Serial Number
int64 1
6k
| Issue Number
int64 75.6k
112k
| Title
stringlengths 3
357
| Labels
stringlengths 3
241
⌀ | Body
stringlengths 9
74.5k
⌀ | Comments
int64 0
867
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
4,201 | 97,248 |
A more systematic API for resolving the "vmap-incompatible in-place operation" error
|
triaged, actionable, needs design, module: functorch
|
# Motivation
Users may run into "vmap-incompatible in-place operation" error when creating a Tensor via a factory function and in-placing into it. For example:
```py
def f(x):
y = torch.empty(x.shape)
y.copy_(x)
return y
x = torch.randn(2, 3)
vmap(f)(x)
```
In this example, inside `f`: `y` is a Tensor of shape [3], but we're trying to copy a BatchedTensor (which has underlying shape [2, 3]) into `y`.
Our general advice for this situation is to use `Tensor.new_empty`. This ends up creating a `y` that is a BatchedTensor:
```py
def f(x):
y = x.new_empty(x.shape)
y.copy_(x)
return y
x = torch.randn(2, 3)
vmap(f)(x)
```
Sometimes, it is not completely obvious to the user what tensor to call new_empty on. Take the following code as example:
```py
def f(x, y)
z = torch.empty(x.shape)
z.copy_(x)
z.copy_(y)
return z
# Case 1
vmap(f, (0, None))(torch.randn(2, 3), torch.randn(3))
# Case 2
vmap(f, (None, 0))(torch.randn(3), torch.randn(2, 3))
```
The way to rewrite f to support both of the above cases is a bit silly:
```py
def f(x, y)
z = torch.cat([x, y]).new_empty(x.shape)
z.copy_(x)
z.copy_(y)
return z
```
# Pitch
One possible API is that we provide an API to construct a BatchedTensor inside a function being vmapped. There are a couple of ideas on how it could look like:
```py
def f(x, y)
# Option 1
z = torch.empty(x.shape)
z = torch.lift(z)
# Option 2
z = torch.lifted_empty(x.shape)
# Option 3
z = torch.empty(x.shape, lift=True)
# Option 4
z = torch.empty(x.shape)
z = torch.lift_as(z, (x, y)) # Grants z the properties of x and y
z.copy_(x)
z.copy_(y)
return z
```
Other ideas welcome.
cc @Chillee @samdow @soumith @kshitij12345 @janeyx99
| 1 |
4,202 | 89,065 |
Improve clarity of meaning of `torch.jit.trace`'s `example_inputs`
|
oncall: jit
|
### 📚 The doc issue
The document in question is the [torch.jit.trace documentation](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.jit.trace.html#torch.jit.trace).
Specifically, it describes the `example_inputs` parameter as follows:
> **example_inputs** ([tuple](https://docs.python.org/3/library/stdtypes.html#tuple) or [torch.Tensor](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/tensors.html#torch.Tensor)) – A tuple of example inputs that will be passed to the function while tracing. The resulting trace can be run with inputs of different types and shapes assuming the traced operations support those types and shapes. *example_inputs* may also be a single Tensor in which case it is automatically wrapped in a tuple.
This may be perfectly clear to most people, but for several days I thought that the plural "example_input**s**" meant that I could provide a tuple of a bunch of different inputs of various shapes as a tuple, and they'd all be traced. That doesn't seem to be the case; at least, in my experience, all of the inputs are passed to my `forward` function at once. What I believe this actually means, in reality, is that if your `forward` function requires multiple inputs, you can pass those inputs as a tuple.
### Suggest a potential alternative/fix
Something like this, in which I've tried to make it more clear that this is really just one example input, but it can be a tuple if the `forward` function uses multiple input values.
> **example_inputs** ([tuple](https://docs.python.org/3/library/stdtypes.html#tuple) or [torch.Tensor](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/tensors.html#torch.Tensor)) – An example input that will be passed to the function while tracing. If the `forward` function requires multiple inputs, then this example input should be a tuple of those inputs. The resulting trace can be run with inputs of different types and shapes assuming the traced operations support those types and shapes. *example_inputs* may also be a single Tensor in which case it is automatically wrapped in a tuple.
If that is correct, then also it's a little confusing that this argument is called `example_inputs`, since it's more like "`example_input`, potentially with multiple parts", but for historical reasons I don't see that changing.
cc @EikanWang @jgong5 @wenzhe-nrv @sanchitintel
| 0 |
4,203 | 89,064 |
UserWarning: The TorchScript type system doesn't support instance-level annotations on empty non-base types in `__init__`.
|
oncall: jit
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
This small script produces a warning, but the warning is not very actionable. Is there something we can do to make this not warn or tell me what to do to fix the warning?
```python
import torch
from torch.fx.experimental.proxy_tensor import make_fx
from functorch._src.compile_utils import strip_overloads
def f(x):
return x
fx = make_fx(f)(torch.ones(2, 3))
strip_overloads(fx)
torch.jit.script(fx)
```
Output:
```
/usr/local/google/home/silvasean/.local/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/jit/_check.py:181: UserWarning: The TorchScript type system doesn't support instance-level annotations on empty non-base types in `__init__`. Instead, either 1) use a type annotation in the class body, or 2) wrap the type in `torch.jit.Attribute`.
warnings.warn("The TorchScript type system doesn't support "
```
### Versions
Collecting environment information...
PyTorch version: 1.14.0.dev20221114+cpu
Is debug build: False
CUDA used to build PyTorch: None
ROCM used to build PyTorch: N/A
OS: Debian GNU/Linux rodete (x86_64)
GCC version: (Debian 12.2.0-3) 12.2.0
Clang version: 14.0.6-2
CMake version: version 3.24.3
Libc version: glibc-2.35
Python version: 3.10.7 (main, Sep 8 2022, 14:34:29) [GCC 12.2.0] (64-bit runtime)
Python platform: Linux-5.18.16-1rodete4-amd64-x86_64-with-glibc2.35
Is CUDA available: False
CUDA runtime version: No CUDA
GPU models and configuration: No CUDA
Nvidia driver version: No CUDA
cuDNN version: No CUDA
HIP runtime version: N/A
MIOpen runtime version: N/A
Is XNNPACK available: True
Versions of relevant libraries:
[pip3] numpy==1.23.4
[pip3] torch==1.14.0.dev20221114+cpu
[pip3] torchvision==0.15.0.dev20221114+cpu
[conda] Could not collect
cc @EikanWang @jgong5 @wenzhe-nrv @sanchitintel
| 3 |
4,204 | 89,060 |
Extend test_proxy_tensor tests to support ops test non floating point types
|
module: tests, triaged, module: ProxyTensor
|
### 🚀 The feature, motivation and pitch
Currently, proxy tensor tests are only run for `torch.float` dtype. This means two things:
1. Ops that don't support floating point types (e.g., `bitwise_{...}` ops, `view_as_real` etc) are completely untested
2. Op behavior is only tested for floating point types and not for other dtypes. This means that we might completely miss on some dtype specific correctness for other dtypes.
### Alternatives
_No response_
### Additional context
_No response_
cc @mruberry
| 0 |
4,205 | 89,054 |
Add a `device` keyword argument to `torch.manual_seed`
|
triaged, module: random
|
### 🚀 The feature, motivation and pitch
I would argue that the default way to set seeds and to retrieve generators in PyTorch ML is to use `torch.manual_seed` which creates a generator underneath.
So it's a common use case to do the following:
```python
import torch
generator = torch.manual_seed(0)
```
and then make use of the generator for downsteam pipelines.
Now in many cases one would like the generator to be directly on GPU if all the computation happens on GPU and random tensors that are created along the way should then also directly be created on gpu:
```python
noise = torch.randn(shape, generator=generator, device="cuda")
```
In the above case, we would like `generator` to be on GPU, but it's currently a bit tedious to do this:
```python
generator = torch.Generator(device="cuda").manual_seed(0)
```
=> IMO a nicer API and easier to adapt API would be:
```python
generator = torch.manual_seed(0, device="cuda")
```
### Alternatives
```python
generator = torch.Generator(device="cuda").manual_seed(0)
```
### Additional context
With the rise of Diffusion Modes for generative tasks in ML making pipelines more deterministic becomes more and more important . E.g. we rely on the above functionality **a lot** in `difffusers`: https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers - a nicer API here would be great here.
cc @pbelevich
| 2 |
4,206 | 89,051 |
caffe2_interface_library CMake macro prevents linking to LibTorch as a transitive dependency
|
module: cpp, triaged
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
I have a CMake C++ library that uses LibTorch. It has a layout like this (if simplified):
* `src/CMakeLists.txt` downloads Torch, finds it with `find_package`, and creates the main library `lib` that publicly links to `${TORCH_LIBRARIES}`
* `tests/CMakeLists.txt` creates executable `tests` that links to `lib`
* Top-level `CMakeLists.txt` adds the above directories with `add_subdirectory` in the order they are written above
Here is the sample project: [project.zip](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/files/10010630/project.zip).
The expected behavior is for the project to build fine but in reality it fails to configure with a lot of errors when `lib` is linked to `tests` (the `lib` itself can be built without any errors if `tests` is removed):
```
CMake Error at tests/CMakeLists.txt:5 (target_link_libraries):
Error evaluating generator expression:
$<TARGET_PROPERTY:torch_cpu,INTERFACE_COMPILE_DEFINITIONS>
Target "torch_cpu" not found.
CMake Error at tests/CMakeLists.txt:5 (target_link_libraries):
Error evaluating generator expression:
$<TARGET_PROPERTY:torch,INTERFACE_COMPILE_DEFINITIONS>
Target "torch" not found.
CMake Error at tests/CMakeLists.txt:5 (target_link_libraries):
Error evaluating generator expression:
$<TARGET_PROPERTY:torch_cpu,INTERFACE_INCLUDE_DIRECTORIES>
Target "torch_cpu" not found.
CMake Error at tests/CMakeLists.txt:5 (target_link_libraries):
Error evaluating generator expression:
$<TARGET_PROPERTY:torch,INTERFACE_INCLUDE_DIRECTORIES>
Target "torch" not found.
CMake Error:
Error evaluating generator expression:
$<TARGET_PROPERTY:torch_cpu,INTERFACE_SYSTEM_INCLUDE_DIRECTORIES>
Target "torch_cpu" not found.
CMake Error:
Error evaluating generator expression:
$<TARGET_PROPERTY:torch_cpu,INTERFACE_INCLUDE_DIRECTORIES>
Target "torch_cpu" not found.
CMake Error:
Error evaluating generator expression:
$<TARGET_PROPERTY:torch,INTERFACE_SYSTEM_INCLUDE_DIRECTORIES>
Target "torch" not found.
CMake Error:
Error evaluating generator expression:
$<TARGET_PROPERTY:torch,INTERFACE_INCLUDE_DIRECTORIES>
Target "torch" not found.
CMake Error at tests/CMakeLists.txt:5 (target_link_libraries):
Error evaluating generator expression:
$<TARGET_PROPERTY:torch_cpu,INTERFACE_COMPILE_OPTIONS>
Target "torch_cpu" not found.
CMake Error at tests/CMakeLists.txt:5 (target_link_libraries):
Error evaluating generator expression:
$<TARGET_PROPERTY:torch,INTERFACE_COMPILE_OPTIONS>
Target "torch" not found.
CMake Error at tests/CMakeLists.txt:5 (target_link_libraries):
Error evaluating generator expression:
$<TARGET_PROPERTY:torch_cpu,INTERFACE_COMPILE_DEFINITIONS>
Target "torch_cpu" not found.
CMake Error at tests/CMakeLists.txt:5 (target_link_libraries):
Error evaluating generator expression:
$<TARGET_PROPERTY:torch,INTERFACE_COMPILE_DEFINITIONS>
Target "torch" not found.
CMake Error at tests/CMakeLists.txt:5 (target_link_libraries):
Error evaluating generator expression:
$<TARGET_PROPERTY:torch_cpu,INTERFACE_INCLUDE_DIRECTORIES>
Target "torch_cpu" not found.
CMake Error at tests/CMakeLists.txt:5 (target_link_libraries):
Error evaluating generator expression:
$<TARGET_PROPERTY:torch,INTERFACE_INCLUDE_DIRECTORIES>
Target "torch" not found.
CMake Error:
Error evaluating generator expression:
$<TARGET_PROPERTY:torch_cpu,INTERFACE_SYSTEM_INCLUDE_DIRECTORIES>
Target "torch_cpu" not found.
CMake Error:
Error evaluating generator expression:
$<TARGET_PROPERTY:torch_cpu,INTERFACE_INCLUDE_DIRECTORIES>
Target "torch_cpu" not found.
CMake Error:
Error evaluating generator expression:
$<TARGET_PROPERTY:torch,INTERFACE_SYSTEM_INCLUDE_DIRECTORIES>
Target "torch" not found.
CMake Error:
Error evaluating generator expression:
$<TARGET_PROPERTY:torch,INTERFACE_INCLUDE_DIRECTORIES>
Target "torch" not found.
CMake Error at tests/CMakeLists.txt:5 (target_link_libraries):
Error evaluating generator expression:
$<TARGET_PROPERTY:torch_cpu,INTERFACE_COMPILE_DEFINITIONS>
Target "torch_cpu" not found.
CMake Error at tests/CMakeLists.txt:5 (target_link_libraries):
Error evaluating generator expression:
$<TARGET_PROPERTY:torch,INTERFACE_COMPILE_DEFINITIONS>
Target "torch" not found.
CMake Error at tests/CMakeLists.txt:5 (target_link_libraries):
Error evaluating generator expression:
$<TARGET_PROPERTY:torch_cpu,INTERFACE_INCLUDE_DIRECTORIES>
Target "torch_cpu" not found.
CMake Error at tests/CMakeLists.txt:5 (target_link_libraries):
Error evaluating generator expression:
$<TARGET_PROPERTY:torch,INTERFACE_INCLUDE_DIRECTORIES>
Target "torch" not found.
```
I opened an issue at CMake's repo [here](https://gitlab.kitware.com/cmake/cmake/-/issues/24163) and one of the devs replied that this happened because [this caffe2_interface_library macro](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/blob/v1.13.0/cmake/public/utils.cmake#L195-L292) uses `$<TARGET_PROPERTY:tgt,prop>` instead of `target_link_libraries` (more details can be found in the reply itself). It seems like this is the expected behavior for CMake's implementation even though it is not properly documented.
### Versions
CMake version: version 3.22.1
Libc version: glibc-2.35
Python version: 3.10.6 (main, Nov 2 2022, 18:53:38) [GCC 11.3.0] (64-bit runtime)
Python platform: Linux-5.10.16.3-microsoft-standard-WSL2-x86_64-with-glibc2.35
Is CUDA available: N/A
CUDA runtime version: Could not collect
CUDA_MODULE_LOADING set to: N/A
GPU models and configuration: GPU 0: NVIDIA GeForce RTX 2060
Nvidia driver version: 526.86
cuDNN version: Could not collect
HIP runtime version: N/A
MIOpen runtime version: N/A
Is XNNPACK available: N/A
Versions of relevant libraries:
[pip3] No relevant packages
[conda] Could not collect
cc @jbschlosser
| 2 |
4,207 | 89,050 |
torch.distributed can't establish connection.
|
oncall: distributed
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
I used three machines in the LAN to esbalish connection, it worked, however, when i can't esbalish connection with three machines in the WAN. I have closed the firewall and established connection by socket.
### Versions
```
PyTorch version: N/A
Is debug build: N/A
CUDA used to build PyTorch: N/A
ROCM used to build PyTorch: N/A
OS: Ubuntu 18.04.6 LTS (x86_64)
GCC version: (Ubuntu 9.4.0-1ubuntu1~18.04) 9.4.0
Clang version: Could not collect
CMake version: version 3.13.4
Libc version: glibc-2.9
Python version: 3.7.0 (default, Jun 28 2018, 13:15:42) [GCC 7.2.0] (64-bit runtime)
Python platform: Linux-4.15.0-169-generic-x86_64-with-debian-buster-sid
Is CUDA available: N/A
CUDA runtime version: Could not collect
GPU models and configuration: Could not collect
Nvidia driver version: Could not collect
cuDNN version: Could not collect
HIP runtime version: N/A
MIOpen runtime version: N/A
Is XNNPACK available: N/A
Versions of relevant libraries:
[pip3] numpy==1.15.1
[pip3] numpydoc==0.8.0
[conda] blas 1.0 mkl defaults
[conda] mkl 2019.0 118 defaults
[conda] mkl-service 1.1.2 py37h90e4bf4_5 defaults
[conda] mkl_fft 1.0.4 py37h4414c95_1 defaults
[conda] mkl_random 1.0.1 py37h4414c95_1 defaults
[conda] numpy 1.15.1 py37h1d66e8a_0 defaults
[conda] numpy-base 1.15.1 py37h81de0dd_0 defaults
[conda] numpydoc 0.8.0 py37_0 defaults
```
cc @mrshenli @pritamdamania87 @zhaojuanmao @satgera @rohan-varma @gqchen @aazzolini @osalpekar @jiayisuse @H-Huang @kwen2501 @awgu
| 1 |
4,208 | 89,041 |
cross compile pytoch using cmake , get an error : protobuf::protoc: command not found
|
needs reproduction, module: build, triaged
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
```
.o
[ 75%] Building CXX object c10/CMakeFiles/c10.dir/util/TypeCast.cpp.o
[ 75%] Building CXX object c10/CMakeFiles/c10.dir/util/TypeList.cpp.o
[ 75%] Building CXX object c10/CMakeFiles/c10.dir/util/TypeTraits.cpp.o
[ 75%] Building CXX object c10/CMakeFiles/c10.dir/util/Type_demangle.cpp.o
[ 75%] Building CXX object c10/CMakeFiles/c10.dir/util/Type_no_demangle.cpp.o
[ 75%] Building CXX object c10/CMakeFiles/c10.dir/util/Unicode.cpp.o
[ 75%] Building CXX object c10/CMakeFiles/c10.dir/util/UniqueVoidPtr.cpp.o
[ 75%] Building CXX object c10/CMakeFiles/c10.dir/util/complex_math.cpp.o
[ 75%] Building CXX object c10/CMakeFiles/c10.dir/util/flags_use_gflags.cpp.o
[ 75%] Building CXX object c10/CMakeFiles/c10.dir/util/flags_use_no_gflags.cpp.o
[ 75%] Building CXX object c10/CMakeFiles/c10.dir/util/int128.cpp.o
[ 75%] Building CXX object c10/CMakeFiles/c10.dir/util/intrusive_ptr.cpp.o
[ 75%] Building CXX object c10/CMakeFiles/c10.dir/util/numa.cpp.o
[ 75%] Building CXX object c10/CMakeFiles/c10.dir/util/signal_handler.cpp.o
In file included from /pytorch/pytorch/third_party/fmt/include/fmt/format.h:49:0,
from /pytorch/pytorch/c10/util/signal_handler.cpp:10:
/pytorch/pytorch/third_party/fmt/include/fmt/core.h: In instantiation of ‘struct fmt::v9::basic_format_specs<char>’:
/pytorch/pytorch/third_party/fmt/include/fmt/core.h:2205:8: required from ‘struct fmt::v9::detail::dynamic_format_specs<char>’
/pytorch/pytorch/third_party/fmt/include/fmt/format.h:3932:38: required from here
/pytorch/pytorch/third_party/fmt/include/fmt/core.h:2154:19: warning: ‘fmt::v9::basic_format_specs<char>::align’ is too small to hold all values of ‘using align_t = enum fmt::v9::align::type {aka enum fmt::v9::align::type}’
align_t align : 4;
^
/pytorch/pytorch/third_party/fmt/include/fmt/core.h:2155:17: warning: ‘fmt::v9::basic_format_specs<char>::sign’ is too small to hold all values of ‘using sign_t = enum fmt::v9::sign::type {aka enum fmt::v9::sign::type}’
sign_t sign : 3;
^
/pytorch/pytorch/third_party/fmt/include/fmt/core.h: In function ‘fmt::v9::detail::float_specs fmt::v9::detail::parse_float_type_spec(const fmt::v9::basic_format_specs<Char>&, ErrorHandler&&) [with ErrorHandler = fmt::v9::detail::error_handler; Char = char]’:
/pytorch/pytorch/third_party/fmt/include/fmt/core.h:2818:5: warning: this statement may fall through [-Wimplicit-fallthrough=]
result.upper = true;
^~~~~~
/pytorch/pytorch/third_party/fmt/include/fmt/core.h:2820:3: note: here
case presentation_type::general_lower:
^~~~
/pytorch/pytorch/third_party/fmt/include/fmt/core.h:2824:5: warning: this statement may fall through [-Wimplicit-fallthrough=]
result.upper = true;
^~~~~~
/pytorch/pytorch/third_party/fmt/include/fmt/core.h:2826:3: note: here
case presentation_type::exp_lower:
^~~~
/pytorch/pytorch/third_party/fmt/include/fmt/core.h:2831:5: warning: this statement may fall through [-Wimplicit-fallthrough=]
result.upper = true;
^~~~~~
/pytorch/pytorch/third_party/fmt/include/fmt/core.h:2833:3: note: here
case presentation_type::fixed_lower:
^~~~
/pytorch/pytorch/third_party/fmt/include/fmt/core.h:2838:5: warning: this statement may fall through [-Wimplicit-fallthrough=]
result.upper = true;
^~~~~~
/pytorch/pytorch/third_party/fmt/include/fmt/core.h:2840:3: note: here
case presentation_type::hexfloat_lower:
^~~~
[ 75%] Building CXX object c10/CMakeFiles/c10.dir/util/thread_name.cpp.o
[ 75%] Building CXX object c10/CMakeFiles/c10.dir/util/typeid.cpp.o
[ 75%] Linking CXX shared library ../lib/libc10.so
[ 75%] Built target c10
Scanning dependencies of target python_copy_files
[ 75%] Built target python_copy_files
Scanning dependencies of target torch_global_deps
[ 75%] Building C object caffe2/CMakeFiles/torch_global_deps.dir/__/torch/csrc/empty.c.o
[ 75%] Linking C shared library ../lib/libtorch_global_deps.so
[ 75%] Built target torch_global_deps
[ 75%] Running C++/Python protocol buffer compiler on /pytorch/pytorch/caffe2/proto/caffe2.proto
/bin/sh: protobuf::protoc: command not found
make[2]: *** [caffe2/proto/CMakeFiles/Caffe2_PROTO.dir/build.make:78: caffe2/proto/caffe2.pb.cc] Error 127
make[1]: *** [CMakeFiles/Makefile2:3404: caffe2/proto/CMakeFiles/Caffe2_PROTO.dir/all] Error 2
make: *** [Makefile:141: all] Error 2
root@ubuntu:/pytorch/pytorch-build #
```
### Versions
cmake version: 3.16.3
cross compile toolchain: gcc-linaro-7.5.0-2019.12-x86_64_aarch64-linux-gnu
pytorch :1.13.0
commmand :cmake -DBUILD_SHARED_LIBS:BOOL=ON -DCMAKE_TOOLCHAIN_FILE=/pytorch/pytorch/arm_linux_setup.cmake -DUSE_MKLDNN=OFF -DUSE_QNNPACK=OFF -DUSE_PYTORCH_QNNPACK=OFF -DBUILD_TEST=OFF -DUSE_NNPACK=OFF -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE:STRING=Release -DPYTHON_EXECUTABLE:PATH=`which python3` -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX:PATH=../pytorch-install-aarch64 ../pytorch
cc @malfet @seemethere
| 0 |
4,209 | 89,034 |
[PT][1.13] torch .numpy() fn broke for some scenario
|
module: cpu, triaged, module: numpy, module: regression, actionable, ZeroTensor
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
when backward tensor of sng operator is converted from torch tensor to numpy then output is not correct.
it was expected that output should be 0's as torch tensor has filled with 0's but we get random output after performing .numpy()
this happens only in 1.13 release, 1.12 works fine. Also if tensor is cloned then it works fine
```
import torch
torch.__version__ # 1.13.0a0
x = torch.randn(20, dtype=torch.float32, requires_grad=True)
res = torch.sgn(x)
res_bwd = res.grad_fn(torch.ones(res.shape))
res_bwd
# tensor([0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.])
np_res = res_bwd.detach().numpy()
np_res
```
```
output = array([5.3426861e-35, 0.0000000e+00, 0.0000000e+00, 0.0000000e+00,
1.4012985e-45, 0.0000000e+00, 7.6396113e-35, 0.0000000e+00,
1.7767014e+09, 4.5693540e-41, 7.6396113e-35, 0.0000000e+00,
9.1476764e-41, 0.0000000e+00, 1.1210388e-43, 0.0000000e+00,
3.5873241e-43, 0.0000000e+00, 1.8342932e+09, 4.5693540e-41],
dtype=float32
```
### Versions
torch.__version__ # 1.13.0a0
cc @VitalyFedyunin @jgong5 @mingfeima @XiaobingSuper @sanchitintel @ashokei @jingxu10 @mruberry @rgommers
| 7 |
4,210 | 89,006 |
Add smoke-tests for CPP extensions compilations
|
high priority, module: cpp-extensions, triaged, module: regression
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
Followup for https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/88290
We should add CI/smoke tests for that by using something like the following:
https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/87615#issuecomment-1289539357
### Versions
CI
cc @ezyang @gchanan @zou3519
| 0 |
4,211 | 88,998 |
Fix fake tensor propagation for nvprims
|
triaged, open source, module: nvfuser, ciflow/inductor, no-stale
|
Fake tensors were not working with `torch.ops.nvprims` functions because the fake tensors code expects to see the "prim_meta_impl" attribute that was missing.
Also fixes https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/87236
cc @kevinstephano @jjsjann123
| 7 |
4,212 | 88,992 |
Incorrect version in the instructions on official website
|
module: docs, triaged
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug

here https://pytorch.org/get-started/previous-versions/ in version 9.1 installation listed torchaudio of incomparable version
### Versions
9.1
cc @svekars @carljparker
| 0 |
4,213 | 88,991 |
nvprims.native_batch_norm doesn't support fake tensor inputs
|
triaged, module: nvfuser, module: primTorch
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
Add `tracing_mode="fake"` here to see the error: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/blob/9943d46aab4465b887039aa1a9b5d9ebc0a01a35/test/test_prims.py#L614
In order to support fake tensors `prim` should have "prim_meta_impl" attribute that is a callable used for propagating fake tensors. See the usage here: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/blob/9943d46aab4465b887039aa1a9b5d9ebc0a01a35/torch/_subclasses/fake_tensor.py#L864-L870
### Versions
latest master
cc @kevinstephano @jjsjann123 @ezyang @mruberry @ngimel @Lezcano @fdrocha @peterbell10
| 0 |
4,214 | 88,980 |
Glog macro redefinition problem when including headers from both libtorch and glog
|
module: build, triaged
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
Hi, I am trying to build a C++ shared library that uses Pytorch C++ custom class (torchscript class). I linked the library aganist Libtorch and glog but got macro redefinition warnings. Those macros are loggers like `LOG` and `CHECK`, which are defined in both Libtorch (`torch/include/c10/util/logging_is_google_glog.h` or `torch/include/c10/util/logging_is_not_google_glog.h`) and glog. I can see Pytorch have similar issues before (#31822, #14724) and a PR (#41504) to solve the redefinition issue when libtorch is not built with glog. However, I still have the redefinition problem when including the headers of glog and `torch/custom_class.h` (which will include `torch/include/c10/util/logging_is_not_google_glog.h` in the end, resulting in macro redefinition). I wonder whether there is a workaround to get rid of this problem?
### Versions
[pip3] mypy-extensions==0.4.3
[pip3] numpy==1.22.1
[pip3] torch==1.12.1+cu113
[pip3] torchaudio==0.12.1+cu113
[pip3] torchmetrics==0.10.0
[pip3] torchvision==0.13.1+cu113
cc @malfet @seemethere
| 0 |
4,215 | 88,968 |
M1 runner i-090e1df32b6f48a20 run out of disk space
|
module: ci, triaged, module: m1
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
See
https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/actions/runs/3453509296/jobs/5764272366
https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/actions/runs/3453862853/jobs/5764898047
https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/actions/runs/3454468047/jobs/5765868837
https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/actions/runs/3454765799/jobs/5766454600
https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/actions/runs/3455173679/jobs/5767115747
### Versions
CI
cc @ezyang @gchanan @zou3519 @seemethere @pytorch/pytorch-dev-infra
| 4 |
4,216 | 93,420 |
[Inductor] Constant folding support
|
triaged, enhancement, oncall: pt2, module: inductor
|
## Motivating Example
Below is a case in MobileBertForMaskedLM which has a concatenation on two model parameters (`hidden_states = hidden_states.matmul(torch.cat([self.decoder.weight.t(), self.dense.weight], dim=0))`). This concat takes >20% of the single-threaded inference time on CPU but this cost can be saved with constant folding.
```python
class MobileBertLMPredictionHead(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, config):
super().__init__()
self.transform = MobileBertPredictionHeadTransform(config)
# The output weights are the same as the input embeddings, but there is
# an output-only bias for each token.
self.dense = nn.Linear(config.vocab_size, config.hidden_size - config.embedding_size, bias=False)
self.decoder = nn.Linear(config.embedding_size, config.vocab_size, bias=False)
self.bias = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(config.vocab_size))
# Need a link between the two variables so that the bias is correctly resized with `resize_token_embeddings`
self.decoder.bias = self.bias
def forward(self, hidden_states: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
hidden_states = self.transform(hidden_states)
hidden_states = hidden_states.matmul(torch.cat([self.decoder.weight.t(), self.dense.weight], dim=0))
hidden_states += self.decoder.bias
return hidden_states
```
cc @mlazos @soumith @voznesenskym @yanboliang @penguinwu @anijain2305 @EikanWang @Guobing-Chen @XiaobingSuper @zhuhaozhe @blzheng @Xia-Weiwen @wenzhe-nrv @jiayisunx @peterbell10 @desertfire @ezyang @msaroufim @wconstab @ngimel @bdhirsh
| 0 |
4,217 | 88,950 |
`torch.nn.functional.embedding_bag` Trigger RuntimeError under UndefinedBehaviorSanitizer
|
triaged, module: sanitizers
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
The implementation of `torch.nn.functional.embedding_bag` contains undefined behavior caught by UB sanitizer. Without sanitizers, the test terminates normally.
Test:
```python
import torch
def test():
arg_1 = torch.randint(-1024,1024,[6], dtype=torch.int32).clone()
arg_2 = torch.rand([5, 2], dtype=torch.float32).clone()
arg_3 = torch.randint(-8192,0,[0], dtype=torch.int64).clone()
arg_9 = torch.rand([6], dtype=torch.float32).clone()
_ = torch.nn.functional.embedding_bag(arg_1, arg_2, arg_3, None, 2.0, False, "sum", False, arg_9, False, None)
test()
```
Error log:
```
pytorch/aten/src/ATen/native/EmbeddingBag.cpp:708:11: runtime error: null pointer passed as argument 2, which is declared to never be null
/usr/include/string.h:44:28: note: nonnull attribute specified here
```
### Versions
```
PyTorch version: 1.14.0a0+git6e5f736
Is debug build: False
CUDA used to build PyTorch: Could not collect
ROCM used to build PyTorch: N/A
OS: Ubuntu 22.04.1 LTS (x86_64)
GCC version: (Ubuntu 11.3.0-1ubuntu1~22.04) 11.3.0
Clang version: 11.1.0-6
CMake version: version 3.22.1
Libc version: glibc-2.35
Python version: 3.9.12 (main, Apr 5 2022, 06:56:58) [GCC 7.5.0] (64-bit runtime)
Python platform: Linux-5.15.0-52-generic-x86_64-with-glibc2.35
Is CUDA available: False
CUDA runtime version: 11.8.89
CUDA_MODULE_LOADING set to: N/A
GPU models and configuration:
GPU 0: NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3090
GPU 1: NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3090
GPU 2: NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3090
Nvidia driver version: 515.65.01
cuDNN version: Probably one of the following:
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_adv_infer.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_adv_train.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_cnn_infer.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_cnn_train.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_ops_infer.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_ops_train.so.8.4.1
HIP runtime version: N/A
MIOpen runtime version: N/A
Is XNNPACK available: True
Versions of relevant libraries:
[pip3] mypy-extensions==0.4.3
[pip3] numpy==1.21.5
[pip3] numpydoc==1.2
[pip3] torch==1.14.0a0+git6e5f736
[conda] blas 1.0 mkl
[conda] cudatoolkit 11.3.1 h2bc3f7f_2
[conda] mkl 2021.4.0 h06a4308_640
[conda] mkl-service 2.4.0 py39h7f8727e_0
[conda] mkl_fft 1.3.1 py39hd3c417c_0
[conda] mkl_random 1.2.2 py39h51133e4_0
[conda] numpy 1.21.5 py39he7a7128_1
[conda] numpy-base 1.21.5 py39hf524024_1
[conda] numpydoc 1.2 pyhd3eb1b0_0
[conda] torch 1.14.0a0+git6e5f736 pypi_0 pypi
```
| 1 |
4,218 | 88,949 |
`torch.set_rng_state` Trigger RuntimeError under UndefinedBehaviorSanitizer
|
triaged, module: sanitizers
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
The implementation of `torch.set_rng_state` contains undefined behavior caught by UB sanitizer.
Test:
```python
import torch
def test():
arg_1 = torch.randint(0,64,[5056], dtype=torch.uint8).clone()
_ = torch.set_rng_state(arg_1,)
test()
```
Error log:
```
pytorch/aten/src/ATen/CPUGeneratorImpl.cpp:167:20: runtime error: load of value 46, which is not a valid value for type 'bool'
```
### Versions
```
PyTorch version: 1.14.0a0+git6e5f736
Is debug build: False
CUDA used to build PyTorch: Could not collect
ROCM used to build PyTorch: N/A
OS: Ubuntu 22.04.1 LTS (x86_64)
GCC version: (Ubuntu 11.3.0-1ubuntu1~22.04) 11.3.0
Clang version: 11.1.0-6
CMake version: version 3.22.1
Libc version: glibc-2.35
Python version: 3.9.12 (main, Apr 5 2022, 06:56:58) [GCC 7.5.0] (64-bit runtime)
Python platform: Linux-5.15.0-52-generic-x86_64-with-glibc2.35
Is CUDA available: False
CUDA runtime version: 11.8.89
CUDA_MODULE_LOADING set to: N/A
GPU models and configuration:
GPU 0: NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3090
GPU 1: NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3090
GPU 2: NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3090
Nvidia driver version: 515.65.01
cuDNN version: Probably one of the following:
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_adv_infer.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_adv_train.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_cnn_infer.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_cnn_train.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_ops_infer.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_ops_train.so.8.4.1
HIP runtime version: N/A
MIOpen runtime version: N/A
Is XNNPACK available: True
Versions of relevant libraries:
[pip3] mypy-extensions==0.4.3
[pip3] numpy==1.21.5
[pip3] numpydoc==1.2
[pip3] torch==1.14.0a0+git6e5f736
[conda] blas 1.0 mkl
[conda] cudatoolkit 11.3.1 h2bc3f7f_2
[conda] mkl 2021.4.0 h06a4308_640
[conda] mkl-service 2.4.0 py39h7f8727e_0
[conda] mkl_fft 1.3.1 py39hd3c417c_0
[conda] mkl_random 1.2.2 py39h51133e4_0
[conda] numpy 1.21.5 py39he7a7128_1
[conda] numpy-base 1.21.5 py39hf524024_1
[conda] numpydoc 1.2 pyhd3eb1b0_0
[conda] torch 1.14.0a0+git6e5f736 pypi_0 pypi
```
| 1 |
4,219 | 88,948 |
torch.linalg.matrix_rank memory leak
|
needs reproduction, module: memory usage, triaged, module: linear algebra
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
Below is a minimal script for reproducing.
```python
import torch
import os, psutil
a = torch.randn(100, 100, 512)
for _ in range(10):
torch.linalg.matrix_rank(a)
print(psutil.Process(os.getpid()).memory_info().rss)
```
The above script gives the following output:
```
4214136832
8331022336
10537857024
12173451264
13269585920
14028787712
14656843776
15086813184
15620276224
16046718976
```
I did some test, and it seems that it only happens when the tensor is high dimensional. For example, if the dimension of `a` is (100, 100, 100) then everything is fine.
### Versions
PyTorch version: 1.13.0a0
Is debug build: False
CUDA used to build PyTorch: 11.6
ROCM used to build PyTorch: N/A
OS: SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 15 SP3 (x86_64)
GCC version: (SUSE Linux) 7.5.0
Clang version: Could not collect
CMake version: version 3.17.0
Libc version: glibc-2.31
Python version: 3.9.7 (default, Sep 16 2021, 13:09:58) [GCC 7.5.0] (64-bit runtime)
Python platform: Linux-5.3.18-150300.59.87-default-x86_64-with-glibc2.31
Is CUDA available: False
CUDA runtime version: 11.6.124
CUDA_MODULE_LOADING set to: N/A
GPU models and configuration: Could not collect
Nvidia driver version: Could not collect
cuDNN version: Could not collect
HIP runtime version: N/A
MIOpen runtime version: N/A
Is XNNPACK available: True
Versions of relevant libraries:
[pip3] mypy==0.982
[pip3] mypy-extensions==0.4.3
[pip3] numpy==1.20.3
[pip3] numpydoc==1.1.0
[pip3] torch==1.13.0a0+gitunknown
[pip3] torchaudio==0.13.0+bc8640b
[pip3] torchtext==0.14.0a0+e2b27f9
[pip3] torchvision==0.14.0a0
[conda] blas 1.0 mkl
[conda] mkl 2021.4.0 h06a4308_640
[conda] mkl-include 2021.4.0 h06a4308_640 <unknown>
[conda] mkl-service 2.4.0 py39h7f8727e_0
[conda] mkl_fft 1.3.1 py39hd3c417c_0
[conda] mkl_random 1.2.2 py39h51133e4_0
[conda] numpy 1.20.3 py39hf144106_0
[conda] numpy-base 1.20.3 py39h74d4b33_0
[conda] numpydoc 1.1.0 pyhd3eb1b0_1
cc @jianyuh @nikitaved @pearu @mruberry @walterddr @IvanYashchuk @xwang233 @Lezcano
| 3 |
4,220 | 88,947 |
`torch.Tensor.msort` Trigger RuntimeError under UndefinedBehaviorSanitizer
|
triaged, module: sanitizers
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
The implementation of `torch.Tensor.msort` contains undefined behavior caught by UB sanitizer. Without sanitizers, the test terminates normally.
Test:
```python
import torch
def test():
arg_1 = torch.rand([0, 16, 1024, 1024], dtype=torch.float16).clone()
res = torch.Tensor.msort(arg_1,)
test()
```
Error log:
```
pytorch/aten/src/ATen/TensorIteratorInternal.h:34:17: runtime error: applying non-zero offset 1048576 to null pointer
```
### Versions
```
PyTorch version: 1.14.0a0+git6e5f736
Is debug build: False
CUDA used to build PyTorch: Could not collect
ROCM used to build PyTorch: N/A
OS: Ubuntu 22.04.1 LTS (x86_64)
GCC version: (Ubuntu 11.3.0-1ubuntu1~22.04) 11.3.0
Clang version: 11.1.0-6
CMake version: version 3.22.1
Libc version: glibc-2.35
Python version: 3.9.12 (main, Apr 5 2022, 06:56:58) [GCC 7.5.0] (64-bit runtime)
Python platform: Linux-5.15.0-52-generic-x86_64-with-glibc2.35
Is CUDA available: False
CUDA runtime version: 11.8.89
CUDA_MODULE_LOADING set to: N/A
GPU models and configuration:
GPU 0: NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3090
GPU 1: NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3090
GPU 2: NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3090
Nvidia driver version: 515.65.01
cuDNN version: Probably one of the following:
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_adv_infer.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_adv_train.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_cnn_infer.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_cnn_train.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_ops_infer.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_ops_train.so.8.4.1
HIP runtime version: N/A
MIOpen runtime version: N/A
Is XNNPACK available: True
Versions of relevant libraries:
[pip3] mypy-extensions==0.4.3
[pip3] numpy==1.21.5
[pip3] numpydoc==1.2
[pip3] torch==1.14.0a0+git6e5f736
[conda] blas 1.0 mkl
[conda] cudatoolkit 11.3.1 h2bc3f7f_2
[conda] mkl 2021.4.0 h06a4308_640
[conda] mkl-service 2.4.0 py39h7f8727e_0
[conda] mkl_fft 1.3.1 py39hd3c417c_0
[conda] mkl_random 1.2.2 py39h51133e4_0
[conda] numpy 1.21.5 py39he7a7128_1
[conda] numpy-base 1.21.5 py39hf524024_1
[conda] numpydoc 1.2 pyhd3eb1b0_0
[conda] torch 1.14.0a0+git6e5f736 pypi_0 pypi
```
| 0 |
4,221 | 88,945 |
`torch.linalg.eigvals` Trigger RuntimeError under UndefinedBehaviorSanitizer
|
triaged, module: sanitizers
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
The implementation of `torch.linalg.eigvals` contains undefined behavior caught by UB sanitizer. Without sanitizers, the test terminates normally.
Test:
```
import torch
def test():
arg_1 = torch.rand([0, 3, 3], dtype=torch.float64).clone()
res = torch.linalg.eigvals(arg_1,)
test()
```
Error log:
```
pytorch/aten/src/ATen/native/BatchLinearAlgebra.cpp:954:18: runtime error: applying non-zero offset 24 to null pointer
```
### Versions
```
PyTorch version: 1.14.0a0+git6e5f736
Is debug build: False
CUDA used to build PyTorch: Could not collect
ROCM used to build PyTorch: N/A
OS: Ubuntu 22.04.1 LTS (x86_64)
GCC version: (Ubuntu 11.3.0-1ubuntu1~22.04) 11.3.0
Clang version: 11.1.0-6
CMake version: version 3.22.1
Libc version: glibc-2.35
Python version: 3.9.12 (main, Apr 5 2022, 06:56:58) [GCC 7.5.0] (64-bit runtime)
Python platform: Linux-5.15.0-52-generic-x86_64-with-glibc2.35
Is CUDA available: False
CUDA runtime version: 11.8.89
CUDA_MODULE_LOADING set to: N/A
GPU models and configuration:
GPU 0: NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3090
GPU 1: NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3090
GPU 2: NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3090
Nvidia driver version: 515.65.01
cuDNN version: Probably one of the following:
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_adv_infer.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_adv_train.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_cnn_infer.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_cnn_train.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_ops_infer.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_ops_train.so.8.4.1
HIP runtime version: N/A
MIOpen runtime version: N/A
Is XNNPACK available: True
Versions of relevant libraries:
[pip3] mypy-extensions==0.4.3
[pip3] numpy==1.21.5
[pip3] numpydoc==1.2
[pip3] torch==1.14.0a0+git6e5f736
[conda] blas 1.0 mkl
[conda] cudatoolkit 11.3.1 h2bc3f7f_2
[conda] mkl 2021.4.0 h06a4308_640
[conda] mkl-service 2.4.0 py39h7f8727e_0
[conda] mkl_fft 1.3.1 py39hd3c417c_0
[conda] mkl_random 1.2.2 py39h51133e4_0
[conda] numpy 1.21.5 py39he7a7128_1
[conda] numpy-base 1.21.5 py39hf524024_1
[conda] numpydoc 1.2 pyhd3eb1b0_0
[conda] torch 1.14.0a0+git6e5f736 pypi_0 pypi
```
| 0 |
4,222 | 88,944 |
`torch.topk` Trigger RuntimError under UndefinedBehaviorSanitizer
|
triaged, module: sanitizers
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
The implementation of `torch.topk` contains undefined behavior caught by UB sanitizer. Without sanitizers, the test terminates normally.
Test:
```python
import torch
def test():
arg_1 = torch.rand([3, 5], dtype=torch.float64).clone()
res = torch.topk(arg_1,0,0,)
test()
```
Error log:
```
pytorch/aten/src/ATen/native/TopKImpl.h:30:45: runtime error: applying non-zero offset 8 to null pointer
```
### Versions
```
PyTorch version: 1.14.0a0+git6e5f736
Is debug build: False
CUDA used to build PyTorch: Could not collect
ROCM used to build PyTorch: N/A
OS: Ubuntu 22.04.1 LTS (x86_64)
GCC version: (Ubuntu 11.3.0-1ubuntu1~22.04) 11.3.0
Clang version: 11.1.0-6
CMake version: version 3.22.1
Libc version: glibc-2.35
Python version: 3.9.12 (main, Apr 5 2022, 06:56:58) [GCC 7.5.0] (64-bit runtime)
Python platform: Linux-5.15.0-52-generic-x86_64-with-glibc2.35
Is CUDA available: False
CUDA runtime version: 11.8.89
CUDA_MODULE_LOADING set to: N/A
GPU models and configuration:
GPU 0: NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3090
GPU 1: NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3090
GPU 2: NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3090
Nvidia driver version: 515.65.01
cuDNN version: Probably one of the following:
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_adv_infer.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_adv_train.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_cnn_infer.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_cnn_train.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_ops_infer.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_ops_train.so.8.4.1
HIP runtime version: N/A
MIOpen runtime version: N/A
Is XNNPACK available: True
Versions of relevant libraries:
[pip3] mypy-extensions==0.4.3
[pip3] numpy==1.21.5
[pip3] numpydoc==1.2
[pip3] torch==1.14.0a0+git6e5f736
[conda] blas 1.0 mkl
[conda] cudatoolkit 11.3.1 h2bc3f7f_2
[conda] mkl 2021.4.0 h06a4308_640
[conda] mkl-service 2.4.0 py39h7f8727e_0
[conda] mkl_fft 1.3.1 py39hd3c417c_0
[conda] mkl_random 1.2.2 py39h51133e4_0
[conda] numpy 1.21.5 py39he7a7128_1
[conda] numpy-base 1.21.5 py39hf524024_1
[conda] numpydoc 1.2 pyhd3eb1b0_0
[conda] torch 1.14.0a0+git6e5f736 pypi_0 pypi
```
| 0 |
4,223 | 88,943 |
`torch.vander` Trigger RuntimeError with UndefinedBehaviorSanitizer
|
triaged, module: linear algebra, module: sanitizers, module: edge cases
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
The implementation of `torch.vander` contains undefined behavior caught by UB sanitizer. Without sanitizers, the test terminates normally.
Test:
```python
import torch
def test():
arg_1 = torch.randint(-1,512,[4], dtype=torch.int64).clone()
res = torch.vander(arg_1,12,)
test()
```
Error log:
```
pytorch/aten/src/ATen/native/cpu/ReduceOpsKernel.cpp:100:3: runtime error: signed integer overflow: 7179408129339016064 * 494 cannot be represented in type 'long'
```
### Versions
```
PyTorch version: 1.14.0a0+git6e5f736
Is debug build: False
CUDA used to build PyTorch: Could not collect
ROCM used to build PyTorch: N/A
OS: Ubuntu 22.04.1 LTS (x86_64)
GCC version: (Ubuntu 11.3.0-1ubuntu1~22.04) 11.3.0
Clang version: 11.1.0-6
CMake version: version 3.22.1
Libc version: glibc-2.35
Python version: 3.9.12 (main, Apr 5 2022, 06:56:58) [GCC 7.5.0] (64-bit runtime)
Python platform: Linux-5.15.0-52-generic-x86_64-with-glibc2.35
Is CUDA available: False
CUDA runtime version: 11.8.89
CUDA_MODULE_LOADING set to: N/A
GPU models and configuration:
GPU 0: NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3090
GPU 1: NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3090
GPU 2: NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3090
Nvidia driver version: 515.65.01
cuDNN version: Probably one of the following:
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_adv_infer.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_adv_train.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_cnn_infer.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_cnn_train.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_ops_infer.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_ops_train.so.8.4.1
HIP runtime version: N/A
MIOpen runtime version: N/A
Is XNNPACK available: True
Versions of relevant libraries:
[pip3] mypy-extensions==0.4.3
[pip3] numpy==1.21.5
[pip3] numpydoc==1.2
[pip3] torch==1.14.0a0+git6e5f736
[conda] blas 1.0 mkl
[conda] cudatoolkit 11.3.1 h2bc3f7f_2
[conda] mkl 2021.4.0 h06a4308_640
[conda] mkl-service 2.4.0 py39h7f8727e_0
[conda] mkl_fft 1.3.1 py39hd3c417c_0
[conda] mkl_random 1.2.2 py39h51133e4_0
[conda] numpy 1.21.5 py39he7a7128_1
[conda] numpy-base 1.21.5 py39hf524024_1
[conda] numpydoc 1.2 pyhd3eb1b0_0
[conda] torch 1.14.0a0+git6e5f736 pypi_0 pypi
```
cc @jianyuh @nikitaved @pearu @mruberry @walterddr @IvanYashchuk @xwang233 @Lezcano
| 3 |
4,224 | 88,942 |
`torch.svd_lowrank` Trigger RuntimeError under UndefinedBehaviorSanitizer
|
module: sparse, triaged, module: linear algebra, actionable, module: sanitizers
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
The implementation of `torch.svd_lowrank` contains undefined behavior caught by UB sanitizer. Without sanitizers, the test terminates normally.
Test:
```python
import torch
def test():
arg_1 = torch.rand([5, 5], dtype=torch.float64).to_sparse()
res = torch.svd_lowrank(arg_1,False,)
test()
```
Error log:
```
pytorch/aten/src/ATen/native/sparse/SparseTensorMath.cpp:1270:19: runtime error: applying non-zero offset 8 to null pointer
```
### Versions
```
PyTorch version: 1.14.0a0+git6e5f736
Is debug build: False
CUDA used to build PyTorch: Could not collect
ROCM used to build PyTorch: N/A
OS: Ubuntu 22.04.1 LTS (x86_64)
GCC version: (Ubuntu 11.3.0-1ubuntu1~22.04) 11.3.0
Clang version: 11.1.0-6
CMake version: version 3.22.1
Libc version: glibc-2.35
Python version: 3.9.12 (main, Apr 5 2022, 06:56:58) [GCC 7.5.0] (64-bit runtime)
Python platform: Linux-5.15.0-52-generic-x86_64-with-glibc2.35
Is CUDA available: False
CUDA runtime version: 11.8.89
CUDA_MODULE_LOADING set to: N/A
GPU models and configuration:
GPU 0: NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3090
GPU 1: NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3090
GPU 2: NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3090
Nvidia driver version: 515.65.01
cuDNN version: Probably one of the following:
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_adv_infer.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_adv_train.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_cnn_infer.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_cnn_train.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_ops_infer.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_ops_train.so.8.4.1
HIP runtime version: N/A
MIOpen runtime version: N/A
Is XNNPACK available: True
Versions of relevant libraries:
[pip3] mypy-extensions==0.4.3
[pip3] numpy==1.21.5
[pip3] numpydoc==1.2
[pip3] torch==1.14.0a0+git6e5f736
[conda] blas 1.0 mkl
[conda] cudatoolkit 11.3.1 h2bc3f7f_2
[conda] mkl 2021.4.0 h06a4308_640
[conda] mkl-service 2.4.0 py39h7f8727e_0
[conda] mkl_fft 1.3.1 py39hd3c417c_0
[conda] mkl_random 1.2.2 py39h51133e4_0
[conda] numpy 1.21.5 py39he7a7128_1
[conda] numpy-base 1.21.5 py39hf524024_1
[conda] numpydoc 1.2 pyhd3eb1b0_0
[conda] torch 1.14.0a0+git6e5f736 pypi_0 pypi
```
cc @ezyang @gchanan @zou3519 @nikitaved @pearu @cpuhrsch @amjames @bhosmer @jianyuh @mruberry @walterddr @IvanYashchuk @xwang233 @Lezcano
| 4 |
4,225 | 88,941 |
`torch.linalg.lstsq` Trigger RuntimeError under UndefinedBehaviorSanitizer
|
triaged, module: linear algebra, actionable, module: sanitizers, module: edge cases
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
The implementation of `torch.linalg.lstsq` contains undefined behavior caught by UB sanitizer. Without sanitizers, the test terminates normally.
Test:
```python
import torch
def test():
arg_1 = torch.rand([2, 3, 5, 5, 0], dtype=torch.float64).clone()
arg_2 = torch.rand([2, 3, 5, 5], dtype=torch.float64).clone()
res = torch.linalg.lstsq(arg_1,arg_2,)
test()
```
Error log:
```
pytorch/c10/core/TensorImpl.h:1521:38: runtime error: applying non-zero offset 40 to null pointer
```
### Versions
```
PyTorch version: 1.14.0a0+git6e5f736
Is debug build: False
CUDA used to build PyTorch: Could not collect
ROCM used to build PyTorch: N/A
OS: Ubuntu 22.04.1 LTS (x86_64)
GCC version: (Ubuntu 11.3.0-1ubuntu1~22.04) 11.3.0
Clang version: 11.1.0-6
CMake version: version 3.22.1
Libc version: glibc-2.35
Python version: 3.9.12 (main, Apr 5 2022, 06:56:58) [GCC 7.5.0] (64-bit runtime)
Python platform: Linux-5.15.0-52-generic-x86_64-with-glibc2.35
Is CUDA available: False
CUDA runtime version: 11.8.89
CUDA_MODULE_LOADING set to: N/A
GPU models and configuration:
GPU 0: NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3090
GPU 1: NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3090
GPU 2: NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3090
Nvidia driver version: 515.65.01
cuDNN version: Probably one of the following:
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_adv_infer.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_adv_train.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_cnn_infer.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_cnn_train.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_ops_infer.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_ops_train.so.8.4.1
HIP runtime version: N/A
MIOpen runtime version: N/A
Is XNNPACK available: True
Versions of relevant libraries:
[pip3] mypy-extensions==0.4.3
[pip3] numpy==1.21.5
[pip3] numpydoc==1.2
[pip3] torch==1.14.0a0+git6e5f736
[conda] blas 1.0 mkl
[conda] cudatoolkit 11.3.1 h2bc3f7f_2
[conda] mkl 2021.4.0 h06a4308_640
[conda] mkl-service 2.4.0 py39h7f8727e_0
[conda] mkl_fft 1.3.1 py39hd3c417c_0
[conda] mkl_random 1.2.2 py39h51133e4_0
[conda] numpy 1.21.5 py39he7a7128_1
[conda] numpy-base 1.21.5 py39hf524024_1
[conda] numpydoc 1.2 pyhd3eb1b0_0
[conda] torch 1.14.0a0+git6e5f736 pypi_0 pypi
```
cc @ezyang @gchanan @zou3519 @jianyuh @nikitaved @pearu @mruberry @walterddr @IvanYashchuk @xwang233 @Lezcano
| 4 |
4,226 | 88,931 |
INTERNAL ASSERT FAILED. Missing scalar type infromation.
|
triaged, module: nvfuser
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
Hi, I'm trying to run [DiffDock](https://github.com/gcorso/diffdock) and I get the following error:
```tensor_type->scalarType().has_value() INTERNAL ASSERT FAILED at "/opt/conda/conda-bld/pytorch_1659484809662/work/torch/csrc/jit/codegen/cuda/type_promotion.cpp":111, please report a bug to PyTorch. Missing Scalar Type information```
I'm not able to share a minimal example as I don't know where the error arises from. Do you have any idea how to investigate this? How do I get a traceback?
### Versions
Collecting environment information...
PyTorch version: 1.12.1
Is debug build: False
CUDA used to build PyTorch: 11.3
ROCM used to build PyTorch: N/A
OS: Debian GNU/Linux 11 (bullseye) (x86_64)
GCC version: (Debian 10.2.1-6) 10.2.1 20210110
Clang version: Could not collect
CMake version: Could not collect
Libc version: glibc-2.31
Python version: 3.9.13 (main, Oct 13 2022, 21:15:33) [GCC 11.2.0] (64-bit runtime)
Python platform: Linux-4.18.0-305.10.2.el8_4.x86_64-x86_64-with-glibc2.31
Is CUDA available: True
CUDA runtime version: Could not collect
CUDA_MODULE_LOADING set to:
GPU models and configuration: GPU 0: NVIDIA A100-SXM4-40GB
Nvidia driver version: 470.57.02
cuDNN version: Could not collect
HIP runtime version: N/A
MIOpen runtime version: N/A
Is XNNPACK available: True
Versions of relevant libraries:
[pip3] numpy==1.23.1
[pip3] torch==1.12.1
[pip3] torch-cluster==1.6.0
[pip3] torch-geometric==2.1.0.post1
[pip3] torch-scatter==2.0.9
[pip3] torch-sparse==0.6.15
[pip3] torch-spline-conv==1.2.1
[pip3] torchaudio==0.12.1
[pip3] torchvision==0.13.1
[conda] blas 1.0 mkl
[conda] cudatoolkit 11.3.1 h2bc3f7f_2
[conda] ffmpeg 4.3 hf484d3e_0 pytorch
[conda] mkl 2021.4.0 h06a4308_640
[conda] mkl-service 2.4.0 py39h7f8727e_0
[conda] mkl_fft 1.3.1 py39hd3c417c_0
[conda] mkl_random 1.2.2 py39h51133e4_0
[conda] numpy 1.23.1 py39h6c91a56_0
[conda] numpy-base 1.23.1 py39ha15fc14_0
[conda] pyg 2.1.0 py39_torch_1.12.0_cu113 pyg
[conda] pytorch 1.12.1 py3.9_cuda11.3_cudnn8.3.2_0 pytorch
[conda] pytorch-cluster 1.6.0 py39_torch_1.12.0_cu113 pyg
[conda] pytorch-mutex 1.0 cuda pytorch
[conda] pytorch-scatter 2.0.9 py39_torch_1.12.0_cu113 pyg
[conda] pytorch-sparse 0.6.15 py39_torch_1.12.0_cu113 pyg
[conda] pytorch-spline-conv 1.2.1 py39_torch_1.12.0_cu113 pyg
[conda] torchaudio 0.12.1 py39_cu113 pytorch
[conda] torchvision 0.13.1 py39_cu113 pytorch
cc @kevinstephano @jjsjann123
| 1 |
4,227 | 93,419 |
torchdynamo is not properly setting up input tracking (e.g., for symbolic shape guards) for view bases
|
triaged, bug, oncall: pt2
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
When we convert a real tensor to a fake tensor, if the original tensor was a differentiable view we will also convert its base to a fake tensor, so we can construct a fake tensor that also looks like a view. In dynamic shapes, this means that we will allocate symbolic sizes for both the base as well as the view, and it turned out that in some circumstances we could end up producing guards on the base! This is problematic, because dynamo only considers the view as a new tensor inputs and only tracks its symints. The assert that fails is typically:
```
assert expr_found, f"Failed to find {expr}"
```
in DynamoGuardPrinter in this case.
In [92ef26b96bf0c36e4b8ad87dc0419f46dfc65c69](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/84246/commits/92ef26b96bf0c36e4b8ad87dc0419f46dfc65c69) we make this problem less likely to occur by suppressing guards that occur when creating fake tensors, since the naughty guard we observed in practice was caused by the `as_strided` call we use to setup the view performing a bounds check. But it would be better to fix this properly, especially since we still have "failed to find sX" in our tests.
The general idea is that whenever we allocate symbolic integers for a tensor, we should ALWAYS set it up in the environment. However, it is difficult to tell how many inputs a tensor will actually be (there is not only the _base field, but also the grad field); so it may be easiest if fake tensor converter communicates this information via a callback that has also says the attribute path, so we can make an appropriate source for the tensor.
cc @soumith @msaroufim @wconstab @ngimel @bdhirsh @voznesenskym
### Error logs
_No response_
### Minified repro
_No response_
| 0 |
4,228 | 88,902 |
MPS test_numpy_ref_mps_nn_functional_group_norm_mps_float32 is flaky?
|
triaged, module: flaky-tests, module: mps
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/actions/runs/3446932166/jobs/5752655448
### Versions
master
cc @kulinseth @albanD @malfet @DenisVieriu97 @razarmehr @abhudev
| 1 |
4,229 | 93,618 |
[dynamo+ddp+symbolic-shapes] Issue Tracker
|
triaged, oncall: pt2
|
we should support these systems working togehter. i think they should compose, but it requires some testing.
- [ ] huggingface accelerate nlp_model crashes ([repro cmd](https://gist.github.com/wconstab/12ce82ceded7a3ee4748b24cc5ec502e#file-repro-instructions), [log](https://gist.github.com/wconstab/12ce82ceded7a3ee4748b24cc5ec502e#file-symbolic_nlp_example-log))
- [ ] torchbench hf_Bert is slow with symbolic-shapes (`python benchmarks/dynamo/distributed.py --torchbench_model hf_Bert --ddp --dynamo inductor` on symbolic-shapes branch)
cc @ezyang @soumith @msaroufim @ngimel @bdhirsh
| 2 |
4,230 | 88,893 |
RuntimeError: derivative for aten::mps_max_pool2d_backward is not implemented
|
triaged, module: mps
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
Hi there, I encountered the runtime error "derivative for aten::mps_max_pool2d_backward is not implemented" when trying to use ```torch.autograd.grad``` to compute the Hessian of the loss function of a ResNet18 model w.r.t. model parameters, which is done by first using ```torch.autograd.grad``` to compute the gradient itself, and then using it again to compute the gradient of the gradient to get the Hessian. (Please kindly see lines 122-131 in the full traceback message below.)
Thank you so much!
```
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
RuntimeError Traceback (most recent call last)
Input In [18], in <cell line: 2>()
1 Hess_eigval, \
----> 2 Hess_eigval_density = Hess.LanczosApproxSpec(init_poly_deg=64, # iterations used to compute spectrum range
3 poly_deg=256)
File ~/Documents/hessian.py:248, in Hessian.LanczosApproxSpec(self, init_poly_deg, poly_deg, spectrum_margin, poly_points, log_hessian, eps, denormalize)
244 print('LanczosApproxSpec')
246 print('Estimating spectrum range')
--> 248 lb, ub = self.compute_lb_ub(init_poly_deg)
249 print('Estimated spectrum range:')
250 print('[{}\t{}]'.format(lb, ub))
File ~/Documents/hessian.py:217, in Hessian.compute_lb_ub(self, init_poly_deg)
216 def compute_lb_ub(self, init_poly_deg):
--> 217 ritz_val, S, alp, bet = self.Lanczos(init_poly_deg)
219 theta_1 = ritz_val[0]
220 theta_k = ritz_val[-1]
File ~/Documents/hessian.py:340, in Hessian.Lanczos(self, M)
337 for j in tqdm(range(M)):
338 sys.stdout.flush()
--> 340 v_next = self.mat_vec(v)
342 if j:
343 v_next = self.my_sub(v_next, self.my_mult_const(v_prev,bet[j-1]))
File ~/Documents/hessian.py:145, in Hessian.mat_vec(self, v)
144 def mat_vec(self, v):
--> 145 Av = self.Hv(v)
147 for eigvec, eigval in zip(self.vecs, self.vals):
148 coeff = eigval * self.my_inner(eigvec, v)
File ~/Documents/hessian.py:127, in Hessian.Hv(self, v)
122 elif self.hessian_type == 'Hessian':
123 grad = torch.autograd.grad(loss,
124 self.model.parameters(),
125 create_graph=True)
--> 127 Hg_ = torch.autograd.grad(grad,
128 self.model.parameters(),
129 v)
130 else:
131 raise Exception('Wrong hessian type!')
File ~/Coding/miniconda3/envs/torch-gpu/lib/python3.9/site-packages/torch/autograd/__init__.py:300, in grad(outputs, inputs, grad_outputs, retain_graph, create_graph, only_inputs, allow_unused, is_grads_batched)
298 return _vmap_internals._vmap(vjp, 0, 0, allow_none_pass_through=True)(grad_outputs_)
299 else:
--> 300 return Variable._execution_engine.run_backward( # Calls into the C++ engine to run the backward pass
301 t_outputs, grad_outputs_, retain_graph, create_graph, t_inputs,
302 allow_unused, accumulate_grad=False)
RuntimeError: derivative for aten::mps_max_pool2d_backward is not implemented
```
### Versions
Jupyter Lab, Python 3.9, PyTorch 1.13.0 Stable, M1 Mac
```
PyTorch version: 1.13.0
Is debug build: False
CUDA used to build PyTorch: None
ROCM used to build PyTorch: N/A
OS: macOS 13.0 (arm64)
GCC version: Could not collect
Clang version: Could not collect
CMake version: Could not collect
Libc version: N/A
Python version: 3.9.13 (main, Aug 25 2022, 18:24:45) [Clang 12.0.0 ] (64-bit runtime)
Python platform: macOS-13.0-arm64-arm-64bit
Is CUDA available: False
CUDA runtime version: No CUDA
CUDA_MODULE_LOADING set to: N/A
GPU models and configuration: No CUDA
Nvidia driver version: No CUDA
cuDNN version: No CUDA
HIP runtime version: N/A
MIOpen runtime version: N/A
Is XNNPACK available: True
Versions of relevant libraries:
[pip3] numpy==1.23.3
[pip3] torch==1.13.0
[pip3] torchaudio==0.13.0
[pip3] torchvision==0.14.0
[conda] numpy 1.23.3 py39h42add53_1
[conda] numpy-base 1.23.3 py39hadd41eb_1
[conda] pytorch 1.13.0 py3.9_0 pytorch
[conda] torchaudio 0.13.0 py39_cpu pytorch
[conda] torchvision 0.14.0 py39_cpu pytorch
```
cc @kulinseth @albanD @malfet @DenisVieriu97 @razarmehr @abhudev
| 4 |
4,231 | 88,883 |
Investigate why `test_aot_autograd_symbolic_exhaustive_masked_median_cpu_float32` is flaky
|
triaged, module: flaky-tests
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
This failed on trunk, but I couldn't reproduce locally on Linux/M1:
```
test_aot_autograd_symbolic_exhaustive_masked_median_cpu_float32 (__main__.TestEagerFusionOpInfoCPU) ... unexpected success (2.010s)
```
For me, it just xfailed as it should. Added a skip for now.
Perhaps related to sample inputs? It has some nan handling in the implementation, but that's just a guess.
Reference: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/88776
### Versions
https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/88776
| 0 |
4,232 | 88,882 |
Can't import torch --> OSError related to libcublasLt.so.11
|
oncall: binaries, module: cuda, module: regression
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
When I try to import torch in my docker container, I get an OSError:
`/usr/local/lib/python3.8/dist-packages/torch/lib/../../nvidia/cublas/lib/libcublas.so.11: undefined symbol: cublasLtGetStatusString, version libcublasLt.so.11`
I've followed the step from [Issue 51080](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/51080), which seems like it might be similar, but to no effect. Note, I don't have conda, so I didn't follow those specific steps, just the pip ones.
However, I have found that if I import tensorflow first, list my devices and then import torch it works fine...
```
try:
import torch
except OSError as e:
print(e)
import tensorflow as tf
tf.config.list_physical_devices()
import torch
print([torch.device(i) for i in range(torch.cuda.device_count())])
```
```
>>> /usr/local/lib/python3.8/dist-packages/torch/lib/../../nvidia/cublas/lib/libcublas.so.11: undefined symbol: cublasLtGetStatusString, version libcublasLt.so.11
>>> [device(type='cuda', index=0), device(type='cuda', index=1)]
```
Which makes me suspect that this is a different issue to [Issue 51080](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/51080).
The full traceback of `import torch` is:
```
OSError Traceback (most recent call last)
/root/GI_Data/KPVESQC5_AI4Q_P/Exp_workflow_a.ipynb Cell 2' in <cell line: 1>()
----> [1](vscode-notebook-cell://attached-container%2B7b22636f6e7461696e65724e616d65223a222f74625f656173657163222c2273657474696e6773223a7b22686f7374223a227373683a2f2f4750555f75736572227d7d/root/GI_Data/KPVESQC5_AI4Q_P/Exp_workflow_a.ipynb#ch0000009vscode-remote?line=0) import torch
File /usr/local/lib/python3.8/dist-packages/torch/__init__.py:191, in <module>
[180](file:///usr/local/lib/python3.8/dist-packages/torch/__init__.py?line=179) else:
[181](file:///usr/local/lib/python3.8/dist-packages/torch/__init__.py?line=180) # Easy way. You want this most of the time, because it will prevent
[182](file:///usr/local/lib/python3.8/dist-packages/torch/__init__.py?line=181) # C++ symbols from libtorch clobbering C++ symbols from other
(...)
[188](file:///usr/local/lib/python3.8/dist-packages/torch/__init__.py?line=187) #
[189](file:///usr/local/lib/python3.8/dist-packages/torch/__init__.py?line=188) # See Note [Global dependencies]
[190](file:///usr/local/lib/python3.8/dist-packages/torch/__init__.py?line=189) if USE_GLOBAL_DEPS:
--> [191](file:///usr/local/lib/python3.8/dist-packages/torch/__init__.py?line=190) _load_global_deps()
[192](file:///usr/local/lib/python3.8/dist-packages/torch/__init__.py?line=191) from torch._C import * # noqa: F403
[194](file:///usr/local/lib/python3.8/dist-packages/torch/__init__.py?line=193) # Appease the type checker; ordinarily this binding is inserted by the
[195](file:///usr/local/lib/python3.8/dist-packages/torch/__init__.py?line=194) # torch._C module initialization code in C
File /usr/local/lib/python3.8/dist-packages/torch/__init__.py:153, in _load_global_deps()
[150](file:///usr/local/lib/python3.8/dist-packages/torch/__init__.py?line=149) here = os.path.abspath(__file__)
[151](file:///usr/local/lib/python3.8/dist-packages/torch/__init__.py?line=150) lib_path = os.path.join(os.path.dirname(here), 'lib', lib_name)
--> [153](file:///usr/local/lib/python3.8/dist-packages/torch/__init__.py?line=152) ctypes.CDLL(lib_path, mode=ctypes.RTLD_GLOBAL)
File /usr/lib/python3.8/ctypes/__init__.py:373, in CDLL.__init__(self, name, mode, handle, use_errno, use_last_error, winmode)
[370](file:///usr/lib/python3.8/ctypes/__init__.py?line=369) self._FuncPtr = _FuncPtr
[372](file:///usr/lib/python3.8/ctypes/__init__.py?line=371) if handle is None:
--> [373](file:///usr/lib/python3.8/ctypes/__init__.py?line=372) self._handle = _dlopen(self._name, mode)
[374](file:///usr/lib/python3.8/ctypes/__init__.py?line=373) else:
[375](file:///usr/lib/python3.8/ctypes/__init__.py?line=374) self._handle = handle
OSError: /usr/local/lib/python3.8/dist-packages/torch/lib/../../nvidia/cublas/lib/libcublas.so.11: undefined symbol: cublasLtGetStatusString, version libcublasLt.so.11
```
### Versions
Python version: 3.8.10
Docker version: 20.10.21
BASE_IMAGE=tensorflow/tensorflow
IMAGE_VERSION=2.9.1-gpu-jupyter
Output of `nvcc -V`:
```
nvcc: NVIDIA (R) Cuda compiler driver
Copyright (c) 2005-2021 NVIDIA Corporation
Built on Sun_Feb_14_21:12:58_PST_2021
Cuda compilation tools, release 11.2, V11.2.152
Build cuda_11.2.r11.2/compiler.29618528_0
```
Output of `torch.__version__` in python:
```
'1.13.0+cu117'
```
Output of collect_env.py:
```
PyTorch version: N/A
Is debug build: N/A
CUDA used to build PyTorch: N/A
ROCM used to build PyTorch: N/A
OS: Ubuntu 20.04.4 LTS (x86_64)
GCC version: (Ubuntu 9.4.0-1ubuntu1~20.04.1) 9.4.0
Clang version: Could not collect
CMake version: Could not collect
Libc version: glibc-2.31
Python version: 3.8.10 (default, Mar 15 2022, 12:22:08) [GCC 9.4.0] (64-bit runtime)
Python platform: Linux-5.15.0-52-generic-x86_64-with-glibc2.29
Is CUDA available: N/A
CUDA runtime version: 11.2.152
CUDA_MODULE_LOADING set to: N/A
GPU models and configuration:
GPU 0: NVIDIA A10
GPU 1: NVIDIA A10
Nvidia driver version: 520.61.05
cuDNN version: Probably one of the following:
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn.so.8.1.0
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_adv_infer.so.8.1.0
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_adv_train.so.8.1.0
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_cnn_infer.so.8.1.0
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_cnn_train.so.8.1.0
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_ops_infer.so.8.1.0
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_ops_train.so.8.1.0
HIP runtime version: N/A
MIOpen runtime version: N/A
Is XNNPACK available: N/A
Versions of relevant libraries:
[pip3] numpy==1.22.4
[pip3] torch==1.13.0
[pip3] torchaudio==0.13.0
[pip3] torchvision==0.14.0
[conda] Could not collect
```
cc @ezyang @seemethere @malfet @ngimel
| 4 |
4,233 | 88,880 |
Add alphatensor support for faster matrix multiplication?
|
feature, triaged, matrix multiplication
|
### 🚀 The feature, motivation and pitch
I didn't find any proposal or issue about it.
In short alphatensor is a way to find a new faster algorithms for matrix multiplication operations.
It even have a functionality to find the best algorithm adapted to particular hardware.
It makes sense to add support for it in some way or another, becuase almost 100% of running models on pytorch
is extensively using matrix multiplication operations.
See - [alphatensor](https://github.com/deepmind/alphatensor)
cc @jianyuh @nikitaved @pearu @mruberry @walterddr @IvanYashchuk @xwang233 @Lezcano
| 2 |
4,234 | 93,617 |
[Inductor] Input Buffers Should Be Representable As Storage And Layout
|
triaged, oncall: pt2
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
[InputBuffer](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/blob/master/torch/_inductor/ir.py#L1897)'s currently do not have an associated storage. This prevents correct handling of aliased inputs - see [TODO here](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/blob/master/torch/_inductor/graph.py#L202).
When calling [require_stride_order](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/blob/master/torch/_inductor/ir.py#L2465), because `is_storage_and_layout` returns False for InputBuffers we fall through to an unnecessary copy.
A shorter term fix would be to handle InputBuffers in `require_stride_order`.
cc @ezyang @soumith @msaroufim @wconstab @ngimel @bdhirsh
| 0 |
4,235 | 88,842 |
test/test_ops.py is segfaulting on master build with DEBUG assets
|
high priority, module: ci, triaged, module: testing
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
```
test_dtypes__refs_add_cpu (__main__.TestCommonCPU) ... terminate called after throwing an instance of 'c10::Error'
what(): !c10::impl::HermeticPyObjectTLS::get_state() INTERNAL ASSERT FAILED at "/scratch/chourdiaanjali/work/pytorch/torch/csrc/autograd/python_variable.cpp":310, please report a bug to PyTorch.
Exception raised from decref at /scratch/chourdiaanjali/work/pytorch/torch/csrc/autograd/python_variable.cpp:310 (most recent call first):
frame #0: <unknown function> + 0xce7f5 (0x7ff1c2c247f5 in /scratch/chourdiaanjali/work/pytorch/torch/lib/libc10.so)
frame #1: std::function<std::__cxx11::basic_string<char, std::char_traits<char>, std::allocator<char> > ()>::operator()() const + 0x4c (0x7ff1f6293cb0 in /scratch/chourdiaanjali/work/pytorch/torch/lib/libtorch_cpu.so)
frame #2: c10::Error::Error(c10::SourceLocation, std::__cxx11::basic_string<char, std::char_traits<char>, std::allocator<char> >) + 0x40 (0x7ff1c2c23676 in /scratch/chourdiaanjali/work/pytorch/torch/lib/libc10.so)
frame #3: c10::detail::torchCheckFail(char const*, char const*, unsigned int, char const*) + 0x97 (0x7ff1c2c216f6 in /scratch/chourdiaanjali/work/pytorch/torch/lib/libc10.so)
frame #4: <unknown function> + 0xae356e (0x7ff204ef856e in /scratch/chourdiaanjali/work/pytorch/torch/lib/libtorch_python.so)
frame #5: <unknown function> + 0x10ad050 (0x7ff2054c2050 in /scratch/chourdiaanjali/work/pytorch/torch/lib/libtorch_python.so)
frame #6: c10::TensorImpl::destroy_pyobj_if_needed() + 0x102 (0x7ff1c2beb724 in /scratch/chourdiaanjali/work/pytorch/torch/lib/libc10.so)
frame #7: c10::TensorImpl::~TensorImpl() + 0x2a (0x7ff1c2bea318 in /scratch/chourdiaanjali/work/pytorch/torch/lib/libc10.so)
frame #8: c10::TensorImpl::~TensorImpl() + 0x18 (0x7ff1c2bea390 in /scratch/chourdiaanjali/work/pytorch/torch/lib/libc10.so)
frame #9: <unknown function> + 0x291d0e8 (0x7ff1f0ab40e8 in /scratch/chourdiaanjali/work/pytorch/torch/lib/libtorch_cpu.so)
frame #10: <unknown function> + 0x29f757e (0x7ff1f0b8e57e in /scratch/chourdiaanjali/work/pytorch/torch/lib/libtorch_cpu.so)
frame #11: <unknown function> + 0x29f6242 (0x7ff1f0b8d242 in /scratch/chourdiaanjali/work/pytorch/torch/lib/libtorch_cpu.so)
frame #12: torch::autograd::SavedVariable::reset_data() + 0x3d (0x7ff1f61ab019 in /scratch/chourdiaanjali/work/pytorch/torch/lib/libtorch_cpu.so)
frame #13: <unknown function> + 0x6874cc9 (0x7ff1f4a0bcc9 in /scratch/chourdiaanjali/work/pytorch/torch/lib/libtorch_cpu.so)
frame #14: torch::autograd::deleteNode(torch::autograd::Node*) + 0x33 (0x7ff1f613653f in /scratch/chourdiaanjali/work/pytorch/torch/lib/libtorch_cpu.so)
frame #15: std::_Sp_counted_deleter<torch::autograd::generated::PowBackward1*, void (*)(torch::autograd::Node*), std::allocator<void>, (__gnu_cxx::_Lock_policy)2>::_M_dispose() + 0x2c (0x7ff1f4c1f7d4 in /scratch/chourdiaanjali/work/pytorch/torch/lib/libtorch_cpu.so)
frame #16: std::_Sp_counted_base<(__gnu_cxx::_Lock_policy)2>::_M_release() + 0x42 (0x7ff204f0dec4 in /scratch/chourdiaanjali/work/pytorch/torch/lib/libtorch_python.so)
frame #17: std::__shared_count<(__gnu_cxx::_Lock_policy)2>::~__shared_count() + 0x27 (0x7ff204f08ad3 in /scratch/chourdiaanjali/work/pytorch/torch/lib/libtorch_python.so)
frame #18: <unknown function> + 0x68660b4 (0x7ff1f49fd0b4 in /scratch/chourdiaanjali/work/pytorch/torch/lib/libtorch_cpu.so)
frame #19: <unknown function> + 0x68660d0 (0x7ff1f49fd0d0 in /scratch/chourdiaanjali/work/pytorch/torch/lib/libtorch_cpu.so)
frame #20: <unknown function> + 0x7f603fc (0x7ff1f60f73fc in /scratch/chourdiaanjali/work/pytorch/torch/lib/libtorch_cpu.so)
frame #21: <unknown function> + 0x7f60444 (0x7ff1f60f7444 in /scratch/chourdiaanjali/work/pytorch/torch/lib/libtorch_cpu.so)
frame #22: std::default_delete<c10::AutogradMetaInterface>::operator()(c10::AutogradMetaInterface*) const + 0x2e (0x7ff205170d88 in /scratch/chourdiaanjali/work/pytorch/torch/lib/libtorch_python.so)
frame #23: std::unique_ptr<c10::AutogradMetaInterface, std::default_delete<c10::AutogradMetaInterface> >::~unique_ptr() + 0x49 (0x7ff20516effb in /scratch/chourdiaanjali/work/pytorch/torch/lib/libtorch_python.so)
frame #24: c10::TensorImpl::~TensorImpl() + 0x6a (0x7ff1c2bea358 in /scratch/chourdiaanjali/work/pytorch/torch/lib/libc10.so)
frame #25: c10::TensorImpl::~TensorImpl() + 0x18 (0x7ff1c2bea390 in /scratch/chourdiaanjali/work/pytorch/torch/lib/libc10.so)
frame #26: <unknown function> + 0xaf9a5a (0x7ff204f0ea5a in /scratch/chourdiaanjali/work/pytorch/torch/lib/libtorch_python.so)
frame #27: <unknown function> + 0xaf4498 (0x7ff204f09498 in /scratch/chourdiaanjali/work/pytorch/torch/lib/libtorch_python.so)
frame #28: <unknown function> + 0xae4420 (0x7ff204ef9420 in /scratch/chourdiaanjali/work/pytorch/torch/lib/libtorch_python.so)
frame #29: <unknown function> + 0xae44a2 (0x7ff204ef94a2 in /scratch/chourdiaanjali/work/pytorch/torch/lib/libtorch_python.so)
frame #30: <unknown function> + 0x10c5e2c (0x7ff2054dae2c in /scratch/chourdiaanjali/work/pytorch/torch/lib/libtorch_python.so)
frame #31: <unknown function> + 0x10ae081 (0x7ff2054c3081 in /scratch/chourdiaanjali/work/pytorch/torch/lib/libtorch_python.so)
frame #32: THPVariable_subclass_dealloc(_object*) + 0x32e (0x7ff2054caa34 in /scratch/chourdiaanjali/work/pytorch/torch/lib/libtorch_python.so)
<omitting python frames>
frame #43: THPSize_NewFromSymSizes(at::Tensor const&) + 0x64 (0x7ff205397d3b in /scratch/chourdiaanjali/work/pytorch/torch/lib/libtorch_python.so)
frame #44: THPVariable_get_shape(THPVariable*, void*) + 0xb9 (0x7ff2054c7e55 in /scratch/chourdiaanjali/work/pytorch/torch/lib/libtorch_python.so)
frame #60: <unknown function> + 0x18add45 (0x7ff205cc2d45 in /scratch/chourdiaanjali/work/pytorch/torch/lib/libtorch_python.so)
frame #61: <unknown function> + 0x18b21b4 (0x7ff205cc71b4 in /scratch/chourdiaanjali/work/pytorch/torch/lib/libtorch_python.so)
frame #62: c10::BoxedKernel::makeFromFunctor<torch::impl::dispatch::PythonKernelHolder>(std::unique_ptr<torch::impl::dispatch::PythonKernelHolder, std::default_delete<torch::impl::dispatch::PythonKernelHolder> >)::{lambda(c10::OperatorKernel*, c10::OperatorHandle const&, c10::DispatchKeySet, std::vector<c10::IValue, std::allocator<c10::IValue> >*)#1}::_FUN(c10::OperatorKernel*, c10::OperatorHandle const&, c10::DispatchKeySet, std::vector<c10::IValue, std::allocator<c10::IValue> >*) + 0x38 (0x7ff205cc71ef in /scratch/chourdiaanjali/work/pytorch/torch/lib/libtorch_python.so)
frame #63: c10::BoxedKernel::callBoxed(c10::OperatorHandle const&, c10::DispatchKeySet, std::vector<c10::IValue, std::allocator<c10::IValue> >*) const + 0x85 (0x7ff2054d5f27 in /scratch/chourdiaanjali/work/pytorch/torch/lib/libtorch_python.so)
Aborted (core dumped)
```
### Versions
master
cc @ezyang @gchanan @zou3519 @seemethere @malfet @pytorch/pytorch-dev-infra
| 12 |
4,236 | 88,838 |
[RFC] PyTorch DistributedTensor
|
oncall: distributed, module: dtensor
|
### 🚀 The feature, motivation and pitch
# RFC: PyTorch DistributedTensor
We have been developing a DistributedTensor (a.k.a DTensor) concept under the [pytorch/tau](https://github.com/pytorch/tau/tree/main/spmd/tensor) repo in the past few months, and now we are moving the implementation over to pytorch with the stack https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/88180. This RFC proposes the DistributedTensor to torch.distributed. Any early feedbacks are welcomed!
**Update**:
DTensor now available in PyTorch 2.0 and nightly build! You can now play around with DTensor even in a co-lab Notebook! see a quick e2e tutorial here https://colab.research.google.com/drive/12Pl5fvh0eLPUrcVO7s6yY4n2_RZo8pLR#scrollTo=stYPKb9Beq4e
## Introduction
We propose distributed tensor primitives to allow easier distributed computation authoring in SPMD(Single Program Multiple Devices) paradigm. The primitives are simple but powerful when used to express tensor distributions with both sharding and replication parallelism strategies. This could empower native Tensor parallelism among other advanced parallelism explorations. For example, to shard a big tensor across devices with 3 lines of code:
```python
import torch
from torch.distributed import DeviceMesh, Shard, distribute_tensor
# Create a mesh topology with the available devices.
mesh = DeviceMesh("cuda", list(range(world_size)))
big_tensor = torch.randn(100000, 88)
# Shard this tensor over the mesh by sharding `big_tensor`'s 0th dimension over the 0th dimension of `mesh`.
my_dtensor = distribute_tensor(big_tensor, mesh, [Shard(dim=0)])
```
## Motivation
Today there are mainly three ways to scale up distributed training: Data Parallel, Tensor Parallel and Pipeline Parallel. Each of them works on a separate dimension where solutions have been built independently (i.e. PyTorch DDP, FSDP, ShardedTensor, PiPPy, etc.). When training really large models, users would like to use these technologies together (i.e. 3-D Parallelism), while the interoperability of the existing solutions are not great and often hard to use (i.e. users might want arbitrary combinations of the data parallel, tensor parallel and pipeline parallel). This is becoming an issue for users and one of the biggest reasons is that there’s no common abstractions that build the bridge between different parallelism strategies.
An ideal scenario is that users could just build their models like in a single node/device, without worrying about how to do distributed training in a cluster, and our solutions could help them run distributed training in an efficient manner. For example, researchers just need to build their big transformer model, and PyTorch Distributed automatically figures out how to split the model and run pipeline parallel across different nodes, how to run data parallel and tensor parallel within each node. In order to achieve this, we need some common abstractions to represent data distribution and run the distributed computation.
There're many recent works that working on tensor level parallelism to provide common abstractions, see the `Related Works` in the last section for more details. Inspired by [GSPMD](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2105.04663.pdf), [Oneflow](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2110.15032.pdf) and [TF’s DTensor](https://www.tensorflow.org/guide/dtensor_overview), we introduce a DistributedTensor concept to represent generic data distributions across hosts. DistributedTensor is the next evolution of ShardedTensor and provides basic abstractions to distribute storage and compute. It serves as one of the basic building blocks for distributed program translations and describes the layout of a distributed training program. With the DistributedTensor abstraction, we can seamlessly build parallelism strategies such as tensor parallelism, DDP and FSDP.
## Value Propsition
DistributedTensor primarily:
- Offers a uniform way to save/load state dict during checkpointing, even when there’re complex data distribution strategies such as combining tensor parallelism with parameter sharding in FSDP.
- Could natively offer Tensor Parallelism solution in eager mode, just like our current ShardedTensor solution. Moreover, it gives additional flexibility for advanced users who want to mix sharding and replication.
- Could be the entry point of a SPMD programming model for ML System Engineers, providing good UX to mix up different types of parallelism, and could be used as a fundamental building block of a compiler based distributed training.
## PyTorch DistributedTensor
### DistributedTensor API
We offer both a lower level DistributedTensor API and a module level API to create a `nn.Module` with “distributed” parameters.
#### Basic DistributedTensor API Examples
Here are some basic DistributedTensor API examples that showcase:
1. How to construct a DistributedTensor directly, to represent different types of sharding, replication, sharding + replication strategies.
2. How to create DistributedTensor from a local `torch.Tensor`.
3. How to “reshard” an existing DistributedTensor to a different DistributedTensor with modified placement strategy or world size.
```python
import torch
import torch.distributed as distributed
from torch.distributed import DTensor, DeviceMesh, Shard, Replicate, distribute_module
# construct a device mesh with available devices (multi-host or single host)
device_mesh = DeviceMesh(device_type="cuda", [0, 1, 2, 3])
# if we want to do row-wise sharding
rowwise_placement=[Shard(0)]
# if we want to do col-wise sharding
colwise_placement=[Shard(1)]
# distributed tensor returned will be sharded across the dimension specified in placements
distributed.empty((8, 12), device_mesh=device_mesh, placements=rowwise_placement)
# if we want to do replication across a certain device list
replica_placement = [Replicate()]
# distributed tensor will be replicated to all four GPUs.
distributed.empty((8, 12), device_mesh=device_mesh, placements=replica_placement)
# if we want to distributed a tensor with both replication and sharding
device_mesh = DeviceMesh(device_type="cuda", [[0, 1], [2, 3]])
# replicate across the first dimension of device mesh, then sharding on the second dimension of device mesh
spec=[Replicate(), Shard(0)]
distributed.empty((8, 8), device_mesh=device_mesh, placements=spec)
# create a DistributedTensor that shards on dim 0, from a local torch.Tensor
local_tensor = torch.randn((8, 8), requires_grad=True)
rowwise_tensor = DTensor.from_local(local_tensor, device_mesh, rowwise_placement)
# reshard the current rowise tensor to a colwise tensor or replicate tensor
colwise_tensor = rowwise_tensor.redistribute(device_mesh, colwise_placement)
replica_tensor = colwise_tensor.redistribute(device_mesh, replica_placement)
```
#### High level User Facing APIs
Users can use DistributedTensor tensor constructors directly to create a distributed tensor (i.e. `distributed.ones/empty`), but for existing modules like nn.Linear that are already having torch.Tensor as parameters, how to make them distributed parameters? We offer a way to directly distribute a torch.Tensor and a module level APIs to directly distribute the module parameters. Below is the high level API we introduce:
```python
def distribute_tensor(tensor: torch.Tensor, device_mesh: DeviceMesh=None, placements: List[Placement]=None):
'''
distribute the tensor according to device_mesh and placements, `tensor` could be a "meta" tensor.
'''
def distribute_module(
module: nn.Module,
device_mesh: DeviceMesh=None,
partition_fn: Callable[[str, nn.Module, DeviceMesh], ...]=None,
input_fn: Callable[...., None]=None,
output_fn: Callable[...., None]=None,
):
'''
This function converts all module parameters to distributed tensor parameters according to the `partition_fn` specified.
It could also control the input/output of the module by specifying the `input_fn` and `output_fn`.
'''
```
#### High level API examples:
```python
def MyModule(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super.__init__()
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(8, 8)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(8, 8)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
def forward(self, input):
return self.relu(self.fc1(input) + self.fc2(input))
mesh = DeviceMesh(device_type="cuda", [[0, 1], [2, 3]])
def shard_params(mod_name, mod, mesh):
rowwise_placement = [Shard(0)]
def to_dist_tensor(t): return distribute_tensor(t, mesh, rowwise_placement)
mod._apply(to_dist_tensor)
sharded_module = distribute_module(model, device_mesh, partition_fn=shard_params)
def shard_fc(mod_name, mod, mesh):
rowwise_placement = [Shard(0)]
if mod_name == "fc1":
mod.weight = torch.nn.Parameter(distribute_tensor(mod.weight, mesh, rowwise_placement))
sharded_module = distribute_module(model, device_mesh, partition_fn=shard_fc)
```
## Compiler and DistributedTensor
DistributedTensor provides efficient solutions for cases like Tensor Parallelism. But when using the DTensor's replication in a data parallel fashion, it might become observably slow compared to our existing solutions like DDP/FSDP. This is mainly because existing solutions like DDP/FSDP could have the global view of entire model architecture, thus could optimize for data parallel specifically, i.e. collective fusion and computation overlap, etc. DistributedTensor itself is only a Tensor-like object and only knows its local computation operation, it does not know the subsequent operations that happened afterwards.
In order to make the performance on par when using DistributedTensor directly to do data parallel training, DistributedTensor also needs the global view to do things like communication optimization. We are exploring a compiler based solution accompanied with DistributedTensor so that we could run optimizations on top of it, which will be shared later.
## Related Works
This work is mainly inspired by [GSPMD](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2105.04663.pdf), [Oneflow](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2110.15032.pdf) and [TF’s DTensor](https://www.tensorflow.org/guide/dtensor_overview). All of these three works use a single “distributed tensor” concept for both replication and sharding, and the solutions could enable users to build up their distributed training program in a uniform SPMD programming model. Specifically:
GSPMD:
- GSPMD is now the fundamental component of JAX/TensorFlow distributed training and enables various optimizations with the XLA compiler to allow users to train their models efficiently in a large scale setting.
- Fundamentally, GSPMD have three types of sharding strategies within a tensor: “tiled”, “replicated”, “partially tiled” to represent sharding and replication.
- At the core of GSPMD Partitioner, it utilizes the XLA compiler to do advanced optimizations, i.e. sharding propagation and compiler based fusion.
- XLA mark_sharding API: PyTorch XLA’s [mark_sharding](https://github.com/pytorch/xla/pull/3476) API uses [XLAShardedTensor](https://github.com/pytorch/xla/issues/3871) abstraction (i.e. sharding specs) in PyTorch/XLA. Under the hood XLAShardedTensor is utilizing the GPSMD partitioner to enable SPMD style training on TPU.
OneFlow GlobalTensor:
- OneFlow is building up their own solution of the “GlobalTensor” concept, which is a variant form of GSPMD sharding, allowing users to explore different parallel strategies with GlobalTensor.
- OneFlow also has three types of tensor, but they are slightly different from GSPMD: “split”, “broadcast”, and “partial sum”. They don’t use partially tiled and instead have a concept of partial sum to partition the values.
TensorFlow DTensor:
- [DTensor Concepts](https://www.tensorflow.org/guide/dtensor_overview) is an extension of TensorFlow synchronous distributed training. its sharding API, supported features and its compilation passes with MLIR.
- DTensor also allows sharding and replication on an n-d mesh like device network.
- DTensor implements MLIR passes to do propagation and operator implementations.
There are also several cutting edge research fields that embeds tensor sharding as part of the system, i.e. [Megatron-LM](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1909.08053.pdf) for tensor parallelism on Transformer based models. [DeepSpeed](https://github.com/microsoft/DeepSpeed) for training large scale models with different optimization techniques on top of tensor sharding.
### Alternatives
In PyTorch, we have existing [ShardedTensor](https://docs.google.com/document/d/1WEjwKYv022rc1lSrYcNWh3Xjx9fJC7zsrTKTg0wbPj0/edit?usp=sharing) work in the prototype stage, which introduces basic PyTorch sharding primitives as our Tensor Parallelism solution. But ShardedTensor only has tensor sharding support, which makes it hard to be used by users to describe other data distributions strategies like replication or replication + sharding. As a distributed system developer who wants to explore more parallelism patterns, it’s crucial to have a basic building block that describes the data distribution in a uniform way. This DistributedTensor RFC aims at solving this and provide a fundamental abstraction for distributed training.
### Additional context
We are gathering early feedbacks about this proposal. We have also posted this [RFC](https://dev-discuss.pytorch.org/t/rfc-pytorch-distributedtensor/740) to the dev-discuss forum, please feel free to comment directly in this issue or in the forum post. To see a complete design doc with additional details about this proposal, please refer to this [doc](https://docs.google.com/document/d/1nFeJ8NSFNhNlCkNgWK31ZGRqm1L9rd0i_XN_RprphaI/edit#heading=h.6sovjqv9jiqn)
cc @mrshenli @pritamdamania87 @zhaojuanmao @satgera @rohan-varma @gqchen @aazzolini @osalpekar @jiayisuse @H-Huang @kwen2501 @awgu @fduwjj @XilunWu @gnadathur @anj-s @zdevito @ezyang @albanD
| 24 |
4,237 | 88,813 |
Inductor may merge two output tensors into one
|
triaged, module: inductor
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
Consider the following example:
```python
import torch._dynamo
import logging
def g(a):
b = a * 2
c = a * 2
return b, c
x = torch.rand((1000000,), device="cuda", requires_grad=True)
expect = g(x)
actual = torch._dynamo.optimize("inductor")(g)(x)
assert expect[0] is not expect[1]
assert actual[0] is actual[1]
```
The outputs have been merged into a single tensor, so downstream users of this function may get silently wrong results if `a` or `b` are mutated.
### Versions
```
PyTorch version: 1.14.0a0+git034872d
Is debug build: False
CUDA used to build PyTorch: 11.7
ROCM used to build PyTorch: N/A
OS: Ubuntu 22.04.1 LTS (x86_64)
GCC version: (conda-forge gcc 9.5.0-17) 9.5.0
Clang version: Could not collect
CMake version: version 3.24.1
Python version: 3.8 (64-bit runtime)
Is CUDA available: True
CUDA runtime version: Could not collect
GPU models and configuration:
GPU 0: NVIDIA GeForce RTX 2060
GPU 1: NVIDIA GeForce RTX 2060
Nvidia driver version: 515.65.01
cuDNN version: Probably one of the following:
/usr/local/cuda-11.7.1/targets/x86_64-linux/lib/libcudnn.so.8
/usr/local/cuda-11.7.1/targets/x86_64-linux/lib/libcudnn_adv_infer.so.8
/usr/local/cuda-11.7.1/targets/x86_64-linux/lib/libcudnn_adv_train.so.8
/usr/local/cuda-11.7.1/targets/x86_64-linux/lib/libcudnn_cnn_infer.so.8
/usr/local/cuda-11.7.1/targets/x86_64-linux/lib/libcudnn_cnn_train.so.8
/usr/local/cuda-11.7.1/targets/x86_64-linux/lib/libcudnn_ops_infer.so.8
/usr/local/cuda-11.7.1/targets/x86_64-linux/lib/libcudnn_ops_train.so.8
HIP runtime version: N/A
MIOpen runtime version: N/A
```
cc @mlazos @soumith @voznesenskym @yanboliang @penguinwu @anijain2305 @EikanWang @jgong5 @Guobing-Chen @chunyuan-w @XiaobingSuper @zhuhaozhe @blzheng @Xia-Weiwen @wenzhe-nrv @jiayisunx @desertfire
| 2 |
4,238 | 88,810 |
Return the attention weights using the Transformer Encoder class.
|
triaged, oncall: transformer/mha
|
### 🚀 The feature, motivation and pitch
Hey, when using the Transformer Encoder class it would be nice to have ```need_weights``` as an additional variable that can be passed down to ```F.multi_head_attention_forward ```. Right now the feature of returning the attention weights is as far as my understanding goes not accessible from the Transformer class since ```need_weights``` is manually set to false. It would be great if this was possible since one could very easily compute the attention rollout.
### Alternatives
_No response_
### Additional context
_No response_
cc @jbschlosser @bhosmer @cpuhrsch @erichan1
| 6 |
4,239 | 93,616 |
[Inductor] Vectorize Embedding Lookup in CPP
|
triaged, oncall: pt2, module: cpu inductor
|
We explicitly disable vectorization on indirect indexing right now:
https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/blob/7c353eb39559f2c8897a0580700dd0a6f943d34f/torch/_inductor/codegen/cpp.py#L929
It is a conservative design choice and would miss some cases like embedding with large enough vector length. Below is the generated code from DistilBertForQuestionAnswering as an example:
```c++
#include "/tmp/torchinductor_jgong5/uh/cuhop6zhqdvygrhcsy2duu7yusyui3ja4mmjk5kccnhxojwtrwhg.h"
extern "C" void kernel(const long* __restrict__ in_ptr0,
const float* __restrict__ in_ptr1,
const long* __restrict__ in_ptr2,
const float* __restrict__ in_ptr3,
const float* __restrict__ in_ptr4,
const float* __restrict__ in_ptr5,
float* __restrict__ out_ptr0,
float* __restrict__ out_ptr1,
float* __restrict__ out_ptr2,
float* __restrict__ out_ptr3)
{
#pragma GCC ivdep
for(long i0=0; i0<128; i0+=1)
{
{
{
float tmp5 = 0;
for(long i1=0; i1<768; i1+=1)
{
{
auto tmp0 = in_ptr0[i0];
auto tmp2 = in_ptr2[i0];
auto tmp1 = in_ptr1[i1 + (768*tmp0)];
auto tmp3 = in_ptr3[i1 + (768*tmp2)];
auto tmp4 = tmp1 + tmp3;
tmp5 += tmp4;
}
}
out_ptr0[i0] = tmp5;
}
}
}
#pragma GCC ivdep
for(long i0=0; i0<128; i0+=1)
{
{
{
float tmp10 = 0;
float tmp11 = 0;
for(long i1=0; i1<768; i1+=1)
{
{
auto tmp0 = in_ptr0[i0];
auto tmp2 = in_ptr2[i0];
auto tmp5 = out_ptr0[i0];
auto tmp1 = in_ptr1[i1 + (768*tmp0)];
auto tmp3 = in_ptr3[i1 + (768*tmp2)];
auto tmp4 = tmp1 + tmp3;
auto tmp6 = static_cast<float>(768);
auto tmp7 = tmp5 / tmp6;
auto tmp8 = tmp4 - tmp7;
auto tmp9 = tmp8 * tmp8;
tmp10 += tmp9;
tmp11 += tmp4;
}
}
out_ptr1[i0] = tmp10;
out_ptr2[i0] = tmp11;
}
}
}
#pragma GCC ivdep
for(long i0=0; i0<128; i0+=1)
{
#pragma GCC ivdep
for(long i1=0; i1<768; i1+=1)
{
{
{
auto tmp0 = in_ptr0[i0];
auto tmp2 = in_ptr2[i0];
auto tmp5 = out_ptr2[i0];
auto tmp9 = out_ptr1[i0];
auto tmp16 = in_ptr4[i1];
auto tmp18 = in_ptr5[i1];
auto tmp1 = in_ptr1[i1 + (768*tmp0)];
auto tmp3 = in_ptr3[i1 + (768*tmp2)];
auto tmp4 = tmp1 + tmp3;
auto tmp6 = static_cast<float>(768);
auto tmp7 = tmp5 / tmp6;
auto tmp8 = tmp4 - tmp7;
auto tmp10 = tmp9 / tmp6;
auto tmp11 = static_cast<float>(1e-12);
auto tmp12 = tmp10 + tmp11;
auto tmp13 = std::sqrt(tmp12);
auto tmp14 = 1 / tmp13;
auto tmp15 = tmp8 * tmp14;
auto tmp17 = tmp15 * tmp16;
auto tmp19 = tmp17 + tmp18;
out_ptr3[i1 + (768*i0)] = tmp19;
}
}
}
}
}
```
cc @ezyang @soumith @msaroufim @wconstab @ngimel @bdhirsh
| 0 |
4,240 | 88,805 |
[feature request] Get/set fastmath CPU bit (and some other FPU flags?)
|
module: numerical-stability, module: cpu, triaged
|
### 🚀 The feature, motivation and pitch
Originally proposed at: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/81690#issuecomment-1309911123
Loading third-party libraries may affect CPU fpu bits such as denormals mode and fastmath (also affecting CPU reproducibility, see https://moyix.blogspot.com/2022/09/someones-been-messing-with-my-subnormals.html). It's useful to be able to detect and reset these bits directly from PyTorch API. Currently there only exists `torch.set_flush_denormal`. There is no `get_flush_denormal`.
It would be useful to have extensive set of functions for getting/setting these CPU flags (FTZ/DAZ?). It may also be good for having a single function for getting/setting all such flags. Then it'd be easy to dump to a file all flags and then recover them in one go and also provide end-user visibility into this age-old concern.
### Alternatives
_No response_
### Additional context
_No response_
cc @VitalyFedyunin @jgong5 @mingfeima @XiaobingSuper @sanchitintel @ashokei @jingxu10
| 5 |
4,241 | 88,802 |
ImportError: libcupti.so.11.2: cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory
|
module: build, module: cuda, triaged
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
ImportError Traceback (most recent call last)
4 import random
5 import copy
----> 6 import torch
7 #import learn2learn as l2l
8 import numpy as np
File /dev_data_1/conda/envs/meta/lib/python3.8/site-packages/torch/__init__.py:202, in <module>
200 if USE_GLOBAL_DEPS:
201 _load_global_deps()
--> 202 from torch._C import * # noqa: F403
204 # Appease the type checker; ordinarily this binding is inserted by the
205 # torch._C module initialization code in C
206 if TYPE_CHECKING:
ImportError: libcupti.so.11.2: cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory
### Versions
torch 1.12.0
python 3.8.13
cc @malfet @seemethere @ngimel
| 2 |
4,242 | 88,801 |
[ONNX] Convert to onnx scatter op and LSTMCell op and for Loop
|
module: onnx, triaged, onnx-needs-info
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
```python
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
class Attention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size, num_classes):
super(Attention, self).__init__()
self.attention_cell = AttentionCell(input_size, hidden_size, num_classes)
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.num_classes = num_classes
self.generator = nn.Linear(hidden_size, num_classes)
def _char_to_onehot(self, input_char, onehot_dim=38):
input_char = input_char.unsqueeze(1)
batch_size = input_char.size(0)
one_hot = torch.FloatTensor(batch_size, onehot_dim).zero_().to(device)
one_hot = one_hot.scatter(1, input_char, 1)
return one_hot
def forward(self, batch_H, text, is_train=False, batch_max_length=25):
batch_size = batch_H.size(0)
num_steps = batch_max_length + 1 # +1 for [s] at end of sentence.
output_hiddens = torch.FloatTensor(batch_size, num_steps, self.hidden_size).fill_(0).to(device)
hidden = (torch.FloatTensor(batch_size, self.hidden_size).fill_(0).to(device),torch.FloatTensor(batch_size, self.hidden_size).fill_(0).to(device))
if is_train:
for i in range(num_steps):
# one-hot vectors for a i-th char. in a batch
char_onehots = self._char_to_onehot(text[:, i], onehot_dim=self.num_classes)
# hidden : decoder's hidden s_{t-1}, batch_H : encoder's hidden H, char_onehots : one-hot(y_{t-1})
hidden, alpha = self.attention_cell(hidden, batch_H, char_onehots)
output_hiddens[:, i, :] = hidden[0] # LSTM hidden index (0: hidden, 1: Cell)
probs = self.generator(output_hiddens)
else:
targets = torch.LongTensor(batch_size.item()).fill_(0).to(device) # [GO] token
probs = torch.FloatTensor(batch_size, num_steps, self.num_classes).fill_(0).to(device)
for i in range(num_steps):
char_onehots = self._char_to_onehot(targets, onehot_dim=self.num_classes)
hidden, alpha = self.attention_cell(hidden, batch_H, char_onehots)
probs_step = self.generator(hidden[0])
probs[:, i, :] = probs_step
_, next_input = probs_step.max(1)
targets = next_input
return probs # batch_size x num_steps x num_classes
class AttentionCell(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size, num_embeddings):
super(AttentionCell, self).__init__()
self.i2h = nn.Linear(input_size, hidden_size, bias=False)
self.h2h = nn.Linear(hidden_size, hidden_size) # either i2i or h2h should have bias
self.score = nn.Linear(hidden_size, 1, bias=False)
self.rnn = nn.LSTMCell(input_size + num_embeddings, hidden_size)
#self.rnn = nn.LSTM(input_size + num_embeddings,hidden_size,1)
#self.c2h = nn.Linear(input_size + num_embeddings,hidden_size)
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
def forward(self, prev_hidden, batch_H, char_onehots):
#k->hi,q->s0
# [batch_size x num_encoder_step x num_channel] -> [batch_size x num_encoder_step x hidden_size]
batch_H_proj = self.i2h(batch_H)
#w*st+wf*fi,j
prev_hidden_proj = self.h2h(prev_hidden[0]).unsqueeze(1)
e = self.score(torch.tanh(batch_H_proj + prev_hidden_proj)) # batch_size x num_encoder_step * 1
alpha = F.softmax(e, dim=1)
context = torch.bmm(alpha.permute(0, 2, 1), batch_H).squeeze(1) # batch_size x num_channel
concat_context = torch.cat([context, char_onehots], 1) # batch_size x (num_channel + num_embedding)
cur_hidden = self.rnn(concat_context, prev_hidden)
return cur_hidden, alpha
if __name__=="__main__":
model = Attention(512,256,38)
batch_H = torch.rand(2,26,512).to(device)
pred = torch.LongTensor(1, 26).fill_(0).to(device)
probs = model(batch_H,pred)
print(probs)
onnx_file_name = "atten.onnx"
input_names = ["input","pred"]
output_names = ["out"]
dynamic_axes = {"input":{1:"width"}}
torch.onnx.export(model,
(batch_H,pred),
onnx_file_name,
#example_outputs=dummy_output,
export_params=True,
opset_version=11,
do_constant_folding=True,
verbose=True,
input_names=input_names, output_names=output_names,
dynamic_axes=dynamic_axes)
```
i try to modify the code to conver onnx , but all failed
### Versions
pytorch 1.6 gpu
| 1 |
4,243 | 88,800 |
Quantization error between fake-quantized model and quantized model using the new observer
|
oncall: quantization, triaged
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
Interesting findings:
```python
from collections import Counter
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import warnings
from distutils.version import LooseVersion
warnings.simplefilter("ignore")
USE_LEGACY_FAKE_QUANT = True
class SimpleConv(nn.Module):
def __init__(self) -> None:
super().__init__()
self.q = torch.quantization.QuantStub()
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(3, 3, 1)
self.dq = torch.quantization.DeQuantStub()
def forward(self, x):
return self.dq(self.conv(self.q(x)))
x = torch.rand(1, 3, 224, 224)
m = SimpleConv()
m.train()
backend = 'qnnpack'
if USE_LEGACY_FAKE_QUANT:
if LooseVersion(torch.__version__) >= '1.12.0':
m.qconfig = torch.quantization.get_default_qat_qconfig(backend, 0)
else:
m.qconfig = torch.quantization.get_default_qat_qconfig(backend, None)
else:
m.qconfig = torch.quantization.get_default_qat_qconfig(backend)
torch.backends.quantized.engine = backend
m = torch.quantization.prepare_qat(m, inplace=True)
for _ in range(10):
m(x)
with torch.no_grad():
m.eval()
m.apply(torch.quantization.disable_observer)
y = m(x)
print('Result is stable during QAT:', torch.allclose(y, m(x)))
m = torch.quantization.convert(m, inplace=True)
y_ = m(x)
print('Result is stable after conversion:', torch.allclose(y_, m(x)))
print('Result is stable regardless of conversion:', torch.allclose(y, y_))
float_diff = (y - m(x)).abs().flatten()
int_diff = torch.round(float_diff / m.conv.scale)
counter = Counter(int_diff.tolist())
total = int_diff.numel()
print('Difference value (ratio):')
for k, v in counter.most_common():
print(f'{k}: {v} ({v/total*100:.2f}%)')
```
With `USE_LEGACY_FAKE_QUANT=True`, I get the following result.
```
Result is stable during QAT: True
Result is stable after conversion: True
Result is stable regardless of conversion: False
Difference value (ratio):
0.0: 150431 (99.94%)
1.0: 97 (0.06%)
```
The difference is always within 1 of the quantized values, and the ratio with conversion error is lower than 0.1%.
However, when I set `USE_LEGACY_FAKE_QUANT=False` (which is the default behavior for `get_default_qat_qconfig`), I get
```
Result is stable during QAT: True
Result is stable after conversion: True
Result is stable regardless of conversion: False
Difference value (ratio):
0.0: 104794 (69.62%)
1.0: 45734 (30.38%)
```
The error rate could be something between 10-30% and there could be some cases for 2 quantized value difference.
I understand that there could be some difference for models for fake-quantized and quantized models but 30% for a layer is just too much.
### Versions
Collecting environment information...
PyTorch version: 1.13.0
Is debug build: False
CUDA used to build PyTorch: None
ROCM used to build PyTorch: N/A
OS: macOS 12.6.1 (x86_64)
GCC version: Could not collect
Clang version: 12.0.0 (clang-1200.0.32.28)
CMake version: version 3.18.0
Libc version: N/A
Python version: 3.8.6 (default, Oct 8 2020, 14:06:32) [Clang 12.0.0 (clang-1200.0.32.2)] (64-bit runtime)
Python platform: macOS-10.16-x86_64-i386-64bit
Is CUDA available: False
CUDA runtime version: No CUDA
CUDA_MODULE_LOADING set to: N/A
GPU models and configuration: No CUDA
Nvidia driver version: No CUDA
cuDNN version: No CUDA
HIP runtime version: N/A
MIOpen runtime version: N/A
Is XNNPACK available: True
Versions of relevant libraries:
[pip3] numpy==1.23.4
[pip3] torch==1.13.0
[pip3] torchvision==0.14.0
[conda] Could not collect
cc @jerryzh168 @jianyuh @raghuramank100 @jamesr66a @vkuzo @jgong5 @Xia-Weiwen @leslie-fang-intel
| 9 |
4,244 | 88,791 |
Potential bug in torch.optim.lr_scheduler.CosineAnnealingWarmRestarts
|
triaged, actionable, module: LrScheduler
| ERROR: type should be string, got "https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/blob/fb5c6ae61f1f622ec388ae9fa00e7683ce1729ce/torch/optim/lr_scheduler.py#L1407\r\n\r\nShould be self.T_cur = self.T_cur % self.T_i, not self.T_cur = self.T_cur - self.T_i." | 3 |
4,245 | 88,775 |
Batched Random Number Generators
|
triaged, module: random
|
### 🚀 The feature, motivation and pitch
Hello there,
The vast majority of PyTorch methods support batched inputs and outputs. However, the random generators are left behind in this regard! This is particularly important for applications were most of the heavy-lifting comes from training many identically-shaped models independently and simultaneously in a batched manner.
I understand that one can sample batched random tensors from a single generator. That being said, you cannot reproduce each slice without reproducing the entire tensor.
There are many applications which could benefit from training many reproducible configurations in a batch-wise manner. For example, take few-shot learning evaluations where most settings deal with 1-layer classifiers but tens of thousands of independent episodes and classifiers. You can create your own batched layers and modules from scratch using batched matrix multiplications and so on, but a truly batched RNG is still unavailable.
### Alternatives
For now, I've written my own "fake" batch RNG shell, where I create many generators in a list and seed them manually. Upon random generation requests, the shell has to call each generator, and stack the resulting random samples. This is of course very inefficient. To improve the time efficiency of this approach, I defined random number caches, in order to reduce the number of calls to the generators. This induces an almost unnecessary memory-computation trade-off, and still loses to a truly efficient batched RNG. The GPU memory also limits the caching benefits.
### Additional context
_No response_
cc @pbelevich
| 0 |
4,246 | 88,765 |
torch.jit.trace() - AttributeError: 'NoneType' object has no attribute '__module__
|
oncall: jit
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
The examples in the following tutorials:
https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.jit.trace.html (the second example)
https://pytorch.org/tutorials/beginner/Intro_to_TorchScript_tutorial.html (examples starting from Tracing Modules)
raise the error ``` AttributeError: 'NoneType' object has no attribute '__module__'``` in the code line ``` torch.jit.trace() ```
### Versions
```
PyTorch version: 1.13.0+cu117
Is debug build: False
CUDA used to build PyTorch: 11.7
ROCM used to build PyTorch: N/A
OS: Microsoft Windows 10 Enterprise
GCC version: Could not collect
Clang version: Could not collect
CMake version: Could not collect
Libc version: N/A
Python version: 3.8.10 (tags/v3.8.10:3d8993a, May 3 2021, 11:48:03) [MSC v.1928 64 bit (AMD64)] (64-bit runtime)
Python platform: Windows-10-10.0.19044-SP0
Is CUDA available: True
CUDA runtime version: 11.7.99
CUDA_MODULE_LOADING set to: LAZY
GPU models and configuration: GPU 0: NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3060
Nvidia driver version: 517.40
cuDNN version: Could not collect
HIP runtime version: N/A
MIOpen runtime version: N/A
Is XNNPACK available: True
Versions of relevant libraries:
[pip3] mypy-extensions==0.4.3
[pip3] numpy==1.22.4
[pip3] pytorch-lightning==1.7.7
[pip3] torch==1.13.0+cu117
[pip3] torch-model-archiver==0.6.0
[pip3] torch-workflow-archiver==0.2.4
[pip3] torchaudio==0.13.0+cu117
[pip3] torchmetrics==0.10.0
[pip3] torchserve==0.6.0
[pip3] torchvision==0.14.0+cu117
[conda] Could not collect
```
cc @EikanWang @jgong5 @wenzhe-nrv @sanchitintel
| 8 |
4,247 | 88,735 |
RuntimeError: method '__torch__.___torch_mangle_0.MyModule.sin' already defined.
|
oncall: package/deploy
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
The following program runs into the following error. It appears that the script and trace somehow collide on their use of the global compilation unit? Adding `_compilation_unit=torch._C.CompilationUnit()` doesn't seem to help though.
```python
import torch
class MyModule(torch.nn.Module):
@torch.jit.export
def sin(self, x):
return torch.ops.aten.sin(x)
module = MyModule()
example_input = torch.ones(2, 3)
torch.jit.script(module)
torch.jit.trace_module(module, {"sin": example_input})
```
```
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "/tmp/repro2.py", line 12, in <module>
torch.jit.trace_module(module, {"sin": example_input})
File "/usr/local/google/home/silvasean/.local/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/jit/_trace.py", line 1049, in trace_module
module._c._create_method_from_trace(
RuntimeError: method '__torch__.___torch_mangle_0.MyModule.sin' already defined.
```
### Versions
Collecting environment information...
PyTorch version: 1.14.0.dev20221028+cpu
Is debug build: False
CUDA used to build PyTorch: None
ROCM used to build PyTorch: N/A
OS: Debian GNU/Linux rodete (x86_64)
GCC version: (Debian 12.2.0-3) 12.2.0
Clang version: 14.0.6-2
CMake version: version 3.24.1
Libc version: glibc-2.35
Python version: 3.10.7 (main, Sep 8 2022, 14:34:29) [GCC 12.2.0] (64-bit runtime)
Python platform: Linux-5.18.16-1rodete1-amd64-x86_64-with-glibc2.35
Is CUDA available: False
CUDA runtime version: No CUDA
GPU models and configuration: No CUDA
Nvidia driver version: No CUDA
cuDNN version: No CUDA
HIP runtime version: N/A
MIOpen runtime version: N/A
Is XNNPACK available: True
Versions of relevant libraries:
[pip3] numpy==1.23.3
[pip3] torch==1.14.0.dev20221028+cpu
[pip3] torchvision==0.15.0.dev20221028+cpu
[conda] Could not collect
| 0 |
4,248 | 88,732 |
scatter_ op convert onnx exception
|
module: onnx, triaged, onnx-needs-info
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
```python
input_char = torch.LongTensor(batch_size).fill_(0).to(device)
def _char_to_onehot(self, input_char, onehot_dim=38):
input_char = input_char.unsqueeze(1)
batch_size = input_char.size(0)
one_hot = torch.FloatTensor(batch_size, onehot_dim).zero_().to(device)
one_hot = one_hot.scatter_(1, input_char, 1)
return one_hot
```
when scatter_ op convert to onnx,,it can convert success,but then run onnx with onnxruntime.InferenceSession(ModelPath)
errors:
failed:Type Error: Type parameter (T) bound to different types (tensor(float) and tensor(int64) in node (ScatterElements_53).
why it hints different types
### Versions
pytorch 1.6 gpu
onnx 1.8
onnxruntime 1.6 cpu
| 1 |
4,249 | 88,721 |
DISABLED test_extract_gradients_from_optimizer_set_to_none (__main__.TestIdentifyGradients)
|
module: flaky-tests, skipped, oncall: profiler
|
Platforms: mac, macos, win, windows
This test was disabled because it is failing in CI. See [recent examples](https://hud.pytorch.org/flakytest?name=test_extract_gradients_from_optimizer_set_to_none&suite=TestIdentifyGradients) and the most recent trunk [workflow logs](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/runs/9376140274).
Over the past 3 hours, it has been determined flaky in 2 workflow(s) with 2 failures and 2 successes.
**Debugging instructions (after clicking on the recent samples link):**
DO NOT BE ALARMED IF THE CI IS GREEN. We now shield flaky tests from developers so CI will thus be green but it will be harder to parse the logs.
To find relevant log snippets:
1. Click on the workflow logs linked above
2. Click on the Test step of the job so that it is expanded. Otherwise, the grepping will not work.
3. Grep for `test_extract_gradients_from_optimizer_set_to_none`
4. There should be several instances run (as flaky tests are rerun in CI) from which you can study the logs.
cc @robieta @chaekit @aaronenyeshi @ngimel @nbcsm @guotuofeng @guyang3532 @gaoteng-git @tiffzhaofb
| 16 |
4,250 | 88,691 |
forward AD for _euclidean_dist
|
module: autograd, triaged, actionable, module: forward ad, module: functorch
|
### 🚀 The feature, motivation and pitch
Submitting this feature request to get functorch.hessians downstream of torch.cdist, and the error issued by pytorch asked me to submit this to prioritize this.
### Alternatives
I'll try autograd hessian.
### Additional context
<img width="1035" alt="image" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/4132346/200657073-54ef92cf-9c51-4f4b-9f57-ac47159c5d88.png">
cc @ezyang @albanD @zou3519 @gqchen @pearu @nikitaved @soulitzer @Lezcano @Varal7 @Chillee @samdow @soumith
| 2 |
4,251 | 88,686 |
Consolidate binary build matrix for core and validation workflows
|
module: ci, triaged
|
cc @seemethere @malfet @pytorch/pytorch-dev-infra
| 0 |
4,252 | 93,614 |
API For Registering Stride Preferences For User Fallback Kernels
|
triaged, oncall: pt2
|
Calling `.contiguous()` or `.contiguous(memory_format=torch.channels_last)` within extern kernels instead of the inputs being passed in the right layout can lead to perf regression as seen by https://github.com/pytorch/torchdynamo/issues/1833.
We should either have an API for registering stride preferences or default to contiguous.
cc @ezyang @soumith @msaroufim @wconstab @ngimel @bdhirsh
| 0 |
4,253 | 88,658 |
nn.Linear allocate too many space which lead to CPUAllocator "allocate memory failure" if it's BF16. good for FP32.
|
module: cpu, triaged, intel
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
Torch version: 1.13.0+cpu
BF16 code
```python
from torch import nn
import torch
lm_head = nn.Linear(1536, 250880, bias=False, dtype=torch.bfloat16)
input=torch.ones(size=(8,1024,1536), dtype=torch.bfloat16)
output=lm_head(input)
```
crash:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
File "/skyrex05/wangyi/miniconda3/envs/compatibility_test/lib/python3.9/site-packages/torch/nn/modules/module.py", line 1190, in _call_impl
return forward_call(*input, **kwargs)
File "/skyrex05/wangyi/miniconda3/envs/compatibility_test/lib/python3.9/site-packages/torch/nn/modules/linear.py", line 114, in forward
return F.linear(input, self.weight, self.bias)
RuntimeError: [enforce fail at alloc_cpu.cpp:75] err == 0. DefaultCPUAllocator: can't allocate memory: you tried to allocate 189079224448 bytes. Error code 12 (Cannot allocate memory)
FP32 code
```python
from torch import nn
import torch
lm_head = nn.Linear(1536, 250880, bias=False)
input=torch.ones(size=(8,1024,1536))
output=lm_head(input)
```
no crash
### Versions
PyTorch version: 1.13.0+cpu
Is debug build: False
CUDA used to build PyTorch: Could not collect
ROCM used to build PyTorch: N/A
OS: Ubuntu 20.04.5 LTS (x86_64)
GCC version: (Ubuntu 9.4.0-1ubuntu1~20.04.1) 9.4.0
Clang version: Could not collect
CMake version: version 3.16.3
Libc version: glibc-2.31
Python version: 3.9.13 (main, Oct 13 2022, 21:15:33) [GCC 11.2.0] (64-bit runtime)
Python platform: Linux-5.15.0-46-generic-x86_64-with-glibc2.31
Is CUDA available: False
CUDA runtime version: 10.1.243
CUDA_MODULE_LOADING set to: N/A
GPU models and configuration: Could not collect
Nvidia driver version: Could not collect
cuDNN version: Could not collect
HIP runtime version: N/A
MIOpen runtime version: N/A
Is XNNPACK available: True
Versions of relevant libraries:
[pip3] intel-extension-for-pytorch==1.12.300
[pip3] mypy-extensions==0.4.3
[pip3] numpy==1.23.4
[pip3] torch==1.13.0+cpu
[pip3] torchaudio==0.13.0+cpu
[pip3] torchvision==0.14.0+cpu
[conda] intel-extension-for-pytorch 1.12.300 pypi_0 pypi
[conda] numpy 1.23.4 pypi_0 pypi
[conda] torch 1.13.0+cpu pypi_0 pypi
[conda] torchaudio 0.13.0+cpu pypi_0 pypi
[conda] torchvision 0.14.0+cpu pypi_0 pypi
cc @VitalyFedyunin @jgong5 @mingfeima @XiaobingSuper @sanchitintel @ashokei @jingxu10
| 5 |
4,254 | 93,613 |
Minifier crash
|
triaged, bug, oncall: pt2
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
Minifier launcher: https://gist.github.com/5f8a42f8f0f72ab96e82a098fa147462
Run on a781b92acd8098018521addc4fbb184ded83e914 (latest symbolic-shapes branch at time of writing) with `TORCHDYNAMO_DYNAMIC_SHAPES=1 AOT_DYNAMIC_SHAPES=1`
Crashes with:
```
File "/scratch/ezyang/work/pytorch/functorch/_src/fx_minifier.py", line 267, in try_granularity
new_state = strategy(failing_state, granularity)
File "/scratch/ezyang/work/pytorch/functorch/_src/fx_minifier.py", line 104, in new_func
new_state = strategy(deepcopy_fx_graph(old_state.graph), list(old_state.inps), granularity)
File "/scratch/ezyang/work/pytorch/functorch/_src/fx_minifier.py", line 245, in delta_debugging
if graph_fails(new_state.graph, new_state.inps):
File "/scratch/ezyang/work/pytorch/functorch/_src/fx_minifier.py", line 92, in graph_fails
return module_fails(mod, inps)
File "/scratch/ezyang/work/pytorch/torch/_dynamo/debug_utils.py", line 670, in backend_accuracy_fails
compiled_gm = compiler_fn(copy.deepcopy(gm), clone_inputs(example_inputs))
File "/scratch/ezyang/work/pytorch/torch/_dynamo/optimizations/training.py", line 94, in compile_fn
return cls(gm, example_inputs).verified_candidate()
File "/scratch/ezyang/work/pytorch/torch/_dynamo/optimizations/training.py", line 116, in __init__
if not is_aot_autograd_safe_to_run(gm, example_inputs):
File "/scratch/ezyang/work/pytorch/torch/_dynamo/optimizations/training.py", line 64, in is_aot_autograd_safe_to_run
mutated = has_mutation(gm, example_inputs, inputs_only=True)
File "/scratch/ezyang/work/pytorch/torch/_dynamo/optimizations/analysis.py", line 144, in has_mutation
ShapeAliasingAndMutationProp(new_gm).run(*example_inputs)
File "/scratch/ezyang/work/pytorch/torch/_dynamo/optimizations/analysis.py", line 113, in run
super().run(*args)
File "/scratch/ezyang/work/pytorch/torch/fx/interpreter.py", line 130, in run
self.env[node] = self.run_node(node)
File "/scratch/ezyang/work/pytorch/torch/_dynamo/optimizations/analysis.py", line 48, in run_node
result = getattr(self, n.op)(n.target, args, kwargs)
File "/scratch/ezyang/work/pytorch/torch/fx/interpreter.py", line 288, in call_module
return submod(*args, **kwargs)
File "/scratch/ezyang/work/pytorch/torch/nn/modules/module.py", line 1423, in _call_impl
return forward_call(*input, **kwargs)
File "/scratch/ezyang/work/pytorch/torch/nn/modules/conv.py", line 463, in forward
return self._conv_forward(input, self.weight, self.bias)
File "/scratch/ezyang/work/pytorch/torch/nn/modules/conv.py", line 459, in _conv_forward
return F.conv2d(input, weight, bias, self.stride,
RuntimeError: Expected 3D (unbatched) or 4D (batched) input to conv2d, but got input of size: [768]
While executing %self_self_blocks_0_local_mp_conv1 : [#users=1] = call_module[target=self_self_blocks_0_local_mp_conv1](args = (%reshape_3,), kwargs = {})
```
### Error logs
_No response_
### Minified repro
_No response_
cc @soumith @msaroufim @wconstab @ngimel @bdhirsh
| 1 |
4,255 | 88,648 |
`MultiMarginLoss` doesn't check the value of `target` on CUDA
|
module: cuda, module: error checking, triaged
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
`MultiMarginLoss` doesn't check the value of `target` on CUDA.
By the [doc](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.nn.MultiMarginLoss.html) of `MultiMarginLoss`, the value of target should be `0<=v<=C−1`, where the shape of input is `C` or `N,C`. The CPU does check the validity of the value of `target` but CUDA will not and may return a value for some invalid `target`
```py
import torch
torch.manual_seed(420)
input = torch.randn(3, 5, requires_grad=True).cuda()
target = torch.tensor([1, 0, 5]).cuda()
loss = torch.nn.MultiMarginLoss()
output = loss(input, target)
print(output)
# CUDA
# tensor(0.7524, device='cuda:0', grad_fn=<MultiMarginLossBackward0>)
```
By contrast,
```py
import torch
torch.manual_seed(420)
input = torch.randn(3, 5, requires_grad=True)
target = torch.tensor([1, 0, 5])
loss = torch.nn.MultiMarginLoss()
output = loss(input, target)
# CPU
# RuntimeError: target out of range
```
### Versions
Collecting environment information...
PyTorch version: 1.12.1+cu113
Is debug build: False
CUDA used to build PyTorch: 11.3
ROCM used to build PyTorch: N/A
OS: Ubuntu 18.04.6 LTS (x86_64)
GCC version: (Ubuntu 7.5.0-3ubuntu1~18.04) 7.5.0
Clang version: 6.0.0-1ubuntu2 (tags/RELEASE_600/final)
CMake version: version 3.22.6
Libc version: glibc-2.26
Python version: 3.7.15 (default, Oct 12 2022, 19:14:55) [GCC 7.5.0] (64-bit runtime)
Python platform: Linux-5.10.133+-x86_64-with-Ubuntu-18.04-bionic
Is CUDA available: True
CUDA runtime version: 11.2.152
CUDA_MODULE_LOADING set to:
GPU models and configuration: GPU 0: Tesla T4
Nvidia driver version: 460.32.03
cuDNN version: Probably one of the following:
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn.so.8.1.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_adv_infer.so.8.1.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_adv_train.so.8.1.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_cnn_infer.so.8.1.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_cnn_train.so.8.1.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_ops_infer.so.8.1.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_ops_train.so.8.1.1
HIP runtime version: N/A
MIOpen runtime version: N/A
Is XNNPACK available: True
Versions of relevant libraries:
[pip3] numpy==1.21.6
[pip3] torch==1.12.1+cu113
[pip3] torchaudio==0.12.1+cu113
[pip3] torchsummary==1.5.1
[pip3] torchtext==0.13.1
[pip3] torchvision==0.13.1+cu113
[conda] Could not collect
cc @ngimel
| 0 |
4,256 | 88,647 |
`ConvTranspose` fails on CPU but returns an empty tensor on CUDA
|
module: cuda, module: error checking, triaged
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
`ConvTranspose` fails on CPU but returns an empty tensor on CUDA
```py
import torch
input = torch.randn(1, 1, 2, 2, requires_grad=True)
weight = torch.randn(1, 1, 2, 2, requires_grad=True)
output = torch.nn.functional.conv_transpose2d(input, weight, stride=2, padding=2)
# CPU
# RuntimeError: Given input size per channel: (2 x 2). Calculated output size per channel: (0 x 0). Output size is too small
```
```py
import torch
input = torch.randn(1, 1, 2, 2, requires_grad=True).cuda()
weight = torch.randn(1, 1, 2, 2, requires_grad=True).cuda()
output = torch.nn.functional.conv_transpose2d(input, weight, stride=2, padding=2)
print(output)
# CUDA
# tensor([], device='cuda:0', size=(1, 1, 0, 0), grad_fn=<ConvolutionBackward0>)
```
I think they should both raise an error or succeed in this case
### Versions
Collecting environment information...
PyTorch version: 1.12.1+cu113
Is debug build: False
CUDA used to build PyTorch: 11.3
ROCM used to build PyTorch: N/A
OS: Ubuntu 18.04.6 LTS (x86_64)
GCC version: (Ubuntu 7.5.0-3ubuntu1~18.04) 7.5.0
Clang version: 6.0.0-1ubuntu2 (tags/RELEASE_600/final)
CMake version: version 3.22.6
Libc version: glibc-2.26
Python version: 3.7.15 (default, Oct 12 2022, 19:14:55) [GCC 7.5.0] (64-bit runtime)
Python platform: Linux-5.10.133+-x86_64-with-Ubuntu-18.04-bionic
Is CUDA available: True
CUDA runtime version: 11.2.152
CUDA_MODULE_LOADING set to:
GPU models and configuration: GPU 0: Tesla T4
Nvidia driver version: 460.32.03
cuDNN version: Probably one of the following:
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn.so.8.1.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_adv_infer.so.8.1.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_adv_train.so.8.1.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_cnn_infer.so.8.1.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_cnn_train.so.8.1.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_ops_infer.so.8.1.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_ops_train.so.8.1.1
HIP runtime version: N/A
MIOpen runtime version: N/A
Is XNNPACK available: True
Versions of relevant libraries:
[pip3] numpy==1.21.6
[pip3] torch==1.12.1+cu113
[pip3] torchaudio==0.12.1+cu113
[pip3] torchsummary==1.5.1
[pip3] torchtext==0.13.1
[pip3] torchvision==0.13.1+cu113
[conda] Could not collect
cc @ngimel @VitalyFedyunin @jgong5 @mingfeima @XiaobingSuper @sanchitintel @ashokei @jingxu10
| 1 |
4,257 | 88,643 |
pack_sequence() always fail after set_default_tensor_type to CUDA
|
module: rnn, triaged
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
It seems that after `torch.set_default_tensor_type('torch.cuda.FloatTensor')`, certain functions does not work, for example, `torch.nn.utils.rnn.pack_sequence`.
```
>>>pack_sequence([torch.tensor([1,2,3]), torch.tensor([4,5])])
Out[1]: PackedSequence(data=tensor([1, 4, 2, 5, 3]), batch_sizes=tensor([2, 2, 1]), sorted_indices=None, unsorted_indices=None)
pack_sequence([torch.tensor([1,2,3]).cuda(), torch.tensor([4,5]).cuda()])
Out[2]: PackedSequence(data=tensor([1, 4, 2, 5, 3], device='cuda:0'), batch_sizes=tensor([2, 2, 1]), sorted_indices=None, unsorted_indices=None)
pack_sequence([torch.tensor([1,2,3]).cuda(0), torch.tensor([4,5]).cuda(0)])
Out[3]: PackedSequence(data=tensor([1, 4, 2, 5, 3], device='cuda:0'), batch_sizes=tensor([2, 2, 1]), sorted_indices=None, unsorted_indices=None)
torch.set_default_tensor_type('torch.cuda.FloatTensor')
pack_sequence([torch.tensor([1,2,3]), torch.tensor([4,5])])
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "/home/xuancong/anaconda3/lib/python3.8/site-packages/IPython/core/interactiveshell.py", line 3441, in run_code
exec(code_obj, self.user_global_ns, self.user_ns)
File "<ipython-input-5-2a6bbd446608>", line 1, in <module>
pack_sequence([torch.tensor([1,2,3]), torch.tensor([4,5])])
File "/home/xuancong/anaconda3/lib/python3.8/site-packages/torch/nn/utils/rnn.py", line 484, in pack_sequence
return pack_padded_sequence(pad_sequence(sequences), lengths, enforce_sorted=enforce_sorted)
File "/home/xuancong/anaconda3/lib/python3.8/site-packages/torch/nn/utils/rnn.py", line 262, in pack_padded_sequence
_VF._pack_padded_sequence(input, lengths, batch_first)
RuntimeError: 'lengths' argument should be a 1D CPU int64 tensor, but got 1D cuda:0 Long tensor
pack_sequence([torch.tensor([1,2,3],device='cpu'), torch.tensor([4,5],device='cpu')])
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "/home/xuancong/anaconda3/lib/python3.8/site-packages/IPython/core/interactiveshell.py", line 3441, in run_code
exec(code_obj, self.user_global_ns, self.user_ns)
File "<ipython-input-6-4b903e3514ab>", line 1, in <module>
pack_sequence([torch.tensor([1,2,3],device='cpu'), torch.tensor([4,5],device='cpu')])
File "/home/xuancong/anaconda3/lib/python3.8/site-packages/torch/nn/utils/rnn.py", line 484, in pack_sequence
return pack_padded_sequence(pad_sequence(sequences), lengths, enforce_sorted=enforce_sorted)
File "/home/xuancong/anaconda3/lib/python3.8/site-packages/torch/nn/utils/rnn.py", line 262, in pack_padded_sequence
_VF._pack_padded_sequence(input, lengths, batch_first)
RuntimeError: 'lengths' argument should be a 1D CPU int64 tensor, but got 1D cuda:0 Long tensor
```
From the error messages above, it seems that each `torch.tensor` has a field called `lengths` which is usually stored in CPU. `torch.set_default_tensor_type('torch.cuda.FloatTensor')` will cause this field to be stored into GPU and then pack_sequence() will always fail even if I put `device="cpu"` in the tensor creation function.
### Versions
PyTorch version: 1.13.0+cu117
Is debug build: False
CUDA used to build PyTorch: 11.7
ROCM used to build PyTorch: N/A
OS: Debian GNU/Linux 11 (bullseye) (x86_64)
GCC version: (Ubuntu 10.3.0-1ubuntu1~20.04) 10.3.0
Clang version: Could not collect
CMake version: version 3.20.4
Libc version: glibc-2.31
Python version: 3.8.2 (default, Mar 26 2020, 15:53:00) [GCC 7.3.0] (64-bit runtime)
Python platform: Linux-5.15.40-x86_64-with-glibc2.10
Is CUDA available: True
CUDA runtime version: Could not collect
CUDA_MODULE_LOADING set to: LAZY
GPU models and configuration: GPU 0: NVIDIA GeForce GTX 1050 Ti with Max-Q Design
Nvidia driver version: 520.56.06
cuDNN version: Probably one of the following:
/usr/local/cuda-11.4/targets/x86_64-linux/lib/libcudnn.so.8.2.2
/usr/local/cuda-11.4/targets/x86_64-linux/lib/libcudnn_adv_infer.so.8.2.2
/usr/local/cuda-11.4/targets/x86_64-linux/lib/libcudnn_adv_train.so.8.2.2
/usr/local/cuda-11.4/targets/x86_64-linux/lib/libcudnn_cnn_infer.so.8.2.2
/usr/local/cuda-11.4/targets/x86_64-linux/lib/libcudnn_cnn_train.so.8.2.2
/usr/local/cuda-11.4/targets/x86_64-linux/lib/libcudnn_ops_infer.so.8.2.2
/usr/local/cuda-11.4/targets/x86_64-linux/lib/libcudnn_ops_train.so.8.2.2
HIP runtime version: N/A
MIOpen runtime version: N/A
Is XNNPACK available: True
Versions of relevant libraries:
[pip3] mypy-extensions==0.4.3
[pip3] numpy==1.19.5
[pip3] numpydoc==1.1.0
[pip3] torch==1.13.0
[pip3] torchaudio==0.13.0
[pip3] torchvision==0.14.0
[conda] blas 1.0 mkl
[conda] mkl 2020.4 intel_304 intel
[conda] mkl-service 2.3.0 py38he904b0f_0
[conda] mkl_fft 1.2.0 py38h23d657b_0
[conda] mkl_random 1.1.1 py38h0573a6f_0
[conda] numpy 1.19.5 pypi_0 pypi
[conda] numpy-base 1.19.2 py38hfa32c7d_0
[conda] numpydoc 1.1.0 pyhd3eb1b0_1
[conda] torch 1.13.0 pypi_0 pypi
[conda] torchaudio 0.13.0 pypi_0 pypi
[conda] torchvision 0.14.0 pypi_0 pypi
cc @zou3519
| 1 |
4,258 | 88,639 |
CUDA unknown error after suspend during debugging
|
module: cuda, triaged
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
On Linux/Debian, during debugging of any CUDA program, if the system suspends and enters standby, after wake up, running any CUDA program will give rise to the following error (which will not occur initially)
```
/opt/anaconda3/lib/python3.8/site-packages/torch/cuda/__init__.py:88: UserWarning: CUDA initialization: CUDA unknown error - this may be due to an incorrectly set up environment, e.g. changing env variable CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES after program start. Setting the available devices to be zero. (Triggered internally at ../c10/cuda/CUDAFunctions.cpp:109.)
return torch._C._cuda_getDeviceCount() > 0
```
Apparently, the explanation is irrelevant and it has nothing to do with CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES, because if I run `rmmod nvidia*` and re-insert `nvidia.ko` (the driver module), CUDA get back working again. Otherwise, it keeps failing.
I have encountered this bug long time ago and have already reported to the NVIDIA driver team years ago, but it still exists now.
### Versions
PyTorch version: 1.13.0+cu117
Is debug build: False
CUDA used to build PyTorch: 11.7
ROCM used to build PyTorch: N/A
OS: Debian GNU/Linux 11 (bullseye) (x86_64)
GCC version: (Ubuntu 10.3.0-1ubuntu1~20.04) 10.3.0
Clang version: Could not collect
CMake version: version 3.20.4
Libc version: glibc-2.31
Python version: 3.8.2 (default, Mar 26 2020, 15:53:00) [GCC 7.3.0] (64-bit runtime)
Python platform: Linux-5.15.40-x86_64-with-glibc2.10
Is CUDA available: True
CUDA runtime version: Could not collect
CUDA_MODULE_LOADING set to: LAZY
GPU models and configuration: GPU 0: NVIDIA GeForce GTX 1050 Ti with Max-Q Design
Nvidia driver version: 520.56.06
cuDNN version: Probably one of the following:
/usr/local/cuda-11.4/targets/x86_64-linux/lib/libcudnn.so.8.2.2
/usr/local/cuda-11.4/targets/x86_64-linux/lib/libcudnn_adv_infer.so.8.2.2
/usr/local/cuda-11.4/targets/x86_64-linux/lib/libcudnn_adv_train.so.8.2.2
/usr/local/cuda-11.4/targets/x86_64-linux/lib/libcudnn_cnn_infer.so.8.2.2
/usr/local/cuda-11.4/targets/x86_64-linux/lib/libcudnn_cnn_train.so.8.2.2
/usr/local/cuda-11.4/targets/x86_64-linux/lib/libcudnn_ops_infer.so.8.2.2
/usr/local/cuda-11.4/targets/x86_64-linux/lib/libcudnn_ops_train.so.8.2.2
HIP runtime version: N/A
MIOpen runtime version: N/A
Is XNNPACK available: True
Versions of relevant libraries:
[pip3] mypy-extensions==0.4.3
[pip3] numpy==1.19.5
[pip3] numpydoc==1.1.0
[pip3] torch==1.13.0
[pip3] torchaudio==0.13.0
[pip3] torchvision==0.14.0
[conda] blas 1.0 mkl
[conda] mkl 2020.4 intel_304 intel
[conda] mkl-service 2.3.0 py38he904b0f_0
[conda] mkl_fft 1.2.0 py38h23d657b_0
[conda] mkl_random 1.1.1 py38h0573a6f_0
[conda] numpy 1.19.5 pypi_0 pypi
[conda] numpy-base 1.19.2 py38hfa32c7d_0
[conda] numpydoc 1.1.0 pyhd3eb1b0_1
[conda] torch 1.13.0 pypi_0 pypi
[conda] torchaudio 0.13.0 pypi_0 pypi
[conda] torchvision 0.14.0 pypi_0 pypi
cc @ngimel
| 0 |
4,259 | 88,631 |
GitHub first-time contributors box pops up unexpectedly
|
module: ci, triaged
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
For example, https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/88504
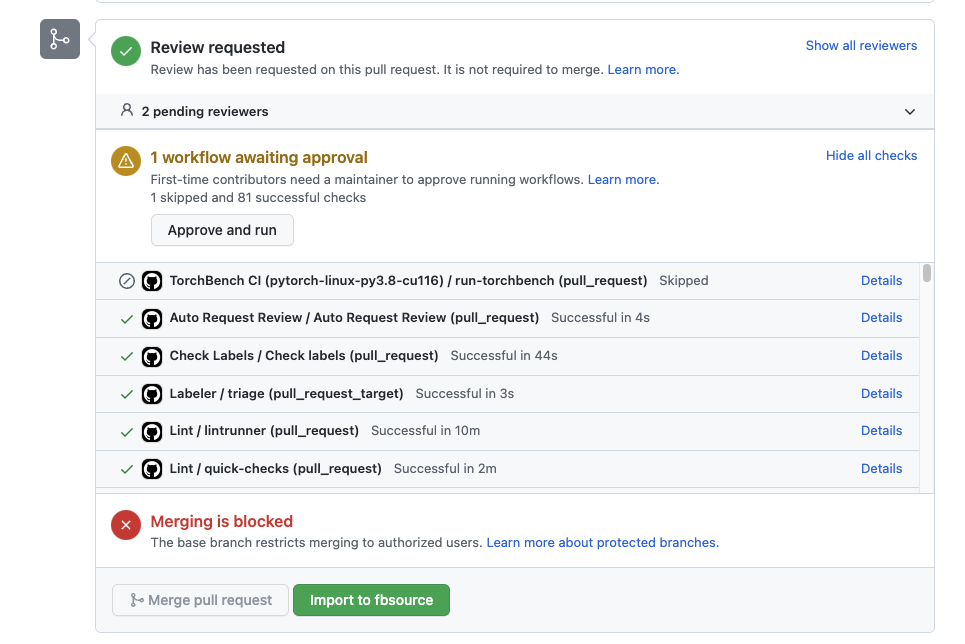
After a quick check, it seems that the issue comes from the new [check-labels](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/blob/master/.github/workflows/check-labels.yml) workflow. There are multiple instances of it shows up on the example PR https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/88504/checks and one of them requires approval from maintainer https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/actions/runs/3395637495
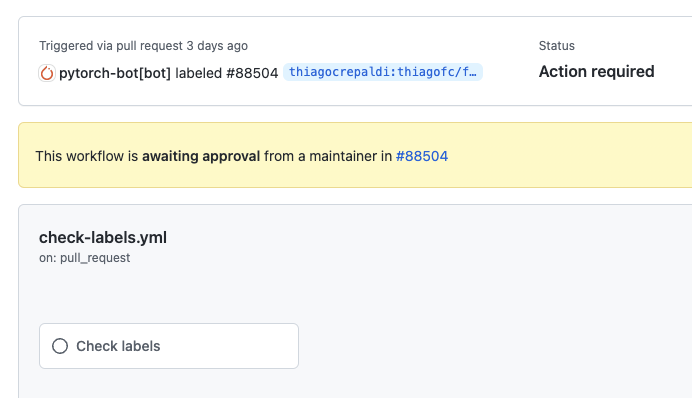
### Versions
CI workflow
cc @seemethere @malfet @pytorch/pytorch-dev-infra
| 0 |
4,260 | 88,626 |
Cloud-based rendezvous backend / distributed store?
|
oncall: distributed
|
We're submitting elastic PyTorch runs on top of Azure Machine Learning
The two in-built rendezvous backends are c10d and etcd. We were wondering if you considered a rendezvous backend based on a cloud storage provider?
Both c10d and etcd require a stable endpoint / dedicated compute. (c10d requires a stable master node in the training cluster, and etcd requires a stable etcd server running on dedicated compute.) We're trying to train only on top of low-priority Spot VMs, which can enter / leave the training at any time.
To unblock ourselves, we implemented `AzureBlobRendezvousBackend` on top of `torch.distributed.elastic.rendezvous.dynamic_rendezvous.RendezvousBackend` and `AzureBlobStore` on top of `torch.distributed.Store`. Using Azure Blob as the key-value store, we didn't need an endpoint hosted by separate dedicated compute.
We were wondering if you've considered this approach before?
(Also, in the same spirit, in addition to `torch.distributed.FileStore`, have you considered something like `FolderStore`, which would be like `FileStore`, but where each key-value pair is stored in a separate file? If this had been present, we could have avoided implementing `AzureBlobStore`. Instead, we could have configured the nodes to use a common file system and then used `FolderStore`. (The common file system could have been a mounted Blob store, a shared NFS, etc.))
cc @mrshenli @pritamdamania87 @zhaojuanmao @satgera @rohan-varma @gqchen @aazzolini @osalpekar @jiayisuse @H-Huang @kwen2501 @awgu
| 1 |
4,261 | 88,621 |
[FSDP] FSDP produces different gradient norms vs DDP, and w/ grad norm clipping creates different training results
|
oncall: distributed, triaged, release notes: distributed (fsdp)
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
Running a T5 large on C4 dataset, and using same random seeding, optimizer, lr scheduler, etc, training with DDP vs FSDP NO_SHARD and FULL_SHARD produce different gradient norms and with norm clipping different training outcomes:

The core issue is shown in this logging of the gradient norms:

Details on grad norm calculations:
Training was run with l2 norm.
FSDP uses FSDP clip_grad_norm_()
DDP uses nn.utils.clip_grad_norm_()
code:
~~~
if isinstance(model, FSDP):
# grad_norm_before_clip = get_grad_norm_fsdp(model, local_rank)
model.clip_grad_norm_(clip_th)
grad_norm_after_clip = get_grad_norm_fsdp(model, local_rank, model_sharding_strategy)
else:
# grad_norm_before_clip = get_grad_norm_local(model)
nn.utils.clip_grad_norm_(model.parameters(), clip_th)
grad_norm_after_clip = get_grad_norm_local(model)
~~~
For logging, this is the code used:
~~~
def get_grad_norm_local(model):
total_norm = 0.0
for p in model.parameters():
local_norm = torch.linalg.vector_norm(p.grad, dtype=p.dtype)
total_norm += local_norm ** 2
return total_norm ** 0.5
def get_grad_norm_fsdp(model, rank, sharding_strategy=ShardingStrategy.FULL_SHARD):
local_norm = get_grad_norm_local(model)
op = torch.distributed.ReduceOp.SUM
return_norm = local_norm.clone().detach().requires_grad_(False).to(rank)**2
dist.all_reduce(return_norm, op=op)
if sharding_strategy == ShardingStrategy.NO_SHARD:
return_norm = return_norm / world_size
return return_norm ** 0.5
~~~
### Versions
pending...opening issue from partner.
cc @mrshenli @pritamdamania87 @zhaojuanmao @satgera @rohan-varma @gqchen @aazzolini @osalpekar @jiayisuse @H-Huang @kwen2501 @awgu
| 0 |
4,262 | 93,612 |
[inductor] Accuracy failure in torchbench hf_T5
|
triaged, oncall: pt2
|
initially thought this was a DDP-Dynamo issue. Turns out to be an inductor issue, with or without DDP.
Log: https://gist.github.com/wconstab/1dfd032ed5cf4ff86b105aa4da6fa32c#file-torchbench_hf_t5_inductor_ddp_no_optimimze-log
@anijain2305 could you triage this? Insofar as, just close the issue if you are already aware/tracking this accuracy failure, or put it in a backlog otherwise?
cc @ezyang @soumith @msaroufim @ngimel @bdhirsh
| 0 |
4,263 | 88,617 |
The libtorch tests Simplify.{SimplifySymbolicMinMax,SimplifyNestedMax,SimplifyNestedMin} fail on Apple Silicon
|
oncall: jit, module: m1
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
Following [these docs](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/blob/v1.13.0/docs/libtorch.rst#building-libtorch-using-python) to build libtorch v1.13.0, then running one of the test binaries:
```sh
gh repo clone pytorch/pytorch && cd pytorch
git checkout v1.13.0
git submodule update --init --recursive
mkdir build_libtorch && cd build_libtorch
python ../tools/build_libtorch.py
build/bin/test_tensorexpr
```
I get these errors:
```
[ RUN ] Simplify.SimplifySymbolicMinMax
/Users/samueles/github/pytorch/pytorch/test/cpp/tensorexpr/test_simplify.cpp:1997: Failure
Expected: (nullptr) != (node_), actual: (nullptr) vs (nullptr)
[ FAILED ] Simplify.SimplifySymbolicMinMax (0 ms)
[ RUN ] Simplify.SimplifyNestedMax
/Users/samueles/github/pytorch/pytorch/test/cpp/tensorexpr/test_simplify.cpp:2020: Failure
Expected: (nullptr) != (max), actual: (nullptr) vs (nullptr)
[ FAILED ] Simplify.SimplifyNestedMax (0 ms)
[ RUN ] Simplify.SimplifyNestedMin
/Users/samueles/github/pytorch/pytorch/test/cpp/tensorexpr/test_simplify.cpp:2296: Failure
Expected: (nullptr) != (min), actual: (nullptr) vs (nullptr)
[ FAILED ] Simplify.SimplifyNestedMin (0 ms)
```
### Versions
PyTorch version: N/A
Is debug build: N/A
CUDA used to build PyTorch: N/A
ROCM used to build PyTorch: N/A
OS: macOS 12.6.1 (arm64)
GCC version: Could not collect
Clang version: 14.0.0 (clang-1400.0.29.202)
CMake version: version 3.24.2
Libc version: N/A
Python version: 3.9.7 (default, Sep 8 2021, 10:47:21) [Clang 12.0.5 (clang-1205.0.22.11)] (64-bit runtime)
Python platform: macOS-12.6.1-arm64-arm-64bit
Is CUDA available: N/A
CUDA runtime version: Could not collect
CUDA_MODULE_LOADING set to: N/A
GPU models and configuration: Could not collect
Nvidia driver version: Could not collect
cuDNN version: Could not collect
HIP runtime version: N/A
MIOpen runtime version: N/A
Is XNNPACK available: N/A
Versions of relevant libraries:
[pip3] mypy-extensions==0.4.3
[pip3] numpy==1.23.2
[pip3] torch==1.12.1
[pip3] torchvision==0.13.1
[conda] Could not collect
cc @EikanWang @jgong5 @wenzhe-nrv @sanchitintel
| 0 |
4,264 | 88,616 |
The libtorch test SequentialTest.ModuleForwardMethodOptionalArg fails on Apple Silicon
|
module: build, triaged, module: m1
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
Following [these docs](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/blob/v1.13.0/docs/libtorch.rst#building-libtorch-using-python) to build libtorch v1.13.0, then running one of the test binaries:
```sh
gh repo clone pytorch/pytorch && cd pytorch
git checkout v1.13.0
git submodule update --init --recursive
mkdir build_libtorch && cd build_libtorch
python ../tools/build_libtorch.py
build/bin/test_api
```
I get this error:
```
[ RUN ] SequentialTest.ModuleForwardMethodOptionalArg
unknown file: Failure
C++ exception with description "Expected argument #1 to be of type c10::optional<c10::ArrayRef<long long> >, but received value of type c10::optional<c10::ArrayRef<long long> >
Exception raised from operator() at /Users/samueles/github/pytorch/pytorch/torch/csrc/api/include/torch/nn/modules/container/any_module_holder.h:55 (most recent call first):
frame #0: c10::detail::torchCheckFail(char const*, char const*, unsigned int, std::__1::basic_string<char, std::__1::char_traits<char>, std::__1::allocator<char> > const&) + 92 (0x105e4669c in libc10.dylib)
frame #1: std::__1::decay<c10::optional<c10::ArrayRef<long long> > const&>::type&& torch::nn::AnyModuleHolder<torch::nn::ConvTranspose1dImpl, at::Tensor const&, c10::optional<c10::ArrayRef<long long> > const&>::CheckedGetter::operator()<c10::optional<c10::ArrayRef<long long> > const&>(unsigned long) + 348 (0x10529c608 in test_api)
frame #2: torch::nn::AnyModuleHolder<torch::nn::ConvTranspose1dImpl, at::Tensor const&, c10::optional<c10::ArrayRef<long long> > const&>::forward(std::__1::vector<torch::nn::AnyValue, std::__1::allocator<torch::nn::AnyValue> >&&) + 480 (0x10529bd24 in test_api)
frame #3: torch::nn::AnyValue torch::nn::AnyModule::any_forward<torch::nn::AnyValue>(torch::nn::AnyValue&&) + 136 (0x1051c6ac8 in test_api)
frame #4: at::Tensor torch::nn::SequentialImpl::forward<at::Tensor, at::Tensor&>(at::Tensor&) + 84 (0x1051c65fc in test_api)
frame #5: SequentialTest_ModuleForwardMethodOptionalArg_Test::TestBody() + 1696 (0x105226274 in test_api)
frame #6: void testing::internal::HandleExceptionsInMethodIfSupported<testing::Test, void>(testing::Test*, void (testing::Test::*)(), char const*) + 116 (0x1055a2588 in test_api)
frame #7: testing::Test::Run() + 812 (0x1055a24bc in test_api)
frame #8: testing::TestInfo::Run() + 840 (0x1055a3de4 in test_api)
frame #9: testing::TestSuite::Run() + 348 (0x1055a4890 in test_api)
frame #10: testing::internal::UnitTestImpl::RunAllTests() + 1632 (0x1055b5a54 in test_api)
frame #11: bool testing::internal::HandleExceptionsInMethodIfSupported<testing::internal::UnitTestImpl, bool>(testing::internal::UnitTestImpl*, bool (testing::internal::UnitTestImpl::*)(), char const*) + 116 (0x1055b523c in test_api)
frame #12: testing::UnitTest::Run() + 124 (0x1055b5194 in test_api)
frame #13: main + 440 (0x104accb30 in test_api)
frame #14: start + 520 (0x105c6508c in dyld)
" thrown in the test body.
[ FAILED ] SequentialTest.ModuleForwardMethodOptionalArg (0 ms)
```
### Versions
PyTorch version: N/A
Is debug build: N/A
CUDA used to build PyTorch: N/A
ROCM used to build PyTorch: N/A
OS: macOS 12.6.1 (arm64)
GCC version: Could not collect
Clang version: 14.0.0 (clang-1400.0.29.202)
CMake version: version 3.24.2
Libc version: N/A
Python version: 3.9.7 (default, Sep 8 2021, 10:47:21) [Clang 12.0.5 (clang-1205.0.22.11)] (64-bit runtime)
Python platform: macOS-12.6.1-arm64-arm-64bit
Is CUDA available: N/A
CUDA runtime version: Could not collect
CUDA_MODULE_LOADING set to: N/A
GPU models and configuration: Could not collect
Nvidia driver version: Could not collect
cuDNN version: Could not collect
HIP runtime version: N/A
MIOpen runtime version: N/A
Is XNNPACK available: N/A
Versions of relevant libraries:
[pip3] mypy-extensions==0.4.3
[pip3] numpy==1.23.2
[pip3] torch==1.12.1
[pip3] torchvision==0.13.1
[conda] Could not collect
cc @malfet @seemethere
| 1 |
4,265 | 88,614 |
The libtorch test TestScalarTensor.TestScalarTensorMPS fails on Apple Silicon
|
triaged, actionable, module: mps, module: m1
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
Following [these docs](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/blob/v1.13.0/docs/libtorch.rst#building-libtorch-using-python) to build libtorch v1.13.0, then running one of the test binaries:
```sh
gh repo clone pytorch/pytorch && cd pytorch
git checkout v1.13.0
git submodule update --init --recursive
mkdir build_libtorch && cd build_libtorch
python ../tools/build_libtorch.py
build/bin/scalar_tensor_test
```
I get this error:
```
[ RUN ] TestScalarTensor.TestScalarTensorMPS
/Users/samueles/github/pytorch/pytorch/aten/src/ATen/test/scalar_tensor_test.cpp:64: Failure
Expected: ss << t << std::endl doesn't throw an exception.
Actual: it throws c10::TypeError with description "Cannot convert a MPS Tensor to float64 dtype as the MPS framework doesn't support float64. Please use float32 instead.
Exception raised from empty_mps at /Users/samueles/github/pytorch/pytorch/aten/src/ATen/mps/EmptyTensor.cpp:40 (most recent call first):
frame #0: at::detail::empty_mps(c10::ArrayRef<long long>, c10::optional<c10::ScalarType>, c10::optional<c10::Layout>, c10::optional<c10::Device>, c10::optional<bool>, c10::optional<c10::MemoryFormat>) + 1048 (0x10e32c944 in libtorch_cpu.dylib)
frame #1: at::native::empty_mps(c10::ArrayRef<long long>, c10::optional<c10::ScalarType>, c10::optional<c10::Layout>, c10::optional<c10::Device>, c10::optional<bool>, c10::optional<c10::MemoryFormat>) + 48 (0x10e3370c4 in libtorch_cpu.dylib)
frame #2: at::native::mps::mps_copy_(at::Tensor&, at::Tensor const&, bool) + 6116 (0x10e368718 in libtorch_cpu.dylib)
frame #3: at::native::copy_impl(at::Tensor&, at::Tensor const&, bool) + 1484 (0x10a4dba5c in libtorch_cpu.dylib)
frame #4: at::native::copy_(at::Tensor&, at::Tensor const&, bool) + 100 (0x10a4db3d0 in libtorch_cpu.dylib)
frame #5: at::_ops::copy_::call(at::Tensor&, at::Tensor const&, bool) + 288 (0x10b114334 in libtorch_cpu.dylib)
frame #6: at::native::_to_copy(at::Tensor const&, c10::optional<c10::ScalarType>, c10::optional<c10::Layout>, c10::optional<c10::Device>, c10::optional<bool>, bool, c10::optional<c10::MemoryFormat>) + 2984 (0x10a801564 in libtorch_cpu.dylib)
frame #7: at::_ops::_to_copy::redispatch(c10::DispatchKeySet, at::Tensor const&, c10::optional<c10::ScalarType>, c10::optional<c10::Layout>, c10::optional<c10::Device>, c10::optional<bool>, bool, c10::optional<c10::MemoryFormat>) + 188 (0x10aca4588 in libtorch_cpu.dylib)
frame #8: at::_ops::_to_copy::redispatch(c10::DispatchKeySet, at::Tensor const&, c10::optional<c10::ScalarType>, c10::optional<c10::Layout>, c10::optional<c10::Device>, c10::optional<bool>, bool, c10::optional<c10::MemoryFormat>) + 188 (0x10aca4588 in libtorch_cpu.dylib)
frame #9: c10::impl::wrap_kernel_functor_unboxed_<c10::impl::detail::WrapFunctionIntoFunctor_<c10::CompileTimeFunctionPointer<at::Tensor (c10::DispatchKeySet, at::Tensor const&, c10::optional<c10::ScalarType>, c10::optional<c10::Layout>, c10::optional<c10::Device>, c10::optional<bool>, bool, c10::optional<c10::MemoryFormat>), &(torch::autograd::VariableType::(anonymous namespace)::_to_copy(c10::DispatchKeySet, at::Tensor const&, c10::optional<c10::ScalarType>, c10::optional<c10::Layout>, c10::optional<c10::Device>, c10::optional<bool>, bool, c10::optional<c10::MemoryFormat>))>, at::Tensor, c10::guts::typelist::typelist<c10::DispatchKeySet, at::Tensor const&, c10::optional<c10::ScalarType>, c10::optional<c10::Layout>, c10::optional<c10::Device>, c10::optional<bool>, bool, c10::optional<c10::MemoryFormat> > >, at::Tensor (c10::DispatchKeySet, at::Tensor const&, c10::optional<c10::ScalarType>, c10::optional<c10::Layout>, c10::optional<c10::Device>, c10::optional<bool>, bool, c10::optional<c10::MemoryFormat>)>::call(c10::OperatorKernel*, c10::DispatchKeySet, at::Tensor const&, c10::optional<c10::ScalarType>, c10::optional<c10::Layout>, c10::optional<c10::Device>, c10::optional<bool>, bool, c10::optional<c10::MemoryFormat>) + 1096 (0x10c836cc8 in libtorch_cpu.dylib)
frame #10: at::_ops::_to_copy::call(at::Tensor const&, c10::optional<c10::ScalarType>, c10::optional<c10::Layout>, c10::optional<c10::Device>, c10::optional<bool>, bool, c10::optional<c10::MemoryFormat>) + 340 (0x10aca4250 in libtorch_cpu.dylib)
frame #11: at::_ops::to_device::call(at::Tensor const&, c10::Device, c10::ScalarType, bool, bool, c10::optional<c10::MemoryFormat>) + 320 (0x10ae5c320 in libtorch_cpu.dylib)
frame #12: at::print(std::__1::basic_ostream<char, std::__1::char_traits<char> >&, at::Tensor const&, long long) + 188 (0x10a323804 in libtorch_cpu.dylib)
frame #13: test(at::DeprecatedTypeProperties&) + 2136 (0x100a1c9c4 in scalar_tensor_test)
frame #14: void testing::internal::HandleExceptionsInMethodIfSupported<testing::Test, void>(testing::Test*, void (testing::Test::*)(), char const*) + 116 (0x100a380c8 in scalar_tensor_test)
frame #15: testing::Test::Run() + 812 (0x100a37ffc in scalar_tensor_test)
frame #16: testing::TestInfo::Run() + 840 (0x100a39924 in scalar_tensor_test)
frame #17: testing::TestSuite::Run() + 348 (0x100a3a3d0 in scalar_tensor_test)
frame #18: testing::internal::UnitTestImpl::RunAllTests() + 1632 (0x100a4b594 in scalar_tensor_test)
frame #19: bool testing::internal::HandleExceptionsInMethodIfSupported<testing::internal::UnitTestImpl, bool>(testing::internal::UnitTestImpl*, bool (testing::internal::UnitTestImpl::*)(), char const*) + 116 (0x100a4ad7c in scalar_tensor_test)
frame #20: testing::UnitTest::Run() + 124 (0x100a4acd4 in scalar_tensor_test)
frame #21: main + 68 (0x100a29234 in scalar_tensor_test)
frame #22: start + 520 (0x100c7508c in dyld)
".
[ FAILED ] TestScalarTensor.TestScalarTensorMPS (20 ms)
```
### Versions
PyTorch version: N/A
Is debug build: N/A
CUDA used to build PyTorch: N/A
ROCM used to build PyTorch: N/A
OS: macOS 12.6.1 (arm64)
GCC version: Could not collect
Clang version: 14.0.0 (clang-1400.0.29.202)
CMake version: version 3.24.2
Libc version: N/A
Python version: 3.9.7 (default, Sep 8 2021, 10:47:21) [Clang 12.0.5 (clang-1205.0.22.11)] (64-bit runtime)
Python platform: macOS-12.6.1-arm64-arm-64bit
Is CUDA available: N/A
CUDA runtime version: Could not collect
CUDA_MODULE_LOADING set to: N/A
GPU models and configuration: Could not collect
Nvidia driver version: Could not collect
cuDNN version: Could not collect
HIP runtime version: N/A
MIOpen runtime version: N/A
Is XNNPACK available: N/A
Versions of relevant libraries:
[pip3] mypy-extensions==0.4.3
[pip3] numpy==1.23.2
[pip3] torch==1.12.1
[pip3] torchvision==0.13.1
[conda] Could not collect
cc @kulinseth @albanD @malfet @DenisVieriu97 @razarmehr @abhudev
| 1 |
4,266 | 88,613 |
The libtorch test ConstantPropagation.CustomClassesCanBePropagated fails on Apple Silicon
|
oncall: quantization, triaged, module: m1
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
I have tried this both on v1.13.0 and on `master` (currently commit 23a3eb37cfa52fcbfb766bd733cfa60b28b83f42) and get the same error. Specifically (following [these docs](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/blob/v1.13.0/docs/libtorch.rst#building-libtorch-using-python)):
```sh
gh repo clone pytorch/pytorch && cd pytorch
git checkout v1.13.0
git submodule update --init --recursive
mkdir build_libtorch && cd build_libtorch
python ../tools/build_libtorch.py
build/bin/test_jit
```
Failing output:
```
[----------] 1 test from ConstantPropagation
[ RUN ] ConstantPropagation.CustomClassesCanBePropagated
unknown file: Failure
C++ exception with description "Expected to not find "quantized::linear_prepack" but found it
%0 : NoneType = prim::Constant()
%11 : QInt8(3, 3, strides=[3, 1], requires_grad=0, device=cpu) = prim::Constant[value= 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 [ QuantizedCPUQInt8Type{3,3}, qscheme: per_tensor_affine, scale: 1, zero_point: 0 ]]()
%8 : __torch__.torch.classes.quantized.LinearPackedParamsBase = quantized::linear_prepack(%11, %0)
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ <--- HERE
return (%8)
From CHECK-NOT: quantized::linear_prepack
" thrown in the test body.
[ FAILED ] ConstantPropagation.CustomClassesCanBePropagated (2 ms)
[----------] 1 test from ConstantPropagation (2 ms total)
```
### Versions
Collecting environment information...
PyTorch version: N/A
Is debug build: N/A
CUDA used to build PyTorch: N/A
ROCM used to build PyTorch: N/A
OS: macOS 12.6.1 (arm64)
GCC version: Could not collect
Clang version: 14.0.0 (clang-1400.0.29.202)
CMake version: version 3.24.2
Libc version: N/A
Python version: 3.9.7 (default, Sep 8 2021, 10:47:21) [Clang 12.0.5 (clang-1205.0.22.11)] (64-bit runtime)
Python platform: macOS-12.6.1-arm64-arm-64bit
Is CUDA available: N/A
CUDA runtime version: Could not collect
CUDA_MODULE_LOADING set to: N/A
GPU models and configuration: Could not collect
Nvidia driver version: Could not collect
cuDNN version: Could not collect
HIP runtime version: N/A
MIOpen runtime version: N/A
Is XNNPACK available: N/A
Versions of relevant libraries:
[pip3] mypy-extensions==0.4.3
[pip3] numpy==1.23.2
[pip3] torch==1.12.1
[pip3] torchvision==0.13.1
[conda] Could not collect
cc @jerryzh168 @jianyuh @raghuramank100 @jamesr66a @vkuzo @jgong5 @Xia-Weiwen @leslie-fang-intel
| 3 |
4,267 | 88,612 |
Bernoulli uses legacy contiguous memory format
|
triaged, module: memory format
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
```
RuntimeError: output 0: meta disagrees with real impl:
aten.bernoulli.default(
tensor(..., device='meta', size=(2, 3, 4)) stride=(1, 2, 6),
) = (
tensor(..., device='meta', size=(2, 3, 4)) stride=(1, 2, 6)
)
but real stride was (12, 4, 1)
```
after patching in bernoulli metas
```
+@register_meta([aten.bernoulli.default, aten.bernoulli.out])
+@out_wrapper()
+def meta_bernoulli(self, *, generator=None):
+ return torch.empty_like(self)
+
+
@register_meta(aten.bernoulli_.float)
def meta_bernoulli_(self, p=0.5, generator=None):
return self
+@register_meta(aten.bernoulli.p)
+def meta_bernoulli_p(self, p=0.5, generator=None):
+ return torch.empty_like(self)
+
+
```
python test/test_meta.py -k test_dispatch_symbolic_meta_outplace_all_strides_bernoulli_cuda_float32
cpu passes with these metas
### Versions
master
cc @VitalyFedyunin @jamesr66a
| 2 |
4,268 | 88,609 |
quantization convert should warn the user if calibration has not happened
|
oncall: quantization, triaged
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
It's an easy mistake to pass the wrong model into `prepare_fx`, such as
```
import copy
import torch
import torch.ao.quantize_fx as quantize_fx
m = M(...)
mp = prepare_fx(copy.deepcopy(m), ...)
# wrong model used for calibration
calibrate(m, data_loader)
mq = convert_fx(mp)
evaluate(mq, data_loader)
```
Currently there is no way for user to realize the mistake until after they evaluated the accuracy, which can take awhile depending on model/dataset. If the user is doing static quantization, we should warn the user during convert if any activation observers have not seen any data.
### Versions
master
cc @jerryzh168 @jianyuh @raghuramank100 @jamesr66a @jgong5 @Xia-Weiwen @leslie-fang-intel
| 3 |
4,269 | 88,598 |
Despite having aten::diag_embed.out, torch.diag_embed doesn't support out= argument
|
triaged, module: codegen
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
Discovered while working on https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/88584 You can test by trying to call diag_embed with an out= argument.
I think it has to do with the autogenerated schema machinery, as I don't see a denylist for diag_embed anywhere in codegen
cc @bhosmer @bdhirsh
### Versions
master
| 0 |
4,270 | 88,591 |
`pack_padded_sequence` not compatible with deterministic mode it calls `torch.scatter`
|
module: rnn, triaged, module: determinism
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
Calling `pack_padded_sequence` in deterministic mode leads to a bug because it calls `torch.scatter` underneath.
```python
import torch
from torch.nn.utils.rnn import pack_padded_sequence
# Preprocessing
minibatch_size = 1
max_seq_length = 1
input_dim = 3
seq_lengths = [
torch.randint(1, max_seq_length + 1, (1,)).item()
for _ in range(minibatch_size)
]
padded_data = torch.zeros((max_seq_length, minibatch_size, input_dim))
for i in range(minibatch_size):
padded_data[: seq_lengths[i], i, :] = torch.randn(seq_lengths[i], input_dim)
# Main problem
torch.use_deterministic_algorithms(True)
packed_data = pack_padded_sequence(
padded_data, seq_lengths, batch_first=False, enforce_sorted=False
)
```
Traceback
```
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
File "/private/home/asablayrolles/miniconda3/envs/_throwaway_nightly/lib/python3.9/site-packages/torch/nn/utils/rnn.py", line 263, in pack_padded_sequence
return _packed_sequence_init(data, batch_sizes, sorted_indices, None)
File "/private/home/asablayrolles/miniconda3/envs/_throwaway_nightly/lib/python3.9/site-packages/torch/nn/utils/rnn.py", line 195, in _packed_sequence_init
data, batch_sizes, sorted_indices, unsorted_indices = _packed_sequence_init_args(
File "/private/home/asablayrolles/miniconda3/envs/_throwaway_nightly/lib/python3.9/site-packages/torch/nn/utils/rnn.py", line 169, in _packed_sequence_init_args
unsorted_indices = invert_permutation(sorted_indices)
File "/private/home/asablayrolles/miniconda3/envs/_throwaway_nightly/lib/python3.9/site-packages/torch/nn/utils/rnn.py", line 204, in invert_permutation
output.scatter_(0, permutation,
RuntimeError: scatter with src tensor and reduce=None does not have a deterministic implementation, but you set 'torch.use_deterministic_algorithms(True)'. You can turn off determinism just for this operation, or you can use the 'warn_only=True' option, if that's acceptable for your application. You can also file an issue at https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues to help us prioritize adding deterministic support for this operation.
```
### Versions
Collecting environment information...
PyTorch version: 1.14.0.dev20221107
Is debug build: False
CUDA used to build PyTorch: Could not collect
ROCM used to build PyTorch: N/A
OS: Ubuntu 20.04.2 LTS (x86_64)
GCC version: (Ubuntu 9.3.0-17ubuntu1~20.04) 9.3.0
Clang version: Could not collect
CMake version: version 3.16.3
Libc version: glibc-2.31
Python version: 3.9.13 (main, Oct 13 2022, 21:15:33) [GCC 11.2.0] (64-bit runtime)
Python platform: Linux-5.4.0-81-generic-x86_64-with-glibc2.31
Is CUDA available: False
CUDA runtime version: 11.6.112
GPU models and configuration:
GPU 0: Quadro GP100
GPU 1: Quadro GP100
Nvidia driver version: 470.57.02
cuDNN version: Could not collect
HIP runtime version: N/A
MIOpen runtime version: N/A
Is XNNPACK available: True
Versions of relevant libraries:
[pip3] numpy==1.23.3
[pip3] torch==1.14.0.dev20221107
[pip3] torchaudio==0.14.0.dev20221107
[pip3] torchvision==0.15.0.dev20221107
[conda] blas 1.0 mkl
[conda] cpuonly 2.0 0 pytorch-nightly
[conda] ffmpeg 4.3 hf484d3e_0 pytorch
[conda] mkl 2021.4.0 h06a4308_640
[conda] mkl-service 2.4.0 py39h7f8727e_0
[conda] mkl_fft 1.3.1 py39hd3c417c_0
[conda] mkl_random 1.2.2 py39h51133e4_0
[conda] numpy 1.23.3 py39h14f4228_1
[conda] numpy-base 1.23.3 py39h31eccc5_1
[conda] pytorch 1.14.0.dev20221107 py3.9_cpu_0 pytorch-nightly
[conda] pytorch-mutex 1.0 cpu pytorch-nightly
[conda] torchaudio 0.14.0.dev20221107 py39_cpu pytorch-nightly
[conda] torchvision 0.15.0.dev20221107 py39_cpu pytorch-nightly
cc @zou3519 @mruberry @kurtamohler
| 0 |
4,271 | 88,581 |
cpp_extension CUDA library path hard-coded as "lib64" but may be "lib"
|
module: cpp-extensions, triaged, actionable
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
The path to libcudart.so is [hard-coded to be "lib64"](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/blob/71fe069d985e97b5947d133f2f2bde9adea01ed7/torch/utils/cpp_extension.py#L1691) when using the "load" and "load_inline" (Ninja) methods for C++ extensions. It may sometimes, however, instead be "lib". This is acknowledged in [the alternative setuptools installation method](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/blob/71fe069d985e97b5947d133f2f2bde9adea01ed7/torch/utils/cpp_extension.py#L1171). This will cause loading C++ extensions to fail for those whose libcudart.so is in "lib".
### Versions
N/A
cc @malfet @zou3519
| 1 |
4,272 | 88,579 |
[Quant] Validate FixedQParams observers in eager mode
|
oncall: quantization, triaged
|
Currently, in eager mode, we treat fixed qparams ops such as `torch.nn.Sigmoid` and `torch.nn.Tanh` as having "special activation post process" according to this mapping:
https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/blob/a16ced03c93dcbc5b08d0f9a36f8feab583f129a/torch/ao/quantization/quantization_mappings.py#L188-L193
Even if the user explicitly configured a QConfig for these modules, we would overwrite the configured observers with a `FixedQParamsFakeQuantize`. https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/88498 recently added a workaround for users to override this behavior, but requires users to explicitly specify these modules in `non_leaf_module_list`.
Instead, what we should do is don't overwrite the observers set by the users, but instead validate whether these observers satisfy our requirements. We did this recently with FX graph mode quantization already (https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/80184) and we should do the same for eager mode.
cc @jerryzh168 @jianyuh @raghuramank100 @jamesr66a @vkuzo @jgong5 @Xia-Weiwen @leslie-fang-intel
| 1 |
4,273 | 88,576 |
Dynamo handling for all methods of torch.Generator
|
triaged, module: dynamo
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
We have a few different conditionals (https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/blob/7076a6481d9f6d3ed40af1eac285fe5046a87531/torch/_dynamo/variables/torch.py#L294-L313, https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/blob/7076a6481d9f6d3ed40af1eac285fe5046a87531/torch/_dynamo/variables/torch.py#L314-L337, https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/blob/7076a6481d9f6d3ed40af1eac285fe5046a87531/torch/_dynamo/variables/tensor.py#L233-L241) to handle methods on torch.Generator and some torch.random functions, but it doesn't cover every function and method, for e.g., https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.Generator.html?highlight=manual_seed#torch.Generator.manual_seed. Creating this issue for a general strategy as well as figure out how to add support for `Generator.manual_seed`
### Versions
master
cc @mlazos @soumith @voznesenskym @yanboliang @penguinwu @anijain2305 @EikanWang @jgong5 @Guobing-Chen @chunyuan-w @XiaobingSuper @zhuhaozhe @blzheng @Xia-Weiwen @wenzhe-nrv @jiayisunx @desertfire
| 0 |
4,274 | 88,574 |
Add support for `torch.Generator` in the FX IR
|
oncall: fx
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
Code samples that don't work:
```
def fn1(x):
return torch.manual_seed(x)
def fn2(x):
g_cpu = torch.Generator()
return g_cpu.manual_seed(x)
```
```
b = make_fx(fn1)
# b = make_fx(fn2)
b(1729).print_readable()
```
```
incomplete graph:
class fn1(torch.nn.Module):
def forward(self, x_1):
pass
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "/scratch/chourdiaanjali/work/pytorch/tryy2.py", line 22, in <module>
b(1729).print_readable()
File "/scratch/chourdiaanjali/work/pytorch/torch/fx/experimental/proxy_tensor.py", line 665, in wrapped
t = dispatch_trace(wrap_key(func, args, fx_tracer), tracer=fx_tracer, concrete_args=tuple(phs))
File "/scratch/chourdiaanjali/work/pytorch/torch/fx/experimental/proxy_tensor.py", line 422, in dispatch_trace
graph = tracer.trace(root, concrete_args)
File "/scratch/chourdiaanjali/work/pytorch/torch/fx/_symbolic_trace.py", line 739, in trace
(self.create_arg(fn(*args)),),
File "/scratch/chourdiaanjali/work/pytorch/torch/fx/experimental/proxy_tensor.py", line 412, in create_arg
return super().create_arg(a)
File "/scratch/chourdiaanjali/work/pytorch/torch/fx/_symbolic_trace.py", line 344, in create_arg
return super().create_arg(a)
File "/scratch/chourdiaanjali/work/pytorch/torch/fx/proxy.py", line 165, in create_arg
raise NotImplementedError(f"argument of type: {type(a)}")
NotImplementedError: argument of type: <class 'torch._C.Generator'>
```
### Versions
master
cc @ezyang @SherlockNoMad @EikanWang @jgong5 @wenzhe-nrv
| 1 |
4,275 | 88,565 |
What causes CPU to degrade when I load the weight with torch.hub.load()
|
module: cpu, triaged, module: hub, intel
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
## My problem
Hi @pytorchbot
I use detect.py file to detect object then CPU: 78.1%.
On the other hand, I load weight by **_torch.hub.load()_** then CPU: 16,2%.
- torch.hub.load()

- run detect.py

Can you point out what the cause is?
### Versions
i load weight by **torch.hub.load()** such as in line 10: https://github.com/TRINHHOANGANH/test_yolov5_torch_hub.git

cc @VitalyFedyunin @jgong5 @mingfeima @XiaobingSuper @sanchitintel @ashokei @jingxu10 @nairbv @NicolasHug @vmoens @jdsgomes
| 6 |
4,276 | 88,563 |
`nn.functional.embedding_bag` Trigger out-of-bound Read under Compute Sanitizer
|
module: cuda, triaged
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
A test case for `torch.nn.functional.embedding_bag` behaves differently under CPU and GPU.
The test is shown as follows:
```python
import torch
def test():
arg_1 = torch.randint(-2048,256,[8], dtype=torch.int64).clone().cuda()
arg_2 = torch.rand([10, 3], dtype=torch.float64).clone().cuda()
arg_3 = torch.randint(-8192,128,[2], dtype=torch.int64).clone().cuda()
arg_4 = False
res = torch.nn.functional.embedding_bag(arg_1,arg_2,arg_3,arg_4,)
test()
```
The test with `.cuda()` is supposed to be run under GPU and it exits with `returncode=0`. If we remove the `.cuda()`, i.e, run the test under CPU, it reports an invalid argument error with `returncode=1`:
```
IndexError: select(): index -1923 out of range for tensor of size [10, 3] at dimension 0
```
Additionally, we use compute sanitizer to run the GPU version test and it reports an out-of-bound read error:
```
# command: compute-sanitizer python3 test.py
========= COMPUTE-SANITIZER
========= Invalid __global__ read of size 8 bytes
========= at 0x310 in void at::native::<unnamed>::renorm_kernel<double, double, long>(T1 *, T3 *, T2, T2, long, long, long, long *)
========= by thread (0,0,0) in block (0,0,0)
========= Address 0x7fb982ffa800 is out of bounds
========= and is 22,528 bytes before the nearest allocation at 0x7fb983000000 of size 2,097,152 bytes
=========
========= Invalid __global__ read of size 8 bytes
========= at 0x310 in void at::native::<unnamed>::renorm_kernel<double, double, long>(T1 *, T3 *, T2, T2, long, long, long, long *)
========= by thread (1,0,0) in block (0,0,0)
========= Address 0x7fb982ffa808 is out of bounds
========= and is 22,520 bytes before the nearest allocation at 0x7fb983000000 of size 2,097,152 bytes
========= ... (omitte)
========= ERROR SUMMARY: 21 errors
```
### Versions
```
PyTorch version: 1.14.0a0+git81042d3
Is debug build: False
CUDA used to build PyTorch: 11.6
ROCM used to build PyTorch: N/A
OS: Ubuntu 22.04.1 LTS (x86_64)
GCC version: (Ubuntu 11.3.0-1ubuntu1~22.04) 11.3.0
Clang version: 11.1.0-6
CMake version: version 3.22.1
Libc version: glibc-2.35
Python version: 3.10.6 (main, Nov 2 2022, 18:53:38) [GCC 11.3.0] (64-bit runtime)
Python platform: Linux-5.15.0-52-generic-x86_64-with-glibc2.35
Is CUDA available: True
CUDA runtime version: 11.6.124
CUDA_MODULE_LOADING set to: LAZY
GPU models and configuration:
GPU 0: NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3090
GPU 1: NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3090
GPU 2: NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3090
Nvidia driver version: 515.65.01
cuDNN version: Probably one of the following:
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_adv_infer.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_adv_train.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_cnn_infer.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_cnn_train.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_ops_infer.so.8.4.1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcudnn_ops_train.so.8.4.1
HIP runtime version: N/A
MIOpen runtime version: N/A
Is XNNPACK available: True
Versions of relevant libraries:
[pip3] numpy==1.21.5
[pip3] torch==1.14.0a0+git81042d3
[pip3] torchvision==0.13.1
[conda] blas 1.0 mkl
[conda] cudatoolkit 11.3.1 h2bc3f7f_2
[conda] mkl 2021.4.0 h06a4308_640
[conda] mkl-service 2.4.0 py39h7f8727e_0
[conda] mkl_fft 1.3.1 py39hd3c417c_0
[conda] mkl_random 1.2.2 py39h51133e4_0
[conda] numpy 1.21.5 py39he7a7128_1
[conda] numpy-base 1.21.5 py39hf524024_1
[conda] numpydoc 1.2 pyhd3eb1b0_0
```
cc @ngimel
| 4 |
4,277 | 93,610 |
We probably are allowing mutations to happen on fake tensor in VariableTracker
|
triaged, bug, module: dynamo
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
VariableTracker is supposed to be immutable, so we can do checkpointing and rollback when instruction translation fails and we need to create a graph break.
However, we (indirectly) store fake tensor in VariableTracker, and fake tensor is not treated immutably. In particular, when we run nodes on fake tensor, those nodes may modify the metadata of the input fake tensor, and I don't see any logic that appropriately duplicates fake tensors so that we can safely run modifications on them.
The hypothetical bug is that we checkpoint, we then run the symbolic evaluator on `squeeze_`, and that mutates the fake tensor, but then we discover we need to rollback, and now subsequent code will see incorrect metadata for the input to squeeze. Discussing this with jansel, this is unlikely to happen in practice today, because the only time we rollback is right before we are generating a graph break, and at that point we're not going to actually insert any more nodes into the graph. But it will be good to get this correct, in case we end up using checkpointing more seriously in the future. More generally, we probably need some sort of lint to make sure that VariableTrackers do not actually get mutated, because they're not going to turn into real bugs immediately if you corrupt the state.
cc @soumith @voznesenskym @yanboliang @penguinwu @anijain2305 @EikanWang @jgong5 @Guobing-Chen @XiaobingSuper @zhuhaozhe @blzheng @Xia-Weiwen @wenzhe-nrv @jiayisunx @desertfire @eellison @jansel
### Error logs
_No response_
### Minified repro
_No response_
| 7 |
4,278 | 88,505 |
quantization: error message when using `convert_fx` on a model on cuda should be better
|
oncall: quantization, triaged
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
When a user tries to use `convert_fx` on a model which is on cuda, the error message doesn't make sense. We should either throw an error message which asks the user to move the model to cuda, or we should lower successfully.
Repro script:
```
import torch
import torch.ao.quantization.quantize_fx as quantize_fx
qconfig_mapping = torch.ao.quantization.get_default_qconfig_mapping('fbgemm')
m = torch.nn.Sequential(torch.nn.Linear(1, 1)).to('cuda')
mp = quantize_fx.prepare_fx(m, qconfig_mapping, (torch.randn(1),))
mq = quantize_fx.convert_fx(mp)
```
Error message:
```
import torch.ao.quantization.quantize_fx as quantize_fx
(pytorch) [vasiliy@devgpu032.ftw6 ~/local/pytorch (master)]$ python ../tmp/test.py
/data/users/vasiliy/pytorch/torch/ao/quantization/observer.py:214: UserWarning: Please use quant_min and quant_max to spe
cify the range for observers. reduce_range will be deprecated in a future release of PyTorch.
warnings.warn(
/data/users/vasiliy/pytorch/torch/ao/quantization/observer.py:1204: UserWarning: must run observer before calling calcula
te_qparams. Returning default scale and zero point
warnings.warn(
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "/data/users/vasiliy/pytorch/../tmp/test.py", line 18, in <module>
mq = quantize_fx.convert_fx(mp)
File "/data/users/vasiliy/pytorch/torch/ao/quantization/quantize_fx.py", line 622, in convert_fx
return _convert_fx(
File "/data/users/vasiliy/pytorch/torch/ao/quantization/quantize_fx.py", line 548, in _convert_fx
quantized = convert(
File "/data/users/vasiliy/pytorch/torch/ao/quantization/fx/convert.py", line 766, in convert
model = lower_to_fbgemm(model, node_name_to_qconfig, node_name_to_scope)
File "/data/users/vasiliy/pytorch/torch/ao/quantization/fx/lower_to_fbgemm.py", line 16, in lower_to_fbgemm
return _lower_to_native_backend(model, qconfig_map, node_name_to_scope)
File "/data/users/vasiliy/pytorch/torch/ao/quantization/fx/_lower_to_native_backend.py", line 928, in _lower_to_native_
backend
_lower_static_weighted_ref_module(model, qconfig_map)
File "/data/users/vasiliy/pytorch/torch/ao/quantization/fx/_lower_to_native_backend.py", line 499, in _lower_static_wei
ghted_ref_module
q_module = q_class.from_reference(ref_module, output_scale, output_zero_point)
File "/data/users/vasiliy/pytorch/torch/ao/nn/quantized/modules/linear.py", line 298, in from_reference
qlinear.set_weight_bias(qweight, ref_qlinear.bias)
File "/data/users/vasiliy/pytorch/torch/ao/nn/quantized/modules/linear.py", line 240, in set_weight_bias
self._packed_params.set_weight_bias(w, b)
File "/data/users/vasiliy/pytorch/torch/ao/nn/quantized/modules/linear.py", line 32, in set_weight_bias
self._packed_params = torch.ops.quantized.linear_prepack(weight, bias)
File "/data/users/vasiliy/pytorch/torch/_ops.py", line 446, in __call__
return self._op(*args, **kwargs or {})
RuntimeError: Unsupported qscheme: per_channel_affine
```
### Versions
master
cc @jerryzh168 @jianyuh @raghuramank100 @jamesr66a @jgong5 @Xia-Weiwen @leslie-fang-intel
| 2 |
4,279 | 93,609 |
Don't store example_value on FX node meta
|
triaged, bug
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
Storing it in the meta dict implies that we will pass it to the backend compiler. But actually we strip all of the example values from the FX graph when we're done. So this is really just an internal concept to Dynamo. I propose we store it on TensorVariable instead.
BTW, you don't want to actually pass this metadata on to the backend, because in the presence of metadata mutation it can be misleading. E.g.:
```
@torch._dynamo.optimize(my_backend)
def f(x):
y = x.clone()
y.transpose_(0, 1)
return y
f(torch.randn(4, 5))
```
What do you expect the example value of y to be?
cc @eellison @Chillee @voznesenskym @jansel
### Error logs
_No response_
### Minified repro
_No response_
| 2 |
4,280 | 88,491 |
torch.set_grad_enabled results in RuntimeError with torch.jit.script
|
oncall: jit
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
Calling `torch.set_grad_enabled` in `nn.Module.forward` results in RuntimeError when compiling a module with `torch.jit.script`.
Minimal Example:
```python
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
class BrokenModule(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, freeze: bool) -> None:
super().__init__()
self.freeze = freeze
self.maybe_frozen = nn.Linear(10, 10)
self.never_frozen = nn.Linear(10, 10)
def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
with torch.set_grad_enabled(not self.freeze):
x = self.maybe_frozen(x)
x = self.never_frozen(x)
return x
# This raises RuntimeError
script = torch.jit.script(BrokenModule(freeze=True)) # type: ignore
```
The full error message:
```
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "/home/xxx/repos/yyy/torchbug.py", line 39, in <module>
script = torch.jit.script(BrokenModule(freeze=True)) # type: ignore
File "/home/xxx/venvs/dev38/lib/python3.8/site-packages/torch/jit/_script.py", line 1286, in script
return torch.jit._recursive.create_script_module(
File "/home/xxx/venvs/dev38/lib/python3.8/site-packages/torch/jit/_recursive.py", line 458, in create_script_module
return create_script_module_impl(nn_module, concrete_type, stubs_fn)
File "/home/lxxx/venvs/dev38/lib/python3.8/site-packages/torch/jit/_recursive.py", line 524, in create_script_module_impl
create_methods_and_properties_from_stubs(concrete_type, method_stubs, property_stubs)
File "/home/xxx/venvs/dev38/lib/python3.8/site-packages/torch/jit/_recursive.py", line 375, in create_methods_and_properties_from_stubs
concrete_type._create_methods_and_properties(property_defs, property_rcbs, method_defs, method_rcbs, method_defaults)
RuntimeError:
With item expression must return an object:
File "/home/xxx/repos/yyy/torchbug.py", line 14
def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
with torch.set_grad_enabled(not self.freeze):
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ <--- HERE
x = self.maybe_frozen(x)
x = self.never_frozen(x)
```
Ugly Workaround:
```python
def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
if self.freeze:
with torch.no_grad():
x = self.maybe_frozen(x)
else:
x = self.maybe_frozen(x)
x = self.never_frozen(x)
return x
```
Why can't I just use the original script?
### Versions
PyTorch version: 1.12.0+cu116
Is debug build: False
CUDA used to build PyTorch: 11.6
ROCM used to build PyTorch: N/A
OS: Ubuntu 20.04.5 LTS (x86_64)
GCC version: (Ubuntu 9.4.0-1ubuntu1~20.04.1) 9.4.0
Clang version: Could not collect
CMake version: version 3.24.3
Libc version: glibc-2.31
Python version: 3.8.10 (default, Jun 22 2022, 20:18:18) [GCC 9.4.0] (64-bit runtime)
Python platform: Linux-5.15.0-52-generic-x86_64-with-glibc2.29
Is CUDA available: True
CUDA runtime version: 11.6.124
CUDA_MODULE_LOADING set to:
GPU models and configuration: GPU 0: NVIDIA GeForce RTX 2080 Ti
Nvidia driver version: 510.85.02
cuDNN version: Could not collect
HIP runtime version: N/A
MIOpen runtime version: N/A
Is XNNPACK available: True
Versions of relevant libraries:
[pip3] mypy-extensions==0.4.3
[pip3] numpy==1.23.1
[pip3] numpy-quaternion==2022.4.2
[pip3] pytorch-lightning==1.6.5
[pip3] torch==1.12.0+cu116
[pip3] torchmetrics==0.9.3
[pip3] torchvision==0.13.0+cu116
[conda] Could not collect
cc @EikanWang @jgong5 @wenzhe-nrv @sanchitintel
| 0 |
4,281 | 88,475 |
DISABLED test_module_attribute_mutation_violation_negative_2 (__main__.MutationExportTests)
|
triaged, module: flaky-tests, skipped, module: dynamo
|
Platforms: linux, mac, macos
This test was disabled because it is failing in CI. See [recent examples](https://hud.pytorch.org/flakytest?name=test_module_attribute_mutation_violation_negative_2&suite=MutationExportTests) and the most recent trunk [workflow logs](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/runs/9284427989).
Over the past 3 hours, it has been determined flaky in 6 workflow(s) with 6 failures and 6 successes.
**Debugging instructions (after clicking on the recent samples link):**
DO NOT BE ALARMED IF THE CI IS GREEN. We now shield flaky tests from developers so CI will thus be green but it will be harder to parse the logs.
To find relevant log snippets:
1. Click on the workflow logs linked above
2. Click on the Test step of the job so that it is expanded. Otherwise, the grepping will not work.
3. Grep for `test_module_attribute_mutation_violation_negative_2`
4. There should be several instances run (as flaky tests are rerun in CI) from which you can study the logs.
cc @mlazos @soumith @voznesenskym @yanboliang @penguinwu @anijain2305 @EikanWang @jgong5 @Guobing-Chen @chunyuan-w @XiaobingSuper @zhuhaozhe @blzheng @Xia-Weiwen @wenzhe-nrv @jiayisunx
| 12 |
4,282 | 88,474 |
Mixed precision training fails due to NaN in batch norm running_mean
|
triaged, module: amp (automated mixed precision)
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
During mixed precision training, the NaN gradient is skipped by grad_scaler. However, the NaN output will destroy the batch norm running mean and variance. This is severe because:
1. It can only be observed during validation since during training the running_mean and running_variance are not used.
2. It will break the whole training process of AMP.
Can batch norm skip NaN samples while updating the running_mean and running_var? Is there any way to achieve such a purpose? Following is an MRE.
```python
import torch
data = torch.rand(2, 3, 10).cuda()
from torch import nn
from torch.cuda.amp import autocast as autocast
network = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv1d(3, 16, 3, padding=1),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.BatchNorm1d(16)).cuda()
with autocast():
data = data.half() * 100000
output = network[0](data)
output = network[1](output)
output = network[2](output)
print(network[1].running_mean)
```
The output is :
```
tensor([nan, nan, nan, nan, nan, nan, nan, nan, nan, nan, nan, nan, nan, nan, nan, nan],
device='cuda:0')
```
### Versions
PyTorch version: 1.10.1
Is debug build: False
CUDA used to build PyTorch: 11.3
ROCM used to build PyTorch: N/A
OS: Ubuntu 20.04.3 LTS (x86_64)
GCC version: (Ubuntu 9.3.0-17ubuntu1~20.04) 9.3.0
Clang version: Could not collect
CMake version: version 3.22.1
Libc version: glibc-2.31
Python version: 3.9.7 (default, Sep 16 2021, 13:09:58) [GCC 7.5.0] (64-bit runtime)
Python platform: Linux-5.10.102.1-microsoft-standard-WSL2-x86_64-with-glibc2.31
cc @VitalyFedyunin @jgong5 @mingfeima @XiaobingSuper @sanchitintel @ashokei @jingxu10 @mcarilli @ptrblck @leslie-fang-intel
| 6 |
4,283 | 88,472 |
DISABLED test_index_put_accumulate_large_tensor_cpu (__main__.TestIndexingCPU)
|
triaged, module: flaky-tests, skipped, module: dynamo
|
Platforms: dynamo
This is related to https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/88413
This test was disabled because it is suspected to cause `test_indexing.py` to become flaky with SIGKILL. Looking into the log such as https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/actions/runs/3388902619/jobs/5631574640, it's unclear which sends SIGKILL to the test, but it's always at `test_index_put_accumulate_large_tensor_cpu`. For example:
```
test_boolean_assignment_value_mismatch_cpu (__main__.NumpyTestsCPU) ... ok
test_boolean_indexing_alldims_cpu (__main__.NumpyTestsCPU) ... ok
test_boolean_indexing_onedim_cpu (__main__.NumpyTestsCPU) ... ok
test_boolean_indexing_twodim_cpu (__main__.NumpyTestsCPU) ... ok
test_boolean_indexing_weirdness_cpu (__main__.NumpyTestsCPU) ...ok
test_boolean_indexing_weirdness_tensors_cpu (__main__.NumpyTestsCPU) ... ok
test_boolean_list_indexing_cpu (__main__.NumpyTestsCPU) ... ok
test_boolean_shape_mismatch_cpu (__main__.NumpyTestsCPU) ... ok
test_broadcast_subspace_cpu (__main__.NumpyTestsCPU) ... ok
test_broaderrors_indexing_cpu (__main__.NumpyTestsCPU) ... ok
test_ellipsis_index_cpu (__main__.NumpyTestsCPU) ... ok
test_empty_fancy_index_cpu (__main__.NumpyTestsCPU) ... ok
test_empty_tuple_index_cpu (__main__.NumpyTestsCPU) ... ok
test_everything_returns_views_cpu (__main__.NumpyTestsCPU) ... ok
test_index_is_larger_cpu (__main__.NumpyTestsCPU) ... ok
test_index_no_floats_cpu (__main__.NumpyTestsCPU) ... ok
test_none_index_cpu (__main__.NumpyTestsCPU) ... ok
test_single_bool_index_cpu (__main__.NumpyTestsCPU) ... ok
test_single_int_index_cpu (__main__.NumpyTestsCPU) ... ok
test_trivial_fancy_out_of_bounds_cpu (__main__.NumpyTestsCPU) ... ok
test_advancedindex_big_cpu (__main__.TestIndexingCPU) ... ok
test_advancedindex_cpu_float16 (__main__.TestIndexingCPU) ... ok
test_advancedindex_cpu_float64 (__main__.TestIndexingCPU) ...ok
test_basic_advanced_combined_cpu (__main__.TestIndexingCPU) ... ok
test_bool_indices_accumulate_cpu (__main__.TestIndexingCPU) ... ok
test_bool_indices_cpu (__main__.TestIndexingCPU) ... ok
test_byte_mask2d_cpu (__main__.TestIndexingCPU) ... ok
test_byte_mask_accumulate_cpu (__main__.TestIndexingCPU) ... ok
test_byte_mask_cpu (__main__.TestIndexingCPU) ... ok
test_byte_tensor_assignment_cpu (__main__.TestIndexingCPU) ... ok
test_cpu_indices_cpu (__main__.TestIndexingCPU) ... skip: Only runs on cuda (0.002s)
test_ellipsis_tensor_cpu (__main__.TestIndexingCPU) ... ok
test_empty_index_cpu (__main__.TestIndexingCPU) ... ok
test_empty_ndim_index_bool_cpu (__main__.TestIndexingCPU) ... ok
test_empty_ndim_index_cpu (__main__.TestIndexingCPU) ... ok
test_empty_slice_cpu (__main__.TestIndexingCPU) ... ok
test_gather_take_along_dim_cross_device_cpu_float32 (__main__.TestIndexingCPU) ... skip: Only runs on cuda
test_getitem_scalars_cpu (__main__.TestIndexingCPU) ... ok
test_index_cpu (__main__.TestIndexingCPU) ... ok
test_index_getitem_copy_bools_slices_cpu (__main__.TestIndexingCPU) ... ok
test_index_ind_dtype_cpu (__main__.TestIndexingCPU) ... ok
test_index_put_accumulate_duplicate_indices_cpu (__main__.TestIndexingCPU) ... ok
test_index_put_accumulate_expanded_values_cpu (__main__.TestIndexingCPU) ... ok
test_index_put_accumulate_large_tensor_cpu (__main__.TestIndexingCPU) ...
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "test/run_test.py", line 1283, in <module>
main()
File "test/run_test.py", line 1258, in main
raise RuntimeError(err_message)
RuntimeError: test_indexing failed! Received signal: SIGKILL
```
I'm trying to do an experimentation and disable this test for a few days to see if it helps and go from there
cc @mlazos @soumith @voznesenskym @yanboliang @penguinwu @anijain2305 @EikanWang @jgong5 @Guobing-Chen @chunyuan-w @XiaobingSuper @zhuhaozhe @blzheng @Xia-Weiwen @wenzhe-nrv @jiayisunx
| 2 |
4,284 | 88,468 |
DISABLED test_module_attribute_mutation_violation_negative_1 (__main__.MutationExportTests)
|
triaged, module: flaky-tests, skipped, module: dynamo
|
Platforms: linux, macos, mac
This test was disabled because it is failing in CI. See [recent examples](https://hud.pytorch.org/flakytest?name=test_module_attribute_mutation_violation_negative_1&suite=MutationExportTests) and the most recent trunk [workflow logs](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/runs/9284368349).
Over the past 3 hours, it has been determined flaky in 4 workflow(s) with 7 failures and 4 successes.
**Debugging instructions (after clicking on the recent samples link):**
DO NOT BE ALARMED IF THE CI IS GREEN. We now shield flaky tests from developers so CI will thus be green but it will be harder to parse the logs.
To find relevant log snippets:
1. Click on the workflow logs linked above
2. Click on the Test step of the job so that it is expanded. Otherwise, the grepping will not work.
3. Grep for `test_module_attribute_mutation_violation_negative_1`
4. There should be several instances run (as flaky tests are rerun in CI) from which you can study the logs.
cc @mlazos @soumith @voznesenskym @yanboliang @penguinwu @anijain2305 @EikanWang @jgong5 @Guobing-Chen @chunyuan-w @XiaobingSuper @zhuhaozhe @blzheng @Xia-Weiwen @wenzhe-nrv @jiayisunx
| 10 |
4,285 | 88,467 |
DISABLED test_module_attribute_mutation_violation_negative_4 (__main__.MutationExportTests)
|
triaged, module: flaky-tests, skipped, module: dynamo
|
Platforms: linux, macos
This test was disabled because it is failing in CI. See [recent examples](https://hud.pytorch.org/flakytest?name=test_module_attribute_mutation_violation_negative_4&suite=MutationExportTests) and the most recent trunk [workflow logs](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/runs/9279095156).
Over the past 3 hours, it has been determined flaky in 3 workflow(s) with 3 failures and 3 successes.
**Debugging instructions (after clicking on the recent samples link):**
DO NOT BE ALARMED IF THE CI IS GREEN. We now shield flaky tests from developers so CI will thus be green but it will be harder to parse the logs.
To find relevant log snippets:
1. Click on the workflow logs linked above
2. Click on the Test step of the job so that it is expanded. Otherwise, the grepping will not work.
3. Grep for `test_module_attribute_mutation_violation_negative_4`
4. There should be several instances run (as flaky tests are rerun in CI) from which you can study the logs.
cc @mlazos @soumith @voznesenskym @yanboliang @penguinwu @anijain2305 @EikanWang @jgong5 @Guobing-Chen @chunyuan-w @XiaobingSuper @zhuhaozhe @blzheng @Xia-Weiwen @wenzhe-nrv @jiayisunx
| 8 |
4,286 | 88,466 |
DISABLED test_module_attribute_mutation_violation_negative_3 (__main__.MutationExportTests)
|
triaged, module: flaky-tests, skipped, module: dynamo
|
Platforms: linux, mac, macos
This test was disabled because it is failing in CI. See [recent examples](https://hud.pytorch.org/flakytest?name=test_module_attribute_mutation_violation_negative_3&suite=MutationExportTests) and the most recent trunk [workflow logs](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/runs/9284454926).
Over the past 3 hours, it has been determined flaky in 5 workflow(s) with 8 failures and 5 successes.
**Debugging instructions (after clicking on the recent samples link):**
DO NOT BE ALARMED IF THE CI IS GREEN. We now shield flaky tests from developers so CI will thus be green but it will be harder to parse the logs.
To find relevant log snippets:
1. Click on the workflow logs linked above
2. Click on the Test step of the job so that it is expanded. Otherwise, the grepping will not work.
3. Grep for `test_module_attribute_mutation_violation_negative_3`
4. There should be several instances run (as flaky tests are rerun in CI) from which you can study the logs.
cc @mlazos @soumith @voznesenskym @yanboliang @penguinwu @anijain2305 @EikanWang @jgong5 @Guobing-Chen @chunyuan-w @XiaobingSuper @zhuhaozhe @blzheng @Xia-Weiwen @wenzhe-nrv @jiayisunx
| 12 |
4,287 | 88,464 |
MaxPool1D output shapes can be negative when ceil_mode=True
|
module: nn, triaged, module: pooling
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
When ceil_mode=True, output shape can potentially be negative, which is nonsensical. I think the calcuation of output shape for that case is wrong.
This seems related to issue https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/88144
```python
import torch
m = torch.nn.MaxPool1d(kernel_size=4, stride=1, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=True)
input = torch.randn(20, 16, 1)
output = m(input)
```
```
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "/Users/mitch/***/avgpool.py", line 6, in <module>
output = m(input)
File "/opt/homebrew/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/nn/modules/module.py", line 1190, in _call_impl
return forward_call(*input, **kwargs)
File "/opt/homebrew/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/nn/modules/pooling.py", line 92, in forward
return F.max_pool1d(input, self.kernel_size, self.stride,
File "/opt/homebrew/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/_jit_internal.py", line 485, in fn
return if_false(*args, **kwargs)
File "/opt/homebrew/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/nn/functional.py", line 696, in _max_pool1d
return torch.max_pool1d(input, kernel_size, stride, padding, dilation, ceil_mode)
RuntimeError: max_pool1d() Invalid computed output size: -2
```
My experiments suggest that output shape for ceil_mode = True should be `ceiling((inputsize + padleft) / stride)`.
### Versions
```
Collecting environment information...
PyTorch version: 1.13.0
Is debug build: False
CUDA used to build PyTorch: None
ROCM used to build PyTorch: N/A
OS: macOS 12.5 (arm64)
GCC version: Could not collect
Clang version: 14.0.0 (clang-1400.0.29.102)
CMake version: version 3.24.2
Libc version: N/A
Python version: 3.10.6 (main, Aug 30 2022, 04:58:14) [Clang 13.1.6 (clang-1316.0.21.2.5)] (64-bit runtime)
Python platform: macOS-12.5-arm64-arm-64bit
Is CUDA available: False
CUDA runtime version: No CUDA
CUDA_MODULE_LOADING set to: N/A
GPU models and configuration: No CUDA
Nvidia driver version: No CUDA
cuDNN version: No CUDA
HIP runtime version: N/A
MIOpen runtime version: N/A
Is XNNPACK available: True
Versions of relevant libraries:
[pip3] numpy==1.23.3
[pip3] torch==1.13.0
[pip3] torchaudio==0.13.0
[pip3] torchvision==0.14.0
[conda] Could not collect
```
cc @albanD @mruberry @jbschlosser @walterddr @kshitij12345 @saketh-are @VitalyFedyunin @jgong5 @mingfeima @XiaobingSuper @sanchitintel @ashokei @jingxu10
| 6 |
4,288 | 88,448 |
linear mm weight and bias dtypes mismatch bypasses
|
oncall: jit
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
Should linear weight and bias must be of the same dtypes?
For linear, I see for {2,3}d rank tensor, weight and bias dtype mismatch is checked in [addmm](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/blob/master/aten/src/ATen/native/LinearAlgebra.cpp#L155-L169). However, for higher rank tensor, weight and bias dtype mismatch is not checked in [mm](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/blob/master/aten/src/ATen/native/LinearAlgebra.cpp#L175). I wonder if
- this is unexpected, and we should add a similar check for dtype mismatch in addmm to mm
- this is expected (weight and bias can have different dtypes)
=========================================
Original Context:
Similar to conv-bn folding #76578, lin-bn folding #86706 with autocast freeze on gpu casts the [inputs to linear to half](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/blob/master/torch/csrc/jit/passes/autocast.cpp#L363), while inputs to batchnorm are not casted, remaining as float. So if the optional linear bias is set to false, bias will remain as float while weight is casted to half during autocast jit freeze, causing inconsistency in linear and bias dtype (half, float respectively).
However, this inconsistency is not checked in linear admm (is checked in mm). I wonder if
- this is unexpected, and linear weight and bias must be of the same dtypes
for {2,3}d tensors, dtype mistmatch is checked in [addmm](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/blob/master/aten/src/ATen/native/LinearAlgebra.cpp#L155-L169); for higher rank tensors, dtype mismatch is not checked in [mm](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/blob/master/aten/src/ATen/native/LinearAlgebra.cpp#L175). If this is unexpected, we can add a similar check as in addmm to mm.
- this is expected, bias can be kept in fp32 for accuracy reason.
```python
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
class LinearBN(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_features, out_features):
super(LinearBN, self).__init__()
self.linear = nn.Linear(in_features, out_features, bias=False)
self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_features)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.linear(x)
return self.bn(x)
net = LinearBN(32, 32).cuda().eval()
print("weight: ", net.linear.weight.dtype) #torch.float32
img = torch.rand((1, 32, 32, 32)).cuda()
with torch.cuda.amp.autocast(True):
net = torch.jit.script(net)
net = torch.jit.freeze(net)
lin_node = net.graph.findNode("aten::linear", True)
print("weight: ", lin_node.namedInput("weight").type().dtype()) #torch.float16
print("bias: ", lin_node.namedInput("bias").type().dtype()) #torch.float32
net(img) #passes without catching weight, bias dtype inconsistency, expected?
```
For 2/3d tensors, the dtypes mismatch is catched in [addmm](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/blob/master/aten/src/ATen/native/LinearAlgebra.cpp#L155-L169).
```python
class LinearBN(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_features, out_features):
super(LinearBN, self).__init__()
self.linear = nn.Linear(in_features, out_features, bias=False)
self.bn = nn.BatchNorm1d(out_features)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.linear(x)
return self.bn(x)
net = LinearBN(32, 32).cuda().eval()
print("weight: ", net.linear.weight.dtype) #torch.float32
img = torch.rand((1, 32)).cuda() #could also replace with 3d tensor, torch.rand((1, 32, 32))
with torch.cuda.amp.autocast(True):
net = torch.jit.script(net)
net = torch.jit.freeze(net)
lin_node = net.graph.findNode("aten::linear", True)
print("weight: ", lin_node.namedInput("weight").type().dtype()) #torch.float16
print("bias: ", lin_node.namedInput("bias").type().dtype()) #torch.float32
net(img) #weight, bias dtype inconsistency catched
```
### Versions
master `2bda2baad787923b064c747e619e62a6af969940` + #86706
cc @EikanWang @jgong5 @wenzhe-nrv @sanchitintel
| 2 |
4,289 | 88,447 |
`unique` will reverse the input when `sort=False` on cpu (not sorting)
|
module: cpu, triaged, intel
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
`unique` will reverse the input when sort=False on cpu (not sorting). By contrast, the cuda will keep the order.
```py
import torch
input = torch.FloatTensor([1, 3])
torch.unique(input, sorted=False)
# tensor([3., 1.])
torch.unique(input.cuda(), sorted=False)
# tensor([1., 3.], device='cuda:0')
```
You can see the input is in the ascending order. Even `sort=True` it should return the `[1, 3]`. But cpu will reverse the input to a descending order
### Versions
torch: 1.13.0
cuda: 11.6
cc @VitalyFedyunin @jgong5 @mingfeima @XiaobingSuper @sanchitintel @ashokei @jingxu10
| 5 |
4,290 | 93,607 |
torch._dynamo.exc.Unsupported: call_function UserDefinedClassVariable() [] {} ([Feature request] Allow custom classes with custom __setattr__ method in torchdynamo)
|
high priority, triage review, triaged, enhancement, oncall: pt2
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
Currently following doesn't work:
```
class Instances:
def __init__(self, image_size: Tuple[int, int]):
self._image_size = image_size
def __setattr__(self, name: str, val) -> None:
super().__setattr__(name, val)
def f(x):
a = Instances((4, 5))
return x
gm, _ = torchdynamo.export(f, torch.ones((4, 5)))
# Error
torch._dynamo.exc.Unsupported: call_function UserDefinedClassVariable() [ConstantVariable(tuple)] {}
```
This is because torchdynamo doesn't allow custom setattr in user provided class. @jansel mentioned it might be doable if the custom setattr doesn't have graph breaks.
### Error logs
_No response_
### Minified repro
_No response_
cc @ezyang @gchanan @zou3519 @kadeng @msaroufim @wconstab @bdhirsh @anijain2305 @soumith @ngimel
| 4 |
4,291 | 88,443 |
Hang: sampling VonMises distribution gets stuck in rejection sampling for small kappa
|
high priority, module: distributions, module: cpu, triaged, module: numpy, module: deadlock
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
Sampling the VonMises distribution gets stuck in rejection sampling for small values of the concentration parameter. With the location parameter set to 1, the problem starts around ~1e-4 for single and ~1e-8 for double precision.
```torch.distributions.von_mises.VonMises(torch.Tensor([1]), torch.Tensor([1e-4])).sample()```
Numpy doesn't have this problem, likely because small values of the concentration are caught and handled explicitly, see [here](https://github.com/numpy/numpy/blob/623bc1fae1d47df24e7f1e29321d0c0ba2771ce0/numpy/random/src/legacy/legacy-distributions.c#L421). Implementing this might solve the issue.
### Versions
Collecting environment information...
PyTorch version: 1.12.1
Is debug build: False
CUDA used to build PyTorch: 10.2
ROCM used to build PyTorch: N/A
OS: Ubuntu 22.04.1 LTS (x86_64)
GCC version: (conda-forge gcc 12.1.0-17) 12.1.0
Clang version: Could not collect
CMake version: version 3.22.1
Libc version: glibc-2.35
Python version: 3.8.13 (default, Oct 21 2022, 23:50:54) [GCC 11.2.0] (64-bit runtime)
Python platform: Linux-5.15.0-52-generic-x86_64-with-glibc2.17
Is CUDA available: True
CUDA runtime version: Could not collect
CUDA_MODULE_LOADING set to:
GPU models and configuration: GPU 0: NVIDIA T600 Laptop GPU
Nvidia driver version: 515.76
cuDNN version: Could not collect
HIP runtime version: N/A
MIOpen runtime version: N/A
Is XNNPACK available: True
Versions of relevant libraries:
[pip3] numpy==1.21.5
[pip3] torch==1.12.1
[pip3] torchaudio==0.12.1
[pip3] torchvision==0.13.1
[conda] blas 1.0 mkl
[conda] cudatoolkit 10.2.89 hfd86e86_1
[conda] ffmpeg 4.3 hf484d3e_0 pytorch
[conda] mkl 2021.4.0 h06a4308_640
[conda] mkl-service 2.4.0 py38h7f8727e_0
[conda] mkl_fft 1.3.1 py38hd3c417c_0
[conda] mkl_random 1.2.2 py38h51133e4_0
[conda] numpy 1.21.5 py38h6c91a56_3
[conda] numpy-base 1.21.5 py38ha15fc14_3
[conda] pytorch 1.12.1 py3.8_cuda10.2_cudnn7.6.5_0 pytorch
[conda] pytorch-mutex 1.0 cuda pytorch
[conda] torchaudio 0.12.1 py38_cu102 pytorch
[conda] torchvision 0.13.1 py38_cu102 pytorch
cc @ezyang @gchanan @zou3519 @fritzo @neerajprad @alicanb @nikitaved @VitalyFedyunin @jgong5 @mingfeima @XiaobingSuper @sanchitintel @ashokei @jingxu10 @mruberry @rgommers
| 9 |
4,292 | 88,423 |
view_as_real and split_with_sizes links in Tensor Views docs are broken
|
module: docs, triaged
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
https://pytorch.org/docs/master/tensor_view.html
### Versions
master and 1.13
cc @svekars @carljparker
| 1 |
4,293 | 88,415 |
Enable AMP for MPS devices
|
feature, triaged, module: amp (automated mixed precision), module: mps
|
### 🚀 The feature, motivation and pitch
https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/78168 States that fp16 support for mps devices in general should be possible, but autocas only works with `cpu` and `cuda` device types. When enabling it manually, on mps it does not show any additional conversions:
```python
>>> torch.set_autocast_enabled(True)
>>> with capture_logs(is_mode=True) as logs, LoggingTensorMode():
... a = torch.rand(10, 10, dtype=torch.float, device='mps')
... b = torch.rand(10, 10, dtype=torch.float, device='mps')
... c = torch.addmm(a, a, b)
>>> for l in logs:
... print(l)
```
prints the following:
```
$0 = torch._ops.aten.rand.default([10, 10], dtype=torch.float32, device=device(type='mps'), pin_memory=False)
$1 = torch._ops.aten.rand.default([10, 10], dtype=torch.float32, device=device(type='mps'), pin_memory=False)
$2 = torch._ops.aten.addmm.default($0, $0, $1)
```
given the fp16 support, it would be nice to have autocast and amp in general working on MPS devices as well
### Alternatives
_No response_
### Additional context
cc @mcarilli @ptrblck @leslie-fang-intel @jgong5 @kulinseth @albanD @malfet @DenisVieriu97 @razarmehr @abhudev as per our discussion on slack.
| 4 |
4,294 | 88,413 |
Flaky dynamo test_indexing flaky with SIGKILL
|
module: ci, triaged, module: dynamo
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
This job starts to be flaky with SIGKILL recently:
* https://hud.pytorch.org/hud/pytorch/pytorch/master/1?per_page=50&name_filter=dynamo
* https://hud.pytorch.org/pytorch/pytorch/commit/b013825c7d104dca2c6c11cd985453d8520577f7
### Versions
Dynamo, linux-bionic-py3.7-clang9
cc @seemethere @malfet @pytorch/pytorch-dev-infra @mlazos @soumith @voznesenskym @yanboliang @penguinwu @anijain2305 @EikanWang @jgong5 @Guobing-Chen @chunyuan-w @XiaobingSuper @zhuhaozhe @blzheng @Xia-Weiwen @wenzhe-nrv @jiayisunx @desertfire @ezyang @gchanan @zou3519
| 1 |
4,295 | 88,410 |
benchmark cache persist
|
module: cudnn, module: cuda, triaged
|
## 🚀 The feature, motivation and pitch
### Background
We've been working on a detection model's training and when setting torch.backends.cudnn.benchmark = True with some padding , the training speed can improve a lot . However if we skip the padding, since the params of convolution vary frequently(e.g. input shapes), it becomes even slower.
### Requests
We are wondering if we can persist the benchmark cache, so that the first person can store some cache and later others will no longer have to suffer from the algorithms choosing overhead.
Will this feature be possible in the future or is already ongoing ?
**Or there are limits that this whole persisting thing is not a good idea**.
## Alternatives
For example, maybe we can define load() and save() functions inside the global variables:
```
BenchmarkCache<cudnnConvolutionFwdAlgoPerf_t> fwd_algos;
BenchmarkCache<cudnnConvolutionBwdDataAlgoPerf_t> bwd_data_algos;
BenchmarkCache<cudnnConvolutionBwdFilterAlgoPerf_t> bwd_filter_algos;
```
then we have to determine the time of load and save are executed, a draft would be like this:
```
template <typename T>
struct BenchmarkCache {
std::mutex mutex;
std::unordered_map<ConvolutionParams, T, ParamsHash<ConvolutionParams>, ParamsEqual<ConvolutionParams>> map;
std::string CACHE_STORED_PATH;
BenchmarkCache(std::string cache_stored_path): CACHE_STORED_PATH(cache_stored_path){}
bool find(const ConvolutionParams& params, T* results) {
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> guard(mutex);
auto it = map.find(params);
if (it == map.end()) {
return false;
}
*results = it->second;
return true;
}
void insert(const ConvolutionParams& params, const T& results) {
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> guard(mutex);
map[params] = results;
}
int load(const &std::string CACHE_STORE_PATH){
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> guard(mutex);
//load the cache;
}
int save(const &std::string CACHE_STORE_PATH){
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> guard(mutex);
//save the cache;
}
};
```
### Additional context
_No response_
cc @csarofeen @ptrblck @xwang233 @ngimel
| 8 |
4,296 | 88,408 |
Unit test with `--subprocess` command doesn't respect the `-k` filter flag and runs all available sub tests
|
module: ci, module: tests, triaged, module: testing
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
Unit test with `--subprocess` command doesn't respect the `-k` filter flag and runs all available sub tests
Example
```python
root@e85f1ff8919d:/opt/pytorch/pytorch# python test/test_nn.py -v -k test_add_relu
test_add_relu (__main__.TestAddRelu) ... ok
test_add_relu_broadcasting (__main__.TestAddRelu) ... ok
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Ran 2 tests in 0.002s
OK
```
However
```
root@e85f1ff8919d:/opt/pytorch/pytorch# python test/test_nn.py -v -k test_add_relu --subprocess
# thousands of lines of output are printed
# all tests in test_nn are executed
```
Distributed tests are executed by default with `--subprocess`, which makes it hard to only test a specific sub test. https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/blob/a8f40b39ce4f9fa9ffd90400b7d10ea4051d623a/test/run_test.py#L634-L635
Something here might need to be changed? https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/blob/a8f40b39ce4f9fa9ffd90400b7d10ea4051d623a/torch/testing/_internal/common_utils.py#L691-L693
### Versions
pytorch: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/commit/ccf6b558a4c58d1ae92689b2a5064916b42eff05
cc @seemethere @malfet @pytorch/pytorch-dev-infra @mruberry @ptrblck @ngimel
| 0 |
4,297 | 88,389 |
Whether to support libtorch source code compilation of C++11 ?
|
module: build, triaged
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
Hello!
I want to use libtorch's c++ api for algorithm inference, but currently the c++ version in my project only supports c++11, corresponding to gcc 4.8.5 and g++ 4.8.5, can I compile it by downloading the source code to support c++ Algorithm running under 11 environment?
### Versions
gcc 4.8.5
g++ 4.8.5
CUDA 11.3
CUDNN 8.2.1
cc @malfet @seemethere
| 2 |
4,298 | 88,388 |
Summary of inductor issues observed on master
|
high priority, module: ci, triaged, module: inductor
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
As we have had inductor tests running in master for a while, here are the list of flaky issues that we have observed on master. The CUDA GPU flakiness https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/88352 is not included here because it's related to AWS G5 runner in general, not inductor workflow.
* Fail to build triton wheel
* https://hud.pytorch.org/pytorch/pytorch/commit/bc03aa6013e101222c9652d04a2b08e48f626dfb
* benchmarks/dynamo/timm_models.py failure with KeyError: 'cubin'
* https://hud.pytorch.org/pytorch/pytorch/commit/8ef9bda1bf7df84483c593f55e704657887120d6
* benchmarks/dynamo/timm_models.py timeout
* https://hud.pytorch.org/pytorch/pytorch/commit/0fc7de398636f4b53e6c3fde38b4e48a5ff5b37d
* https://hud.pytorch.org/pytorch/pytorch/commit/f132c171ac542c8abe8f6bf54befd9f2e14ad9b6
* https://hud.pytorch.org/pytorch/pytorch/commit/1e2c4a6e0e60dda763b53f00f25ee5c1f1e5233d
* fbnetc_100 model fails
* https://hud.pytorch.org/pytorch/pytorch/commit/5b75b19f51837e162cc0e5e5757dfd9bef437c67
* Internal Triton PTX codegen error
* https://hud.pytorch.org/pytorch/pytorch/commit/7354368fd5a8dec5c9fc26dddf5f7da37f1d2499
* https://hud.pytorch.org/pytorch/pytorch/commit/12dd877395a47d4de382b06fda9623da37782226
Let's try to address them to keep master green
### Versions
Inductor, A10G G5 runner, sm86
cc @ezyang @gchanan @zou3519 @seemethere @malfet @pytorch/pytorch-dev-infra @mlazos @soumith @voznesenskym @yanboliang @penguinwu @anijain2305 @EikanWang @jgong5 @Guobing-Chen @chunyuan-w @XiaobingSuper @zhuhaozhe @blzheng @Xia-Weiwen @wenzhe-nrv @jiayisunx @peterbell10 @desertfire
| 6 |
4,299 | 88,380 |
cuDNN error (CUDNN_STATUS_NOT_SUPPORTED) for torch.nn.functional.grid_sample()
|
module: cudnn, module: cuda, triaged
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
A cuDNN error (`CUDNN_STATUS_NOT_SUPPORTED`) occurs when using the `grid_sample()` method on a GPU (and it appears that the exact shape of the `grid` is relevant here).
Possibly related to #7435 (although that one was marked as completed).
### Minimal example
Running this:
```python
import torch
B, C, W, H = 65_536, 1, 16, 16
device = torch.device('cuda')
grid = torch.zeros(B, W, H, 2).to(device)
data = torch.randn(B, C, W, H).to(device)
sampled = torch.nn.functional.grid_sample(data, grid, align_corners=True)
```
results in the following `RuntimeError`:
```
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "/lustre/home/tgebhard/test.py", line 9, in <module>
sampled = torch.nn.functional.grid_sample(data, grid, align_corners=True)
File "/lustre/home/tgebhard/.virtualenvs/ml4ptp/lib/python3.9/site-packages/torch/nn/functional.py", line 4223, in grid_sample
return torch.grid_sampler(input, grid, mode_enum, padding_mode_enum, align_corners)
RuntimeError: cuDNN error: CUDNN_STATUS_NOT_SUPPORTED. This error may appear if you passed in a non-contiguous input.
```
Adding `.contiguous()` calls to the inputs of `grid_sample()` does not resolve the problem.
### Additional information
It seems that the problem depends on the exact shape of the `grid`, in particular the batch size. Here are some observations from a lot of trial-and-error:
* If `B < 65_536`, it never seems to fail.
* For `B >= 65_536`, the spatial size (or the total number of elements in the `grid`?) seems to play a role.
* The smallest example that crashes for me is `B, C, W, H = 65_536, 1, 11, 12`.
* `B, C, H, W = 4_194_240, 1, 2, 2` works, but `B, C, H, W = 4_194_241, 1, 2, 2` crashes. This is the smallest difference in total number of elements between a working and a non-working example that I found.
I did not check if the number of channels `C` has an impact (for my particular use case, it's always 1).
### Possible workarounds
If you've found this issue because you are encountering the same problem, and you are only interested in a quick fix, I found that locally disabling cuDNN can do the trick:
```python
# Works even for B, C, W, H = 65_536, 1, 16, 16
with torch.backends.cudnn.flags(enabled=False):
sampled = torch.nn.functional.grid_sample(data, grid, align_corners=True)
```
Of course, disabling cuDNN globally via `torch.backends.cudnn.enabled = False` also works, but that slows down _everything_ (i.e., also parts that are not affected by this issue).
### Versions
```
PyTorch version: 1.12.1+cu116
Is debug build: False
CUDA used to build PyTorch: 11.6
ROCM used to build PyTorch: N/A
OS: Ubuntu 20.04.2 LTS (x86_64)
GCC version: (Ubuntu 9.3.0-17ubuntu1~20.04) 9.3.0
Clang version: Could not collect
CMake version: version 3.16.3
Libc version: glibc-2.31
Python version: 3.9.7 (default, Sep 9 2021, 23:20:13) [GCC 9.3.0] (64-bit runtime)
Python platform: Linux-5.4.0-80-generic-x86_64-with-glibc2.31
Is CUDA available: True
CUDA runtime version: Could not collect
CUDA_MODULE_LOADING set to:
GPU models and configuration: GPU 0: Tesla V100-PCIE-16GB
Nvidia driver version: 470.42.01
cuDNN version: Could not collect [see below]
HIP runtime version: N/A
MIOpen runtime version: N/A
Is XNNPACK available: True
Versions of relevant libraries:
[pip3] numpy==1.23.2
[pip3] torch==1.12.1+cu116
[conda] Could not collect
```
When I manually run `python -c "import torch; print(torch.backends.cudnn.version())"`, I get `8302`.
cc @csarofeen @ptrblck @xwang233 @ngimel
| 1 |
4,300 | 88,375 |
[PrimTorch] Functionalization pass removes Instance Norm / Batch Norm running stats transformations
|
high priority, triaged, module: primTorch
|
### 🐛 Describe the bug
The alias ops on running stats for Instance Norm are removed after functionalization pass. NvFuser uses the alias ops to map the running stats back to the fusion input's original shape, stride, and dtype.
References:
https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/blob/master/aten/src/ATen/native/Normalization.cpp#L664-L670
https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/blob/master/functorch/_src/aot_autograd.py#L393-L413
```python
====== Input graph ======
class joint_forward_backward(torch.nn.Module):
def forward(self, primals, tangents):
primals_1: f32[32, 32, 1, 1], primals_2: f32[32], primals_3: f32[32], primals_4: i64[], primals_5: f32[2, 32, 8, 8], tangents_1: f32[2, 32, 8, 8], = fx_pytree.tree_flatten_spec([primals, tangents], self._in_spec)
# File: /home/rspring/workspace/debug_repro/dynamo_instance_norm.py:20, code: out = self.conv(inp)
convolution: f32[2, 32, 8, 8] = torch.ops.aten.convolution.default(primals_5, primals_1, None, [1, 1], [0, 0], [1, 1], False, [0, 0], 1)
# File: /home/rspring/workspace/debug_repro/dynamo_instance_norm.py:21, code: out = out.relu()
relu: f32[2, 32, 8, 8] = torch.ops.aten.relu.default(convolution); convolution = None
detach: f32[2, 32, 8, 8] = torch.ops.aten.detach.default(relu)
# File: /home/rspring/workspace/debug_repro/dynamo_instance_norm.py:22, code: out = self.bn(out)
repeat: f32[64] = torch.ops.aten.repeat.default(primals_2, [2])
repeat_1: f32[64] = torch.ops.aten.repeat.default(primals_3, [2])
view: f32[1, 64, 8, 8] = torch.ops.aten.view.default(relu, [1, 64, 8, 8]); relu = None
empty: u8[0] = torch.ops.aten.empty.memory_format([0], dtype = torch.uint8, layout = torch.strided, device = device(type='cuda', index=0))
native_batch_norm = torch.ops.aten.native_batch_norm.default(view, None, None, repeat, repeat_1, True, 0.1, 1e-05)
getitem: f32[1, 64, 8, 8] = native_batch_norm[0]
getitem_1: f32[64] = native_batch_norm[1]
getitem_2: f32[64] = native_batch_norm[2]; native_batch_norm = None
# ===========================================
# running mean for instance_norm
alias: f32[32] = torch.ops.aten.alias.default(primals_2); primals_2 = None
view_1: f32[2, 32] = torch.ops.aten.view.default(repeat, [2, 32])
mean: f32[32] = torch.ops.aten.mean.dim(view_1, [0]); view_1 = None
copy_: f32[32] = torch.ops.aten.copy_.default(alias, mean); alias = mean = None
# ===========================================
# ===========================================
# running var for instance_norm
alias_1: f32[32] = torch.ops.aten.alias.default(primals_3); primals_3 = None
view_2: f32[2, 32] = torch.ops.aten.view.default(repeat_1, [2, 32])
mean_1: f32[32] = torch.ops.aten.mean.dim(view_2, [0]); view_2 = None
copy__1: f32[32] = torch.ops.aten.copy_.default(alias_1, mean_1); alias_1 = mean_1 = None
# ===========================================
view_3: f32[2, 32, 8, 8] = torch.ops.aten.view.default(getitem, [2, 32, 8, 8]); getitem = None
# No stacktrace found for following nodes
is_same_size = torch.ops.aten.is_same_size.default(view_3, tangents_1)
# File: /home/rspring/workspace/debug_repro/dynamo_instance_norm.py:22, code: out = self.bn(out)
view_4: f32[1, 64, 8, 8] = torch.ops.aten.view.default(tangents_1, [1, 64, 8, 8]); tangents_1 = None
native_batch_norm_backward = torch.ops.aten.native_batch_norm_backward.default(view_4, view, None, repeat, repeat_1, getitem_1, getitem_2, True, 1e-05, [True, False, False]); view_4 = view = repeat = repeat_1 = getitem_1 = getitem_2 = None
getitem_3: f32[1, 64, 8, 8] = native_batch_norm_backward[0]
getitem_4 = native_batch_norm_backward[1]
getitem_5 = native_batch_norm_backward[2]; native_batch_norm_backward = None
view_5: f32[2, 32, 8, 8] = torch.ops.aten.view.default(getitem_3, [2, 32, 8, 8]); getitem_3 = None
# File: /home/rspring/workspace/debug_repro/dynamo_instance_norm.py:21, code: out = out.relu()
detach_1: f32[2, 32, 8, 8] = torch.ops.aten.detach.default(detach); detach = None
threshold_backward: f32[2, 32, 8, 8] = torch.ops.aten.threshold_backward.default(view_5, detach_1, 0); view_5 = detach_1 = None
# File: /home/rspring/workspace/debug_repro/dynamo_instance_norm.py:20, code: out = self.conv(inp)
convolution_backward = torch.ops.aten.convolution_backward.default(threshold_backward, primals_5, primals_1, [0], [1, 1], [0, 0], [1, 1], False, [0, 0], 1, [False, True, False]); threshold_backward = primals_5 = primals_1 = None
getitem_6 = convolution_backward[0]
getitem_7: f32[32, 32, 1, 1] = convolution_backward[1]
getitem_8 = convolution_backward[2]; convolution_backward = None
return pytree.tree_unflatten([view_3, getitem_7, None, None, None, None], self._out_spec)
```
Joint graph after functionalization pass:
https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/blob/master/functorch/_src/aot_autograd.py#L419
```python
====== Joint graph ======
class fake_fn(torch.nn.Module):
def forward(self, primals, tangents):
primals_1: f32[32, 32, 1, 1], primals_2: f32[32], primals_3: f32[32], primals_4: i64[], primals_5: f32[2, 32, 8, 8], tangents_1: f32[2, 32, 8, 8], = fx_pytree.tree_flatten_spec([primals, tangents], self._in_spec)
# File: /home/rspring/workspace/debug_repro/dynamo_instance_norm.py:20, code: out = self.conv(inp)
convolution: f32[2, 32, 8, 8] = torch.ops.aten.convolution.default(primals_5, primals_1, None, [1, 1], [0, 0], [1, 1], False, [0, 0], 1)
# File: /home/rspring/workspace/debug_repro/dynamo_instance_norm.py:21, code: out = out.relu()
relu: f32[2, 32, 8, 8] = torch.ops.aten.relu.default(convolution); convolution = None
detach_1: f32[2, 32, 8, 8] = torch.ops.aten.detach.default(relu)
detach_2: f32[2, 32, 8, 8] = torch.ops.aten.detach.default(detach_1); detach_1 = None
# File: /home/rspring/workspace/debug_repro/dynamo_instance_norm.py:22, code: out = self.bn(out)
repeat: f32[64] = torch.ops.aten.repeat.default(primals_2, [2]); primals_2 = None
repeat_1: f32[64] = torch.ops.aten.repeat.default(primals_3, [2]); primals_3 = None
view: f32[1, 64, 8, 8] = torch.ops.aten.view.default(relu, [1, 64, 8, 8]); relu = None
native_batch_norm = torch.ops.aten.native_batch_norm.default(view, None, None, repeat, repeat_1, True, 0.1, 1e-05)
getitem: f32[1, 64, 8, 8] = native_batch_norm[0]
getitem_1: f32[64] = native_batch_norm[1]
getitem_2: f32[64] = native_batch_norm[2]; native_batch_norm = None
# ===========================================
# view_1 and view_2 are dropped after functionalization pass.
view_3: f32[2, 32, 8, 8] = torch.ops.aten.view.default(getitem, [2, 32, 8, 8]); getitem = None
# ===========================================
view_4: f32[1, 64, 8, 8] = torch.ops.aten.view.default(tangents_1, [1, 64, 8, 8]); tangents_1 = None
native_batch_norm_backward = torch.ops.aten.native_batch_norm_backward.default(view_4, view, None, repeat, repeat_1, getitem_1, getitem_2, True, 1e-05, [True, False, False]); view_4 = view = repeat = repeat_1 = getitem_1 = getitem_2 = None
getitem_3: f32[1, 64, 8, 8] = native_batch_norm_backward[0]; native_batch_norm_backward = None
view_5: f32[2, 32, 8, 8] = torch.ops.aten.view.default(getitem_3, [2, 32, 8, 8]); getitem_3 = None
# File: /home/rspring/workspace/debug_repro/dynamo_instance_norm.py:21, code: out = out.relu()
detach_3: f32[2, 32, 8, 8] = torch.ops.aten.detach.default(detach_2); detach_2 = None
detach_4: f32[2, 32, 8, 8] = torch.ops.aten.detach.default(detach_3); detach_3 = None
threshold_backward: f32[2, 32, 8, 8] = torch.ops.aten.threshold_backward.default(view_5, detach_4, 0); view_5 = detach_4 = None
# File: /home/rspring/workspace/debug_repro/dynamo_instance_norm.py:20, code: out = self.conv(inp)
convolution_backward = torch.ops.aten.convolution_backward.default(threshold_backward, primals_5, primals_1, [0], [1, 1], [0, 0], [1, 1], False, [0, 0], 1, [False, True, False]); threshold_backward = primals_5 = primals_1 = None
getitem_7: f32[32, 32, 1, 1] = convolution_backward[1]; convolution_backward = None
return pytree.tree_unflatten([view_3, getitem_7, None, None, None, None], self._out_spec)
```
Debug repro:
```python
import torch
import functorch
from torch._dynamo.optimizations.training import aot_nvprims_nvfuser, aot_nvprims_aten
from torch._prims.context import TorchRefsNvfuserCapabilityMode
optimize = torch._dynamo.optimize(aot_nvprims_aten)
torch.cuda.cudart().cudaProfilerStart()
class Fusion(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self) :
super(Fusion, self).__init__()
self.conv = torch.nn.Conv2d(32, 32, (1, 1), bias=False)
self.norm = torch.nn.InstanceNorm2d(32, track_running_stats=True)
def forward(self, inp) :
out = self.conv(inp)
out = out.relu()
out = self.norm(out)
return out
model = Fusion().cuda()
input1 = torch.randn(2, 32, 8, 8, device="cuda")
optimized_model = optimize(model)
with torch.cuda.amp.autocast(False):
for _ in range(5):
out = optimized_model(input1)
out.sum().backward()
torch.cuda.synchronize()
torch.cuda.cudart().cudaProfilerStop()
```
### Versions
upstream: a6acbad5
cc @ezyang @gchanan @zou3519 @mruberry @ngimel @Lezcano @fdrocha @peterbell10
| 8 |
Subsets and Splits
No community queries yet
The top public SQL queries from the community will appear here once available.