
Python platform: Linux-5.18.9-arch1-1-x86_64-with-glibc2.35
Is CUDA available: True
CUDA runtime version: 11.7.64
GPU models and configuration:
GPU 0: NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3090
GPU 1: NVIDIA GeForce RTX 2080 Ti
Nvidia driver version: 515.57
cuDNN version: Probably one of the following:
/usr/lib/libcudnn.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/libcudnn_adv_infer.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/libcudnn_adv_train.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/libcudnn_cnn_infer.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/libcudnn_cnn_train.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/libcudnn_ops_infer.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/libcudnn_ops_train.so.8.4.1
HIP runtime version: N/A
MIOpen runtime version: N/A
Is XNNPACK available: True
Versions of relevant libraries:
[pip3] numpy==1.22.3
[pip3] torch==1.13.0a0+gitd8d8a48
[pip3] torch-ucc==1.0.0
[pip3] torchani==2.2
[pip3] torchvision==0.2.2.post3
[conda] Could not collect
```
cc @ezyang @mruberry @ngimel
| 0 |
Subsets and Splits
No community queries yet
The top public SQL queries from the community will appear here once available.